Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1. A Brief History and Overview of Technology in HR
Chapter 1. A Brief History and Overview of Technology in HR
Uploaded by
Mohammad Sohail Rashid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views24 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views24 pagesChapter 1. A Brief History and Overview of Technology in HR
Chapter 1. A Brief History and Overview of Technology in HR
Uploaded by
Mohammad Sohail RashidCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
Chapter 1
A Brief History and Overview of
Technology in HR
HISTORICAL ERAS IN HRIS
• Pre–World War II
– Reactive, “caretaker” role
– Recordkeeping – manual
– “Scientific management” philosophy
– Not major part of business
– Few government regulations
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
2
POSTWAR: 1945–1960
• Importance of employee morale
• HR part of operating costs, not in mainstream
• Labor inions established
• Job descriptions gain popularity
• Payroll function among the first for automation
• Job analysis, employee skills begin to be tracked
• R & D in selection
• Mainframe usage by defense industry in HR
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
3
SOCIAL ISSUES PERIOD: 1963–1980
• Social issues legislation impact HR
• Protector of employees
• Intro of IBM 360
• Advent of MIS
• Paperwork and reporting increases
• HR now more in mainstream of operating
budget
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
4
COST-EFFECTIVENESS: 1980-1990
• HR cost justification activities
• Increased role due to paperwork required in
legislation
• Microcomputers and software advances
• HRIS capabilities lower in cost
• Increased emphasis on R&D
• Utility analysis critical
• Smaller companies can utilize HRIS
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
5
TECHNOLOGY ADVANCEMENT ERA
(’90s–TODAY)
• Internet-enabled Web services
• HRIS more commonplace
• Business process re-engineering
• HR balanced scorecard
• Strategic HR management
• HR becoming more visible as a “strategic business
partner”
• Globalization of companies
• Hardware–software tools in decision-making
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
6
THE EVOLUTION OF STRATEGIC HRM
• Contingency perspective and fit
• Resource-based view of the firm and social capital
• HR system components and structure
• Expanding the scope of HRM beyond the focal
organization
• Achieving HR implementation and execution by
translating the rhetoric into practice,
• Measuring the outcomes of SHRM by (e.g., balanced
scorecard approach)
• Research methodological issues that stress the
importance of evidence-based management
• Adoption and use of HR metrics
• Application of “Six Sigma” processes to HRM
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
7
COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
Three Categories of Resources
• Physical
• Organizational
• Human Most Critical
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
8
ACTIVITIES OF HR
Transformational
Traditional
Transactional
Wright, McMahan, Snell, & Gerhart, 1998
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
9
HR ACTIVITIES & TIME SPENT
• Transactional (65–75%)
– Benefits Administration, Recordkeeping, Employee
Services
• Traditional (15–30%)
– Recruitment, Selection, Training, Performance
Management, Compensation, Employee Relations
• Transformational (5–15%)
– Knowledge Management, Strategic Redirection
and Renewal, Cultural Change, Management
Development
– Added Value
Wright, McMahan, Snell, & Gerhart, 1998
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
10
INTERFACE BETWEEN HR AND
TECHNOLOGY
• IT as a tool, not a substitute for people
• How might the changes in technology impact
the role and perceptions of HR departments
and professionals?
• How might technology aid in the
advancement of strategic HRM?
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
11
HRIS
• Human Resources Information System (HRIS)
– Computerized system that provides current and
accurate data for purposes of control and decision
making
– Benefits
• Store and retrieve large quantities of data
• Combine and reconfigure data to create new information
• Institutionalization of organizational knowledge
• Easier communications
• Lower administrative costs
• Increased productivity and response times
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
12
HRIS DEFINITION
• Not just hardware–software
• Includes people, forms, policies, procedures, and
data
• Purpose – provide accurate and timely
“information” to the “clients” (or stakeholders) of
HR
• Variety of users
– Strategic
– Tactical
– Operational decisions
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
13
E-HRM & HRIS
• Electronic human resource management (E-
HRM)
– Information technology (e.g., Web) – central
component
– Application and HR-function focused
• HRIS
– Technology and processes (e.g., databases,
enterprise resources planning [ERP]
architecture, smartphones, etc.) that support
employee access to HR data and the move to
E-HRM
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
14
BIGGEST ADVANTAGES OF HRIS
Reduced manual handling and paperwork
Or
Enables greater impact of paperwork on business
operation
– Reports
– Analysis
– Negotiations
– Communications
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
15
Why Do We Need an HRIS?
