Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beri151216 w1
Beri151216 w1
Uploaded by
Angga Mardana Arya KencengOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Beri151216 w1
Beri151216 w1
Uploaded by
Angga Mardana Arya KencengCopyright:
Available Formats
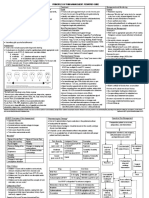
Visual summary
Managing low back Person with
pain and sciatica low back pain
A brief overview the new NICE
guidelines, from the perspective of With or without sciatica
a patient presenting in primary care.
Consider Exclude specific causes of low back pain, for example:
Referral
alternatives Cancer Infection Trauma Inflammatory disease Cauda equina
Imaging Assess likely recovery outcomes
Only consider imaging: The complexity and intensity of treatment may vary depending on
In specialist care how likely it is that the patient will have a good functional outcome
and
Consider using risk stratification Possible indicators of poor outcomes
If likely to alter management –such as the STarT Back risk Fear / pain avoidance Low mood
assessment tool Job dissatisfaction Ongoing litigation
Good Likely outcomes Poor
Provide self management information Self management is important for all patients,
Information on nature of pain Encouragement to continue activities even those with acute symptoms and/or sciatica
To manage a Pain is persistent /
specific episode treatment resistant
Managing
acute sciatica
Group
+ Manual
therapy Combined
physical +
Neuropathic exercise psychological
Psychological
pain medication
+ therapy
programme
Epidural injections
Steroid
+
Local anaesthetic
Consider pain relief options
Paracetamol NSAIDs* Weak opioids
Spinal decompression Not Consider If NSAID ineffective /
effective oral not tolerated /
After acute symptoms of sciatica alone NSAIDs contraindicated
are controlled, it may be
appropriate to (re)enter an
excercise programme to manage
* NSAIDs = non-steroidal
underlying low back pain Do not offer acupuncture anti-inflammatory drugs
© 2016 BMJ Publishing group Ltd.
Read the full http://bmj.co/lbpNICE
Disclaimer: This infographic is not a validated clinical decision aid. This information is provided without
any representations, conditions or warranties that it is accurate or up to date. BMJ and its licensors
article online assume no responsibility for any aspect of treatment administered with the aid of this information. Any
reliance placed on this information is strictly at the user's own risk. For the full disclaimer wording see
BMJ's terms and conditions: http://www.bmj.com/company/legal-information/
You might also like
- Journal Prompts For Shadow WorkDocument3 pagesJournal Prompts For Shadow WorkIsamar Lopez Rodriguez75% (4)
- Rudolf Steiner - Geographic Medicine GA 178Document35 pagesRudolf Steiner - Geographic Medicine GA 178Raul PopescuNo ratings yet
- Emotional AbuseDocument3 pagesEmotional AbuseHicham Abbassi100% (4)
- The Right Brain and The Unconscious - Discovering The Stranger Within (PDFDrive)Document422 pagesThe Right Brain and The Unconscious - Discovering The Stranger Within (PDFDrive)Eva DeganoNo ratings yet
- Successful Cross-Cultural Management: A Guide For International ManagersDocument19 pagesSuccessful Cross-Cultural Management: A Guide For International ManagersBusiness Expert Press100% (13)
- Radical Acceptance WorksheetsDocument14 pagesRadical Acceptance WorksheetsChristina RossettiNo ratings yet
- Demonstrate: Pain Coping TechniquesDocument4 pagesDemonstrate: Pain Coping TechniquesMae Therese B. MAGNO100% (1)
- Nursing Interventions For Acute PainDocument5 pagesNursing Interventions For Acute Painrosita d. ramosNo ratings yet
- Pain Free 1-2-3: A Proven Program for Eliminating Chronic Pain NowFrom EverandPain Free 1-2-3: A Proven Program for Eliminating Chronic Pain NowRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- The Aura-Soma Colour Essences PDFDocument2 pagesThe Aura-Soma Colour Essences PDFhelen100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background of Knowledge Nursing Objectives/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background of Knowledge Nursing Objectives/Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationIvy Lapore100% (1)
