Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bronchodilators Corticosteroids Other Agents
Uploaded by
Alexandra AlexaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bronchodilators Corticosteroids Other Agents
Uploaded by
Alexandra AlexaCopyright:
Available Formats
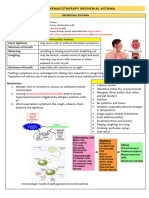
COPD Bronchodilators Corticosteroids Other agents
-β2-adrenergic agonists and -may improve symptoms, lung function and -Roflumilast is an oral phosphodiesterase-4
anticholinergic agents ipratropium and quality of life in COPD patients with FEV1 of inhibitor used to reduce exacerbations in patients with severe
tiotropium are the foundation of therapy less than 60% predicted chronic bronchitis
for COPD -increased risk of pneumonia -reduce inflammation by increasing levels of intracellular
->increase airflow, alleviate symptoms, and -Although often used for acute cAMP in lung cells
decrease exacerbation rates exacerbations, oral corticosteroids are not -nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,
-LABAs and tiotropium are preferred as recommended for long-term treatment and headache
first-line treatment
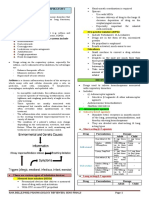
Allergic Antihistamines (H1-receptor bl.) Corticosteroids α-Adrenergic agonists Other agents
rhinitis -useful for the management of -Intranasal corticosteroids, such as -nasal decongestants such -Intranasal cromolyn may be useful in allergic
symptoms of allergic rhinitis caused by beclomethasone, budesonide, as rhinitis, particularly when administered before
histamine fluticasone, ciclesonide, phenylephrine, constrict contact with an allergen
-more effective for prevention mometasone, and triamcinolone, dilated arterioles in the ->dosing should begin at least 1 to 2 weeks
of symptoms, rather than treatment are the most effective medications nasal mucosa and reduce prior to allergen
once symptoms have begun for treatment of allergic rhinitis airway resistance Exposure
-First-generation antihistamines, such as -improve sneezing, itching, -aerosol->drugs have a -Although potentially inferior to other
diphenhydramine and rhinorrhea, and nasal congestion rapid onset of action and treatments, some LT antagonists are effective
chlorpheniramine, are usually not -Systemic absorption is minimal show few systemic effects for allergic rhinitis (monotherapy
preferred due to adverse effects, such -nosebleed, sore throat, and, -no longer than 3 days due or in combination)->pat. with also asthma
as sedation, performance impairment, rarely, candidiasis to the risk of rebound -intranasal formulation of ipratropium is
and other anticholinergic effects -just for the nose, don’t inhale nasal congestion (rhinitis available to treat rhinorrhea associated with
-fexofenadine, loratadine, -chronic rhinitis->improvement medicamentosa) allergic rhinitis or common cold
desloratadine, cetirizine, and intranasal after 1 to 2 weeks
azelastine are generally better tolerated
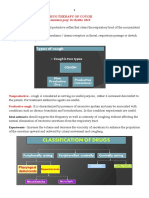
Cough Opioids Benzonatate
-Codeine decreases the sensitivity of cough centers in the CNS to peripheral stimuli and decreases mucosal -benzonatate suppresses the cough reflex
secretion through peripheral action
-therapeutic effects occur at doses lower than those required for analgesia ->anesthetizes the stretch receptors located in
->constipation, dysphoria, and fatigue, still occur the respiratory passages, lungs, and pleura
-Dextromethorphan is a synthetic derivative of morphine that has no analgesic effects in antitussive doses -Side effects include dizziness, numbness of
-low doses-> a low addictive profile but potential drug of abuse, since it may cause dysphoria at high doses the tongue, mouth, and throat
-Dextromethorphan has a significantly safer side effect profile than codeine and is equally effective for ->may be particularly problematic if the
cough suppression capsules are broken or chewed and the
-Guaifenesin available as a single-ingredient formulation and is also a common ingredient in combination medication comes in direct contact with the
products with codeine or dextromethorphan oral mucosa
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CPG On Chronic CoughDocument93 pagesCPG On Chronic Coughgail100% (2)
