Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Equation Practice 1: P Momentum (KG M/S) M Mass (KG) V Velocity (M/S)
Uploaded by
DavidAnnorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Equation Practice 1: P Momentum (KG M/S) M Mass (KG) V Velocity (M/S)
Uploaded by
DavidAnnorCopyright:
Available Formats
CP2f.
7 Equation practice 1
You will be expected to recall the formula linking momentum, mass and velocity in your examination. You
should also be able to change the subject of the formula and to use the correct units.
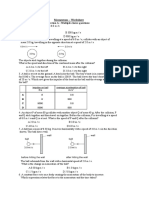
1 The table contains some information
about moving objects. Calculate the Object Mass Velocity Momentum
missing values in the table. (kg m/s)
2 A loaded lorry has a mass of a car 1800 kg 30 m/s
40 tonnes. Its momentum is
800 000 kg m/s. Calculate its b cyclist 75 kg 10 m/s
velocity. (1 tonne = 1000 kg)
c sprinter 60 kg 300
3 A flea with a mass of 1 mg is
d golf ball 40 m/s 1.8
moving at 1 m/s. Calculate its
momentum. e cricket ball 40 m/s 6.4
4 A 2000 kg car accelerates from f bowling ball 7 kg 10 cm/s
5 m/s to 20 m/s. What is the change
in its momentum? (Hint: calculate g tennis ball 58 g 3.19
the momentum at each velocity then h snooker ball 160 g 10 m/s
find the difference.)
i snooker ball 160 g 0.1
5 Blood flowing through a blood
vessel is moving at 20 cm/s. The
mass of a red blood cell is
-15
approximately 30 × 10 kg.
Calculate the momentum of a blood
cell.
6 Trolley A has a mass of 2 kg and is moving at 2 m/s. It collides with trolley B, which has the same mass but
is stationary.
a Calculate the momentum of trolley A before the collision.
b The two trolleys stick together after they collide. What is their total mass?
c What is the momentum of the two trolleys after the collision?
d Calculate the velocity of the two trolleys after the collision.
7 A 30 000 kg truck moving at 25 m/s collides with a stationary car with a mass of 2000 kg. The vehicles stick
together after the crash. Calculate their velocity just after the collision.
8 Trolley C (mass 2 kg) is moving at 1.5 m/s and collides with trolley D. The trolleys stick together and move
at 1 m/s after the collision. Calculate the mass of trolley D.
9 Two stationary trolleys are fastened together with a spring between them. When they are disconnected the
spring pushes them apart. Trolley E has a mass of 5 kg and moves away at 2 m/s. Trolley F has a mass of
4 kg. Calculate its velocity after the trolleys separate.
10 Trolley G has a mass of 2 kg and is moving at 3 m/s. Trolley H has a mass of 1.5 kg and is moving at 5 m/s
in the opposite direction. The trolleys collide and stick together. Calculate the velocity of the combined
trolleys after the collision.
p = momentum (kg m/s)
m = mass (kg) momentum = mass × velocity
v = velocity (m/s)
© Pearson Education Ltd 2015. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
1
You might also like
- Momentum Cw Hw 1 Problems 2021-07-14Document16 pagesMomentum Cw Hw 1 Problems 2021-07-14whis2022No ratings yet
- Work Sheet-Ch8Document2 pagesWork Sheet-Ch8DeemaNo ratings yet
- Momentum Assignment Class 9Document4 pagesMomentum Assignment Class 9Apex Institute0% (1)
- IGCSE 14 MomentumDocument39 pagesIGCSE 14 MomentumHakim Abbas Ali Phalasiya36% (11)
- ch4 - 1d MomentumDocument8 pagesch4 - 1d Momentumapi-301275445No ratings yet
- Physics Exercise Force and MotionDocument9 pagesPhysics Exercise Force and MotionAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion: Calculating Force, Inertia and VelocityDocument2 pagesLaws of Motion: Calculating Force, Inertia and VelocityMonika SanghviNo ratings yet
- Momentum 1Document40 pagesMomentum 1alanjoshuakentshitsweNo ratings yet
- IGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 16 - Work and Power PDFDocument2 pagesIGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 16 - Work and Power PDFmurugan BharathiNo ratings yet
- Elastic collisions and momentum problemsDocument4 pagesElastic collisions and momentum problemsMuhammad Chabibur ANo ratings yet
- Momentum NpteDocument30 pagesMomentum NptediliniNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Science 9 Impulse and MomentumDocument22 pages4th Quarter Science 9 Impulse and Momentumvengie arellano60% (5)
