Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3.8 Testing of Insulator: Rohini College of Engineering & Technology
Uploaded by
موسي النحلهOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3.8 Testing of Insulator: Rohini College of Engineering & Technology
Uploaded by
موسي النحلهCopyright:
Available Formats
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
3.8 TESTING OF INSULATOR
To ensure the desired performance of an electrical insulator, that is for avoiding
unwanted insulator failure, each insulator has to undergo numbers of insulator
test. Before going through testing of insulator we will try to understand different causes
of insulator failure. Because insulator testing ensures the quality of electrical
insulator and chances for failure of insulation depend upon the quality of insulator.
(i) Cracking Of Insulator
The porcelain insulator mainly consists of three different materials. The main porcelain
body, steel fitting arrangement and cement to fix the steel part with porcelain. Due to
changing climate conditions, these different materials in the insulator expand and contract
in different rate. These unequal expansion and contraction of porcelain, steel and cement
are the chief cause of cracking of insulator.
(ii) Defective Insulation Material
If the insulation material used for insulator is defective anywhere, the insulator may have
a high chance of being puncher from that place.
(iii) Porosity In The Insulation Materials
If the porcelain insulator is manufactured at low temperatures, it will make it porous, and
due to this reason it will absorb moisture from air thus its insulation will decrease
and leakage current will start to flow through the insulator which will lead to insulator
failure.
(iv) Improper Glazing on Insulator Surface
If the surface of porcelain insulator is not properly glazed, moisture can stick over it. This
moisture along with deposited dust on the insulator surface, produces a conducting path.
As a result the flash over distance of the insulator is reduced. As the flash over distance
is reduced, the chance of failure of insulator due to flash over becomes more.
(v) Flash Over Across Insulator
If flash over occurs, the insulator may be over heated which may ultimately results into
shuttering of it.
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
(vi) Mechanical Stresses on Insulator
If an insulator has any weak portion due to manufacturing defect, it may break from that
weak portion when mechanical stress is applied on it by its conductor. These are the main
causes of insulator failure. Now we will discuss the different insulator test procedures
to ensure minimum chance of failure of insulation.
3.8.1 Types of Testing Of Insulators
Following are the different types of tests that are carried out on overhead line insulators.
1. Flashover tests
2. Performance tests
3. Routine tests
Flashover Tests Of Insulators
Three types of flashover tests are conducted before the insulator is said to have passed
the flashover test.
1. Power frequency dry flashover test
2. Power frequency wet flashover test
3. Impulse frequency flashover test
Power Frequency Dry Flashover Test
The insulator to be tested is mounted in the same manner in which it is to be used. Then,
a variable voltage source of power frequency is connected between the electrodes of the
insulator. The voltage is gradually increased up to the specified voltage. This specified
voltage is less than the minimum flashover voltage. The voltage at which surrounding air
of the insulator breaks down and become conductive is known as flashover voltage. The
insulator must be capable of withstanding the specified voltage for one minute without
flashover.
Power Frequency Wet Flashover Test (Rain Test)
In this test also, the insulator to be tested is mounted in the same manner in which it is to
be used. Similar to the above test, a variable voltage source of power frequency is
connected between the electrodes. Additionally, in this test, the insulator is sprayed with
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
water at an angle of 45° in such a manner that its precipitation should not be more than
5.08 mm/min. The voltage is then gradually increased up to the specified voltage. The
voltage is maintained at the specified value for 30 seconds or one minute and the insulator
is observed for puncture or breakdown. If the voltage is maintained for one minute, this
test is also called as one-minute rain test.
Impulse Frequency Flashover Test
This test is to ensure that the insulator is capable of sustaining high voltage surges caused
by lightning. The insulator under test is mounted in the same manner as in above tests.
An impulse voltage generator which generates a very high voltage at a frequency of
several hundred kilohertz is connected to the insulator. This voltage is applied to the
insulator and spark-over voltage is noted. The ratio of impulse spark-over voltage to
spark-over voltage at power frequency is called as the impulse ratio. This ratio should be
approximately 1.4 for pin type insulators and 1.3 for suspension type insulators.
3.8.2 Performance Tests Of Insulators
1. Temperature cycle test
2. Puncture voltage test
3. Mechanical strength test
4. Electro-mechanical test
5. Porosity test
Temperature Cycle Test
In this test, the insulator under test is first heated in water at 70° for one hour. Then the
insulator is immediately cooled at 7° for another hour. This cycle is repeated three times.
Then the insulator is dried and its glazing is thoroughly observed for any damages or
deterioration.
