Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nashrah202670023 FinalTermAssignment
Uploaded by
Nashrah ShakeelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nashrah202670023 FinalTermAssignment
Uploaded by
Nashrah ShakeelCopyright:
Available Formats
ENG-226-Phonetics and Phonology
Submitted by: Nashrah Shakeel
Roll no: 202670023
Department: BS English
Semester: 3rd
Final Term Assignment: Comparison between English and Punjabi Stops
Submitted to: Sir Asad Habib
________________________________________________________
Phonetics is the branch of linguistics that deals with the production of sound and its reception.
Whereas, phonology is the branch of phonetics that deals with the study of the sound systems in
a language.
Although both English and Punjabi are widely different languages from each other, their
phonemes have some similarities and some differences in place of articulation, manner of
articulation, and assimilation.
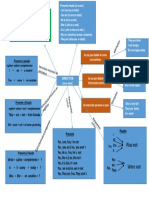
There are a total of six stops/plosives in the English language /p/, /b/, /t/, /d/, /k/, /g/ and there
are twelve stops in the Punjabi language /p/, /b/, /t̪ /, /d̪/, /k/, /g/, /ph/, /kh/, /ʈh/, /ʈ/, / t̪ h/, and /ɖ/.
These plosives/stops /p/, /b/, /k/, and /g/ are same in both languages English and Punjabi.
/p/ and /b/: In both stops, the place of articulation is bilabial, manner of articulation is
plosives/stops, non-syllabic, and /p/ is unvoiced but /b/ is voiced in both languages.
/k/: Place of articulation is velar, manner of articulation is plosives/stops, non-syllabic,
and it is unvoiced.
/g/: Place of articulation is velar, manner of articulation is plosives/stopes, non-syllabic,
and it is voiced.
/ph/, /kh/, and /th/: These stops are not available in English. These are in Punjabi only.
/ph/: Place of articulation is bilabial, manner of articulation is plosives/stops, non-syllabic
and it is unvoiced.
/kh/: Place of articulation is velar, manner of articulation is plosives/stops, non-syllabic
and it is unvoiced.
/ʈh/: Place of articulation is retroflex, manner of articulation is plosives/stops, non-
syllabic, and it is unvoiced.
/ʈ/, and/ɖ/: Both stops/plosives are Punjabi. Place of articulation is retroflex, manner of
articulation is plosives, non-syllabic, and /ʈ/ is unvoiced, and /ɖ/ is voiced. In English /t/
and /d/ stops are present like Punjabi retroflex stops but their place of articulation is
alveolar, manner of articulation is plosives, and /t/ is unvoiced and /d/ is voiced.
/t̪ /, /d̪/, and /t̪ h/: These are Punjabi dental stops. Place of articulation is dental, manner of
articulation is stops, non-syllabic, /t̪ / and /t̪ h/ is unvoiced and /d̪/ is voiced. These dental
stops are not present in the English language.
Difference between an English and Punjabi Stops:
Place of articulation
Manner of articulation
Assimilation
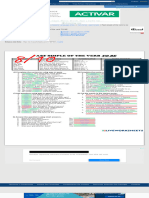
English Stops Punjabi Stops Similarities/Differences
/p/ /p/ This stop has the same
Place: +bilabial Place: +bilabial features in both languages.
Manner: +plosive Manner: +plosive Examples:
-voiced -syllabic English /p/: Pat
-voiced Punjabi /p/: ( پارcross)
/b/ /b/ This stop has the same
Place: +bilabial Place: +bilabial features in both languages.
Manner: +Plosive Manner: +plosive Examples:
+voiced -syllabic English /b/: Bell
+voiced Punjabi /b/: ( بارoutside)
/k/ /k/ This stop has the same
Place: +velar Place: +velar features in both languages.
Manner: +plosive Manner: +plosive Examples:
-voiced -syllabic English /k/: Kid
-voiced Punjabi /k/: ( کالcall)
/g/ /g/ This stop has the same
Place: +velar Place: +velar features in both languages.
