Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reproductive System
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Salman Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views25 pagesThe document discusses the reproductive systems of males and females. It covers the functions of the testes and ovaries, including sperm and egg production. It also describes the hormonal control of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Key hormones discussed are testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, HCG, and HCS. The roles of these hormones in reproduction and pregnancy are summarized.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the reproductive systems of males and females. It covers the functions of the testes and ovaries, including sperm and egg production. It also describes the hormonal control of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Key hormones discussed are testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, HCG, and HCS. The roles of these hormones in reproduction and pregnancy are summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views25 pagesReproductive System
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Salman KhanThe document discusses the reproductive systems of males and females. It covers the functions of the testes and ovaries, including sperm and egg production. It also describes the hormonal control of the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Key hormones discussed are testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, HCG, and HCS. The roles of these hormones in reproduction and pregnancy are summarized.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
Reproductive System
Mir Arif Hussain
BSPT, M.Sc.PT (NMSPT), Ph.D.* (PT)
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 1
Sciences
Reproductive System
• Section 1 Reproductive and Hormonal
Functions of the Male
• Section 2. Reproductive and Hormonal
Functions of the Female
• Section 3. Hormonal control of the menstrual
cycle
• Section 4 Pregnancy
• Section 5 Oxytocin
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 2
Sciences
Section 1 Reproductive and
Hormonal Functions of the Male
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 3
Sciences
Functions of testes
• spermatogenesis
– seminiferous tubules
• secrete hormones
– testosterone - by the instestitial cels of Leydig,
– inhibin - by Sertoil cells
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 4
Sciences
I. Endocrine Function of Testes
• Androgens: testosterone, dihydrotesterone and
androstenodione
• Function of testosterone
– Maintenance of spermatogenesis
– Stimulation of development of genitalia.
– Development and maintenance of the male secondary sexual
characteristics.
– Maintenance of libido.
– Effect on metabolism.
• increases anabolism of protein,
• causes growth of the bones
• deposition of calcium salts
• enhancement of production of red cells.
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 5
Sciences
Plasma Testosterone at Different Age in Male
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 6
Sciences
Endocrine Function of Testes (cont.)
• Inhibin
– a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 31,000-
32,000
– Secreted by by Sertoil cells in testis
– potent inhibitory effect on FSH secretion by
pituitary gland.
– slightly inhibitory in GnRH secretion.
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 7
Sciences
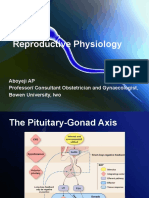
II. Regulation of Testis Function
• Hypothalamic-Pituitary-
Testis Axis
– GnRH
– FSH, LH
– Testerone
• Negative Feedback
Mechanism
– Testosterone
– Inhibin
• Local regulation in testes
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 8
Sciences
Section 2 Reproductive and
Hormonal Functions of the Female
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 10
Sciences
I. Menstruation, Ovulation and Hormonal
Regulation
• Menstruation cycle or female sexual cycle
– Uterine cycle
• Proliferative phase (estrogen phase)
• Secretary phase (progesterone phase)
• Menstruation
– Ovarian Cycle
• Follicular phase
• Ovulation
• Luteal phase
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 11
Sciences
Uterine Cycle
• Proliferative phase (estrogen phase)
• Secretary phase (progesterone phase)
• Menstruation
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 12
Sciences
Ovarian Cycle
• Follicular phase
• Ovulation
• Luteal phase
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 13
Sciences
Endocrine Functions of Ovaries
• Physiological function of estrogen
– On sexual organs
– On secondary female sexual characteristics
– On metabolism
– others
• Physiological function of progesterone
– on uterus
– on breasts
– thermogenic effect
– others
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 14
Sciences
Section 3. Hormonal control of
the menstrual cycle
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 15
Sciences
16
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 17
Sciences
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 18
Sciences
Section 4 Pregnancy
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 19
Sciences
I. Fertilization and Implantation
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 20
Sciences
II. Hormones of Placenta
• Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)
• Progesterone and Estrogen
• Human Chorionic Somatommotropin (HCS)
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 21
Sciences
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)
• glycoprotein with a molecular weight of
39,000
• secreted by the syncytial trophoblast cells
• can be measured in the blood 8 to 9 days
after ovulation
• Function:
• identical to LH in its effect
• maintain the corpus letum
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 22
Sciences
Progesterone and Estrogen
• Secreted by corpus luteum
before 5-6 weeks of
pregancy and by placenta
later
• maintain the endometrium
and prevent menstruation
• Estrogen: cause
enlargement of uterus,
breasts and mother’s
female external genitalia
• Progesterone: decrease the
contractility of pregnant
uterus
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 23
Sciences
Human Chorionic Somatommotropin (HCS)
• protein with molecular weight of 38,000
• begins to be secreted by the placenta at the
5th week of pregnancy
• Secretion in direct proportion to the weight of
placenta.
