Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midsem Spring 2022 HS1349
Uploaded by
Rituraj TripathyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midsem Spring 2022 HS1349
Uploaded by
Rituraj TripathyCopyright:
Available Formats
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, ROURKELA
MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2022
SESSION: Spring
Subject Code: HS-1349 Dept. Code: HS
Subject Name: Industry and Development Full Marks: 30
Duration of Examination: 2 hours
Figures at the right-hand margin indicate marks
All parts of a question should be answered in one place
Q. N. Section A Marks
Answer any FOUR 4x4=16
1. What is marginal cost? Explain graphically the relationship between marginal cost (MC),
average cost (AC) and total cost (TC).
2. What are economies and diseconomies of scale? Derive the long run average cost (LRAC)
curve from short run average cost (SRAC) curves of firms.
3. With the aid of labelled diagrams, explain the impact of entry of new firms on the
equilibrium conditions in a perfectly competitive market? Are these markets economically
efficient?
4. Illustrate using graphs the following scenarios in a monopolistically competitive market:
a. Economic profit
b. Economic loss
c. Break-even
d. Shut down
5. What is price discrimination? Discuss how price elasticity affects price discrimination with
suitable real-life examples.
6. What is Bertrand Paradox in oligopoly? Discuss the factors that lead to this paradox. How
can firms come out of this paradox?
Section B Marks
Answer any TWO 2x7=14
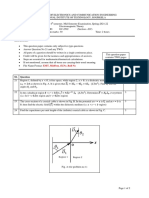
1. A monopolist serves a market with an aggregate demand function given by Q = 38 – 3P.
This market can be partitioned into submarkets 1 and 2 with submarket demand functions
given by Q1 = 24 – 2P1 and Q2 = 14 – P2. The monopolist’s cost function is given by C(Q)
= 2Q.
a) What price will prevail in the market under no price discrimination?
b) What prices will the monopolist set if she decides to practice third-degree price
discrimination?
c) Does price discrimination lead to higher economic welfare under these conditions?
2. The market for dental care has S number of consumers.
Each consumer has demand D(p) = 200 – 2p. Firms have to invest fixed cost F to enter the
market and then pay C(q) = q2 to produce q units.
a) Compute the inverse demand curve p(Q).
b) Plot p(Q) for S = 1, S = 5 and S = 100. Show and explain what happens to p(Q) when
the number of consumers in the market increases?
c) What should be the value of S such that a monopolist may earn positive economic
profits?
3. The inverse market demand is given by P = 36 – Q, where P is price and Q = q1 + q2. The
cost function for firm 1 is given by C(q1) = 12q1 and the cost function for firm 2 is given
by C(q2) = 12q2.
a) If each firm acts to maximize its profits taking its rival’s output as given, compute the
reaction functions for firm 1 and firm 2.
b) Determine the equilibrium level of output in the market and the price
c) Calculate the profits for each firm.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- EMT 2022 Mid Sem - Final - SubjectiveDocument2 pagesEMT 2022 Mid Sem - Final - SubjectiveRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Rituraj Tripathy: ContactDocument1 pageRituraj Tripathy: ContactRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics SyllabusDocument3 pagesAnalog Electronics SyllabusRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Qualki Instagram ContentDocument7 pagesQualki Instagram ContentRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Qualki Instagram ContentDocument7 pagesQualki Instagram ContentRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Communicative English, A.K. Rath, Practice Set 6Document1 pageCommunicative English, A.K. Rath, Practice Set 6Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Trial Rate (Mole L Sec) Initial Conc. Ofa (Molel) Initial Conc. Ofb (Molel)Document2 pagesTrial Rate (Mole L Sec) Initial Conc. Ofa (Molel) Initial Conc. Ofb (Molel)Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Practice AssignmentDocument5 pagesClass 8 Practice AssignmentRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Communicative English, A.K. Rath, Practice Set 6Document1 pageCommunicative English, A.K. Rath, Practice Set 6Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Communicative English, AK Rath, Practice Test 2Document2 pagesCommunicative English, AK Rath, Practice Test 2Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - B Section EC1000Document1 pageAssignment 2 - B Section EC1000Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Leader Online Test Series For JEE Main 2020Document1 pageSchedule of Leader Online Test Series For JEE Main 2020Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Assignment A NPDocument2 pagesAssignment A NPRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Trial Rate (Mole L Sec) Initial Conc. Ofa (Molel) Initial Conc. Ofb (Molel)Document2 pagesTrial Rate (Mole L Sec) Initial Conc. Ofa (Molel) Initial Conc. Ofb (Molel)Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Communicative English, AK Rath, Practice Test 2Document2 pagesCommunicative English, AK Rath, Practice Test 2Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Ta 2Document1 pageTa 2Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- What Is Hack Odisha ?Document7 pagesWhat Is Hack Odisha ?Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Electrical vs Electronics - Key Differences Between the Two FieldsDocument52 pagesElectrical vs Electronics - Key Differences Between the Two FieldsRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Bsection EC1000Document3 pagesAssignment 3 - Bsection EC1000Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Ta 2Document1 pageTa 2Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Nested Classes 235-245: Durgasoft MR - RatanDocument4 pagesNested Classes 235-245: Durgasoft MR - RatanRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Slater'S Rules and Periodicity (Worksheet) : Skills To DevelopDocument3 pagesSlater'S Rules and Periodicity (Worksheet) : Skills To DevelopRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Bsection EC1000Document3 pagesAssignment 3 - Bsection EC1000Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Ta 2Document1 pageTa 2Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Core Java Syllabus: 1. Introduction 6-26Document3 pagesCore Java Syllabus: 1. Introduction 6-26Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- 01 Core Java PDFDocument401 pages01 Core Java PDFKASIM INFO0% (1)
- IIT Entrance Exam Preparation Course PlannerDocument4 pagesIIT Entrance Exam Preparation Course PlannerRituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- Spring ReferenceDocument827 pagesSpring Referenceanaga1982No ratings yet
- Corejava Ratan 23aug2016Document1 pageCorejava Ratan 23aug2016Rituraj TripathyNo ratings yet
- 2015 MarchDocument64 pages2015 Marchehlaban100% (3)
- Fermin ResumeDocument1 pageFermin Resumeapi-460105426No ratings yet
- Business 2257 Tutorial #2Document17 pagesBusiness 2257 Tutorial #2westernbebeNo ratings yet
- Traditional Functions of RBIDocument3 pagesTraditional Functions of RBIomkarmbaNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica HysterDocument8 pagesFicha Tecnica HysterMoises GilNo ratings yet
- Amended 2018 Financials Cover SheetDocument1 pageAmended 2018 Financials Cover SheetJowelyn DesabilleNo ratings yet
- Market Feasibility Report-OfCDocument11 pagesMarket Feasibility Report-OfCShashank SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Educational Tour Notice 2022-23-1Document2 pagesEducational Tour Notice 2022-23-1sanket12032002No ratings yet
- L T Sustainability Report 2011 FinalDocument112 pagesL T Sustainability Report 2011 FinalMayur KundarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Current Scenario of Stock Markets in Bangladesh From Investors™ PerspectiveDocument46 pagesAnalysis of Current Scenario of Stock Markets in Bangladesh From Investors™ PerspectiveTariqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Negotiating International Joint Ventures: Presenter: 鄭于琦 (Becky Cheng) g9929707 陳楷琍 (Kelly) m10061013 周柏君 (Wilson) m10022038Document24 pagesNegotiating International Joint Ventures: Presenter: 鄭于琦 (Becky Cheng) g9929707 陳楷琍 (Kelly) m10061013 周柏君 (Wilson) m10022038imwkyaNo ratings yet
- AC2101 SemGrp4 Team1 (Updated)Document43 pagesAC2101 SemGrp4 Team1 (Updated)Kwang Yi JuinNo ratings yet
- The Air Conditioner and the Transformation of Southern CultureDocument33 pagesThe Air Conditioner and the Transformation of Southern CultureBRIAN STOLLNo ratings yet
- Hindi Excel Sample FileDocument12 pagesHindi Excel Sample FileAyush KumarNo ratings yet
- MASA MASID Guidelines for Community Reporting of AnomaliesDocument9 pagesMASA MASID Guidelines for Community Reporting of AnomaliesjejemonchNo ratings yet
- Forex Trading Income CalculatorDocument8 pagesForex Trading Income CalculatorjamesNo ratings yet
- English VersionDocument106 pagesEnglish VersionAmrFarahatNo ratings yet
- DataDocument272 pagesDataomgan1042No ratings yet
- Labour Economics Ps1 SolutionsDocument10 pagesLabour Economics Ps1 SolutionsMANUEL GONZÁLEZNo ratings yet
- ECO121 Assignment 02 Đ M NH Qu NH HE170282Document3 pagesECO121 Assignment 02 Đ M NH Qu NH HE170282Do Manh Quynh (K17 HL)No ratings yet
- Rhythm ChangesDocument5 pagesRhythm ChangesNicolás Ocampo100% (1)
- P&H Mining Equipment Offices: Back To IndexDocument4 pagesP&H Mining Equipment Offices: Back To Indexfernando chinchazoNo ratings yet
- FDI in India Case Study WalmartDocument32 pagesFDI in India Case Study WalmartSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Community Development Programmeits Political ImpactDocument10 pagesCommunity Development Programmeits Political ImpactJenica SharuNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship EXAM AugDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship EXAM AugBJ ShNo ratings yet
- EIEF/LUISS, Graduate Program Asset Pricing: 1 PresentationDocument9 pagesEIEF/LUISS, Graduate Program Asset Pricing: 1 Presentation曹华珅No ratings yet
- Micro & Macro Economics:: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesMicro & Macro Economics:: ObjectivesGod BoyNo ratings yet
- MIT14 01SCF11 Exam02 f07Document19 pagesMIT14 01SCF11 Exam02 f07Saad MalikNo ratings yet
- Imyb2011 - Expln & DevlptDocument61 pagesImyb2011 - Expln & Devlptmujib uddin siddiquiNo ratings yet
- Inbiuro Road-Rail VehiclesDocument25 pagesInbiuro Road-Rail VehiclesInbiuroNo ratings yet