Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Lecture Notes
Uploaded by
Khushi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
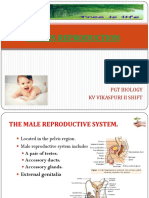
2 views2 pagesThe male reproductive system produces sperm in the testes, which are located in the scrotum outside of the body to maintain a lower temperature necessary for sperm production. The sperm travel through the male sex accessory ducts and are mixed with fluids from accessory glands to form semen, which is ejaculated through the penis during sexual intercourse. The female reproductive system contains ovaries that produce eggs and release them monthly through the oviducts. If an egg is fertilized, it travels down the oviducts and implants in the uterus.
Original Description:
They are not yet completed
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe male reproductive system produces sperm in the testes, which are located in the scrotum outside of the body to maintain a lower temperature necessary for sperm production. The sperm travel through the male sex accessory ducts and are mixed with fluids from accessory glands to form semen, which is ejaculated through the penis during sexual intercourse. The female reproductive system contains ovaries that produce eggs and release them monthly through the oviducts. If an egg is fertilized, it travels down the oviducts and implants in the uterus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesBiology Lecture Notes
Uploaded by
KhushiThe male reproductive system produces sperm in the testes, which are located in the scrotum outside of the body to maintain a lower temperature necessary for sperm production. The sperm travel through the male sex accessory ducts and are mixed with fluids from accessory glands to form semen, which is ejaculated through the penis during sexual intercourse. The female reproductive system contains ovaries that produce eggs and release them monthly through the oviducts. If an egg is fertilized, it travels down the oviducts and implants in the uterus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Lecture Notes
Topic: Human Reproduction
OVERVIEW OF THE CHAPTER FROM NCERT TEXTBOOK
The male reproductive system is located in the pelvis region.
Male reproductive system includes a pair of testes, accessory
ducts , glands and external genitalia.
The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a
pouch called Scrotum. The scrotum helps in maintaining a low
temp of the testes ( 2-2.5 degree Celsius ) lower than normal
body temperature necessary for spermatogenesis.
Each testes has about 250 compartments called testicular
lobules. Each lobule contains one to three highly
coiledSeminiferous tubules in which sperms are produced.
Each seminiferous tubule is lined on inside by two types of cells
called Male germ cells (spermatogonia) and Sertoli cells.
The male germ cell undergo mitotic divisions finally leading to
sperm formation, while sertoli cells provide nutrition to germ
cells.
The region outside the seminiferous tubules called interstitial
spaces contain small blood vessels and interstitial cells or
Leydig cells.
Leydig cells synthesise and secrete testicular hormone called
androgens.
The male sex accessory ducts include Rete testes, Vasa
effrentia, Epididymis and Vas deferens.
The enlarged end of penis called the glans penis is covered by a
loose fold of skin called foreskin.
The male sex accessory glands included paired Seminal
vesicles, a prostate and paired bulbourethral glands.
Secretions of these glands constitute the seminal plasma.
Seminal plasma which is rich in fructose, calcium and certain
enzymes.
The secretions of bulbourethral glands also helps in the
lubrication of the penis.
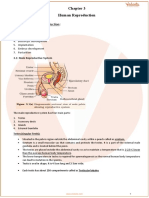
The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries
alongwith a pair oviducts, uterus, cervix, vagina, and the
external genitalia located in the pelvic region.
Ovaries are the primary female sex organs that produce the
female gamete and several steroid hormones.
The part of the oviduct closer to the ovary is the funnel shaped
Infundibulum . The edge of the infundibulum posses finger like
projections called Fimbriae, which help in collection of the ovum
after ovulation.
The infundibulum leads to a wider part of the oviduct called
Ampulla.
The last part of the oviduct Isthmus has a narrow lumen and it
joins the uterus.
