Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reports Weakness, and Flu-Like Symptom For 3-4 Days
Uploaded by
Alliana Denice Vicencio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesOriginal Title
NCP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesReports Weakness, and Flu-Like Symptom For 3-4 Days
Uploaded by
Alliana Denice VicencioCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
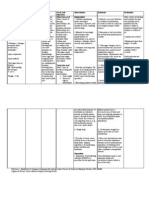
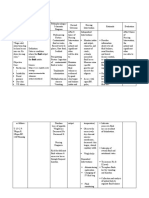
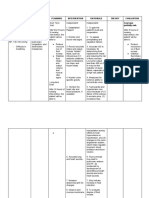
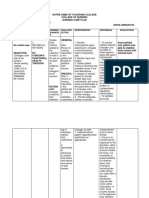
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT NURSING EXPECTED PLANNING/ RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS OUTCOME INTERVENTION
SUBJECTIVE DATA The patient is This fundamental 1. Maintain regular oral 1. Due to fluid loss in Outcomes have been
The patient reports feverish. balance, as shown by hygiene. the interstitial spaces, met, and the client
weakness, and flu- Electrolytes in the 2. Weigh yourself every the oral mucous reports that her illness
like symptom for 3-4 blood and muscle day and keep track of membranes become is under control.
days power are not to be trends. dry and sticky.
compromised. 3. When necessary, 2. Weight aids in
OBJECTIVE DATA Deficient Fluid Fluid balance is monitor vital signs. determining fluid
Volume related to demonstrated by 4. Administer IV therapy balance.
Temp: 38.6
PR: 86BPM nausea, vomiting, maintaining the specific as directed. 3. Vital sign changes,
RR: 24CPM
and diarrhea as gravity of urine, the 5. Collect samples for such as an increase in
BP: 130/90
Diagnostic Data evidenced by turgor of the skin, moist potassium level analysis. heart rate or a
Urine specific
decreased urine mucous membranes, potassium levels in decrease in blood
gravity: 1.0357
Serum Sodium: output, increased body temperature, pulse serum and urine as pressure
155meq/ L urine concentration, rate, and blood instructed 4. Hypokalemia is
CXR: negative
weakness, fever, pressure. characterized by low
s
decreased blood pressure and a
skin/tongue turgor, rise in temperature.
dry mucous
membranes,
increased pulse rate,
and decreased blood
pressure
5.Urine analysis
determines whether a
substance was
retained or lost.
sodium and the ability
of the kidneys to
concentrate or dilute
urine
in response to fluid
changes
You might also like
- Chronic Disease Management for Small AnimalsFrom EverandChronic Disease Management for Small AnimalsW. Dunbar GramNo ratings yet
- Dengue NCPDocument3 pagesDengue NCPingridNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Aguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningDocument9 pagesAguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningSophia Kaye AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Dengue NCPDocument3 pagesDengue NCPnj_pink08179456% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: Age: Sex: Address:: Nursing-Notes/communicable - Diseases - Notes/amoebiasisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: Age: Sex: Address:: Nursing-Notes/communicable - Diseases - Notes/amoebiasisGILIANNE MARIE JIMENEANo ratings yet
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPjsksNo ratings yet
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- HYPONATREMIADocument3 pagesHYPONATREMIADienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- Sample: Duquesne University School of Nursing Care Map TemplateDocument6 pagesSample: Duquesne University School of Nursing Care Map TemplateDevin Nikole BlattnerNo ratings yet
- Actual Nursing Care Plan #1: Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument7 pagesActual Nursing Care Plan #1: Deficient Fluid VolumeAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Group 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaDocument6 pagesGroup 47 NCP Bicarbonate DisordersHyperbicarbonatemia and HypobicarbonatemiaAngel Joyce MontezaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument31 pagesNursing Care PlansCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNo ratings yet
- Lab Result 2020Document17 pagesLab Result 2020Farah HusseinNo ratings yet
- Module 2 1Document3 pagesModule 2 1Lacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- As Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ADocument2 pagesAs Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ATanya Alyssa Untalan AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP JaundiceDocument9 pagesNCP JaundiceMeena Koushal100% (1)
- But He Hated The Taste of Water: Nursing Assessment RationaleDocument4 pagesBut He Hated The Taste of Water: Nursing Assessment RationaleJiv Rouziell DoroteoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1 DiagDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1 Diagguysornngam100% (1)