• Function
– stimulates growth of fetus
– regulates metabolism of carbohydrate, fat and
protein in both the fetus and the mother
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 24
Sciences
Changes of Hormones during Pregancy
11/27/2018 Riphah College of Rehabilitation 25
Sciences
Riphah College of Rehabilitation
11/27/2018 26
Sciences
You might also like
- ISSA Corrective ExerciseDocument268 pagesISSA Corrective ExerciseSalman Khan100% (2)
- Gastrointestinal PhysiologyDocument152 pagesGastrointestinal PhysiologyHabib BerrandjiaNo ratings yet
- Day Study Schedule For USMLE Step 1 LecturioDocument12 pagesDay Study Schedule For USMLE Step 1 LecturioDany Paulbaby100% (1)
- Oestrogen, Progesterone, AndrogensDocument58 pagesOestrogen, Progesterone, AndrogensTandin SonamNo ratings yet
- 6.motor AssessmentDocument32 pages6.motor AssessmentSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Larsen's Human EmbryologyDocument526 pagesLarsen's Human EmbryologyJulie100% (2)
- Sexual Reproductive HealthDocument29 pagesSexual Reproductive HealthAlen VukosavljevicNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Obstetrics and Gynecology A Pictorial GuideDocument301 pagesVeterinary Obstetrics and Gynecology A Pictorial Guidegnpobs100% (5)
- Bones & Joints of Head & NeckDocument91 pagesBones & Joints of Head & NeckSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Puberty: Dr. Valérie M. SchwitzgebelDocument66 pagesPuberty: Dr. Valérie M. SchwitzgebelJoshua RomeroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Grade 10 ScienceDocument29 pagesLesson Plan in Grade 10 ScienceMarrell Unajan100% (2)
- Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyKenneth Reigne ArguidasNo ratings yet
- Physiology of PubertyDocument4 pagesPhysiology of PubertyHakimah K. Suhaimi100% (3)
- BurnsDocument16 pagesBurnsSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction PDFDocument35 pagesHuman Reproduction PDFsqhaa100% (4)
- Oral Contraceptives: Presented byDocument24 pagesOral Contraceptives: Presented byfarmasi_hm100% (1)
- Endocrine Reproduction of Female: Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera UtaraDocument24 pagesEndocrine Reproduction of Female: Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera UtaracandyslibioNo ratings yet
- Bony Pelvis & Fetal SkullDocument130 pagesBony Pelvis & Fetal SkullSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Week 2 REPRODUCTION Organismal BiologyDocument7 pagesQuarter 4 Week 2 REPRODUCTION Organismal BiologyJEAN MARIE LOREDONo ratings yet
- Oral ContraceptivesDocument25 pagesOral ContraceptivesAdhitya Yudha MaulanaNo ratings yet
- The Sexual SelfDocument26 pagesThe Sexual SelfMalaika Aubrey Cao PalomoNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Disorders and PCOS Webinar EMBRYO FKUI 2022Document49 pagesMenstrual Disorders and PCOS Webinar EMBRYO FKUI 2022angelinputri100% (1)
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDocument28 pagesAssisted Reproductive TechnologyftvyvyvNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pregnancy 050918Document75 pagesPhysiology of Pregnancy 050918Anonymous 96LTCx100% (2)
- P4 Reproduksi 2017Document61 pagesP4 Reproduksi 2017Christian AngoNo ratings yet
- Sex HarmoneDocument22 pagesSex Harmonesuyash jainNo ratings yet
- EndocrinologyDocument21 pagesEndocrinologySANCHAYEETANo ratings yet
- DR: Khalil K. Hussain, Assistant Professor University of Central Punjab, Sports Complex, Cabin # 06Document66 pagesDR: Khalil K. Hussain, Assistant Professor University of Central Punjab, Sports Complex, Cabin # 06Huzaifa ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Endocrine System. Care of Patients With Problems of The Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands.Document86 pagesAssessment of The Endocrine System. Care of Patients With Problems of The Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands.AndrewNo ratings yet