- GUIDANCE COUNSELOR - COORDINATOReditedDocument12 pagesGUIDANCE COUNSELOR - COORDINATOReditedRodel AriolaNo ratings yet
- Sympathomimetic Agents: CLIN. PHARM (Dr. Salvador) Asthma 05 SEPT 2017Document3 pagesSympathomimetic Agents: CLIN. PHARM (Dr. Salvador) Asthma 05 SEPT 2017Seff Causapin100% (1)
- Essential ENT by Rogan J Corbridge MB BS, BSC, 2nd Ed 2011 2 PDFDocument1 pageEssential ENT by Rogan J Corbridge MB BS, BSC, 2nd Ed 2011 2 PDFMariam Qais100% (1)
- TFN-Theorist Midterm Part2Document49 pagesTFN-Theorist Midterm Part2kNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Respiratory SystemDocument65 pagesDrugs Affecting Respiratory SystemvivianNo ratings yet
- Pain Assessment and ManagementDocument37 pagesPain Assessment and ManagementRNdrei dela Cruz100% (3)
- Adime Note GDMDocument2 pagesAdime Note GDMapi-242547654100% (1)
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanDudil Goat100% (1)
- The Effect of Chamomile Tea To Induce A Persons Sleepiness FINALDocument47 pagesThe Effect of Chamomile Tea To Induce A Persons Sleepiness FINALMaxinne Alquilos MadroñalNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Pulmonary System 2: Dr. Dita Hasni, M.BiomedDocument24 pagesDrugs Acting On The Pulmonary System 2: Dr. Dita Hasni, M.BiomedYeny ElfiyantiNo ratings yet
- CoughDocument16 pagesCoughRwapembe StephenNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PharmacologyDocument34 pagesRespiratory PharmacologyHirpâsà MămoNo ratings yet
- Cough: Drug Therapy of CoughDocument4 pagesCough: Drug Therapy of CoughAbdul HameedNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument6 pagesRespiratory DrugsCurtney PedriaNo ratings yet
- By: Cirilo Albert Hicban RN, RMDocument26 pagesBy: Cirilo Albert Hicban RN, RMrongan008No ratings yet
- Midterm PharmaDocument25 pagesMidterm PharmaKaye Honeylee ManibogNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reviewer - SemisDocument7 pagesPharmacology Reviewer - SemisNhica GrandeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Disorders (Asthma & COPD ..)Document5 pagesRespiratory System Disorders (Asthma & COPD ..)KC PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Lo 4 Sk1 Rhinitis AlergiDocument4 pagesLo 4 Sk1 Rhinitis AlergiFullyNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Week 9 Charlene Fidellaga BSN Y2-11Document8 pagesDRUG STUDY Week 9 Charlene Fidellaga BSN Y2-11Charlene FidellagaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs 1Document7 pagesRespiratory Drugs 1Kim Harold SalasNo ratings yet
- PHL Drugs Used in COPDDocument4 pagesPHL Drugs Used in COPDFadhlina OmarNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractDocument12 pagesDrugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractPrincess C. SultanNo ratings yet
- Pascual LaboratoriesDocument2 pagesPascual LaboratoriesAlyssa Marie Petonio BialaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Chapter - Respiratory SystemDocument25 pages4 - Chapter - Respiratory SystemleonNo ratings yet
- Common ColdDocument4 pagesCommon ColdJohnMyu Beler Jibuy JibuyNo ratings yet
- 8respiratory DrugsDocument2 pages8respiratory DrugsSOFIA ALYSSA MARIE ABUDENo ratings yet
- Pharmacology ReviewerDocument7 pagesPharmacology ReviewerNhica GrandeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System DrugsDocument5 pagesRespiratory System DrugsHamad AlshabiNo ratings yet
- Pharm: Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesPharm: Respiratory SystemNathan BarrerasNo ratings yet
- Hapit Naumay FinalDocument5 pagesHapit Naumay FinalGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- BeclomethasoneDocument2 pagesBeclomethasoneDiane Bonita HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug PresentationDocument4 pagesDrug Presentationchaudharitrushar007No ratings yet
- COPDwith Steroidsand BronchodilatorsDocument3 pagesCOPDwith Steroidsand BronchodilatorsTom MallinsonNo ratings yet
- AntitussivesDocument5 pagesAntitussivesAditya PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Pharma Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesPharma Respiratory SystemGallel PanumNo ratings yet
- Asthma Drugs PDFDocument2 pagesAsthma Drugs PDFRahmat PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Urti Lrti Drugs 2023Document8 pagesUrti Lrti Drugs 2023dlabdon0310No ratings yet
