Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 CB 30
Uploaded by
Priya Agrawal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesOriginal Title
5cb30
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pages5 CB 30
Uploaded by
Priya AgrawalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
AMITY INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL, NOIDA(2022-23)
CLASS IX, WORKSHEET-2
KINETIC ENERGY & POTENTIAL ENERGY
1. What happens to the kinetic and potential energy of a stone if it is thrown
upwards?
2. An object of mass 5kg is dropped from a height of 10m. Find its kinetic
energy, when it is half way down.
3. In an oscillating pendulum, at what position are the kinetic and potential
energy maximum?
4. What will cause greater change in kinetic energy of a body –changing its
mass or changing its velocity?
5. If the speed of a body is halved, what is the change in its kinetic energy?
6. A horse of mass 210kg and dog of mass 25kg are running at the same
speed. Which of the two possesses more kinetic energy? Why?
7. A body of mass 5kg is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of 10m/s.
What is its kinetic energy when it is thrown? Find its potential energy when
it reaches the highest point. Also find the maximum height attained by the
body. (g=10m/s2)
8. A slinky is (a) compressed (b) stretched. What happens to its potential
energy in each case?
9. Two balls of masses m each are raised to a height h and 2h respectively.
What will be the ratio of their potential energies?
10.A bag of wheat is dropped from a height h. What energy conversion takes
place as it reaches the ground?
11.A force of 10N acts on a body of 2kg for 3 seconds. Find the kinetic energy
acquired by the body in 3 seconds.
12.A car weighing 1200kg is uniformly accelerated from rest and covers a
distance of 40m in 5 seconds. Calculate the work done by the engine of the
car during this time. What is the final kinetic energy of the car?
13.(a) Define Kinetic energy.
(b) The masses of scooter and bike are in the ratio of 2:3, but both are
moving with the same speed of 108km/h. Compute the ratio of their kinetic
energies.
14.(a) A moving body of mass 20kg has 40 joules of kinetic energy. Calculate its
speed.
15.A body of mass 2kg is thrown up with a speed of 25m/s. Find the maximum
potential energy.
16.A body of mass 25g has a momentum of 0.40 kg m/s. Find its kinetic energy.
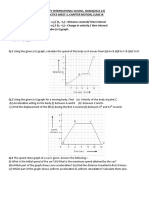
17. Consider the falling and rolling motion of the ball in the following two
resistance-free situations. In one situation, the ball falls off the top of the
platform to the floor. In the other situation, the ball rolls from the top of
the platform along the staircase-like pathway to the floor. For each
situation, indicate what types of forces are doing work upon the ball.
Indicate whether the energy of the ball is conserved and explain why.
Finally, fill in the blanks for the 2-kg ball.
You might also like
- CBSE Class 9 Physics Worksheet - Work & EnergyDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 9 Physics Worksheet - Work & EnergyAtharva VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Work and Energy NumericalsDocument6 pagesClass 9 Work and Energy NumericalsPathikrit Das67% (6)
- Forces of equilibrium and motion problemsDocument4 pagesForces of equilibrium and motion problemsKurt Allen PadillaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet NameDocument3 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet NameSymphanie ChilesNo ratings yet
- KE and PE Energy Worksheet 2Document3 pagesKE and PE Energy Worksheet 2Roxanne QuebadaNo ratings yet
- Take Home Assig-Wps OfficeDocument2 pagesTake Home Assig-Wps OfficeMakame AliNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Rev Ch05 02 WADocument3 pagesGr10 Rev Ch05 02 WAAidanNo ratings yet
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheet RHSDocument3 pagesPotential and Kinetic Energy Worksheet RHSlisa grinbergNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential EnergyDocument3 pagesKinetic and Potential EnergyTAE0% (1)
- Work Energy Chapter Problems-2009-05-13Document21 pagesWork Energy Chapter Problems-2009-05-13Liam ReillyNo ratings yet
- 2 - Work and Energy Treasure HuntDocument2 pages2 - Work and Energy Treasure Huntapi-276813042No ratings yet
- Force and Laws of Motion QuestionsDocument5 pagesForce and Laws of Motion QuestionsrekhaNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Secunderabad Nacharam Concept Wise Worksheet Grade 9 Physics Topic: Work and EnergyDocument5 pagesDelhi Public School Secunderabad Nacharam Concept Wise Worksheet Grade 9 Physics Topic: Work and EnergytnmscharanNo ratings yet
