Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CRJ 311: Forensic Science Lecture 10 - Documents, Computer Forensics and The Future
CRJ 311: Forensic Science Lecture 10 - Documents, Computer Forensics and The Future
Uploaded by
Moke Fetane AmboOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CRJ 311: Forensic Science Lecture 10 - Documents, Computer Forensics and The Future
CRJ 311: Forensic Science Lecture 10 - Documents, Computer Forensics and The Future
Uploaded by
Moke Fetane AmboCopyright:
Available Formats
CRJ 311: Forensic Science
Lecture 10 - Documents, Computer Forensics and the Future
1. Introduction to Document Examination
a. Document examiners:
b. What is handwriting?
2. What is a Questioned Document?
a. Questioned document:
b. Examples:
3. Forensic Document Examination
a. Forensic document examination:
i. GOAL:
b. Forensic linguist:
4. The Unabomber
a. Who is Ted Kaczynski?
b. Who did he target?
c. How did he get caught?
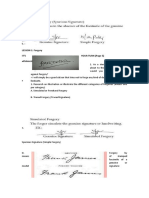
5. Handwriting Comparisons
a. How do we determine authenticity?
b. What are the different types of variations?
c. What are the “other factors”?
6. Kurt Cobain Suicide
a. Why was Kurt Cobain’s suicide letter up for debate?
7. Typewriters and Printing Devices
a. Examiners are asked the two most common requests?
b. Style, shape and size are…
8. Typewriters and Printing Devices “Characteristics from Use”
a. Wear and damage to printer or typewriters moving parts will occur.
b. How can we identify the machine?
1
c. Why is typewriter ribbon useful?
d. Are modern computers helpful?
9. Digital Technology
a. Today, examiners identify the make and model of photocopiers, fax machines and
computer printers used to produce questioned documents.
b. A side-by-side comparison is made to compare what?
10. Alterations
a. Erasures:
i. Examples:
b. Additions and obliterations:
c. Infrared photography:
d. How are inks useful?
11. Other Document Problems
a. Indented writing:
b. Can you tell what was written on a pad of paper?
c. What do they use to determine this?
12. Voice Examination
a. The human voice is unique and can provide evidence to indentify an individual.
b. What makes for unique voice patterns?
c. What makes for different voice articulations?
13. Sound Spectrograph
a. Sound spectrograph can compare two voice samples.
b. What are the seven categories?
14. Intro to Computer Forensics
a. Computers have permeated society and are used in countless ways with innumerable
applications.
b. What do computers and other electronic data leave behind?
c. Computer forensics:
15. Forensic Image Acquisition
2
a. Items that have been seized will need to be analyzed for data
b. Example: Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
16. Visible Data
a. Visible data:
b. From an evidentiary standpoint, it can be any type of user create data like:
17. Latent Data
a. Latent data:
i. RAM slack:
ii. File slack:
b. Where else can latent data be found?
18. BTK Killer
a. Who was the BTK killer?
b. What does BTK stand for?
c. How did he get caught?
19. Introduction to Internet Technology
a. Internet:
b. Is anyone untouched by the internet?
c. What is the major impact to forensic science?
20. Scott Peterson
a. Who was Scott Peterson?
b. What crime did he commit?
c. How did he get caught?
21. The Future of Forensics
a. Crime laboratories:
b. Chromatography and spectrophotometry:
c. DNA typing:
22. New Developments
a. New instruments and techniques:
b. What has undergone a major facelift?