- Momentum and Inertia Physics ProblemsDocument5 pagesMomentum and Inertia Physics ProblemsAnna GonzagaNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet1 MomentumDocument1 pageProblemSet1 MomentumGathy BrayohNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56Document2 pagesCH 2 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56rb8q9sz8hrNo ratings yet
- Momentum ProblemsDocument5 pagesMomentum ProblemsawbNo ratings yet
- Cons of MomentumDocument35 pagesCons of MomentumTrixia AmorNo ratings yet
- Momentum WorksheetDocument1 pageMomentum WorksheetMichelle BaguioNo ratings yet
- Combined - Momentum QPDocument6 pagesCombined - Momentum QPssaimal816No ratings yet
- 7 Momentum HWDocument5 pages7 Momentum HWampay ayubNo ratings yet
- PS3 Impulse MomentumDocument1 pagePS3 Impulse MomentumArchie BertolfoNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Momentum SteDocument2 pagesPractice Problems Momentum SteCamillekatesoberanoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionDocument2 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Physics: Chapter-4 Momentum Study QuestionMahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- 5 CB 30Document2 pages5 CB 30Priya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Booklet Momentum BWFDocument22 pagesBooklet Momentum BWFReem AshrafNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 8Document3 pagesTutorial 7 8Zahida ParnisNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3.2: Impulse and MomentumDocument1 pageWorksheet 3.2: Impulse and MomentumRoua .thixccNo ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion QuestionsDocument5 pagesForce and Laws of Motion QuestionsrekhaNo ratings yet
- Collision PracticeDocument11 pagesCollision PracticeYohanes Ratnodiyanto100% (1)
- Momentum LessonDocument77 pagesMomentum LessonJennifer Magango100% (3)
- Collisions & CM WorksheetDocument10 pagesCollisions & CM WorksheetMona Mohamed SafwatNo ratings yet
- 2.50 KG 3.90 KG .850 M/s 11.5 Kgm/s 2.06 M/s 5.10 KG 1.00 KG 0.900 M/s 4.60 M/s - 4.60 M/sDocument2 pages2.50 KG 3.90 KG .850 M/s 11.5 Kgm/s 2.06 M/s 5.10 KG 1.00 KG 0.900 M/s 4.60 M/s - 4.60 M/scaleb fNo ratings yet
- 6 10a10b Conservation of Momentum WKST KeyDocument2 pages6 10a10b Conservation of Momentum WKST KeySheryl Nishmae Bernardo SantosNo ratings yet
- Homeworks MomentumDocument4 pagesHomeworks MomentumNipuna LaksithaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document15 pagesLesson 4Ryan KoNo ratings yet
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Document5 pagesCE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- ConsofMomentum QuestionsDocument2 pagesConsofMomentum QuestionsSafaNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument4 pagesMomentumijaddjuesNo ratings yet
- Momentum and Impulse WorksheetDocument1 pageMomentum and Impulse WorksheetCurtis CollinsNo ratings yet
- Momentum Questions and Answer Keys Convertedpart 2Document3 pagesMomentum Questions and Answer Keys Convertedpart 2David M. IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Ch04 05 Force Problem BankDocument11 pagesCh04 05 Force Problem Banknicky1213aNo ratings yet
- Calculate Momentum and Velocity of Colliding ObjectsDocument8 pagesCalculate Momentum and Velocity of Colliding ObjectsRadziah MohamedNo ratings yet
- Center of MassDocument1 pageCenter of Massbangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- 1.6 MomentumDocument8 pages1.6 MomentumWei yet ChuNo ratings yet
- 4 IGCSE MomentumDocument61 pages4 IGCSE MomentumHoracio FerrándizNo ratings yet
- Impulse and MomentumDocument18 pagesImpulse and MomentumChezka GuerzonNo ratings yet
- Physics Finals Week-4Document4 pagesPhysics Finals Week-4Kate Lea Marie DeguiñonNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Momentum WorksheetDocument5 pagesConservation of Momentum WorksheetJahmar MattisNo ratings yet
- Center of Mass WorksheetDocument3 pagesCenter of Mass Worksheetfatma khatoonNo ratings yet
- Momentum - Worksheet: Section A - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesMomentum - Worksheet: Section A - Multiple Choice Questionshakky gamyNo ratings yet
- Momentum 2.0Document29 pagesMomentum 2.0Esther SparksNo ratings yet
- MomentumDocument7 pagesMomentumKarl TolosaNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument2 pagesProblemszamabakhmatNo ratings yet
- C - 1D Collisions PhET LabDocument2 pagesC - 1D Collisions PhET Labcaleb fNo ratings yet
- MotionDocument44 pagesMotionNagashwini HebbarNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy WorksheetDocument2 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy Worksheetbarcelot tortogoNo ratings yet
