Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isothermal Expansion of A Gas
Uploaded by
ShankarMukherjee0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesCalculation of change in entropy in isothermal expansion of a gas.
Original Title
Isothermal expansion of a gas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCalculation of change in entropy in isothermal expansion of a gas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesIsothermal Expansion of A Gas
Uploaded by
ShankarMukherjeeCalculation of change in entropy in isothermal expansion of a gas.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
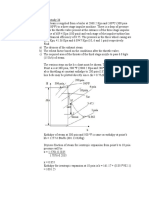
Case Study 16
Determine the change in the entropy of 1 mole of an ideal gas undergoing
expansion in a piston cylinder arrangement isothermally. The initial
pressure of the gas is 300 Kpa and the final pressure is 100 Kpa. The
piston is surrounded by atmosphere which exerts a constant pressure of
100 Kpa on the outer face of the piston. Moreover the device is always in
thermal equilibrium with the atmosphere which is at 300 K. During the
expansion process a frictional force is exerted on the piston and this force
varies in such a way that it always almost balances the net pressure force
on the piston. Thus the piston moves very slowly and experiences a
negligible acceleration. The piston and cylinders are good conductors.
Determine the entropy change of the gas, the entropy change of the
atmosphere and the total entropy change brought about by the process
When we consider the piston cylinder as our system the external force on
the system is caused by atmospheric pressure Po surrounding the
system.Work done by the system is W=PoΔV, where ΔV is given by the
ideal gas laws,
ΔV = V2- V1
= RT/P2 – RT/P1
= RT(P1-P2)
P1P2
Thus W = PoRT(P1-P2)
P1P2
However Po =P2
W = RT(P1-P2)
P1
Since the process is isothermal ΔU = 0
By 1st law of thermodynamics,
W= Q and Qsurr = -Q = -W
ΔS surr = Qsurr/T = -W/T = -R(P1-P2)
P1
= - R (300-100)
300
= -0.666 R = -5.542 KJ/mol°K
Entropy change of the gas is given by equation(1.11), which for contant T
is
ΔS = - R ln(P2/P1) = - R ln(100/300) = 9.133 KJ/mol°K
The total entropy change is therefore ΔStotal = ΔS + ΔSsurr = 9.133-5.542
= 3.59 KJ/mol °K
[Calculation of change in entropy of a gas undergoing expansion in
a piston cylinder apparatus isothermally.]
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Gas turbine cycle calculationsDocument33 pagesGas turbine cycle calculationsShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Flare Gas Flow Measurement and ControlDocument5 pagesFlare Gas Flow Measurement and ControlShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- FLARENET Reference Manual PDFDocument330 pagesFLARENET Reference Manual PDFErin Brady0% (1)
- Process Safety ManagementDocument74 pagesProcess Safety ManagementShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Enthalpy and Internal Energy and Work 1.1.3Document1 pageRelation Between Enthalpy and Internal Energy and Work 1.1.3ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Case 36Document4 pagesCase 36ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Estimating Equilibrium Phase Distribution RatiosDocument4 pagesEstimating Equilibrium Phase Distribution RatiosShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Basics of Thermodynamic CalculationsDocument26 pagesBasics of Thermodynamic CalculationsShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- (Calculation of Heat Removed For An Isothermal Compression Process.) (Calculation of Work Done in Case of An Isothermal Compression Process)Document1 page(Calculation of Heat Removed For An Isothermal Compression Process.) (Calculation of Work Done in Case of An Isothermal Compression Process)ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- (Calculation of Heat Removed For An Isothermal Compression Process.) (Calculation of Work Done in Case of An Isothermal Compression Process)Document1 page(Calculation of Heat Removed For An Isothermal Compression Process.) (Calculation of Work Done in Case of An Isothermal Compression Process)ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Sil Classification Sheet: Risk Factors From MatricesDocument18 pagesSil Classification Sheet: Risk Factors From MatricesShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant and Performance 1.3.5Document1 pageSteam Power Plant and Performance 1.3.5ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Case 20Document2 pagesCase 20ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Case 21Document2 pagesCase 21ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Case 21Document2 pagesCase 21ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Cascade Refrigeration Cycle AnalysisDocument24 pagesCascade Refrigeration Cycle AnalysisShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Case 17Document2 pagesCase 17ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Case 17Document2 pagesCase 17ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Case 24Document2 pagesCase 24ShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine CalculationsDocument9 pagesSteam Turbine CalculationsShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Basics of Thermodynamic CalculationsDocument26 pagesBasics of Thermodynamic CalculationsShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Cascade Refrigeration Cycle AnalysisDocument24 pagesCascade Refrigeration Cycle AnalysisShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Compressor calculation using Mollier chartDocument11 pagesCompressor calculation using Mollier chartShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Tube Rupture CaseDocument2 pagesTube Rupture CaseShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Cascade Refrigeration Cycle AnalysisDocument24 pagesCascade Refrigeration Cycle AnalysisShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- VLE Calculation Convergence PressureDocument36 pagesVLE Calculation Convergence PressureShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- HP OHCorrosionDocument3 pagesHP OHCorrosionJamie MorganNo ratings yet
- Henley - Equilibrium-Stage Separation Operations in Chemical EngineeringDocument384 pagesHenley - Equilibrium-Stage Separation Operations in Chemical EngineeringpriscilaeqNo ratings yet
- Equilibria, Bubble Points, Dewpoints, Flash Calculations, and Activity Coef FicientsDocument46 pagesEquilibria, Bubble Points, Dewpoints, Flash Calculations, and Activity Coef FicientsShankarMukherjeeNo ratings yet