- Personal Development Lesson 8Document14 pagesPersonal Development Lesson 8Nikka Irah CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Why Love Turns Into Hate PDFDocument2 pagesWhy Love Turns Into Hate PDFindrani royNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Mrs. Patao Ob Ward, GSGH Assessment SubjectiveDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Mrs. Patao Ob Ward, GSGH Assessment Subjectiveraizelc100% (2)
- Pain - Post Partum MotherDocument2 pagesPain - Post Partum Motherulrikov91% (11)
- Difflam Drug StudyDocument1 pageDifflam Drug StudyDanlee EstandaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Chlordiazepoxide, Lorazepam)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Chlordiazepoxide, Lorazepam)Kuro Hanabusa100% (2)
- Principles of Pain Management: Pediatric GuideDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Pain Management: Pediatric Guideblaziken123No ratings yet
- Knowledge and Philosophical Foundation in Social Work Unit 3 The Philosophical and Values Foundation in Social Work OutlineDocument6 pagesKnowledge and Philosophical Foundation in Social Work Unit 3 The Philosophical and Values Foundation in Social Work OutlineKendrick L. BuchanNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Tuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Acute PainDocument2 pagesTuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Acute PainSALMA M. TUANONo ratings yet
- Migraines: Migraine Treatment and Prevention Options: The most important information you need to improve your healthFrom EverandMigraines: Migraine Treatment and Prevention Options: The most important information you need to improve your healthNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- CV Prof Husni TanraDocument1 pageCV Prof Husni Tanramimil100% (1)
- Infographic CMRO Commentary Wolfarth2022Document1 pageInfographic CMRO Commentary Wolfarth2022sofianealvarrezNo ratings yet
- Pain Agitation and Delirium (PAD) UHL Critical Care GuidelineDocument35 pagesPain Agitation and Delirium (PAD) UHL Critical Care GuidelineLollapallooza 23No ratings yet
- PAiN SYnDrOmEs (Reviewer)Document19 pagesPAiN SYnDrOmEs (Reviewer)Agum, Philip James P.No ratings yet
- Know Acute Pain-Standard Slide-Approve For Use - DR - ZuhadDocument42 pagesKnow Acute Pain-Standard Slide-Approve For Use - DR - Zuhadteguh cahyonoNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease ED Vasocclusive Crises Pain Management GuidelineDocument1 pageSickle Cell Disease ED Vasocclusive Crises Pain Management GuidelineLakshmanan KrishnamurtiNo ratings yet
- OrthopeadicsDocument30 pagesOrthopeadicsharshaNo ratings yet
- NCP Multple MyelomaDocument2 pagesNCP Multple Myelomavia macarioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationAgnes GeolinaNo ratings yet
- Neck Pain ProtocolsDocument3 pagesNeck Pain Protocolsrizk86No ratings yet
- 016unit 3 - Concepts and Challenges in Patient ManagementDocument3 pages016unit 3 - Concepts and Challenges in Patient ManagementSweet HeartNo ratings yet
- Actual NCP - RabiesDocument2 pagesActual NCP - RabiesDenice Tamayo De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain TeresitoDocument3 pagesNCP Pain TeresitoTheresa Reyes De JesusNo ratings yet
- Nonopioid Treatments For Chronic PainDocument2 pagesNonopioid Treatments For Chronic PainSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- 3 NCP FinalDocument7 pages3 NCP FinalJames PanlaanNo ratings yet
- Care PlanDocument3 pagesCare Planapi-381438480No ratings yet
- London Final Ch42Document26 pagesLondon Final Ch42kafosidNo ratings yet
- 1 Semester: Anti-Migraine Agents Are Used To Treat Migraine HeadachesDocument26 pages1 Semester: Anti-Migraine Agents Are Used To Treat Migraine HeadachesMARY BERNADETTE EGANANo ratings yet
- Nonnarcotic Methods of Pain ManagementDocument1 pageNonnarcotic Methods of Pain ManagementVanessa PasikNo ratings yet
- TVP-2020 Pain-Management EbookDocument44 pagesTVP-2020 Pain-Management Ebookizabelle.pereiraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Case ScenarioDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan: Case ScenarioShelvin Jules LayvaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: List Priority Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: List Priority Nursing DiagnosisLen meloNo ratings yet
- Subacute Low Back PainDocument49 pagesSubacute Low Back Painsayid najibullahNo ratings yet
- Algoritma Handling NyeriDocument21 pagesAlgoritma Handling Nyeriscan resepNo ratings yet