- Intervention Materials Grade 9 Work Power and EnergyDocument6 pagesIntervention Materials Grade 9 Work Power and Energythivon thivonNo ratings yet
- Miaca Masiddo March 12,2020: Physics Ix Work, Power, and EnergyDocument6 pagesMiaca Masiddo March 12,2020: Physics Ix Work, Power, and EnergyMatthew DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Practice CpoDocument6 pagesPotential and Kinetic Energy Practice Cpoapi-319102793No ratings yet
- g8 - q1w3 - Kinetic and Potential Energy Worded ProblemsDocument14 pagesg8 - q1w3 - Kinetic and Potential Energy Worded ProblemsMa Dolores GuiaoNo ratings yet
- Icse X Work, Power & Energy Question BankDocument5 pagesIcse X Work, Power & Energy Question BankanimeshtechnosNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56Document2 pagesCH 2 - Problems 2023-12-27 22 - 14 - 56rb8q9sz8hrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Work & Energy - Questions - Class 9 Physics Question Bank With Solutions CBSE - PDF Download (2023-2024)Document4 pagesChapter 8 - Work & Energy - Questions - Class 9 Physics Question Bank With Solutions CBSE - PDF Download (2023-2024)rajatv271722No ratings yet
- Energy WorksheetDocument4 pagesEnergy WorksheetAlyssa Cole100% (1)
- Ke WorksheetDocument2 pagesKe WorksheetDark DevilNo ratings yet
- Energy: Energy Is The Ability of A Body or Object To Produce ADocument13 pagesEnergy: Energy Is The Ability of A Body or Object To Produce AJorge Rodríguez SedanoNo ratings yet
- GPE and PEDocument60 pagesGPE and PEervin matthew ranceNo ratings yet
- KE and PE worksheetDocument3 pagesKE and PE worksheetInnade IllevanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy WSDocument3 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy WSKiyu ImanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy WSDocument3 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy WSNheilzen Aelee Velasco MercaderNo ratings yet
- Energy Worksheet KE and PE CalculationsDocument3 pagesEnergy Worksheet KE and PE Calculationsbarcelot tortogoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class XI Work Power EnergyDocument4 pagesWorksheet Class XI Work Power Energyroythomasc100% (2)
- Assessment - PhysicsDocument3 pagesAssessment - PhysicselizabethNo ratings yet
- Force N Laws of Motion - WORKSHEETDocument2 pagesForce N Laws of Motion - WORKSHEETMeher KodwaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Kinetic and Potential ProblemsDocument1 pageMechanical Kinetic and Potential Problemsnicolasenciso.alumNo ratings yet
- 3 - Potential and Kinetic Energy Ws 3Document3 pages3 - Potential and Kinetic Energy Ws 3api-276813042No ratings yet
- Exercise For Final Physics 10thDocument3 pagesExercise For Final Physics 10thWilsen JeftaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper Work and Energy IXDocument2 pagesCBSE Test Paper Work and Energy IXAtharva VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Physics Assignment Chapter IXDocument1 pageWork and Energy Physics Assignment Chapter IXgurdeepsarora873867% (3)
- Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet Name: - KE 1/2 M V PE MGH F HDocument3 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet Name: - KE 1/2 M V PE MGH F HCayenne PepperNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet Name: - KE 1/2 M V PE MGH F HDocument3 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy Worksheet Name: - KE 1/2 M V PE MGH F HANGIELINA MAE CARREONNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument3 pagesWork Energy and Powerdil19860209No ratings yet
- Potentialandkineticenergyworksheet PDFDocument2 pagesPotentialandkineticenergyworksheet PDFAndrew SorianoNo ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy WorksheetDocument2 pagesKinetic and Potential Energy Worksheetbarcelot tortogoNo ratings yet
- Sci 8 Quarter 1 WK 3 Work Power EnergyDocument45 pagesSci 8 Quarter 1 WK 3 Work Power EnergyJadelence MacalindongNo ratings yet
- LKPD Ep & Ek 2Document10 pagesLKPD Ep & Ek 2Iken WidiyantiNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet 4Document3 pagesWork Sheet 4Afaan OromooNo ratings yet
- Energy QuestionsDocument2 pagesEnergy QuestionsPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- WEP Ws 002Document4 pagesWEP Ws 002JASBIR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Momentum NpteDocument30 pagesMomentum NptediliniNo ratings yet
- ch4 - 1d MomentumDocument8 pagesch4 - 1d Momentumapi-301275445No ratings yet
- Kinetic and Potential EnergyDocument4 pagesKinetic and Potential EnergyLarie Bajares33% (3)