- Treatment of Cough: General Topics: Chapter 6Document3 pagesTreatment of Cough: General Topics: Chapter 6Martijn JohanNo ratings yet
- I. A D I: Rugs FOR SthmaDocument7 pagesI. A D I: Rugs FOR SthmaratheeshkumarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessorDocument40 pagesDr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessortamaNo ratings yet
- Defn: Periodic Spasm of Bronchial Smooth Muscles, Increased Secretion, andDocument5 pagesDefn: Periodic Spasm of Bronchial Smooth Muscles, Increased Secretion, andSambit BeheraNo ratings yet
- Acute Asthma Exacerbations: DR Abdelmoniem Saeed Mohammed Er SpecialistDocument36 pagesAcute Asthma Exacerbations: DR Abdelmoniem Saeed Mohammed Er SpecialistYousef Al-AmeenNo ratings yet
- Drug Used For The Treatment of Cough - DR - AnilaDocument28 pagesDrug Used For The Treatment of Cough - DR - AnilarameshbmcNo ratings yet
- Sinusitis & Its TreatmentDocument20 pagesSinusitis & Its Treatmentfarmasi_hmNo ratings yet
- Aerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaDocument4 pagesAerovent, Apovent Atronase, Ipraxa, Ipvent Rhinovent, Rinatecrinovagos, Atrovent, Atrovent HfaGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Respiratory SystemDocument62 pagesDrugs Affecting Respiratory Systemyunita ekawatiNo ratings yet
- Pharm Exam Ii NotesDocument24 pagesPharm Exam Ii Noteskatiana louisNo ratings yet
- PHL1 - Pharmacotherapy Bronchial AsthmaDocument7 pagesPHL1 - Pharmacotherapy Bronchial AsthmaFadhlina OmarNo ratings yet
- Opioid Induced PruritusDocument2 pagesOpioid Induced PruritusJavierNo ratings yet
- MorningDocument9 pagesMorningCamelle DiniayNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument2 pagesCholinergic AntagonistsAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Asthma MedicationDocument2 pagesAsthma MedicationAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Document21 pagesP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Sadam ArigaNo ratings yet
- Decongestant - WikipediaDocument7 pagesDecongestant - WikipediaMuhammadafif SholehuddinNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs 2Document4 pagesRespiratory Drugs 2Ella RivaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Management of COPDDocument6 pagesDrugs Used in The Management of COPDASWINI GNo ratings yet
- Drugs For CoughDocument18 pagesDrugs For CoughAbraham BanjoNo ratings yet
- Antiasthma and Cough MedicineDocument47 pagesAntiasthma and Cough MedicineYordanos EshetuNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument12 pagesAnesthesiaعلي الاسديNo ratings yet
- Ipratroprium Drug CardDocument3 pagesIpratroprium Drug CardXiaoDuckyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesPharmacology Gas ExchangekatrinasdNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Pharmacology Anticoughing AgentsDocument10 pagesPulmonary Pharmacology Anticoughing AgentsanaNo ratings yet
- Cough, Cold, and Allergy: AntitussivesDocument8 pagesCough, Cold, and Allergy: AntitussivesSalsabila RaniahNo ratings yet
- Intracranial HaemorrhageDocument3 pagesIntracranial HaemorrhageAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- PED1213Patterson OLODocument6 pagesPED1213Patterson OLOAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Circardian Variation On Febrile SeizuresDocument4 pagesCircardian Variation On Febrile SeizuresAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- HIV and NeurologyDocument2 pagesHIV and NeurologyAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 DIURETICSDocument14 pagesChapter 18 DIURETICSAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Quinidine Procainamide Disopyramide Quinidine Flecainide: Class 1A Class 1B Class 1CDocument3 pagesQuinidine Procainamide Disopyramide Quinidine Flecainide: Class 1A Class 1B Class 1CAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agents Mucosal Protective Agents: Amoxicillin Clarithromycin SucralfateDocument2 pagesAntimicrobial Agents Mucosal Protective Agents: Amoxicillin Clarithromycin SucralfateAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Senna: Irritants and Stimulants Stool Softeners (Emollient Laxatives or Surfactants)Document1 pageSenna: Irritants and Stimulants Stool Softeners (Emollient Laxatives or Surfactants)Alexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument2 