• Providing a comprehensive information picture as a single,
integrated database; this enables organizations to provide
structural connectivity across units and activities and to
increase the speed of information transactions
• Increasing competitiveness by improving HR operations and
management processes
• Collecting appropriate data and converting them to information
and knowledge for improved timeliness and quality of decision
making
• Producing a greater number and variety of accurate and real-
time HR-related reports
• Streamlining and enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of
HR administrative functions
• Shifting the focus of HR from the processing of transactions to
strategic HRM
• Reengineering HR processes and functions
• Improving employee satisfaction by delivering HR services more
quickly
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
16
Harnessing the Potential of an HRIS
The ability of any organization to gain effectiveness and
efficiencies from human resources technology depend on
factors such as these:
• the size of the organization, with large firms generally reaping
greater benefits;
• the amount of top-management support and commitment;
• the availability of resources (time, money, and personnel);
• the HR philosophy of the company, as well as its vision,
organizational culture, structure, and systems;
• managerial competence in cross-functional decision making,
employee involvement, and coaching; and
• the ability and motivation of employees in adopting change, such as
increased automation across and between functions (Ngai & Wat,
2004).
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
17
INFORMATION SYSTEMS PROVIDING
SUPPORT FOR HRM (Table 1.1)
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
18
INFORMATION SYSTEMS PROVIDING
SUPPORT FOR HRM (Table 1.1 Cont.)
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
19
SYSTEM DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE (SDLC)
• Five General Phases
(1) Planning
(2) Analysis
(3) Design
(4) Implementation
(5) Maintenance
– Begins with planning and ends with continuous
evaluation
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
20
SuccessFactors Employee Home Screen
A MODEL OF ORGANIZATIONAL
FUNCTIONING
• Organic model
• HRIS is critical to the efficient operation of an
organization
• Interrelatedness between the strategic
management system, the strategic HRM
system, and the performance goals
• Business and HR are generated during the
strategic planning process
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
22
A MODEL OF ORGANIZATIONAL
FUNCTIONING
• The HR goals drive the HR programs that provide
management the tools for the efficient and effective
use of employees
• The HRIS has become increasingly important in
supporting the HR management system, as well as in
strategic planning
• HR metrics and cost–benefit results (value added
and return on investment [ROI]) are in continual
interaction
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
23
A MODEL OF ORGANIZATIONAL
FUNCTIONING
• National culture impacts entire model through
strong effects on external environment
• External environment influences internal functioning
of organization
• Interaction between strategic management system
and strategic HRM will improve the functioning of
the organization
Kavanagh, Human Resource Information Systems 4e.
SAGE Publications, 2018.