Manner: +plosive Manner: +plosive Examples:
+voiced -syllabic English /g/: Gun
+voiced Punjabi /g/: ( گالabuse)
Not available in English. /ph/ Example:
Place: +bilabial /ph/: ( پ ھاڑtorn)
Manner: +plosive
-voiced
Not available in English. /ʈh/ Example:ٹ
Place: +retroflex /ʈh/: ( ھرcold)
Manner: +plosive
-voiced
Not available in English. /kh/ Example:
Place: +velar /kh/: ( کھادfertilizer)
Manner: +plosive
-voiced
/t/ /ʈ/ In the English language,
Place: +alveolar Place: +retroflex the place of articulation is
Manner: +plosive Manner: +plosive alveolar but in the Punjabi
-voiced -voiced language, the place of
articulation is retroflex.
Examples:
/ʈ/: ( ٹ پtub)
/t/: term
/d/ /ɖ/ In the English language,
Place: +alveolar Place: +retroflex the place of articulation is
Manner: +plosive Manner: +plosive alveolar but in the Punjabi
+voiced +voiced language, the place of
articulation is retroflex.
Examples:
/ɖ/: ( ڈاکmail)
/d/: dead
Not available in English. /t̪ / Example:
Place: +dental /t̪ /: ( تاڑwire)
Manner: +plosive
-voiced
Not available in English. /t̪ h/ Example: ت
Place: +dental /t̪ h/: ( ھالPlatter)
Manner: +plosive
-voiced
Not available in English. /d̪/ Example:
Place: +dental
Manner: +plosive /d̪/: Dal (lentil)
+voiced
To conclude, comparison between English and Punjabi stops, some features are similar in both
languages, but some are present in one language and not in the other. There are no retroflexes
and dental stops in the Punjabi language.
_____________________________________________
You might also like
- Phonetics & PhonologyDocument10 pagesPhonetics & Phonologysmxlpxngx98No ratings yet
- Who Is Allah by Sakina Hirschfelder PDFDocument276 pagesWho Is Allah by Sakina Hirschfelder PDFEzaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Phonetics 12 - Aspects of Connected SpeechDocument100 pagesPhonetics 12 - Aspects of Connected SpeechThảo Lê100% (1)
- Revision Unit 1-13 - KeyDocument8 pagesRevision Unit 1-13 - KeyPhương Thảo100% (1)
- Phonetics Vs PhonologyDocument53 pagesPhonetics Vs PhonologyValquiria CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- English Consonant Clusters: The Commonwealth and International Library: Pergamon Oxford English Series for Overseas StudentsFrom EverandEnglish Consonant Clusters: The Commonwealth and International Library: Pergamon Oxford English Series for Overseas StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Branches of PhonologyDocument4 pagesBranches of PhonologyJhon Rey Sumampong100% (1)
- Pucminas: IEC Fonética E FonologiaDocument54 pagesPucminas: IEC Fonética E FonologiaValcarolNo ratings yet
- The Sound /P/ & /B/: Lesson 5Document3 pagesThe Sound /P/ & /B/: Lesson 5ammagraNo ratings yet
- Ch03 Ans To ExercisesDocument3 pagesCh03 Ans To ExercisesdecarvalhothiNo ratings yet
- Lower Sorbian LanguageDocument6 pagesLower Sorbian LanguagenataliaNo ratings yet
- Daypo UnidosDocument55 pagesDaypo UnidosMaria.Fer79No ratings yet
- 6 - Task 2 - Janice Martinez ParraDocument4 pages6 - Task 2 - Janice Martinez ParraJanice Susana Martinez ParraNo ratings yet
- Phonetics vs. PhonologyDocument3 pagesPhonetics vs. PhonologyDaniel Garzia AizragNo ratings yet
- Making It ClearDocument36 pagesMaking It ClearWilson ZuletaNo ratings yet
- Makalah Discribing ConsonantDocument13 pagesMakalah Discribing ConsonantHandika Galih PrakasaNo ratings yet
- EL120 Week 5-Unit 5Document46 pagesEL120 Week 5-Unit 5hawracvniNo ratings yet
- Angie Phonemes and AllophonesDocument9 pagesAngie Phonemes and AllophonesFabiola sandy Huaman maquiNo ratings yet
- Workshop 2Document11 pagesWorkshop 2Ilse AlvarezNo ratings yet