- Steroids JenniferKettelDocument25 pagesSteroids JenniferKettelvinay0717No ratings yet
- Disorders of The Ovaries 2Document92 pagesDisorders of The Ovaries 2rerenNo ratings yet
- Female Endocrinology - AnimalDocument37 pagesFemale Endocrinology - AnimalLevi Junho SongNo ratings yet
- BIOS5130 Week 9 Slides W - o AnswersDocument47 pagesBIOS5130 Week 9 Slides W - o AnswersOkikiola JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Physiology: Aboyeji AP Professor/ Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, Bowen University, IwoDocument21 pagesReproductive Physiology: Aboyeji AP Professor/ Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, Bowen University, IwoAkinbani MoyosoreNo ratings yet
- PRABHUDocument22 pagesPRABHUnarrarakesh4290No ratings yet
- Hormones and It's TypesDocument10 pagesHormones and It's TypesSidraNo ratings yet
- Bio InvestigatoryprojectDocument17 pagesBio InvestigatoryprojectPushkar MishraNo ratings yet
- Overview of Endocrine SystemDocument16 pagesOverview of Endocrine System2023ph17No ratings yet
- Ebook Gastrointestinal Physiology Mosby Physiology Series PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Gastrointestinal Physiology Mosby Physiology Series PDF Full Chapter PDFbobbi.murphy331100% (23)
- Mechanisms of Obesity-Induced Male Infertility PDFDocument24 pagesMechanisms of Obesity-Induced Male Infertility PDFshishir kumarNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Physiology Mosby Physiology Series 9Th Edition Edition Leonard R Johnson Full ChapterDocument51 pagesGastrointestinal Physiology Mosby Physiology Series 9Th Edition Edition Leonard R Johnson Full Chapterpeter.mcgillivray908100% (12)
- Physiology of The Menstrual CycleDocument17 pagesPhysiology of The Menstrual Cyclezianab aliNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument60 pagesPhysiology of Female Reproductive SystemSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Pharmacology PDFDocument45 pagesEndocrine Pharmacology PDFNur TzNo ratings yet
- L23 PDFDocument43 pagesL23 PDFMiles HuiNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Dr. Nikunj BhattDocument37 pagesReproductive System: Dr. Nikunj BhattSejal khumamNo ratings yet
- B. Hormones, General Principles by D SiwaleDocument73 pagesB. Hormones, General Principles by D SiwaleDonald SiwaleNo ratings yet
- PDF Crash Course Endocrinology 4e Pdftahir99 VRG CompressDocument60 pagesPDF Crash Course Endocrinology 4e Pdftahir99 VRG CompressNabila Azahara PutriNo ratings yet
- Sun 800 RoidRage Innovative Trends Treatment Male HypogonadismDocument19 pagesSun 800 RoidRage Innovative Trends Treatment Male HypogonadismM. Sz.No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Sex Hormones: Molly Downing, PHD Clinical Instructor College of Pharmacy Downing.211@Osu - EduDocument25 pagesPharmacology of Sex Hormones: Molly Downing, PHD Clinical Instructor College of Pharmacy Downing.211@Osu - EduKaish DahiyaNo ratings yet
- 01 Animal Physiology - Foundations of PhysiologyDocument26 pages01 Animal Physiology - Foundations of PhysiologyMinette EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Reproduction: DR - R - PrameelaDocument76 pagesDrugs Affecting Reproduction: DR - R - PrameelaRamadi PrameelaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument94 pagesEndocrineSuzana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- Materi 5 Endokrinologi Selama Siklus EstrusDocument42 pagesMateri 5 Endokrinologi Selama Siklus EstrusSaparuddin UINAMNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Toxicity Testing: What and Why?: TOPRA Annual Veterinary SymposiumDocument51 pagesReproductive Toxicity Testing: What and Why?: TOPRA Annual Veterinary Symposiuml3ly0709No ratings yet
