0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views4 pagesPower Electronic System Design Exam
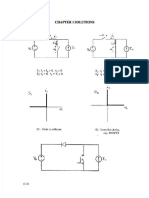
The document contains a final exam for a power electronics course. It is divided into two sections, with the first section containing short answer questions and the second containing longer problems. Some of the topics covered include power MOSFETs, magnetic components, capacitors, switching devices, and thermal design of power devices.
Uploaded by
Bitata Sarkar ee21s059Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
103 views4 pagesPower Electronic System Design Exam
The document contains a final exam for a power electronics course. It is divided into two sections, with the first section containing short answer questions and the second containing longer problems. Some of the topics covered include power MOSFETs, magnetic components, capacitors, switching devices, and thermal design of power devices.
Uploaded by
Bitata Sarkar ee21s059Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd