Paavai Engineering College
(Autonomous)
Department of Aeronautical Engineering
Aircraft Structures II
Question Bank
Unit I
Part A
1. Define neutral axis and give expression to determine it.
2. Define principle axis of a section and give an expression to determine it.
3. Draw bending stress variation across the depth for (a) Rectangular section (b) I-section.
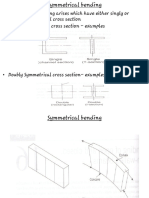
4. Distinguish between symmetric and unsymmetric bending.
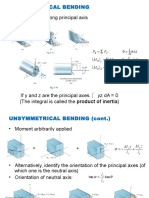
5. What do you understand by unsymmetrical bending? Explain a method to find the stress in an unsymmetrical bending
6. When does unsymmetrical bending takes place.
7. Explain unsymmetrical bending with examples.
8. A rectangular cross section is subjected to a skew load P inclined at an angle θ=40. To the vertical. write down the expression for the
orientation of the neutral axis to the vertical ?
9. Write down the expression for orientation of neutral axis of the beam with unsymmetrical cross section in z-x plane and subjected to bending
moments Mx and My.
10. Sketch a semi-monocoque wing and state assumptions made in its analysis? 11. .Find Ixx and Iyy for a thin walled I-section with thickness t
and flange width=w height =h.
�12. Define stress?
13. Define strain and explain types of strain?
14. Explain shear stress?
15. What is a centroid of a section?
16. Explain principal plane?
17. What is a principal stress?
18. Define moment of inertia?
19. What is a bending stress?
20. How will you define pure bending?
21. Explain oblique bending?
22. Reasons for unsymmetrical bending?
23. Difference between symmetrical and unsymmetrical bending?
24. Explain neutral axis and neutral surface?
25. State parallel axes theorem?
26. State perpendicular theorem?
27. Methods used to find bending stress for unsymmetrical section?
28. A rectangular section is subject to a skew load P inclined at θ=40⁰ to the vertical. Write down the expression for the orientation of the
neutral axis to the vertical?
29. Define redundancy in a structure .How do you determine the order of redundancy?
30. Explain how unsymmetrical bending is developed in a beam?
�31. Writ e down the expression for orientation of neutral axis of beam with unsymmetrical cross section in z-x plane and subjected to bending
moments Mx and My .
Part B
1. Determine the normal stress at location A and G(refer fig.1)for the following cases of loading:
(i) Vx=1.2 kN acting through shear center.
(ii) Vy=1.2 kN acting through shear center.
Vx and Vy are applied0.8 m away from the indicated cross-section
2. The section shown in fig. is subjected to bending moment Mx=30kNm.determine the bending stress at the corner points A, B, C and D.
�3. (i)Derive and obtain an expression for the bending stress in an unsymmetrical section subjected to bending, using the generalized ‘k’ method
(ii) Explain the neutral axis method of bending stress determination mhen an arbitrary section is subjected to bending moments Mx and My.
4. A Z- section with 12 cm x 3 cm flanges and 20 cm x 3 cm web is subjected to Mx=10 kN-m and My=10 kN-m . Determine the maximum
bending stress.
5. A box beam with 50 cm length is subjected to loads Px=8kN and Py=25kN as shown in fig.3. The stringer area is 3 cm2 each. Find the
maximum bending stress.
6. A beam section shown in fig.has four stringers. Area of the stringers A, B, C and D are 6.25, 3.125, 4.5 and 6sq.cm respectively. Find the
stresses in all the four stringers of the section due to Mx=50kNm and My=-20kNm where x and y are the centriodal axes. Assume that webs
� and walls are ineffective in bending.
7. Refer fig..The section is subjected to an 8 kNm bending moment in the x-z plane and a 10 kNm bending in the y-z plane. Determine the
bending stresses in all the corner points, indicating whether they are tensile or compressive. All the dimensions are in cm.
8. An angle section with flange 15 cm x 3 cm and web 20 cm x 3 cm is subjected to Mx=15 kN-m and My=15kN-m.find the maximum bending
stress.
9. Derive an expression for bending stress in an unsymmetrical section subjected to Mx and My and modify this expression with respect to
� principal axis and neutral axis.
10. A beam of z-section is subjected to a Bending moment Mx having its vector directed along the x-axis as shown in fig.calculate the max
tensile
stress σ(t) andmax compressive σ(c) if the moment Mx=4kNm and the dimensions are b=90mm and h=180mm and t=15mm.
Unit II
Part A
1. Define shear center.
2. Define shear center and sketch the shear flow distribution for a thin walled vertical channel section subjected to a vertical load through the
shear center.