- American Journal of Neuroscience 3Document17 pagesAmerican Journal of Neuroscience 3Made YudanaNo ratings yet
- Iranian Journal of Basic Medical SciencesDocument10 pagesIranian Journal of Basic Medical SciencesDeaz Fazzaura PutriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Endocrinology, Hormones and Their Classification Lecture NO: 2 MbbsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Endocrinology, Hormones and Their Classification Lecture NO: 2 MbbsOmaraye JoshuaNo ratings yet
- VOG602 - 1225 - Lesson 6 - PPTDocument26 pagesVOG602 - 1225 - Lesson 6 - PPTSai ChanduNo ratings yet
- The Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandDocument71 pagesThe Hypothalamus and Pituitary GlandRujha Haniena Ahmad RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument26 pagesMale Reproductive SystemRahil PatelNo ratings yet
- RollNo - 02 PTSM - II Teratogenicity & GenotoxicityDocument55 pagesRollNo - 02 PTSM - II Teratogenicity & GenotoxicityJayesh KadamNo ratings yet
- (L-6) - Endocrine System - Dec 9, 2019Document49 pages(L-6) - Endocrine System - Dec 9, 2019Omar Gill0% (1)
- Pict Guide To Vet Obs and Gynaecology PDFDocument301 pagesPict Guide To Vet Obs and Gynaecology PDFVigin JacobNo ratings yet
- Puberty: Dr. Valérie M. SchwitzgebelDocument66 pagesPuberty: Dr. Valérie M. SchwitzgebelnenyNo ratings yet
- Puberty PDFDocument66 pagesPuberty PDFnenyNo ratings yet
- Lanete1318221 AnaPhy Endocrinesystem (IL#6) ADocument1 pageLanete1318221 AnaPhy Endocrinesystem (IL#6) ACarlyne LaneteNo ratings yet
- Puberty PDFDocument66 pagesPuberty PDFnenyNo ratings yet
- Energy Metabolism-General 3Document75 pagesEnergy Metabolism-General 3Amanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Human ReproductionDocument48 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Human ReproductionErmiasNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument34 pagesThe Reproductive SystemMA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- 1 Neurological RehabilitationDocument20 pages1 Neurological RehabilitationSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury ManagementDocument63 pagesSpinal Cord Injury ManagementSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Stroke 15.1Document27 pagesStroke 15.1Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- 4.sensorry ExaminationDocument27 pages4.sensorry ExaminationSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Congenital and Developmental Conditions in ChildhoodDocument28 pagesOrthopedic Congenital and Developmental Conditions in ChildhoodSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- 10 StrokeDocument24 pages10 StrokeSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Neuorlogical Assessment-1Document52 pagesNeuorlogical Assessment-1Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Examination of CoordinationDocument17 pagesExamination of CoordinationSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Neuorlogical AssessmentDocument41 pagesNeuorlogical AssessmentSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- 4 AsthmaDocument32 pages4 AsthmaSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Neuorlogical AssessmentDocument38 pagesNeuorlogical AssessmentSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- 2.presentation NeuroDocument14 pages2.presentation NeuroSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- 1a. OrthopaedicsDocument19 pages1a. OrthopaedicsSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Burns LectureDocument51 pagesBurns LectureSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- 1a. Obstetric Emergencies Koros E.KDocument225 pages1a. Obstetric Emergencies Koros E.KSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument17 pagesCarbohydratesSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument29 pagesCarbohydratesSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Boundaries of AxillaDocument2 pagesBoundaries of AxillaSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer FinalDocument22 pagesBreast Cancer FinalSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Reproductive System (Anatomy)Document7 pagesIntroduction To Reproductive System (Anatomy)Hamza MalikNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Life Science EmbryologyDocument20 pagesLecture 2 Life Science EmbryologyjoeNo ratings yet
- Male Factor InfertilityDocument53 pagesMale Factor InfertilityMarcel MusteaNo ratings yet
- Ovozoa Vol. 7, No. 2, Oktober 2018 ISSN: 2302-6464Document6 pagesOvozoa Vol. 7, No. 2, Oktober 2018 ISSN: 2302-6464Miftah LailiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Chiot NewDocument8 pagesJurnal Chiot NewamelyaNo ratings yet
- Diasino® One-Step Sandwich Anti-Mullerian Hormone (Amh) AssayDocument4 pagesDiasino® One-Step Sandwich Anti-Mullerian Hormone (Amh) AssayAbdalazeez AlsayedNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Part 2 DRAFTDocument6 pagesEndocrine Part 2 DRAFTPreeti Joan BuxaniNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Reproductive SystemDocument180 pagesPhysiology of Reproductive Systemnirilib0% (1)
- The Reproductive System A. Male: Human Anatomy & Physiology, Sixth EditionDocument44 pagesThe Reproductive System A. Male: Human Anatomy & Physiology, Sixth EditionFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Fertility AwarenessDocument5 pagesFertility AwarenessGabriela GascaNo ratings yet
- MRP in Farm and Pet AnimalsDocument21 pagesMRP in Farm and Pet AnimalsShantha VardhanNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Kurma Muda (Phoenix Dactylifera) Terhadap Kadar FSH Dan Reseptor FSH Ovarium Tikus Putih (Rattus Norvegicus)Document5 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Kurma Muda (Phoenix Dactylifera) Terhadap Kadar FSH Dan Reseptor FSH Ovarium Tikus Putih (Rattus Norvegicus)ninizarNo ratings yet
- JSS2 Basic Science Lesson Note PDFDocument40 pagesJSS2 Basic Science Lesson Note PDFJuddy ScienceNo ratings yet
- Prelab One-Flower IntroductionDocument29 pagesPrelab One-Flower IntroductionArwa ZayedNo ratings yet
- Ajol File Journals - 79 - Articles - 85618 - Submission - Proof - 85618 937 209980 1 10 20130219Document5 pagesAjol File Journals - 79 - Articles - 85618 - Submission - Proof - 85618 937 209980 1 10 20130219IcicNo ratings yet
- MCHN OutlineDocument15 pagesMCHN OutlineAngel Strauss KmpsnNo ratings yet
- Bahagian B Dan C PPT SC 2019 t1Document15 pagesBahagian B Dan C PPT SC 2019 t1Anonymous RfKC0LciBKNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument4 pagesHow Do Organisms ReproduceNilkanth PatelNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Hormonal Contraception On The Voice Rodney SataloffDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Hormonal Contraception On The Voice Rodney SataloffIvory PlatypusNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Contraceptives in CanadaDocument3 pagesHormonal Contraceptives in CanadaNida Saghir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyanglogaliboNo ratings yet