24
You might also like
- Chapter 12 Recruitment and Selection in An Internet ContextDocument20 pagesChapter 12 Recruitment and Selection in An Internet ContextMumtaj ShimuNo ratings yet
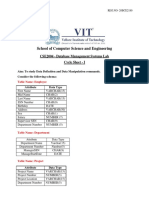
- School of Computer Science and Engineering: CSE2004 - Database Management Systems Lab Cycle Sheet - IDocument21 pagesSchool of Computer Science and Engineering: CSE2004 - Database Management Systems Lab Cycle Sheet - Iaashay kumar100% (2)
- Ch07 Cost Justifying HRIS InvestmentsDocument21 pagesCh07 Cost Justifying HRIS InvestmentsHajar AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Prodelin 1385Document33 pagesProdelin 1385bebebrenda100% (1)
- Solectron Cases - 1Document36 pagesSolectron Cases - 1kundan50% (2)
- MTI ch01Document29 pagesMTI ch01Mahabub AlomNo ratings yet
- HRISDocument21 pagesHRISAnkita BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Ch10 Recruitment and Selection in An Internet ContextDocument21 pagesCh10 Recruitment and Selection in An Internet ContextHajar Almalki100% (1)
- Cipd Article - HR and Technology, Cancer Research CaseDocument18 pagesCipd Article - HR and Technology, Cancer Research CasemtkhansNo ratings yet
- Monetary Incentives and Employee Engagement of Selected Supermarket Employees in Sta. Rosa, LagunaDocument45 pagesMonetary Incentives and Employee Engagement of Selected Supermarket Employees in Sta. Rosa, LagunaJill SulitNo ratings yet
- Ba7204 Human Resource ManagementDocument167 pagesBa7204 Human Resource ManagementAjay_mane22No ratings yet
- Notes On StaffingDocument61 pagesNotes On StaffingDrRam Singh KambojNo ratings yet
- IIPM Manpower Planning 1Document76 pagesIIPM Manpower Planning 1roopalimohiteNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management (Notes Theory)Document31 pagesHuman Resource Management (Notes Theory)Sandeep SahadeokarNo ratings yet
- E-HRM PresentationDocument11 pagesE-HRM PresentationSajal MishraNo ratings yet
- HRIS PresentationDocument20 pagesHRIS PresentationShahjahan Mushtaq100% (1)
- Explain How You Would Conduct A Job Analysis in A Company That Has Never Had Job DescriptionsDocument3 pagesExplain How You Would Conduct A Job Analysis in A Company That Has Never Had Job DescriptionsN. AzadNo ratings yet
- Presentation On HRIS of Unique Group: Independent University, BangladeshDocument18 pagesPresentation On HRIS of Unique Group: Independent University, BangladeshRejaul KarimNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument12 pagesMotivationLioness93No ratings yet
- HR in The Knowledge and Application of Project Management and Its ToolsDocument8 pagesHR in The Knowledge and Application of Project Management and Its ToolsUday DokrasNo ratings yet
- Talent ManagementDocument16 pagesTalent ManagementSõúmëñ AdhikaryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Nature and Scope of HRM: 1.1 Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Nature and Scope of HRM: 1.1 Introduction To Human Resource Managementbeing selfNo ratings yet
- Retaining Top Talent - BEC Working Paper SeriesDocument9 pagesRetaining Top Talent - BEC Working Paper SeriesJuikabloth100% (1)
- CaseDocument3 pagesCasePrashant Pandit100% (1)
- 206 ER NotesDocument126 pages206 ER NotesAvinash RathodNo ratings yet
- Organisational InterventionDocument11 pagesOrganisational InterventionRizwana BaigNo ratings yet
- Assignment Marks: 30: InstructionsDocument2 pagesAssignment Marks: 30: InstructionsCherin SamNo ratings yet
- B. Com Dcom102Document296 pagesB. Com Dcom102brijesh2016mittalNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Ethics, Justice, and Fair Treatment in HR ManagementDocument41 pagesHuman Resource Management: Ethics, Justice, and Fair Treatment in HR Managementrakibul islam rakibNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Strategic Human Resource ManagemDocument16 pagesUnit 10 Strategic Human Resource ManagemAngelo VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Learning N DevelopmentDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire On Learning N DevelopmentsptharunNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument42 pagesCase StudyHarshadaNo ratings yet