c. Linking of personal computers to analytical equipment
You might also like
- Bookbinders Book Club Case: Assignment 5: Identifying Target Customers (Individual Assignment)Document4 pagesBookbinders Book Club Case: Assignment 5: Identifying Target Customers (Individual Assignment)stellaNo ratings yet
- Bioplasm NLS Use Manual (Training) v3.8.2Document104 pagesBioplasm NLS Use Manual (Training) v3.8.2Juan Carlos Robayov85% (13)
- PGP - Cet 2019Document25 pagesPGP - Cet 2019Yadav Nisha100% (1)
- Rebecca Exercises Answers Key PDFDocument2 pagesRebecca Exercises Answers Key PDFdante00006No ratings yet
- (Weiting Zang, Dong Yang - 2019) Data-Driven Methods For Predictive Maintenance ofDocument15 pages(Weiting Zang, Dong Yang - 2019) Data-Driven Methods For Predictive Maintenance ofMarcos RamisNo ratings yet
- Sample EssayDocument3 pagesSample EssayGunawan AdhigunaNo ratings yet
- F Chapter 13 Forensic)Document5 pagesF Chapter 13 Forensic)mohdNo ratings yet
- 8-25-2022MODULE - 1 QDE - SY 22-23 (Ist Sem)Document25 pages8-25-2022MODULE - 1 QDE - SY 22-23 (Ist Sem)Vanessa CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Abstract Definitions: Abstract Definitions Kinds Drafting History in Law See Also References Further ReadingDocument2 pagesAbstract Definitions: Abstract Definitions Kinds Drafting History in Law See Also References Further ReadingJey VlackNo ratings yet
- Indiana State Police Forensic Document Unit Test MethodsDocument20 pagesIndiana State Police Forensic Document Unit Test Methodsdenis alvarezNo ratings yet
- Lapius Nadin QDEDocument10 pagesLapius Nadin QDEFrances ChugyawiNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature (Application of Image Processing)Document7 pagesDigital Signature (Application of Image Processing)giridharkumarabNo ratings yet
- Indiana State Police Forensic Document Unit Test Methods: 10.12. ReferencesDocument20 pagesIndiana State Police Forensic Document Unit Test Methods: 10.12. Referencesdenis alvarezNo ratings yet
- Question Documents UnfinishedDocument5 pagesQuestion Documents UnfinishedJaryl HernandezNo ratings yet
- SssDocument5 pagesSssJuLievee LentejasNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo Cal 2014Document25 pagesCuadernillo Cal 2014Carlos HormigoniNo ratings yet
- Juli Layton's-"How Handwriting Analysis Works" Available at (Visited On Oct20,2019)Document12 pagesJuli Layton's-"How Handwriting Analysis Works" Available at (Visited On Oct20,2019)Vanshdeep Singh SamraNo ratings yet
- Digital Signature: Presented by K.ANITHA (19065) T.DIVYA (19074) T.PAVAN (19082) P.Venu Gopal Reddy (19104)Document19 pagesDigital Signature: Presented by K.ANITHA (19065) T.DIVYA (19074) T.PAVAN (19082) P.Venu Gopal Reddy (19104)Divya TammineediNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Scientific EvidenceDocument118 pagesChapter3 Scientific EvidenceCeara ManausNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument22 pagesDigital SignatureDiptendu BasuNo ratings yet
- Legal Recognition of E-Signature: Seminar OnDocument14 pagesLegal Recognition of E-Signature: Seminar OngambovNo ratings yet
- Balanquit QD Output 1-3Document900 pagesBalanquit QD Output 1-3BALANQUIT RENATO JR. S.No ratings yet
- Isabela State University Cauayan Campus Criminology DepartmentDocument34 pagesIsabela State University Cauayan Campus Criminology DepartmentCalixtro Sunshine OreniaNo ratings yet
- Unidentifiable Handwriting An Anonymous Note CaseDocument6 pagesUnidentifiable Handwriting An Anonymous Note CaseManjula Nadeeth De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Charred Documents Their Handling and Decipherment - A Summary of PDFDocument16 pagesCharred Documents Their Handling and Decipherment - A Summary of PDFSpdahiya 0786No ratings yet
- Notes Questioned DocsDocument4 pagesNotes Questioned DocsApple GayyaNo ratings yet
- pp11Document31 pagespp11FahadNo ratings yet
- Toprank Criminology Closed-Door CoachingDocument145 pagesToprank Criminology Closed-Door CoachingElyciel FernandezNo ratings yet
- 33 Forensic Document ExaminationDocument13 pages33 Forensic Document ExaminationKate Serrano ManlutacNo ratings yet