You might also like
- Expectant Mother and Baby Information SheetDocument3 pagesExpectant Mother and Baby Information SheetKristine HP100% (7)
- Human Reproduction and Reproductive HealthDocument16 pagesHuman Reproduction and Reproductive HealthHemanth GowdaNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 3. Human Reproduction: The Male Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesChapter: 3. Human Reproduction: The Male Reproductive Systemlogi nageshNo ratings yet
- 3 Human ReproductionDocument43 pages3 Human ReproductionBread OmeletNo ratings yet
- Dpue Biology Notes: Chapter - 3 Human ReproductionDocument15 pagesDpue Biology Notes: Chapter - 3 Human ReproductionvdfeNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument26 pagesHuman Reproductionbarunmahto001No ratings yet
- Chapter 25Document38 pagesChapter 25Konishko DeyNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesDocument23 pagesHuman Reproduction - II Puc - Regular NotesVasudevNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument96 pagesHuman Reproductionsanya razaNo ratings yet
- HumanreproductionpptDocument59 pagesHumanreproductionpptsugi sivamNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-XiiDocument69 pagesHuman Reproduction CH-03, Bio, Class-Xiisumitdhakad543No ratings yet
- Physics Class 10 ICSEDocument5 pagesPhysics Class 10 ICSEmohammedumar7864521No ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive System: It Cchapteronsists ofDocument8 pagesThe Male Reproductive System: It Cchapteronsists ofDikansha JasaiwalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemFarhan haiderNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chpt3 NotesDocument8 pagesClass 12 Chpt3 NotesAarfa khanNo ratings yet
- Reparoductive SystemDocument4 pagesReparoductive SystemAhmed Mohammed omarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 M&Freprod 2304Document55 pagesChapter 26 M&Freprod 2304sairahhannahNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument12 pagesReproduction in AnimalsYuh moddaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive SystemRiaz siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Science 10Document22 pagesReproductive Science 10palicpicbea50No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument19 pagesMale Reproductive SystemAli JafriNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesReproductive SystembokkNo ratings yet
- Department of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsDocument69 pagesDepartment of Zoology Govt Hss Mylachal: PresentsBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of Human-80Document7 pagesReproductive System of Human-80joshidipesh770No ratings yet
- CH 3Document8 pagesCH 3api-288494741No ratings yet
- Physiology - Ii Year BemsDocument10 pagesPhysiology - Ii Year BemsKumar M V ScNo ratings yet
- Rerproduction NotesDocument16 pagesRerproduction NotesSheryl Lou AngelesNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction NotesDocument9 pagesHuman Reproduction NotesVicky VickyNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Male Reproduction SystemDocument9 pagesBiology Notes Male Reproduction SystemSunderNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument43 pagesHuman Reproductive Systembabaaijaz01No ratings yet
- The Reproductive Systems: Ms. Vernon Administrative and Clinical ProceduresDocument26 pagesThe Reproductive Systems: Ms. Vernon Administrative and Clinical ProceduresJustin MilliganNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction (Edustudy Point)Document10 pagesHuman Reproduction (Edustudy Point)Vishal UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument4 pagesSCIENCEMa. Isabel AtanesNo ratings yet
- Vinay Kevati (Bio)Document21 pagesVinay Kevati (Bio)Vinay KevatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Human ReproductionvidushivbpsNo ratings yet
- Xii Zool Ch3 Human Reproduction HssliveDocument8 pagesXii Zool Ch3 Human Reproduction HsslivePrituNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction PDFDocument4 pagesHuman Reproduction PDFIpshita PathakNo ratings yet
- Vpy 606 SeminarDocument67 pagesVpy 606 SeminarMohd Zakiuddin SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Human ReproductionDocument3 pagesChapter - 3 Human ReproductionMr.Prashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: 3.1: Male Reproductive SystemDocument27 pagesHuman Reproduction: 3.1: Male Reproductive SystemAvik BhaumikNo ratings yet
- 2776NEETZoologyReproductiveSystemTheory - Unlocked Opt PDFDocument21 pages2776NEETZoologyReproductiveSystemTheory - Unlocked Opt PDFMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Physiology Lesson 16 Part 1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMDocument54 pagesAnatomy - Physiology Lesson 16 Part 1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMAubrey Princess F. CaceresNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemSejuta AdaNo ratings yet
- 03 Human Reproductions PDFDocument57 pages03 Human Reproductions PDFBEENIT DASNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - ReproductiveDocument18 pagesChapter 19 - Reproductiveapi-220531452No ratings yet