- Ch04 05 Force Problem BankDocument11 pagesCh04 05 Force Problem Banknicky1213aNo ratings yet
- 7 Momentum HWDocument5 pages7 Momentum HWampay ayubNo ratings yet
- 2 Energy, Power, Work #2Document5 pages2 Energy, Power, Work #2Lil homieNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document11 pagesUnit 5sabirdxb107No ratings yet
- Superb Academy: Superb in Education Physics Work Power and EnergyDocument2 pagesSuperb Academy: Superb in Education Physics Work Power and EnergyKashif Ali MagsiNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Assignment-1Document3 pagesWork and Energy Assignment-1Aditi KumariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4&5 Review and Chapter 7 IntroductionDocument22 pagesChapter 4&5 Review and Chapter 7 IntroductionJunyi JiNo ratings yet
- AP Physics I - Problem Set #4 - Energy Kinetic & Potential EnergyDocument5 pagesAP Physics I - Problem Set #4 - Energy Kinetic & Potential EnergyJoseph LaMontagneNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws of Motion NumericalsDocument3 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion Numericalsdayanandan150% (2)
- SDG PossibilitiesDocument15 pagesSDG PossibilitiesPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- AI Curriculum Handbook PDFDocument126 pagesAI Curriculum Handbook PDFAyanNo ratings yet
- Amity School Class Notes on Pressure and BuoyancyDocument3 pagesAmity School Class Notes on Pressure and BuoyancyPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Press Release ScholarshipDocument1 pagePress Release ScholarshipPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- ApplicationForm Scholarship2022Document4 pagesApplicationForm Scholarship2022Priya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Senior National Championship 2022 1Document6 pagesSenior National Championship 2022 1Priya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Event Details 2022Document11 pagesEvent Details 2022Priya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Handout - Story Writing - Class IX - 2022-23Document3 pagesHandout - Story Writing - Class IX - 2022-23Priya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- (Ii) They Do Not Add To The Flow of Goods and Services in The EconomyDocument7 pages(Ii) They Do Not Add To The Flow of Goods and Services in The EconomyPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- The Healing Power of RainfallDocument3 pagesThe Healing Power of RainfallPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- HistDocument4 pagesHistPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Handout - in The Kingdom of Fools - Class IX - 2022-23Document3 pagesHandout - in The Kingdom of Fools - Class IX - 2022-23Priya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Marker)Document1 pageVery Short Answer Type Questions (1 Marker)Priya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Different kinds of fathersDocument3 pagesDifferent kinds of fathersPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- German SpeakingDocument1 pageGerman SpeakingPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Handout - A Truly Beautiful Mind - Class IX - 2022-23Document2 pagesHandout - A Truly Beautiful Mind - Class IX - 2022-23Priya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- GeoDocument4 pagesGeoPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- On An Outline Map of France Mark The Following Places-Paris, Nantes, Bordeaux, Brest and MarseillesDocument1 pageOn An Outline Map of France Mark The Following Places-Paris, Nantes, Bordeaux, Brest and MarseillesPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- TH THDocument3 pagesTH THPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Instructions For PT - 2 Class Ix - StudentsDocument1 pageInstructions For PT - 2 Class Ix - StudentsPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Drainage Handout: Class IX, GeographyDocument6 pagesChapter 3: Drainage Handout: Class IX, GeographyPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- AI: What is Artificial IntelligenceDocument7 pagesAI: What is Artificial IntelligencePriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HardwareDocument14 pagesIntroduction To HardwarePriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- AI: What is Artificial IntelligenceDocument7 pagesAI: What is Artificial IntelligencePriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Priya Agrawal 8m Ai WorksheetDocument4 pagesPriya Agrawal 8m Ai WorksheetPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chess Base Database InformationDocument1 pageChess Base Database InformationPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Lab Activity - 4.1 To Create A Form of A Future Job AdvertisementDocument14 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Lab Activity - 4.1 To Create A Form of A Future Job AdvertisementPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Klasse 7 Lektion 1 AB. Modul 3 - 20200330195955 PDFDocument9 pagesKlasse 7 Lektion 1 AB. Modul 3 - 20200330195955 PDFPriya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Hallo Deustch 2Document28 pagesHallo Deustch 2Priya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Basics Heat Mass Transfer Convection Processes PropertiesDocument14 pagesChapter 9 Basics Heat Mass Transfer Convection Processes PropertiesHajra AamirNo ratings yet
- Determine Mass Absorption CoefficientDocument4 pagesDetermine Mass Absorption CoefficientWasimNo ratings yet
- A Control Strategy For An Autonomous Robotic Vacuum Cleaner For Solar PanelsDocument9 pagesA Control Strategy For An Autonomous Robotic Vacuum Cleaner For Solar PanelsAntonio MoisesNo ratings yet
- HGL & EglDocument5 pagesHGL & EglMoch. Dimas PratamaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Proteus ReportDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Proteus ReportTaimoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Optimize Your Water Supply System with Grundfos Horizontal PumpsDocument12 pagesOptimize Your Water Supply System with Grundfos Horizontal Pumpsnightmare_hong5818No ratings yet
- Psychrometric ReviewDocument27 pagesPsychrometric ReviewfarinNo ratings yet
- Dark MatterDocument6 pagesDark MatterRanjit Edward100% (1)
- DatasheetDocument6 pagesDatasheetLuis Gustavo ReisNo ratings yet
- CIU - Communication Interface Unit: Installation and Operating InstructionsDocument10 pagesCIU - Communication Interface Unit: Installation and Operating InstructionszporvkasNo ratings yet
- Act. Module 4 - Resonance, Bandwidth, Non-Sinusoidal WaveformDocument6 pagesAct. Module 4 - Resonance, Bandwidth, Non-Sinusoidal WaveformSherwin PagpaguitanNo ratings yet
- Electricity Rules of Sarawak 1999Document130 pagesElectricity Rules of Sarawak 1999Muhammad Zakwan MasriNo ratings yet
- Ref Aircon1A ReviewerDocument105 pagesRef Aircon1A Reviewerperezismael69% (49)
- Transformer Ratio Measurements: by M Ohlen, MeggerDocument3 pagesTransformer Ratio Measurements: by M Ohlen, MeggerAfia MaktekNo ratings yet
- CO1 - Problems - Magnetic PropertiesDocument8 pagesCO1 - Problems - Magnetic Propertieskowshik ReddyNo ratings yet
- Solar Catalog Sherwin SolarbusDocument212 pagesSolar Catalog Sherwin Solarbusfastidious_5No ratings yet
- University PhysicsDocument358 pagesUniversity PhysicsAlex Kraemer100% (5)
- Motor Sizing CalculationDocument3 pagesMotor Sizing CalculationRizwan TahirNo ratings yet
- How Much Ac Ripple in A DC Power Supply Is Too Much?: Editor'S Note: Pdfs of This Article AreDocument2 pagesHow Much Ac Ripple in A DC Power Supply Is Too Much?: Editor'S Note: Pdfs of This Article Areparvinder ranaNo ratings yet
- Infineon-General Description EVAL 1K6W PSU G7 DD-ATI-V01 00-EnDocument16 pagesInfineon-General Description EVAL 1K6W PSU G7 DD-ATI-V01 00-EnCattNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument21 pagesThesisamalendu_biswas_1No ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Document34 pagesElectronic Circuits For Biological Engineering Laboratory: BE154L/A43/4Q1920Kylle SaligumbaNo ratings yet
- FS7M0680, FS7M0880: Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)Document19 pagesFS7M0680, FS7M0880: Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)Arokiaraj RajNo ratings yet
- PSE100 Datenblatt - DC-DC Wandler Polyamp - 01.2017Document4 pagesPSE100 Datenblatt - DC-DC Wandler Polyamp - 01.2017paresh joshiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Fans - Determination of Fan Sound Power Levels Under Standardized Laboratory ConditionsDocument44 pagesIndustrial Fans - Determination of Fan Sound Power Levels Under Standardized Laboratory ConditionsMarianaNo ratings yet
- Thermal power plants and coal production in IndiaDocument7 pagesThermal power plants and coal production in Indiaanup kumarNo ratings yet
- Condensate Recovery Pump: ModelDocument2 pagesCondensate Recovery Pump: ModelCTHNo ratings yet
- Driver Install Guide Specification: Model Description 1Document22 pagesDriver Install Guide Specification: Model Description 1julio cesar calveteNo ratings yet
- Eddy Current Inspection FormulaDocument4 pagesEddy Current Inspection FormulaUdhayakumar VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- BODY OF THE BOOK-Statics PDFDocument110 pagesBODY OF THE BOOK-Statics PDFChristian J SebellinoNo ratings yet