Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parts of Speech & Basic Sentence Patterns
Uploaded by
ghephOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parts of Speech & Basic Sentence Patterns
Uploaded by
ghephCopyright:
Available Formats
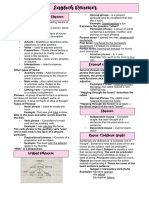
PARTS OF SPEECH & BASIC SENTENCE PATTERNS
Parts of Speech (e.g. The window is over the
radiator, Go into her room
• Noun and take the papers, etc.)
→ A word used to identify a • Conjunctions
person, places, things or → Join together words, phrases
events. and independent clauses.
(e.g. man, woman, table, (e.g. She usually eats at
car, dog, etc.) home, because she likes
• Pronouns cooking, He is very funny
→ A pronoun is a word that whereas she is boring, but,
replaces a noun in a although, yet, unless, nor,
sentence. while, etc.)
(e.g. me, he, she, herself, • Interjections
you, it, I, they, each, few, → Conveys what an author is
many, etc.) feeling.
• Adjectives (e.g. alas, blah, nah, oops,
→ Are descriptive words that OMG, yikes, etc.)
modify or enhance a noun.
(e.g. perfect, cruel, gentle,
huge, tasty, etc.) Basic Sentence Patterns
• Verbs
→ Are the action words in a
• S-TV-DO
sentence that describe what Subject + Transitive Verb + Direct
the subject is doing. Object
(e.g. dance, run, jump, slide, → A verb is the doer of the
etc.) action/ topic of the
sentence.
• Adverbs
→ A transitive verb that
→ Can add further description,
requires both a subject and
or intensity the meaning of
a direct object.
another word.
→ A direct object is a word or
(e.g. He cleans his phone
phrase that receives the
once a week, She doesn’t
action of the verb. (what?
usually go to work by bus,
whom?)
etc.)
• S-IV
• Preposition
Subject + Intransitive Verb
→ Used to show a relationship
→ An intransitive verb is a verb
between a noun and a
without a direct object.
pronoun.
PARTS OF SPEECH & BASIC SENTENCE PATTERNS
• S-TV-IO-DO
Subject + Transitive Verb + Indirect
Object + Direct Object
→ The indirect object of a
sentence is the recipient of
the direct object ( to whom?
For whom?)
• S-TV-DO-OC
Subject + Transitive Verb + Direct
Object + Object Compliment
→ An object complement is a
noun, pronoun, or adjective
which follows a direct object
and renames or tells what
the direct object has
become.
• S-LV-SC
Subject + Linking Verb + Subject
Complement (aka Predicate
Nominative)
→ Linking verbs are verbs that
serve as a connection
between a subject and
further information about
that subject. They do not
show any action; rather, they
“link” the subject with the
rest of the sentence.
→ A subject complement
(predicate nominative /
predicate noun) completes a
linking verb and renames the
subject.
• S-LV-PA
Subject + Linking Verb + Predicate
Adjective
→ A predicate adjective follows
a linking verb and describes
the subject.
You might also like
- Eed 111 (Lesson 3 Structure of Predication)Document25 pagesEed 111 (Lesson 3 Structure of Predication)Andal Bianzon Leslie AnnNo ratings yet
- English MT Reviewer 1Document3 pagesEnglish MT Reviewer 1AnikaNo ratings yet
- CPHTH - c7 - w4 - SlidesDocument49 pagesCPHTH - c7 - w4 - SlidesHuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Grammar 6 Student Book - Jolly PhonicsDocument110 pagesGrammar 6 Student Book - Jolly PhonicsMassiel EscobarNo ratings yet
- Phrasal Categories: The Internal StructureDocument6 pagesPhrasal Categories: The Internal StructureAlyiah Zhalel LawasNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of Speechjerica tanaNo ratings yet
- Morphology - Lexical WordsDocument5 pagesMorphology - Lexical WordsĐặng Lê Khánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Sentence PatternsDocument20 pagesLesson 6 Sentence Patternsbenjie panlicanNo ratings yet
- VHU - Syntax ContextDocument22 pagesVHU - Syntax ContextkhangtammedNo ratings yet
- Materi Nouns and AdjecivesDocument14 pagesMateri Nouns and AdjecivesTri WijayantiNo ratings yet
- Syntax 1Document36 pagesSyntax 1Rani Dwi HandayaniNo ratings yet
- CRDI312 TECHNICAL ENGLISH PrelimsDocument7 pagesCRDI312 TECHNICAL ENGLISH PrelimsCATHLEENE MAYNE BELIRANNo ratings yet
- (Done) Phrases and Types 43 MEDocument13 pages(Done) Phrases and Types 43 ME7706hasanabdalNo ratings yet
- Summer '23Document44 pagesSummer '23mvela8No ratings yet
- Bhs InggrisDocument16 pagesBhs InggrisMuhammad WardiNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Grammar: Read and Make A Summary of Your LearningDocument10 pagesUnit I - Grammar: Read and Make A Summary of Your LearningMariangel PerezNo ratings yet