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 pagesRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Lahore School of Nursing 9Document4 pagesLahore School of Nursing 9Ayesha ImtiazNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument67 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionTrisha OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Dengue Hemorhagic Fever (DHF)Document30 pagesDengue Hemorhagic Fever (DHF)Octa VianiNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Hemodialysis - Chronic Kidney FailureDocument31 pagesGroup 5 - Hemodialysis - Chronic Kidney FailureKimberly Abella CabreraNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationpamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument20 pagesCase StudyYiella AlagarNo ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- CKD Presentation GroupDocument49 pagesCKD Presentation GroupAhmad BaolayyanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis 1Document5 pagesNursing Diagnosis 1Kim TangoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HypovolemiaDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan HypovolemiaGusmila SariNo ratings yet
- Decrease Cardiac Output - NCPDocument4 pagesDecrease Cardiac Output - NCPLindy JaneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care PlanKirstin del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesTissue Perfusionnursezey100% (3)
- NCP Nausea and VomitingDocument4 pagesNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument22 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureSampada GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Facto NCPDocument3 pagesFacto NCPkkd nyleNo ratings yet
- Cholera N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesCholera N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Prado NCPDocument4 pagesPrado NCPalleah pradoNo ratings yet
- Geriatic Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance NCPDocument4 pagesGeriatic Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance NCPCA Candido JavierNo ratings yet
- Concept Map PedsDocument6 pagesConcept Map Pedsapi-498759347No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- Prado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Document52 pagesPrado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Catherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Surg2 Primary Aldosteronism AssignmentDocument8 pagesSurg2 Primary Aldosteronism AssignmentDarain Mohammed MeirNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentDocument2 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentArabelle GONo ratings yet
- NCP CKDDocument5 pagesNCP CKDDbktNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Actual and Potencial NCP Peptic Ulcer. Adepoju Iyinoluwa EDocument3 pagesActual and Potencial NCP Peptic Ulcer. Adepoju Iyinoluwa EAdepoju IyinoluwaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted byDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Submitted byKarl Angelo MontanoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationMargareth DandanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal DiseaseDocument12 pagesChronic Renal DiseaseNohaira SADANGNo ratings yet
- Activity # 7 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance (WITH NCP)Document15 pagesActivity # 7 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance (WITH NCP)Louise OpinaNo ratings yet
- HydroceleDocument10 pagesHydroceleRyan ReNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess (CRF)Document4 pagesFluid Volume Excess (CRF)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- Evaluationandmanagement Ofdehydrationinchildren: Genevieve Santillanes,, Emily RoseDocument15 pagesEvaluationandmanagement Ofdehydrationinchildren: Genevieve Santillanes,, Emily RoseSandra Díaz MercadoNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Document5 pagesSubjective Data: Long Term Goal: Diagnostic:: "I Was Trying To Vomit in The Emergency Department."Erle Gray CadangenNo ratings yet
- Guinitaran, Christine Ann P. BSN 4 Abruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanDocument19 pagesGuinitaran, Christine Ann P. BSN 4 Abruptio Placenta Nursing Care PlanGemmalene PaclebNo ratings yet
- The Nursing Process Health Assessment Week 1 LecDocument27 pagesThe Nursing Process Health Assessment Week 1 LecAlliana Denice VicencioNo ratings yet
- C1 Carbohydrates Part2 Cyclic FormDocument27 pagesC1 Carbohydrates Part2 Cyclic FormAlliana Denice VicencioNo ratings yet