- Sample Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageSample Nursing Care PlanQuiannë Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Otc Advisor PainDocument24 pagesOtc Advisor Painfarzad100% (2)
- US - Article - 1col - Peri-Op - June22Document12 pagesUS - Article - 1col - Peri-Op - June22Odett NuñezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJoselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Clin Management Cancer Pain Pedi Web AlgorithmDocument28 pagesClin Management Cancer Pain Pedi Web AlgorithmRuben Santiago LassoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP - Acute PainMA. CONSOLACION DILAGNo ratings yet
- Ards DSDocument11 pagesArds DSP BNo ratings yet
- 10 Consejos en La SedacionDocument3 pages10 Consejos en La SedacionAntonio AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Pain Dr. HenryDocument36 pagesPain Dr. Henryreagan setiawanNo ratings yet
- Pain ManagementDocument68 pagesPain Managementapi-734449276No ratings yet
- Drug Study (Tramadol)Document1 pageDrug Study (Tramadol)Baji ۦۦNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument22 pagesUntitledTheo Roi MusniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanAcob, Jean LykaNo ratings yet
- Yanga - NCP, Drug Study, FdarDocument7 pagesYanga - NCP, Drug Study, Fdar3amabelle arevaloNo ratings yet
- Headache Management Guideline For Adults Version 10Document6 pagesHeadache Management Guideline For Adults Version 10TomiNo ratings yet
- The Pharmacotherapy of Low Back Pain: S Afr Fam Pract ReviewDocument3 pagesThe Pharmacotherapy of Low Back Pain: S Afr Fam Pract Reviewskola onlajnNo ratings yet
- NCP Infectious - Docx 2Document7 pagesNCP Infectious - Docx 2Diana Anne MarisNo ratings yet
- NCP Ortho WardDocument2 pagesNCP Ortho WardAira MaeNo ratings yet
- CP 94d - Information Sheet 4 - Acute Shoulder PainDocument2 pagesCP 94d - Information Sheet 4 - Acute Shoulder PainJanetNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyFrances Katherine GarciaNo ratings yet
- PainartDocument1 pagePainartapi-581236671No ratings yet
- The Art of Holistic Pain Management: A Practical HandbookFrom EverandThe Art of Holistic Pain Management: A Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Inglés II - Unidad 2Document10 pagesInglés II - Unidad 2pgomezg35No ratings yet
- Chapter Ii Self AwarenessDocument9 pagesChapter Ii Self AwarenessJenelyn RusianaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Therapeutic Modalities - 060200-1Document16 pages2023 Therapeutic Modalities - 060200-1rtarroma24No ratings yet
- PD 2ndq Module Week 2Document15 pagesPD 2ndq Module Week 2It’s yanaNo ratings yet
- Margaret Jean Watson: "Theory of Human Caring" EducationDocument8 pagesMargaret Jean Watson: "Theory of Human Caring" EducationMa. Pia Lorein JacintoNo ratings yet
- Sense of TouchDocument2 pagesSense of TouchTr WycliffeNo ratings yet
- PFA PosttestDocument30 pagesPFA PosttestLEAH FE DAYRITNo ratings yet
- Love LettersDocument65 pagesLove LettersMonica IonNo ratings yet
- The Data Compiled by The Organisation Was Very Useful.: Answer & SolutionDocument46 pagesThe Data Compiled by The Organisation Was Very Useful.: Answer & SolutionAli AliNo ratings yet
- UnknownDocument23 pagesUnknownAli BulganNo ratings yet
- Numerology 222 MeaningDocument2 pagesNumerology 222 MeaningLlNo ratings yet
- Possibilities of HumanDocument4 pagesPossibilities of HumanDionysios StravopodisNo ratings yet
- Four Pillars of Communication Speaking SkillsDocument47 pagesFour Pillars of Communication Speaking Skillsanbhute3484100% (1)
- PST Documentation of Planning Cycle TemplateDocument3 pagesPST Documentation of Planning Cycle TemplateAnh Pham QuynhNo ratings yet
- Merleau-Ponty's Embodied SemanticsDocument27 pagesMerleau-Ponty's Embodied SemanticsGabe Flacks100% (3)
- Families and Influence On ChildrenDocument10 pagesFamilies and Influence On ChildrenFAPOHUNDA Omotosho AmonbiNo ratings yet
- 1b. Havik, Tielens in Conversation With J.Palaasmaa - Atmosphere - Compassion - and - Embodied - ExperienceDocument10 pages1b. Havik, Tielens in Conversation With J.Palaasmaa - Atmosphere - Compassion - and - Embodied - ExperienceLOGAN LEYTONNo ratings yet
- 12s Mental Health Brochure 04272022Document2 pages12s Mental Health Brochure 04272022Amoxi CelineNo ratings yet
- Gilbert 2009Document11 pagesGilbert 2009Administrador ContaNo ratings yet