- 6455646-1 (Autosaved)Document35 pages6455646-1 (Autosaved)ley leynNo ratings yet
- Classes of VerbDocument28 pagesClasses of VerbChristian CapuyanNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument2 pagesEnglishANEES FURHANNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - VerbsDocument16 pagesLecture Notes - VerbsKamalesh SivaNo ratings yet
- ELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Document38 pagesELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Becira LiNo ratings yet
- De Juan - Written Activity No. 1 (English)Document15 pagesDe Juan - Written Activity No. 1 (English)J.L Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- Grammar 5Document46 pagesGrammar 5drakness722No ratings yet
- English Fundamentals 1 - Qs PDFDocument4 pagesEnglish Fundamentals 1 - Qs PDFKhát Vọng100% (1)
- Structure of EnglishDocument9 pagesStructure of EnglishCherry Mae PalilioNo ratings yet
- Word ClassesDocument39 pagesWord ClassesRahmasitha FajrinNo ratings yet
- Quick English Lesson I. Parti-: Sat Reading Going PassDocument5 pagesQuick English Lesson I. Parti-: Sat Reading Going PassPrashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduce Yourself:: Thanks For Your AttentionDocument5 pagesIntroduce Yourself:: Thanks For Your Attentionkaterine mosqueraNo ratings yet
- Gen Ed - EnglishDocument315 pagesGen Ed - EnglishJayson BoteNo ratings yet
- 88 Parts-of-Speech USDocument23 pages88 Parts-of-Speech USfredy96295No ratings yet
- Relative Clauses: Bảo Nhi & Phương UyênDocument21 pagesRelative Clauses: Bảo Nhi & Phương UyênPhúc ThịnhNo ratings yet
- Phrasal Verb Prepositional Verb Verb + Adverbial Particle Verb + PrepDocument8 pagesPhrasal Verb Prepositional Verb Verb + Adverbial Particle Verb + PrepNhư QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- English Guide 1Document38 pagesEnglish Guide 1norelkys sanchezNo ratings yet
- CEBGADocument28 pagesCEBGACZYSTYNo ratings yet
- CEBallDocument70 pagesCEBallCZYSTYNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 4Document12 pagesKelompok 4Saya egenNo ratings yet
- #3 Meeting-WORD POSITION, PART OF SPEECH & WORD FORMATIONDocument31 pages#3 Meeting-WORD POSITION, PART OF SPEECH & WORD FORMATIONRobiah HamidahNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument21 pagesPart of Speechryzalsatria999No ratings yet
- M7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Document25 pagesM7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Aline TriciaNo ratings yet
- (Part 1) English ProjectDocument304 pages(Part 1) English ProjectCharnes mae Abegania100% (1)
- Euro Management Indonesia: Part of Speech (Verb-Adjective)Document13 pagesEuro Management Indonesia: Part of Speech (Verb-Adjective)Umul KhairinaNo ratings yet
- Phrases and Types 43 MEDocument15 pagesPhrases and Types 43 MEDawood Ab.No ratings yet
- Unit 2 LS 01 Content Words PDFDocument7 pagesUnit 2 LS 01 Content Words PDFAnfal ZaneNo ratings yet
- Is 102 Midterm ReviewerDocument36 pagesIs 102 Midterm ReviewerKaye Honeylee ManibogNo ratings yet
- Transitive and Intransitive VerbDocument11 pagesTransitive and Intransitive VerbHannieNo ratings yet
- Who, Whoever, Whom, WhomeverDocument7 pagesWho, Whoever, Whom, WhomeverNadiadelVelizNo ratings yet
- The NounDocument7 pagesThe Noun081286sgopiNo ratings yet
- Transitive and Intransitive VerbDocument11 pagesTransitive and Intransitive VerbHannieNo ratings yet
- Linear AnalysisDocument40 pagesLinear AnalysisEnglish LessonsNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument4 pagesPart of SpeechJibran AyazNo ratings yet
- Lesson #2 - Writing ConventionsDocument2 pagesLesson #2 - Writing Conventionshoomanpizz4No ratings yet
- PrepositionsDocument14 pagesPrepositionsLuna GoghNo ratings yet
- 5 - Living Words School - GRAMATICADocument11 pages5 - Living Words School - GRAMATICAShalomPC SystemsNo ratings yet
- English Word Order: Who-What-Where-When-How-WhyDocument4 pagesEnglish Word Order: Who-What-Where-When-How-WhySkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- Entrance Exam ReviewerDocument24 pagesEntrance Exam ReviewerBhenice AmparoNo ratings yet
- Tech Eng PrelimDocument7 pagesTech Eng PrelimLourdes Anne LandaoNo ratings yet
- Verbals Week 8 Flinguis 3Document18 pagesVerbals Week 8 Flinguis 3Shane Mendoza BSED ENGLISHNo ratings yet