- Dana AssignmentDocument10 pagesDana AssignmentDana khalidNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Module - 3 - Male Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesLecture Notes Module - 3 - Male Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyMariaImranNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemAbbasi KahumaNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument16 pagesHuman Reproductiontamalbio7No ratings yet
- Basic Steps in Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesBasic Steps in Human ReproductionMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Human Reproduction - STUDY RATEDocument14 pagesChapter 3 - Human Reproduction - STUDY RATEsriharshitha darapuNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 3 Human Reproduction (Notes)Document22 pagesClass 12 Chapter 3 Human Reproduction (Notes)Prabhu100% (1)
- REPRODUCTIVEDocument89 pagesREPRODUCTIVEJohn MichaelMackayNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument60 pagesHuman ReproductionOmiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReproductive SystemThảo NgânNo ratings yet
- 2080 Reproductive System of Frog Grade XIDocument1 page2080 Reproductive System of Frog Grade XIkunalkumaryadav086No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesReproductive SystemMatt MasilonganNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument52 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAjay DNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesReproductive Systemclar29No ratings yet
- DPR - Head Duty Sateve 24.12.22Document11 pagesDPR - Head Duty Sateve 24.12.22bobbyrianto2210No ratings yet
- Reproductive and Child Health Programme: Prepared By: Dr. Charan Singh RN, RM, MSN, PH.DDocument27 pagesReproductive and Child Health Programme: Prepared By: Dr. Charan Singh RN, RM, MSN, PH.Dcharan pooniaNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Terminolog Y: Mrs.V.Elizebeth Rani ReaderDocument14 pagesMidwifery Terminolog Y: Mrs.V.Elizebeth Rani ReaderSamira MohamudNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During PregnancyDocument41 pagesBleeding During PregnancyMustafa SHawkiNo ratings yet
- (See Rule 4) The Maternity Benefit Rules, 1961: Form BDocument1 page(See Rule 4) The Maternity Benefit Rules, 1961: Form BAbhishek Mishra100% (1)
- Topic 11.4 Worksheet (Answers)Document4 pagesTopic 11.4 Worksheet (Answers)ika100% (1)
- LPM 602 Bits..Document4 pagesLPM 602 Bits..Vijaya lakshmiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Oral Contraceptive PillsDocument13 pagesChemistry of Oral Contraceptive PillsJuan Carlos UriarteNo ratings yet
- Key Words: Bali Cattle, Spermatozoa, Livability, MPU, TAU: Et Al., 2014)Document9 pagesKey Words: Bali Cattle, Spermatozoa, Livability, MPU, TAU: Et Al., 2014)Ergha TriadyNo ratings yet
- Hypo Oligo Menorrhea Modern AADocument14 pagesHypo Oligo Menorrhea Modern AAdr anjna takNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Physical and Sexual SelfDocument80 pagesGroup 1 Physical and Sexual SelfMarc Eric GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Sperm Counts Among Western Men Have Halved in Last 40 Years - Study - Men's Health - The GuardianDocument32 pagesSperm Counts Among Western Men Have Halved in Last 40 Years - Study - Men's Health - The GuardianSamNo ratings yet
- Position Paper About Safe AbortionDocument23 pagesPosition Paper About Safe AbortionHanif Hadji JamilNo ratings yet
- Essay - Not Agree With The AbortionDocument2 pagesEssay - Not Agree With The AbortionRenz Gabriel Fabros FornolesNo ratings yet
- 2 Puberty Quiz True of False With Answers 1Document1 page2 Puberty Quiz True of False With Answers 1pisit poladpraoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Reproductive Life Planning 2023Document13 pagesModule 3 Reproductive Life Planning 2023AinaB ManaloNo ratings yet
- Partograph Case StudyDocument3 pagesPartograph Case StudyAfra Minong100% (1)
- sCIENCE 7Document3 pagessCIENCE 7Julien PitogoNo ratings yet
- CAMCA QUIZ ReviewDocument3 pagesCAMCA QUIZ ReviewShyla mayNo ratings yet
- The COMPLETE BOOK of PENIS - The Effective Guide To Penis From Size To Function and Everything in BetweenDocument70 pagesThe COMPLETE BOOK of PENIS - The Effective Guide To Penis From Size To Function and Everything in BetweenRyan GiocondoNo ratings yet
- Review of The Reproductive System 4Document44 pagesReview of The Reproductive System 4Shermaigne Ananayo BuyaNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument21 pagesHuman ReproductionShazia KhatoonNo ratings yet
- MT1 MTCPH Lab M4Document4 pagesMT1 MTCPH Lab M4Sofia SiyNo ratings yet
- Abortion, What Is ItDocument3 pagesAbortion, What Is ItAssero EricNo ratings yet
- Labor - Diagnosis and Management of An Abnormal First Stage - UpToDateDocument13 pagesLabor - Diagnosis and Management of An Abnormal First Stage - UpToDatesandrogvaladzeNo ratings yet
- AbPSy 4.3Document17 pagesAbPSy 4.3히로 GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Write Your Answer in Each Activity in Your MAPEH NotebookDocument3 pagesWrite Your Answer in Each Activity in Your MAPEH NotebookbwahahaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kuda 1Document21 pagesJurnal Kuda 1Yulistia FadhilahNo ratings yet
- MCN MT1 RefresherDocument7 pagesMCN MT1 RefresherRogerQuxNo ratings yet