- Closer Look: Take ADocument20 pagesCloser Look: Take ADavide Alberto DriNo ratings yet
- The Latest in U.S. Currency DesignDocument11 pagesThe Latest in U.S. Currency DesignAlexis Gonzalez PerezNo ratings yet
- Forensic Science: Document AnalysisDocument28 pagesForensic Science: Document AnalysisMcNavy PANo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document14 pagesPresentation 1Mahwish AamirNo ratings yet
- Line Crossing Interpol Final Report 12 Jul 2013Document45 pagesLine Crossing Interpol Final Report 12 Jul 2013Nikolaos Kalantzis100% (1)
- Take A: Closer LookDocument20 pagesTake A: Closer Lookmusham9No ratings yet
- Training PosterDocument1 pageTraining PosterDoug GreggNo ratings yet
- RBI Salient Features of Genuine NoteDocument29 pagesRBI Salient Features of Genuine Notemusham9No ratings yet
- Kinds of TypewritersDocument2 pagesKinds of TypewritersNick BantoloNo ratings yet
- The New Color of Money:: Safer. Smar Ter. More SecureDocument1 pageThe New Color of Money:: Safer. Smar Ter. More SecureLuis FernadndoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Document AnalysisDocument17 pagesUnit 3 Document Analysisapi-292042538100% (1)
- Digital Signature PRJCTDocument23 pagesDigital Signature PRJCTGANESH KANDNo ratings yet
- Questioned Documents Examination: Prepared By: Geraldine B. Tuliao, RcrimDocument53 pagesQuestioned Documents Examination: Prepared By: Geraldine B. Tuliao, RcrimChristian QuebecNo ratings yet
- 100 SecurityFeaturesInsert en WEB031210Document1 page100 SecurityFeaturesInsert en WEB031210Luis FernadndoNo ratings yet
- 4 Preliminary Examination of DocumentsDocument10 pages4 Preliminary Examination of DocumentsRavali VelpulaNo ratings yet
- Questioned Ducument Chapter Leg 2 2021 ModuleDocument5 pagesQuestioned Ducument Chapter Leg 2 2021 ModuleLayug Lorence JadeNo ratings yet
- Impsevid 09Document8 pagesImpsevid 09api-203306348No ratings yet
- Digest of QD NotesDocument8 pagesDigest of QD NotesVincentNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Project Phase I PresentationDocument18 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Project Phase I PresentationArun ManojNo ratings yet
- JSJSJZDocument6 pagesJSJSJZNover BundaNo ratings yet
- Group6 3b QDDocument27 pagesGroup6 3b QDCalvinderwin MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- 50 2004-Present FeaturesDocument1 page50 2004-Present FeaturesKGW NewsNo ratings yet
- Name of Issuing Authority, - Guarantee, - Promise - Signature, - Portrait of Mahatma Gandhi - Water MarkDocument26 pagesName of Issuing Authority, - Guarantee, - Promise - Signature, - Portrait of Mahatma Gandhi - Water MarkRam KrishNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint Analysis Examination Paper II, L 1-6 PDFDocument86 pagesFingerprint Analysis Examination Paper II, L 1-6 PDFsrivenramanNo ratings yet
- VSC5000Document6 pagesVSC5000Nedelcu MariusNo ratings yet
- PS 006a Qde (Ay 2022-2023)Document39 pagesPS 006a Qde (Ay 2022-2023)Magsayo JoefreyNo ratings yet
- Questioned DocumentsDocument27 pagesQuestioned Documentsab-azzehNo ratings yet
- Questioned Documents and Handwriting AnalysisDocument8 pagesQuestioned Documents and Handwriting AnalysisRavi ShahNo ratings yet
- Authentication of Questioned Documents Using HPLCDocument19 pagesAuthentication of Questioned Documents Using HPLCab-azzehNo ratings yet
- Impression EvidenceDocument8 pagesImpression Evidenceapi-262815720No ratings yet
- Document Examination AbroadDocument4 pagesDocument Examination AbroadChrissian Lei Mateo PedralvezNo ratings yet
- DactylosDocument150 pagesDactylosJay-r Pabualan DacoNo ratings yet
- Questioned Document ExaminationDocument4 pagesQuestioned Document ExaminationAj AjNo ratings yet
- Forensic Questioned Document ExaminationDocument26 pagesForensic Questioned Document ExaminationWankey MarlonNo ratings yet
- Examinati ONDocument20 pagesExaminati ONPrincess Trina Galapon RamosNo ratings yet
- It Quiz 1,2 & 3Document6 pagesIt Quiz 1,2 & 3denzzaidNo ratings yet
- EXAMDocument2 pagesEXAMrheacristine.tribunaloNo ratings yet