3. Draw the shear stress and bending stress variation across the depth for
i. Rectangular section
ii.I-section and explain why structural section are used for beams.
�4. Draw the bending stress and shear stress distribution for a c-section.
5. Define shear flow and shear center
6. What type of structural elements require the computation of shear flow?
7. Sketch the shear flow for a channel section subjected to a vertical load?
8. How do you define the boom?Explain how do they resist the loads?
9. Define the shear flow and tortional stiffness of a thin walled closed section subjected to torque?
10. With a neat sketch indicate the shear center location for channel section and angle section?
11. Shear flow can be defined both thin and thick walled section.(True/False)
12. What is a shear web?
13. Define shear flow.how shear stress is obtained from shear flow?
14. Show that for a curved web shear center distance e=2A/L
15. A thin walled channel section is subjected to a downward vertical shearing load applied through the shear center .the moment of the shear
flow distribution about the shear center will be (in the clockwise sense /zero/equal to the shearing load multiplied by the distance between the
shear center ant the vertical web)
16. Define elastic axis.
17. Define center of twist.
18. What is a thin walled section?
19. Explain the difference between shear flow and shear stress?
20. A thin walled channel section is subject to a downward vertical shearing load appliedthrough the shear center . the moment of the shear flow
distribution about the shear center will be (in the clockwise sence/zero/equal to the shearing load multiplied by the distance between the shear
centre and the vertical web)
�21. Explain the effect of wall thickness in a beam when it undergoes bending.
22. Locate the shear center for the following sections.
i. Channel
ii. Angle with unequal length
iii. Open ring
iv. Closed ring
23. Sketch the shear flow distribution when a thin walled L-section is subjected to a vertical load.
24. Indicate the shear center for channel section and angle section
25. Define shear flow .How the shear stress is obtained from the shear flow?
Part B
1. Derive and obtain an expression for shear flow due to bending in the case of an arbitrary thin walled open section subjected to bending.
How to modify the results you obtained for the case of closed section.
2. 2. Plot the shear flow and locate the shear center for the section shown in fig. Thickness=2mm and stringer Area=300 mm2
�3. Plot the shear flow and locate the shear center for the section shown in fig. All the dimensions are in cm. Area of stringer
A=1cm2,B=1cm2,C=1.5cm2 and D=1cm2
4. Find the shear flow for the section shown in fig.11.The Area of the each stringer =6 cm2.the loads are Sx=10kN and Sy=50kN through the
shear center .Also find the Shear center All the dimensions are in cm.
�5. Find the shear center of the section shown in fig.12.Area a=b=4 cm2 and c=d=2 cm2 All the dimensions are in cm.
6. Find the shear flow distribution and locate the shear center for the section shown in fig.13.Each of the stringers has an area of 4 cm2 and the
section subjected to vertical shear of 50 kN. All dimensions are in cm.
�7. Find the shear flow distribution in a thin walled Z-section, whose thickness is‘t’, height’h’. Flange width ‘h/2’ and subjected to vertical shear
load through shear center.
8. Find the shear flow distribution and shear center for a thin walled channel section of thickness of thickness 3 mm, flange width 5 cm, web
height 10 cm and subjected to a vertical load of 5 kN through the shear center.
9. Find the shear flow distribution and locate the shear center for the section shown in Fig Each of the stringers has an area of 4 cm2 and the
section is subjected vertical shear of 50 kN.
10. The section shown in Fig is subjected to vertical shear of 60 kN applied through shear center. Obtain the shear flow for the section. Areas of
all the stringers are same and is equal to 7 cm2.
11. Obtain the shear flow distribution and shear center location for the section shown in Fig. when it is subjected to a shear load of 5 kN.
�12. (i) Does the shear center always lies outside for the open section? Explain.
(ii) Obtain the shear flow and shear center location for the channel section subjected to a vertical shear load of 5 kN. The height of the
vertical web is 50 mm and width of flanges is 25 mm. Thickness of the flanges and the web is 1.5 mm.
13. Obtain the shear flow and shear center location for the channel section subjected to a vertical shear load of 5 kN. The height of the vertical
web is 50 mm and width of flanges is 25mm. Thickness of the flanges and the web is 1.5 mm.
14. Find the shear flow distribution and shear center for a thin walled channel section of thickness of thickness 3 mm, flange width 5 cm, web
height 10 cm and subjected to a vertical load of 5 kN through the shear center.
Unit III
Part A
1. Sketch the assumptions made in the derivation of Bredt-Batho formula?
2. Derive the expression for shear flow in a single cell tube under the torque?
3. A thin walled multicell tube subjected to a torque load is statically indeterminate.why?
�4. Find an expression for angle of twist per unit length of a thin walled closed section .