- New Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetFrom EverandNew Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Acid Fast StainingDocument11 pagesAcid Fast StainingghephNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test: Dilution Test Method Pre-Analytical Phase (Materials)Document2 pagesAntimicrobial Susceptibility Test: Dilution Test Method Pre-Analytical Phase (Materials)ghephNo ratings yet
- Week I - Laboratory SafetyDocument64 pagesWeek I - Laboratory SafetyghephNo ratings yet
- Course Guide ENGL 111 Basic Communication SkillsDocument3 pagesCourse Guide ENGL 111 Basic Communication SkillsghephNo ratings yet
- AnaChem Lab W2Document11 pagesAnaChem Lab W2ghephNo ratings yet
- Tools of Analytical Chemistry: Chemicals, Apparatus, and Unit Operations of AnachemDocument53 pagesTools of Analytical Chemistry: Chemicals, Apparatus, and Unit Operations of AnachemghephNo ratings yet
- 978-0393617542 Research MethodsDocument18 pages978-0393617542 Research MethodsReccebacaNo ratings yet
- Generation Transmission and Distribution Notes.Document88 pagesGeneration Transmission and Distribution Notes.Abhishek NirmalkarNo ratings yet
- Saes TABLEDocument13 pagesSaes TABLERiyaz BasheerNo ratings yet
- Juan LunaDocument2 pagesJuan LunaClint Dave OacanNo ratings yet
- 500KVA Rigsafe Framed Generator (8900Kgs)Document1 page500KVA Rigsafe Framed Generator (8900Kgs)Elsad HuseynovNo ratings yet
- Draft Technical Notes SGLG 2023 - National OrientationDocument109 pagesDraft Technical Notes SGLG 2023 - National OrientationZane ZyneNo ratings yet
- Docs Grails Org 4 0 0 Guide Single HTMLDocument296 pagesDocs Grails Org 4 0 0 Guide Single HTMLlicface13No ratings yet
- Step Buying Process in LazadaDocument4 pagesStep Buying Process in LazadaAfifah FatihahNo ratings yet
- Major06 QP DLP NEET2019 (Pmtcorner - In) PDFDocument40 pagesMajor06 QP DLP NEET2019 (Pmtcorner - In) PDFMegha HazarikaNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Industrial Engineering: Part - B (10 Marks) : Answer All The QuestionsDocument4 pagesNational Institute of Industrial Engineering: Part - B (10 Marks) : Answer All The QuestionsTulasi PatleNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Exam 2 Practice QuestionsDocument1 pageOrganizational Behavior Exam 2 Practice QuestionsSydney EverettNo ratings yet
- Wooden Buildings: exposed to tiếp xúc với dramatic renewal sự làm mới đáng kểDocument6 pagesWooden Buildings: exposed to tiếp xúc với dramatic renewal sự làm mới đáng kểNguyễn Phạm Thảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- The Eminence in Shadow, Vol. 4Document255 pagesThe Eminence in Shadow, Vol. 4Ezra Salvame83% (6)
- The Light BulbDocument6 pagesThe Light Bulbapi-244765407No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 EtherchannelDocument3 pagesTutorial 2 EtherchannelOng CHNo ratings yet
- Orifice Plate Calculator Pressure Drop CalculationsDocument4 pagesOrifice Plate Calculator Pressure Drop CalculationsAnderson Pioner100% (1)
- Calydracomfort PiDocument16 pagesCalydracomfort PiionNo ratings yet
- Language - Introduction To The Integrated Language Arts CompetenciesDocument7 pagesLanguage - Introduction To The Integrated Language Arts CompetenciesHari Ng Sablay100% (1)
- Brunswick Manual Preinstalacion GSXDocument33 pagesBrunswick Manual Preinstalacion GSXroberto dominguezNo ratings yet
- The Macquarie Australian Slang DictionarDocument7 pagesThe Macquarie Australian Slang DictionarnetshidoNo ratings yet
- EKOFLUID PRODUCT SHEET FILOIL 6000 210x297 EN WEBDocument4 pagesEKOFLUID PRODUCT SHEET FILOIL 6000 210x297 EN WEBjunaidi.036No ratings yet
- Management From RamayanaDocument14 pagesManagement From Ramayanasaaket batchuNo ratings yet
- AQA Power and Conflict GCSE Revision Guide LADocument49 pagesAQA Power and Conflict GCSE Revision Guide LAderaw11557No ratings yet
- Data Science BooksDocument11 pagesData Science BooksAnalytics Insight100% (1)
- ParaklesisDocument23 pagesParaklesisDiana ObeidNo ratings yet
- Inspection and Test Plan (ITP) For Spherical Storage Tanks: Dehloran Olefin PlantDocument9 pagesInspection and Test Plan (ITP) For Spherical Storage Tanks: Dehloran Olefin PlantbahmanNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Students Name Contact Number CAP 10TH: Ideal Institute of Pharamacy, Wada SESSION-2020-21Document12 pagesS.NO. Students Name Contact Number CAP 10TH: Ideal Institute of Pharamacy, Wada SESSION-2020-21DAMBALENo ratings yet
- Understanding EarsDocument1 pageUnderstanding EarsmerkyworksNo ratings yet
- Short Stories Planet Earth AnswersDocument2 pagesShort Stories Planet Earth AnswersLina Vasquez Vasquez100% (2)
- ADCD LowDocument8 pagesADCD LowrahulmultivisionNo ratings yet