pagesCholinergic AntagonistsAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Asthma MedicationDocument2 pagesAsthma MedicationAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- B-Blockers Ca Channel Blockers Organic Nitrates Sodium Channel BlockersDocument1 pageB-Blockers Ca Channel Blockers Organic Nitrates Sodium Channel BlockersAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Prochlorperazine Lorazepam Alprazolam: Phenothiazines BenzodiazepinesDocument1 pageProchlorperazine Lorazepam Alprazolam: Phenothiazines BenzodiazepinesAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic AgonistsDocument1 pageCholinergic AgonistsAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Measles - RubeolaDocument3 pagesMeasles - RubeolaAlexandra AlexaNo ratings yet
- Attitude of Medical Students About Their Role in The Covid-19 PandemicDocument4 pagesAttitude of Medical Students About Their Role in The Covid-19 PandemicIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Year 4 PPT Paper 1 2018Document9 pagesYear 4 PPT Paper 1 2018Anonymous PYH3CmFNo ratings yet
- Planning of Action (Poa) Hse Program Proposed For Pt. Abc: PIC Schedule Remark Description ADocument2 pagesPlanning of Action (Poa) Hse Program Proposed For Pt. Abc: PIC Schedule Remark Description Aru dieNo ratings yet
- Download full chapter Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice Nurse Prescribers Fifth Edition Teri Moser Woo Marylou V Robinson pdf docxDocument64 pagesDownload full chapter Pharmacotherapeutics For Advanced Practice Nurse Prescribers Fifth Edition Teri Moser Woo Marylou V Robinson pdf docxdenise.root891No ratings yet
- 4-Hampshire Falls ProtocolDocument5 pages4-Hampshire Falls ProtocolsheenaNo ratings yet
- Skills ChecklistDocument2 pagesSkills Checklistapi-300770497No ratings yet
- Current Issues - BullyDocument2 pagesCurrent Issues - BullyNOOR SYAHRINA AZWEEN BINTI MD. SARU (PMM)No ratings yet
- LLL - Week 1Document9 pagesLLL - Week 1Reggie AbañoNo ratings yet
- Are We Making The Most of SupplementsDocument3 pagesAre We Making The Most of SupplementsEmmanuel SánchezNo ratings yet
- Amblyopia eDocument3 pagesAmblyopia eIeien MuthmainnahNo ratings yet
- Virtual Trials and Real-World Evidence Data CollectionDocument4 pagesVirtual Trials and Real-World Evidence Data CollectionRoopali AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Death Obituary Cause of Death CMFLD PDFDocument4 pagesDeath Obituary Cause of Death CMFLD PDFMayerRhodes8No ratings yet
- East Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust Staff DeclarationsDocument11 pagesEast Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust Staff DeclarationsDom DomNo ratings yet
- Coloproctology Brochure English 01 2019Document4 pagesColoproctology Brochure English 01 2019Gino PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Nutrition and Nutritional Status of HaDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Nutrition and Nutritional Status of HaVione rizkiNo ratings yet
- Aeroperl 300-30 MsdsDocument10 pagesAeroperl 300-30 Msdsjrobs314No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Care 3rd Edition Burke Test BankDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Care 3rd Edition Burke Test BankMatthew Song100% (37)
- Emergency Medicine EducationHyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State: ED PRDocument19 pagesEmergency Medicine EducationHyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State: ED PRSyed Shahrul Naz SyedNo ratings yet
- II. Comparison: I. DescriptionDocument7 pagesII. Comparison: I. DescriptionAbu RoninNo ratings yet
- Division of Cebu Province: Curriculum Implementation Supervisory Plan (Cisp) SY 2018-2019Document3 pagesDivision of Cebu Province: Curriculum Implementation Supervisory Plan (Cisp) SY 2018-2019Charie P. GraciaNo ratings yet
- Sharps Injury Checklist: TrainingDocument2 pagesSharps Injury Checklist: TrainingjosiasNo ratings yet
- 2nd Announcement PIN 2024Document25 pages2nd Announcement PIN 2024astariarum88No ratings yet
- Planning: 4.3 4.3.1 Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Determining ControlsDocument1 pagePlanning: 4.3 4.3.1 Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Determining Controlsdoctor59No ratings yet