- Maslow - Applications and CriticismDocument6 pagesMaslow - Applications and CriticismDana DanutzaNo ratings yet
- Method of Job AnalysisDocument10 pagesMethod of Job AnalysisRAIHAANA MINONG NAMLANo ratings yet
- Training and Developing Employees: Global Edition 12eDocument46 pagesTraining and Developing Employees: Global Edition 12edenden007No ratings yet
- HrisDocument24 pagesHrisSujeet MundariNo ratings yet
- Personnel Planning and Recruiting: Gary DesslerDocument48 pagesPersonnel Planning and Recruiting: Gary DesslerAnamul Haque SazzadNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Managing Global Human ResourcesDocument24 pagesHuman Resource Management: Managing Global Human ResourcesANCHURI NANDININo ratings yet
- Syllabus HrisDocument1 pageSyllabus HrisashokdgaurNo ratings yet
- Impact of Job Analysis On Job PerformanceDocument20 pagesImpact of Job Analysis On Job Performancehgupta017100% (1)
- Final HRMDocument6 pagesFinal HRMDeepak KathrotiyaNo ratings yet
- SHRMDocument31 pagesSHRMritusinghtoor4291No ratings yet
- Syllabus SHRMDocument1 pageSyllabus SHRMShona ShonaNo ratings yet
- L1 - HCM An Overview (nMARCH2018) PDFDocument40 pagesL1 - HCM An Overview (nMARCH2018) PDFMuhammad Syazwan Haziq100% (1)
- Group III Personnel Management - II Xavier Institute of Social Service, RanchiDocument62 pagesGroup III Personnel Management - II Xavier Institute of Social Service, RanchiAdeel KhanNo ratings yet
- HRM in NepalDocument11 pagesHRM in NepalSuman PoudelNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Labour Relations November 2020Document64 pagesAn Introduction To Labour Relations November 2020Shante MorganNo ratings yet
- HR Analytics Unit IDocument28 pagesHR Analytics Unit IManivelanNo ratings yet
- MIRDocument21 pagesMIRSoitda BcmNo ratings yet
- TQM by Dale H. Besterfield Et Al (001-017)Document17 pagesTQM by Dale H. Besterfield Et Al (001-017)Zamien edanNo ratings yet
- HRDDocument12 pagesHRDMohammed AlastalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Systems Considerations in The Design of An HRISDocument18 pagesChapter 3 - Systems Considerations in The Design of An HRISMohammad Sohail Rashid100% (1)
- Human Resource Management Notes For All 5 UnitsDocument127 pagesHuman Resource Management Notes For All 5 UnitsAafreen MuhibbahNo ratings yet
- Organizational Agility and Organizational Learning Do They Accelerate Organizational Innovation and CompetencyDocument10 pagesOrganizational Agility and Organizational Learning Do They Accelerate Organizational Innovation and Competencytotherethym100% (1)
- Activity HRM HadayaDocument2 pagesActivity HRM HadayaHANS CHRISTIAN ADAYANo ratings yet
- MANAGEMENT - MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION 3rd SemDocument2 pagesMANAGEMENT - MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATION 3rd SemUzair ShahNo ratings yet
- The Application of Motivation Theory in Manufacturing CompanyDocument6 pagesThe Application of Motivation Theory in Manufacturing Companyblurking2002No ratings yet
- HR Practices and Issues in Manufacturing IndustriesDocument14 pagesHR Practices and Issues in Manufacturing Industriessandeep shrestha100% (1)
- The Human in Human ResourceFrom EverandThe Human in Human ResourceNo ratings yet
- Ch08 HR Administration and HRISDocument44 pagesCh08 HR Administration and HRISHajar AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Ch09 Talent ManagementDocument14 pagesCh09 Talent ManagementHajar AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document6 pagesChap 1Mahabub AlomNo ratings yet
- Introduction HrisDocument2 pagesIntroduction HrisMariah WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Data BasicsDocument81 pagesData BasicscolinNo ratings yet
- 000442Document18 pages000442colinNo ratings yet