- Chem113Lec-Activity 2-Carbohydrates ActivityDocument3 pagesChem113Lec-Activity 2-Carbohydrates ActivityAlliana Denice VicencioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interview Guide To Collect Subjective Data From The ClientDocument6 pagesNursing Interview Guide To Collect Subjective Data From The ClientAlliana Denice VicencioNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Regression AnalysisDocument23 pagesWeek 11 Regression AnalysisAlliana Denice VicencioNo ratings yet
- Using Formal and Informal Language AppropriatelyDocument22 pagesUsing Formal and Informal Language AppropriatelyAlliana Denice VicencioNo ratings yet
- Case Study About: OsteoporosisDocument15 pagesCase Study About: OsteoporosisAlliana Denice VicencioNo ratings yet
- Caught in Between Modern & Contemporary ADocument119 pagesCaught in Between Modern & Contemporary AAlliana Denice Vicencio100% (2)
- MCNDocument12 pagesMCNIan CarodanNo ratings yet
- Full Download Book Harrisons Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine 3E Nov 21 2016 - 1259835804 - Mcgraw Hill PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Book Harrisons Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine 3E Nov 21 2016 - 1259835804 - Mcgraw Hill PDFjessica.fox123100% (23)
- Breast Pathology Fumc 2022Document145 pagesBreast Pathology Fumc 2022Bahzad AkramNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Reproductive HealthDocument12 pagesBiology Investigatory Reproductive HealthSubath KumarNo ratings yet
- Resume - Armaghan Gharehaghaji ZareDocument3 pagesResume - Armaghan Gharehaghaji ZareSepideh MirzaeiNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Rheumatoid and OsteoarthritisDocument4 pagesComparison of Rheumatoid and OsteoarthritisWaseem Khan AfridiNo ratings yet
- GALS Examination OSCE GuideDocument10 pagesGALS Examination OSCE GuideSandarekha PereraNo ratings yet
- Positive Behavior Support PlanDocument21 pagesPositive Behavior Support Planapi-316958999No ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Thalassemia Major: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Thalassemia Major: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina Aubrey0% (1)
- Program Implementation With The Health Team: Packages of Essential Services For Primary HealthcareDocument1 pageProgram Implementation With The Health Team: Packages of Essential Services For Primary Healthcare2A - Nicole Marrie HonradoNo ratings yet
- 5 - Effectiveness of Vitamin D in Prevention of DHF & DssDocument3 pages5 - Effectiveness of Vitamin D in Prevention of DHF & DssSameer SamouaNo ratings yet
- OET WRITING EXAM Fast TrackDocument27 pagesOET WRITING EXAM Fast Tracksyed100% (2)
- 209 Handouts High RiskDocument26 pages209 Handouts High RiskxiumethemoneyNo ratings yet
- English: Fourth Quarter - Module 5Document14 pagesEnglish: Fourth Quarter - Module 5Nathalie Jefsieji Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ascitic Fluid AnalysisDocument3 pagesAscitic Fluid AnalysisLohJNo ratings yet
- Autis PDFDocument15 pagesAutis PDFMutia RahmyNo ratings yet
- Data Base Worldcat 4Document41 pagesData Base Worldcat 4Melinda Tri PutriNo ratings yet
- New Synopsis PranjalDocument5 pagesNew Synopsis PranjalPranjalNo ratings yet
- How Can Mental Health Be Less Taboo - Avery MageeDocument12 pagesHow Can Mental Health Be Less Taboo - Avery Mageeapi-608889159No ratings yet
- Advances in Therapeutic Peptides Targeting G Protein-Coupled ReceptorsDocument25 pagesAdvances in Therapeutic Peptides Targeting G Protein-Coupled ReceptorsAyberk BinbayNo ratings yet
- May 2022 RecallDocument40 pagesMay 2022 RecalljohnNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base and Electrolyte Abnormalities With Diarrhea PDFDocument9 pagesAcid-Base and Electrolyte Abnormalities With Diarrhea PDFAdi CărbunaruNo ratings yet
- Perception and Practice of Community Pharmacist Towardsantimicrobial Stewardship in Lahore, PakistanDocument19 pagesPerception and Practice of Community Pharmacist Towardsantimicrobial Stewardship in Lahore, Pakistanaji gumelarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For VirusesDocument6 pagesLesson Plan For VirusesAudrey LeonnaNo ratings yet
- De Boo Barker HypothesisDocument11 pagesDe Boo Barker HypothesisIamJmlingconNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Hemostaza Kao Fiziološki Mehanizam Pozitivne Povratne SpregeDocument10 pagesHemostaza Kao Fiziološki Mehanizam Pozitivne Povratne SpregeCrvena LoknicaNo ratings yet
- Icici Lombard Complete Health Insurance Proposal FormDocument4 pagesIcici Lombard Complete Health Insurance Proposal FormMonal RajNo ratings yet
- PulmonologyDocument175 pagesPulmonologyJohanna GarciaNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Dialysis Sao PauloDocument8 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis Sao PauloRemberto RamosNo ratings yet