- English Phonemes Not in KhmerDocument2 pagesEnglish Phonemes Not in KhmerMENGLY MeyliNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Vs Phonology 1Document3 pagesPhonetics Vs Phonology 1Saheli GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dagomba Tree NamesDocument36 pagesDagomba Tree NamesYussif Mohammed SaniNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and FonologyDocument3 pagesPhonetics and FonologyGeorgett VasquezNo ratings yet
- Phonological Translation: X A HereDocument7 pagesPhonological Translation: X A HereNahru FalahNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Vs Phonology by ColemenDocument4 pagesPhonetics Vs Phonology by ColemenDestianNo ratings yet
- In PhonologyDocument5 pagesIn Phonologyسہۣۗيزار سہۣۗيزارNo ratings yet
- Portuguese NorwegianDocument4 pagesPortuguese NorwegianPedro FelipeNo ratings yet
- Who Is Allah by Sakina Hirschfelder PDFDocument276 pagesWho Is Allah by Sakina Hirschfelder PDFEzaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- PhonolDocument6 pagesPhonolAvinash RawalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 (2022-2023)Document58 pagesLecture 4 (2022-2023)A. zelezkoNo ratings yet
- Norwegian On The WebDocument4 pagesNorwegian On The WebAlka Vidya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Places of Articulation: in What Area of Oral Cavity A Consonant Is ProducedDocument7 pagesPlaces of Articulation: in What Area of Oral Cavity A Consonant Is ProducedShanti.R. AfrilyaNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Connected Speech 2022Document6 pagesAspects of Connected Speech 2022RocioNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument13 pagesPhonetics and Phonologynikol.elias2305No ratings yet
- Phonetics, Week 5, Part Two. Classification of Vowels-1Document22 pagesPhonetics, Week 5, Part Two. Classification of Vowels-1Brwa KamilNo ratings yet
- PanduniaDocument44 pagesPanduniamaeslorNo ratings yet
- ORAL II - ALLPHONES - CONSONANTS and VOWELSDocument36 pagesORAL II - ALLPHONES - CONSONANTS and VOWELSMaría M MalakNo ratings yet
- Laya & Quintana EnglishDocument8 pagesLaya & Quintana EnglishMaría Andreina DíazNo ratings yet
- English and Cantonese Phonology in Contrast: Explaining Cantonese ESL Learners' English Pronunciation ProblemsDocument20 pagesEnglish and Cantonese Phonology in Contrast: Explaining Cantonese ESL Learners' English Pronunciation ProblemsTerry TungNo ratings yet
- P/, /B/, and /MDocument5 pagesP/, /B/, and /MKumang Sonna JouseNo ratings yet
- Itl Lesson 6-Place of ArticulationDocument3 pagesItl Lesson 6-Place of ArticulationEve RulonaNo ratings yet
- Ch4 Phonology WRDocument13 pagesCh4 Phonology WRDianna Rose AndanNo ratings yet
- Connected SpeechDocument9 pagesConnected SpeechBlanca LebowskiNo ratings yet
- The Place of ArticulationDocument4 pagesThe Place of Articulationcandygold66No ratings yet
- Phonology 3 PDFDocument64 pagesPhonology 3 PDFLingua Academy-club LacNo ratings yet
- MidtermDocument41 pagesMidtermmr.pidatoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - STT 27, STT 29, STT 33Document27 pagesModule 3 - STT 27, STT 29, STT 33Trà Nguyễn HươngNo ratings yet
- Phonetics vs. Phonology: /kip/ The Place of Articulation Is Fronter in (K)Document4 pagesPhonetics vs. Phonology: /kip/ The Place of Articulation Is Fronter in (K)tariqNo ratings yet
- Karai Karai Karekare English Hausa Dictionary CompressDocument127 pagesKarai Karai Karekare English Hausa Dictionary CompressDorschner BarinovNo ratings yet
- Resumen Basico de ConsonantesDocument5 pagesResumen Basico de ConsonanteslcracaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Articulation and CoarticulationDocument3 pagesMultiple Articulation and CoarticulationshahrierrahmanNo ratings yet
- Grammatical Analysis (Autosaved)Document16 pagesGrammatical Analysis (Autosaved)arre jay m cercadoNo ratings yet
- Approximant and SemivowelsDocument4 pagesApproximant and SemivowelsmarkcordovarojasNo ratings yet
- English 5Document5 pagesEnglish 5EINSTEINNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument7 pagesResearchmostapha dibNo ratings yet