- P3F/F) + Jflif (S Fwf/0F Ef Dalgw "RGFDocument1 pageP3F/F) + Jflif (S Fwf/0F Ef Dalgw "RGFlakpaNo ratings yet
- CAIE Examinations Timetable GCE June 2021 Session - PokharaDocument2 pagesCAIE Examinations Timetable GCE June 2021 Session - PokharalakpaNo ratings yet
- 2518253520-April June 2013Document267 pages2518253520-April June 2013lakpaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Digitally Manipulated Documents Using Matlab 7.10.0 and Adobe Photoshop 7.0Document14 pagesExamination of Digitally Manipulated Documents Using Matlab 7.10.0 and Adobe Photoshop 7.0lakpaNo ratings yet
- Pu Bba 1st Semester SyllabusDocument6 pagesPu Bba 1st Semester SyllabuslakpaNo ratings yet
- S / L Km'6/Of) D) NDRLSF) D'Vo U) 6 : CF) DGL K - S/0Fdf TFLGP PKK - WFGDGQLDocument12 pagesS / L Km'6/Of) D) NDRLSF) D'Vo U) 6 : CF) DGL K - S/0Fdf TFLGP PKK - WFGDGQLlakpaNo ratings yet
- +QMLDTX¿ 3/D) : K - LT: KWF (5Ng 6'S - Ofp/ &@ Ca (SF 7) SSFDocument12 pages+QMLDTX¿ 3/D) : K - LT: KWF (5Ng 6'S - Ofp/ &@ Ca (SF 7) SSFlakpaNo ratings yet
- Chemographic Methods in Gunshot Residue Analysis 0Document16 pagesChemographic Methods in Gunshot Residue Analysis 0lakpaNo ratings yet
- Questioned DocumentsDocument29 pagesQuestioned DocumentslakpaNo ratings yet
- FingerprintsDocument33 pagesFingerprintslakpaNo ratings yet
- Forensics Test 1Document1 pageForensics Test 1lakpaNo ratings yet
- 14 Harlot woman09.XIVDocument7 pages14 Harlot woman09.XIVNoahNo ratings yet
- Exp No. 11 Chem Process Lab ReportDocument5 pagesExp No. 11 Chem Process Lab ReportSourav SutradharNo ratings yet
- Types of Strategies in Strategic ManagementDocument6 pagesTypes of Strategies in Strategic ManagementHan O100% (3)
- 2020 Education ResumeDocument2 pages2020 Education Resumeapi-245627476No ratings yet
- DLL 7 2nd Health Nutritional GuidelinesDocument3 pagesDLL 7 2nd Health Nutritional Guidelinesivonne100% (2)
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPThina Cruz Torres0% (1)
- Everyday Use Standardized Test PrepDocument3 pagesEveryday Use Standardized Test PrepJaclyn Aldridge BoydNo ratings yet
- Steve BikoDocument2 pagesSteve BikoTNo ratings yet
- TaylorDocument12 pagesTaylorHajar AllamNo ratings yet
- Transpo CasesDocument141 pagesTranspo CasesKaren Gina DupraNo ratings yet
- Good Manners and God BehaviorDocument36 pagesGood Manners and God BehaviorJhanette De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Geometry Review Additional Practice Answer KeyDocument3 pagesGeometry Review Additional Practice Answer Keyapi-368121935No ratings yet
- Idioms - Ingles - Run Into & Come AcrossDocument3 pagesIdioms - Ingles - Run Into & Come Acrossjcpm0916No ratings yet
- English I MQPDocument6 pagesEnglish I MQPBanoth GaneshNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 2 TipsDocument2 pagesCFA Level 2 TipsgregdebickiNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of AffirmationDocument6 pagesAffidavit of AffirmationJanice GaboteroNo ratings yet
- Games RulesDocument10 pagesGames RulesZaini AkmalNo ratings yet
- Partial Pressure - Dalton's Law of Partial PressureDocument2 pagesPartial Pressure - Dalton's Law of Partial PressureJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- A Gauze of Misted Silver SampleDocument5 pagesA Gauze of Misted Silver SampleJustin_Merritt_8944No ratings yet
- RPS English MorphologyDocument12 pagesRPS English MorphologynurulwasilaturrahmahNo ratings yet
- J. P. Rizal Ext., West Rembo, Makati City: University of Makati Higher School NG Umak Department of Social SciencesDocument3 pagesJ. P. Rizal Ext., West Rembo, Makati City: University of Makati Higher School NG Umak Department of Social SciencesmaricrisNo ratings yet
- Roe-088-All-5-Units-235 QuDocument90 pagesRoe-088-All-5-Units-235 QuApoorv GargNo ratings yet
- Is Your Child Doctor or Engineer? - : Combinations For Medical ProfessionDocument4 pagesIs Your Child Doctor or Engineer? - : Combinations For Medical ProfessionjanakrajchauhanNo ratings yet
- PQLI Control Strategy Model and ConceptsDocument10 pagesPQLI Control Strategy Model and ConceptspakdekroNo ratings yet