- Potentialandkineticenergyworksheet PDFDocument2 pagesPotentialandkineticenergyworksheet PDFAndrew SorianoNo ratings yet
- Solutio TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesSolutio TermodinamicaLeritoNo ratings yet
- 0500 s19 QP 11Document16 pages0500 s19 QP 11sohamNo ratings yet
- 0500 s19 in 11Document4 pages0500 s19 in 11sohamNo ratings yet
- Feep108 PDFDocument16 pagesFeep108 PDFjoswa masagandaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary Ready To Go Lessons For Maths Stage 6 Answers To Photocopiable PagesDocument12 pagesCambridge Primary Ready To Go Lessons For Maths Stage 6 Answers To Photocopiable PagesRicco ChettNo ratings yet
- CahmDocument3 pagesCahmakkivish37No ratings yet
- Different Types of Printer 1Document14 pagesDifferent Types of Printer 1jeremy dinangwatanNo ratings yet
- Intel ScanDocument10 pagesIntel ScanberoroNo ratings yet
- Kegiatan Magang Perancangan Lanskap Kawasan Perumahan Green Permata Di Pt. Tropica Greeneries, JakartaDocument156 pagesKegiatan Magang Perancangan Lanskap Kawasan Perumahan Green Permata Di Pt. Tropica Greeneries, JakartamuhamadrivanNo ratings yet
- Stadium "Georgios Karaiskakis"Document9 pagesStadium "Georgios Karaiskakis"djsmolituNo ratings yet
- 1999-09 The Computer Paper - BC EditionDocument154 pages1999-09 The Computer Paper - BC EditionthecomputerpaperNo ratings yet
- Disney and PixarDocument17 pagesDisney and Pixarazrenn75% (4)
- Alliance Electronics Truck Electronic & Electrical Parts Catalogue 2018Document36 pagesAlliance Electronics Truck Electronic & Electrical Parts Catalogue 2018Alliance Transport Technologies Ltd100% (3)
- Sunbeam Beadmaker Instruction & Recipe BookletDocument43 pagesSunbeam Beadmaker Instruction & Recipe BookletAlberto SalibyNo ratings yet
- Palm Jumeirah by GaneshDocument10 pagesPalm Jumeirah by GaneshJidhin VijayanNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary: Ficha de Revisão - Módulo 3Document2 pagesVocabulary: Ficha de Revisão - Módulo 3mjtviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Iii'sDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Iii'sMark Rodil LptNo ratings yet
- Insert Manual Back Insert Manual CoverDocument16 pagesInsert Manual Back Insert Manual CoverRich MackNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 22 Handout and HWDocument4 pagesLesson - 22 Handout and HWHoàng VũNo ratings yet
- PRIMAX 95 (Unleaded Gasoline)Document1 pagePRIMAX 95 (Unleaded Gasoline)batugiokNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs May FileDocument3 pagesCurrent Affairs May FileAayush10No ratings yet
- Berroco FreePattern MallowDocument5 pagesBerroco FreePattern MallowMimi Basso100% (1)
- AirienDocument3 pagesAirienSarah Mae Sequijor FadolNo ratings yet
- Coolmate Marketing Analysis ReportDocument41 pagesCoolmate Marketing Analysis ReportTrNguyen Giang HuongNo ratings yet
- Aurox Armoured TrAnsporT (ImperIAlIs mIlITIA & CulTs)Document1 pageAurox Armoured TrAnsporT (ImperIAlIs mIlITIA & CulTs)kenny tranNo ratings yet
- My Everythig Ukulele Tab - Ariana Grande - ULTIMATE-TABSDocument2 pagesMy Everythig Ukulele Tab - Ariana Grande - ULTIMATE-TABSValerie VanoNo ratings yet
- Module Dressmaking 9Document16 pagesModule Dressmaking 9Wendy ArnidoNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Luyen Thi Ioe Lop 6Document9 pagesBai Tap Luyen Thi Ioe Lop 6Minh ThưNo ratings yet
- Vibgyor Literature Grade 7 Question PaperDocument5 pagesVibgyor Literature Grade 7 Question Paperdeepika dalmiaNo ratings yet
- What To Bring Camping For A Safe Trip (Not Survivalist) 562020Document21 pagesWhat To Bring Camping For A Safe Trip (Not Survivalist) 562020LauraLee FoleyNo ratings yet
- Understanding Muscle Contraction at the Molecular LevelDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Muscle Contraction at the Molecular LevelMaggie-Louise BellamyNo ratings yet
- Russian or ContinentalDocument5 pagesRussian or ContinentalMae Cleofe G. SelisanaNo ratings yet
- Nokia 9500 MPR MPT Short-Haul R6-1 ANSI Data Sheet enDocument2 pagesNokia 9500 MPR MPT Short-Haul R6-1 ANSI Data Sheet enSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Divine Blessings SelûneDocument5 pagesDivine Blessings SelûneThalison OliveiraNo ratings yet
- The Basics of How A Lever Action Works PDFDocument5 pagesThe Basics of How A Lever Action Works PDFtwinscrewcanoeNo ratings yet