- Costing: Approaches and TechniquesDocument51 pagesCosting: Approaches and TechniquescolinNo ratings yet
- Summary of MeasurementsDocument7 pagesSummary of MeasurementscolinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Assignment Questions Descriptive V Analytic StudentDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Assignment Questions Descriptive V Analytic StudentcolinNo ratings yet
- Organization StudiesDocument20 pagesOrganization StudiescolinNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Worksheet - Excel BasicsDocument2 pagesWeek 10 Worksheet - Excel BasicscolinNo ratings yet
- Performance Management, Compensation, Benefits, Payroll, and HRISDocument33 pagesPerformance Management, Compensation, Benefits, Payroll, and HRIScolinNo ratings yet
- Ocs Inventory Packager Usage Guide Version 1.0Document13 pagesOcs Inventory Packager Usage Guide Version 1.0infobitsNo ratings yet
- S0 HandoutDocument4 pagesS0 HandoutJ Reach (JR3ach)No ratings yet
- P2P and Mobile TV 11052007Document21 pagesP2P and Mobile TV 11052007Ted Chao100% (12)
- Survey123 TipsDocument12 pagesSurvey123 TipsCarlosNo ratings yet
- Downloads 100% Clear Mullvadvpn-2021.1.ExeDocument9 pagesDownloads 100% Clear Mullvadvpn-2021.1.Exekuya manNo ratings yet
- Supermicro C2SBX, C2SBX+ (User Manual)Document92 pagesSupermicro C2SBX, C2SBX+ (User Manual)MechDRNo ratings yet
- SAP ERP OverviewDocument89 pagesSAP ERP Overviewmrbasic042No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Application Development and Emerging TechnologiesDocument18 pagesModule 2 - Application Development and Emerging TechnologiesArvin BuzonNo ratings yet
- Livebox CliDocument102 pagesLivebox CliMichał DąbrowskiNo ratings yet
- Basic Wind Speed MapDocument1 pageBasic Wind Speed MapMunzuara AktherNo ratings yet
- 16 Inheritance TutorialDocument2 pages16 Inheritance Tutorialmattgirv0% (1)
- Network Computing: Data Communications & Networking BasicsDocument24 pagesNetwork Computing: Data Communications & Networking BasicsVara AppavooNo ratings yet
- Khan y Kellner-Opositional Politics and The Internet PDFDocument27 pagesKhan y Kellner-Opositional Politics and The Internet PDFcanicanitaNo ratings yet
- Mk5pfc ArticleDocument24 pagesMk5pfc ArticleenzolnNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Electronic Stethoscope: 2 Conceptual Design and MethodologyDocument3 pagesEnhanced Electronic Stethoscope: 2 Conceptual Design and MethodologyTushar Kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- PY064Document7 pagesPY064Shaheryar Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Orion DDIO/DCIO Module: User ManualDocument107 pagesOrion DDIO/DCIO Module: User Manualkomiks0609No ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Iot and Python ProgrammingDocument77 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Iot and Python ProgrammingKranti KambleNo ratings yet
- Cake CentralDocument159 pagesCake CentralValerya MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Harmony iPC - HMIDID64DTD1Document6 pagesHarmony iPC - HMIDID64DTD1MohanChandraNo ratings yet
- Mining Frequent, Patterns, Associations, and CorrelationsDocument13 pagesMining Frequent, Patterns, Associations, and CorrelationsSasi S INDIANo ratings yet
- Associated Sites Bill Payment (Single Account) Bill Payment (Multiple Account) View Bill Lodge A Complaint Payment HistoryDocument1 pageAssociated Sites Bill Payment (Single Account) Bill Payment (Multiple Account) View Bill Lodge A Complaint Payment Historyamit2010itNo ratings yet
- ACDSee Video Studio 2.0 EULADocument6 pagesACDSee Video Studio 2.0 EULAibrahimNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Arts - Q1 - DW4Document3 pagesContemporary Arts - Q1 - DW4nica pidlaoanNo ratings yet
- ICT in The Junior SchoolDocument25 pagesICT in The Junior Schoolsharpjacqui100% (29)
- SCTPDocument87 pagesSCTPHa Dinh ThanhNo ratings yet
- Quick Start Guide PN-PN Coupler v1 EN 08 2018Document12 pagesQuick Start Guide PN-PN Coupler v1 EN 08 2018DondoNo ratings yet