5. Find an expression for shear flow in a circular tube subjected to a vertical load through its center.
6. What is cladding ?
7. Explain with neat sketch , shear flow around a multicell structure?
8. .Show that for a curved web T=2Aq.
9. Derive an expression for the angle of twist per unit length.
10. Explain how the shear flow around a multicell structure subjected to tortional moment is determined ?
11. Find an expression for angle of twist of thin walled closed section subjected to a torque?
12. Differentiate between statically determinate and indeterminate box beams. give examples.
13. What is a shear web?
Part B
1) Compute the shear flow distribution and locate the shear center for the case shown in fig assume the webs are ineffective in bending.All
dimension are in cm.
�2) Compute the shear flow and the twist of the three cell thin walled section shown in fig. a torque of 16 kN-m is applied clockwise .E=200GP
and the Poisson ratio =0.3 vertical portions thickness is 2mm and the horizontal portions thickness is 1 mm.Dimensions are in cm.
3) the fig. shows a single cell beam with four flanges .find the internal shear flow force system when the beam carries the external load of
2000N. as shown in fig.take t=0.1cmvertical load v=2000N
4. find the shear flow ,shear stress and the angle of twist per unit length of the two cell structure as shown in fig.take G=25x10^(5) N/cm^(2) and
the thickness is 0.1cm.
�5. i. Derive the expression for the shear flow in thin walled single cell subjected to torque load.
ii. Obtain the shear flow for the thin walled structure shown in the Fig
6. Obtain the shear flow for the box beam shown in Fig A1=A5 =25cm2, A2=A3=A6=A7=7cm2 and A4=A8=12cm2.
�7. A multicell structure shown in Fig. is subjected to a clockwise torque of 1000 Nm. Compute the shear flow in the cell structure and the
associated twist.
8. Obtain the shear flow around a three cell box beam Fig when it is subjected to a torque of T=100 kNm The thickness of vertical members,
horizontal members and semicircle are 1.25, 0.75 and 0.6 cm respectively
�9. Obtain the shear flow distribution for the closed section shown in Fig. Each stringer area is 6.5 cm2.
10. Compute the shear flow distribution for the three cell structure shown in fig.the section is subjected to a torque load of 19 kN-m in the
anticlockwise direction.
�11. Compute the load on the lumped flanges due to bending of the section shown in Fig. Assume the webs do not take part in bending. Compute
the loads using moments values with respect to x and y axes and principal axes.
Unit IV
�Part A
1. Explain any one method used to compute crippling stress.
2. Explain the significance of effective width.
3. What do you understand by lips and bulbs in structural elements.
4. Distinguish between primary & secondary buckling.
5. Explain effective width and give an expression to determine it.
6. Explain buckling in shear for a sheet and sketch the mode shape.
7. What is a buckling stress.
8. Explain the difference between plate and column buckling .
9. .Explain Buckling in compression for a Plate.
10. i) For bending elastic buckling the equation is
ii) Margin of safety (MOS) is equal to ______________________
11. sketch buckling modes of a plate in
a.compression
b.shear
12. what is effective width?
13. Explain effective width and give an expression to determine it .
14. Explain buckling in compression of plates?
15. How a structure will behave when it is subjected to eccentric load?
16. Explain how thin sheets and webs used in airplane structures are very efficient in resisting loads.
17. In designing sheet stiffener panels,what is the main criterion from the failure point of view?
18. Explain the difference between a flat plate in bending and a narrow beam?
19. Explain the functions of ribs and stringers?
20. Explain buckling of a sheet in shear.find the shear buckling stress for a sheet panel with a=200cm,b=10cm,t=1mm and all edges simply
supported .Material is 2024- T3.given ks=6
21. List the different failure modes of thin walled column.
22. To carry a given load a monocoque structure is heavier than semi-monocoque construction.(true/false)- why?
23. Give expression for buckling stress for
a.Column
b.Sheet
24. What is a lip ?how does it affects the strength of a section?
25. Explain clearly the distinction between the strength and stiffness problems instructures?
�26. Explain how a thin beam subjected to shear resists the load?
27. Define load factor and classify aircraft based on load factor?
Part B
1. Differentiate between buckling and crippling and explain any one method to determine crippling strength.
2. Find the crippling load for an angle section of aluminium alloy, 50mm x 25mm x 1mm.
3. Derive the governing equation for buckling of thin plates .obtain the buckling load for a simply supported plate of length A and width B
and subjected to uniform in pane compression along the width.
4. (i) What is a rib? How does it transfer the load?
(ii) Determine the load distribution in all the members of the rib shown in Fig.