- Consonants Place and Manner of Articulation and VowelsDocument11 pagesConsonants Place and Manner of Articulation and VowelsKrisha EderaNo ratings yet
- Linguistics Kelompok 3Document17 pagesLinguistics Kelompok 3Salman Farizi100% (1)
- Liworiz Reading NotesDocument4 pagesLiworiz Reading NotesRenz RayarkNo ratings yet
- Voluspa and Helgi Halfdanarson - Shockin PDFDocument5 pagesVoluspa and Helgi Halfdanarson - Shockin PDFnada88peNo ratings yet
- Class8th - Unit4 - Section2 - August 2 Week PlanningDocument4 pagesClass8th - Unit4 - Section2 - August 2 Week PlanningArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Missioning & Visioning ExerciseDocument4 pagesMissioning & Visioning ExerciseDikshit TallapragadaNo ratings yet
- Test 2 MoiDocument2 pagesTest 2 MoiĐỗ Mai PhươngNo ratings yet
- OPT B1plus WB Answers: WorkbookDocument25 pagesOPT B1plus WB Answers: Workbookirene martin bugalloNo ratings yet
- Mapa Mental Verbo To BeDocument1 pageMapa Mental Verbo To Belusmeli100% (1)
- Easy QuestionsDocument9 pagesEasy QuestionsAhaan DoshiNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test in ENGLISHDocument8 pagesThird Periodical Test in ENGLISHEliza Mea LamosteNo ratings yet
- Yesterday by The Beatles Lyric Review by JForrest EnglishDocument5 pagesYesterday by The Beatles Lyric Review by JForrest EnglishraduNo ratings yet
- LOMLOE Key2e 2023Document4 pagesLOMLOE Key2e 2023Montse RodmurNo ratings yet
- 1bai Tap Dung Kem SGK - Anh 11 - Phan 1Document60 pages1bai Tap Dung Kem SGK - Anh 11 - Phan 1Phung Thi Kim DungNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Interactivo de Past Simple of The Verb To BeDocument1 pageEjercicio Interactivo de Past Simple of The Verb To Bejenniffer urracaNo ratings yet
- Modul PDPR English Year 3 Bestari: Name: .. .Document19 pagesModul PDPR English Year 3 Bestari: Name: .. .WARDAH BINTI MD NOR KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Non-Fiction TextsDocument21 pagesAnalyzing Non-Fiction TextsRedemption Caoile GuintoNo ratings yet
- Summary TESTING VOCABULARYDocument3 pagesSummary TESTING VOCABULARYWilma AnugrahNo ratings yet
- CSE 326 Lecture 1Document22 pagesCSE 326 Lecture 1Asnad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Commutative EnglishDocument43 pagesCommutative EnglishGuruKPO100% (4)
- Uan Sma 2005Document90 pagesUan Sma 2005Agus Wuryanto100% (1)
- Ortho TypographyDocument10 pagesOrtho TypographyDiego Sendín TorresNo ratings yet
- 2 Sources and Targets in Primary Metaphor Theory: Looking Back and Thinking AheadDocument19 pages2 Sources and Targets in Primary Metaphor Theory: Looking Back and Thinking AheadrosenbergalapeNo ratings yet
- (123doc) Dap An Mon Tu Vung Ngu Nghia Hoc En11 Dai Hoc MoDocument22 pages(123doc) Dap An Mon Tu Vung Ngu Nghia Hoc En11 Dai Hoc MoTutyNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Present Perfect 1 (I Have Done)Document3 pagesUnit 7. Present Perfect 1 (I Have Done)LopezNo ratings yet
- CCS Q1 Module 3Document31 pagesCCS Q1 Module 3Ivy Grace AndradeNo ratings yet
- Online Quiz - English 9Document6 pagesOnline Quiz - English 9Santa Esmeralda GuevaraNo ratings yet
- EPOS - TOEFL EXERCISE 1 - IF1 - Friday08 - 195410033 - Moh - FauziDocument1 pageEPOS - TOEFL EXERCISE 1 - IF1 - Friday08 - 195410033 - Moh - FauziAnonymous HackerNo ratings yet
- Detailes English GrammerDocument25 pagesDetailes English GrammerJbour LaithNo ratings yet
- DistrictFactbook Madhya Pradesh BhopalDocument28 pagesDistrictFactbook Madhya Pradesh BhopalYashita SinghNo ratings yet
- Bilingualism and Bilingual EducationDocument26 pagesBilingualism and Bilingual EducationLau RamirezNo ratings yet
- Using Games To Teach Parts of SpeechDocument14 pagesUsing Games To Teach Parts of SpeechVictor GiardinaNo ratings yet