Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise #12: Muscular Tissue
Uploaded by
Daks Zabate0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Lab-Exercise-12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesExercise #12: Muscular Tissue
Uploaded by
Daks ZabateCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Exercise #12
Muscular Tissue
Results
A. Draw and label the observations in the space provided
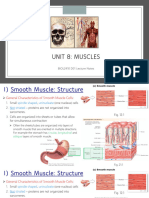
Skeletal Muscle
Visceral (smooth) Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
B. Answer the following questions.
1. How do the three types of muscles differ based on their structures?
Each type of muscle tissue in the human body has a unique structure and a specific
role.
Skeletal muscle attach to and moves bones and other structures by contracting
and relaxing in response to voluntary messages from the nervous system.
Skeletal muscle tissue is composed of long cells called muscle fibers that have a
striated appearance. Muscle fibers are organized into bundles supplied by blood
vessels and innervated by motor neurons.
Cardiac muscle contracts the heart to pump blood. Cardiac muscle is made from
cells called cardiocytes, like skeletal muscle cells cardiocytes have a striated
appearance, but their overall structure is shorter and thicker.
Smooth muscle tissue is found in the walls of hollow organs throughout the body
that forms organs like the stomach and bladder it changes shape to facilitate
bodily functions. Smooth muscle contractions are involuntary movements
triggered by impulses that travel through the autonomic nervous system to the
smooth muscle tissue.
2. Why do muscle cells have more mitochondria than other cells like the skin cells?
The number of mitochondria within a cell differs based on the organism, tissue type, or
cell type. Cells that are more active and/or move more will require a greater energy
produced via cellular respiration. Therefore, cells that are more active usually contain
more mitochondria than cells that are not as active. Since muscle cells are required for
the movement of an organism, they will have more mitochondria than skin cells.
You might also like
- Cell Specialization LabDocument19 pagesCell Specialization LabKayseri PersaudNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Tissues Post-Lab WorksheetDocument5 pagesMammalian Tissues Post-Lab WorksheetharrisonNo ratings yet
- Activity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtDocument9 pagesActivity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtAMEER MUHMIEN JALMAANI. LERIOSNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Document55 pagesBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 (Muscular System)Document7 pagesUNIT 3 (Muscular System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Muscular Tissue Worksheet - Comparing Cardiac, Smooth, and Skeletal MuscleDocument4 pagesMuscular Tissue Worksheet - Comparing Cardiac, Smooth, and Skeletal MuscleCedrick MedinaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Lecture #1: General Properties and StructureDocument26 pagesMuscular System Lecture #1: General Properties and StructureErnest VincentNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue and Nervous TissueDocument5 pagesMuscle Tissue and Nervous TissueChristine Angela ManguiatNo ratings yet
- Musc Nerv PDFDocument9 pagesMusc Nerv PDFJoshua RaninNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 15 - Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesLearning Activity 15 - Muscular SystemCraigyyNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Notes Part B - Smooth and Cardiac Muscles 2Document95 pagesUnit 8 Notes Part B - Smooth and Cardiac Muscles 2shrilpatel2001No ratings yet
- Module MS Revised 2022Document22 pagesModule MS Revised 2022Jahred CantornaNo ratings yet
- (Iin Tuhumury) Paper Anatomy of The Muscle System in HumansDocument11 pages(Iin Tuhumury) Paper Anatomy of The Muscle System in Humansyance djilarNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemZoological science classesNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- CHP 6 Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesCHP 6 Muscular SystemPatricia Sofia De LeonNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument23 pagesMuscular SystemAland BakrNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument29 pagesMuscular SystemJoanna Alecxa PagunsanNo ratings yet
- Human Biology 11th Edition Starr Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesHuman Biology 11th Edition Starr Solutions Manualjillhenrysetcjnzrfp100% (26)
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument13 pagesMakalah Bahasa InggrisYesli MadubunNo ratings yet
- Human Biology 11Th Edition Starr Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesHuman Biology 11Th Edition Starr Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFninhdermotc1u100% (8)
- Muscular System ReviewerDocument21 pagesMuscular System ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Nobody Knows The Muscles I've Seen!: The Major Function Is For Movement Either of The Skeleton or in The IntestinesDocument17 pagesNobody Knows The Muscles I've Seen!: The Major Function Is For Movement Either of The Skeleton or in The Intestinesapi-305603050No ratings yet
- Physiology U-4 Excitable Muscle TissueDocument154 pagesPhysiology U-4 Excitable Muscle Tissuesinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceMenchie Czylaire MirandaNo ratings yet
- Biological Systems and Processes BookletDocument31 pagesBiological Systems and Processes Bookletapi-422428700100% (1)
- Submodule 2.5 - 2.6Document14 pagesSubmodule 2.5 - 2.6Zeejiah NelleNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument3 pagesMUSCULAR SYSTEMJv sNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- The Muscular TissueDocument23 pagesThe Muscular TissueMuhammad Salisu IliyasuNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument20 pagesMuscular SystemAltaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Summary of SystemsDocument26 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Summary of SystemsSofia LiNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument13 pagesMusclessoulpatch_85100% (1)
- Ave Maria College Weekly Exam 3Document4 pagesAve Maria College Weekly Exam 3Mylene EsicNo ratings yet
- Lesson-VI-The-Muscular-SystemDocument13 pagesLesson-VI-The-Muscular-Systemmikaelladoles02No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesMuscular SystemANGEL ESTRADANo ratings yet
- The Muscular System NotesDocument32 pagesThe Muscular System NotesVivien Talavera0% (1)
- Pair Activity: B. Concept MasteryDocument3 pagesPair Activity: B. Concept MasteryNichole DequitoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular Systemnur100% (1)
- Muscular-System-Handouts - BiologyDocument7 pagesMuscular-System-Handouts - BiologyApril Joy T. GrijaldoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesIntroduction to the Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System-251606Document8 pagesThe Muscular System-251606sselt gayNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemJoyce Kathreen Ebio LopezNo ratings yet
- Nervous System OralDocument7 pagesNervous System OralThieza Mecca LucenaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDocument46 pagesLecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- The Tissue Level of Organization General ObjectivesDocument5 pagesThe Tissue Level of Organization General ObjectivesRjosheNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Laboratory Exercise No. 6Document3 pagesMuscular System: Laboratory Exercise No. 6Joy borlagdanNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMuscular SystemTyrone LeeNo ratings yet
- Muscular System Chapter 6 SummaryDocument2 pagesMuscular System Chapter 6 SummaryMyat NyanNo ratings yet
- 1.2 TheMuscularSystemDocument60 pages1.2 TheMuscularSystemchaaarrNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfDocument30 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfYego EdwinNo ratings yet
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 pagesModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR SYSTEM Q&ADocument11 pagesMUSCULAR SYSTEM Q&ARashini FernandoNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR-SYSTEM-TRANS-WEEK-1Document9 pagesMUSCULAR-SYSTEM-TRANS-WEEK-1olaya.xyzanigaia.bsnNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Reading and ComprehensionDocument3 pagesMuscular System: Reading and ComprehensionChainna Justine CubaoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary - Muscular SystemDocument3 pagesVocabulary - Muscular SystemArxk DevNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissuDocument3 pagesMuscular Tissunikifarnaz8No ratings yet
- Muscles WorksheetDocument4 pagesMuscles WorksheetAndreea BuicuNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue: Exercise 10Document5 pagesConnective Tissue: Exercise 10Daks ZabateNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8: Embryology of The FrogDocument4 pagesExercise 8: Embryology of The FrogDaks ZabateNo ratings yet
- Exercise #7 Reproduction in AnimalsDocument5 pagesExercise #7 Reproduction in AnimalsDaks ZabateNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue CellsDocument4 pagesEpithelial Tissue CellsDaks ZabateNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 11Document2 pagesLab Exercise 11Daks ZabateNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 5Document2 pagesLab Exercise 5Daks ZabateNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 6Document3 pagesLab Exercise 6Daks ZabateNo ratings yet
- Central Philippine University Exercise #13 External Anatomy of The FrogDocument4 pagesCentral Philippine University Exercise #13 External Anatomy of The FrogDaks ZabateNo ratings yet