5. What is meant by effective width?explain the method of estimating the ultimate load carrying capacity of a stiffened flat sheet under
compression .
6. Two sheets of aluminium and steel are given .both have the same weight. Compare the load required to buckle the sheets.
7. i) Write short notes on strength prediction of thin walled open section column. ii)Explain antielastic curvature
8. Explain how the crippling stress is computed for a composite structure section.
9. Compute the crippling stress for the section shown in fig . E=70 Gpa . effective width is 100 cm. thickness is constant through the section
and is equal to 2 mm.
�10. Obtain the expression for critical stress value for a sheet under compression with simply supported loaded edges and free unloaded edge.
11. Determine the value of the buckling stressfor an equal flanged angle section 25 x 25 x 2 mm. assume E=70 Gpa ; poisons ratio=0.3 and
end fixity coefficient =0.43
12. Explain in detail the needham and Gerard methods of finding the failure strengths of open and closed sections subjected to compressive
loads.
13. a. Clearly bring out the difference between shear resistance beams and tension field beams.
b. Find the crippling load for an angle section of aluminium alloy, 50mm x 25 x 1mm.
14. A fuselage bulkhead of 1m radius, has 12 stringers equally placed around the section starting from top point. Each stringer area is 6.25
cm.The bulk head is subjected to a symmetrical vertical shear load of 10 kN. Find the shear flow around the bulk head.
15. Derive the expression for buckling stress for a thin plate under compression.
Unit V
Part A
1. List various structural components of fuselage.
2. Define shear resistant web beam
3. What is a diagonal tension field beam
4. Draw a neat sketch of a fuselage structure showing all the structural details. Mention the loads resisted by each of them.
5. What are the advantages of semi-cantilever wing.
6. Explain safe life and fail safe design with example.
7. Sketch v-n diagram.
8. What is the difference between tension field beam semi tension field beam
9. List down various structural components in the fuselage
10. List down various structural components in an aircraft wing.
�11. Sketch a semi-monocoque structure and explain its advantage?
12. Specify any one alluminium alloy used in aircraft construction and its properties?
13. Sketch a semi-monocoque wing and state the assumptions made in its analysis?
14. Explain wagner beam and its advantages.
15. What is meant by a tension field beam?
16. Explain the difference between monocoque and semi-monocoque structures?
17. Show how a typical wing structure is idealized for structural analysis.
18. Draw a neat sketch of a typical aircraft wing and mark all the structural components.
19. Explain the difference between tension field beam and semi-tension field beam.
20. Sketch lift distribution on a wing and draw the corresponding shear force and bending moment diagrams.
21. Briefly explain structural idealization usind the aircraft wing structure as an example.
22. State the advantages of having a semicantilever type of wing construction?
23. Sketch the bending moment diagram for a semi-cantilever type of wing construction for a constant upward airloads?
24. List down the various structural components in aircraft wing?
25. List down the various structural components in the fuselage?
26. Is it convenient to have engine fitted to the aircraft wing from the structural design point of view? Justify the answer?
27. What is the difference between tension field beam and semi tension fiend beam?
28. Sketch semi monocoque structure and name the parts?
29. What is a lip and how does it affect the strength of a section?
30. What is a semi tention fied beam?
31. What do you understand by monocoque and semi monocoque type of aircraft construction?
Part B
1. Explain wagner beam.
2. Explain lift distribution on a cantilever wing.
3. Explain the principle of semi-tension field beams and find expression for
i) Web stiffener load
ii) Flange axial load
4. Explain in detail the stress analysis of a thin webbed beam using the pure tension field beam theory.
5. What are the loads acting on an airplane and the gust loads.
6. Explain stress analysis on fuselage.
7. Write short notes on any TWO of the following:
� (i) Definition and analysis of monocoque and semimonocoque structures.
(ii) Idealisation and analysis of aircraft wing structure.
(iii) Idealisation and analysis of aircraft fuselage.
8. (i)Differentiate between buckling and crippling and explain any one method to determine crippling strength.
(ii) Explain Wagner beam.
9. Explain lift load distribution, structural load distribution on a cantilever wing and draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams.
10. Explain the tention and semi tention field beams.
11. (i). what do you understand by idealization in structural analysis?
(ii). Explain the procedure to find the shear and bending moment distribution in a fuselage structure.
12. Write short notes on any TWO of the following:
(i) Definition and analysis of monocoque and semi monocoque structures.
(ii) Idealisation and analysis of aircraft wing structure.
(iii) Idealisation and analysis of aircraft fuselage.
13. Explain lift load distribution, structural load distribution on a cantilever wing and draw the shear force and bending mo ment diagrams.
14.Explain the V-n Diagram