Puncture Voltage Test
The purpose of this test is to determine the puncture voltage. The insulator to be tested is
suspended in insulating oil. A voltage is applied and increased gradually until the
puncture takes place. The voltage at which insulator starts to puncture is called
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
as puncture voltage. This voltage is usually 30% higher than that of the dry flash-over
voltage for a suspension type insulators.
Mechanical Strength Test
In this test, the insulator under test is applied by 250% of the maximum working load for
one minute. This test is conducted to determine the ultimate mechanical strength of the
insulator.
Electro-Mechanical Test
This test is conducted only for suspension type insulators. In this test, a tensile stress of
250% of maximum working tensile stress is applied to the insulator. After this, the
insulator is tested for 75% of dry spark-over voltage.
Porosity Test
In this test, a freshly manufactured insulator sample is broken into pieces. These pieces
are then immersed into a 0.5% to 1% alcohol solution fuchsine dye under pressure of 150
kg/cm2 for several hours (say 24 hours). After that, the pieces are removed from the
solution and examined for the penetration of the dye into it. This test indicates the degree
of porosity.
3.8.3 Routine Tests Of Insulators
1. High voltage test
2. Proof load test
3. Corrosion test
High Voltage Test
This test is usually carried out for pin insulators. In this test, the insulator is inverted and
placed into the water up to the neck. The spindle hole is also filled with water and a high
voltage is applied for 5 minutes. The insulator should remain undamaged after this test.
Proof Load Test
In this test, each insulator is applied with 20% in excess of working mechanical load (say
tensile load) for one minute. The insulator should remain undamaged after this test.
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Corrosion Test
In this test, the insulator with its metal fitting is suspended into a copper sulfate solution
for one minute. Then the insulator is removed from the solution and wiped and cleaned.
This procedure is repeated for four times. Then the insulator is examined for any metal
deposits on it. There should be zero metal deposits on the insulator.
EE8402 TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION
You might also like
- Electrical Insulator Testing - Cause of Insulator Failure - Electrical EngineeringDocument6 pagesElectrical Insulator Testing - Cause of Insulator Failure - Electrical EngineeringBattinapati ShivaNo ratings yet
- Corona Effect and Testing of InsulatorsDocument33 pagesCorona Effect and Testing of InsulatorsBilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 - High Voltage Testing of EquipmentDocument16 pagesChap 6 - High Voltage Testing of Equipmenthadrien100% (1)
- The Benefits of Surge and Hipot Testing of Electric MotorsDocument5 pagesThe Benefits of Surge and Hipot Testing of Electric Motorsamk2009No ratings yet
- 1502957487lectrure 7 KUETDocument13 pages1502957487lectrure 7 KUETAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Insulation Resistance of Motors GeneratorsDocument5 pagesMethod Statement Insulation Resistance of Motors Generatorssite.eng1100% (1)
- DD and IRC TestDocument7 pagesDD and IRC Testamrit403No ratings yet
- Transmission and Distribution: UNIT-4 Insulators Testing of InsulatorsDocument9 pagesTransmission and Distribution: UNIT-4 Insulators Testing of InsulatorsJeya RamNo ratings yet
- قيم التوترات المستمرة لقياس مقاومة العزلDocument7 pagesقيم التوترات المستمرة لقياس مقاومة العزلMohamedHussein MohamedHusseinNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Testing: Application NoteDocument8 pagesInsulation Resistance Testing: Application Notefernando_aragon2001No ratings yet
- High Voltage Testing & Insulation CoordinationDocument60 pagesHigh Voltage Testing & Insulation CoordinationAnish John Paul MNo ratings yet
- High Voltage TestingDocument60 pagesHigh Voltage TestingAnish John Paul M100% (1)
- Insulation Resistance Testing of Electric MotorsDocument12 pagesInsulation Resistance Testing of Electric Motorszy44cwfjjgNo ratings yet
- A Review of Polarization Index and IEEE Standard 43-2000Document5 pagesA Review of Polarization Index and IEEE Standard 43-2000vasanth11kvNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Insulator Tests For Testing Reliability of Power Systems (All Steps)Document3 pagesTop 10 Insulator Tests For Testing Reliability of Power Systems (All Steps)m khNo ratings yet
- Wisdom: Insulation and Jacket ShrinkbackDocument2 pagesWisdom: Insulation and Jacket ShrinkbackFelipe GustavoNo ratings yet
- Unit Vi: High Voltage Testing and .H.V.Lines DesignDocument76 pagesUnit Vi: High Voltage Testing and .H.V.Lines DesignAman DeoleNo ratings yet
- Test HVDocument110 pagesTest HVChandru BadachiNo ratings yet
- The Dielectric Discharge Test: Figure 1. Insulation Test Currents During ChargingDocument4 pagesThe Dielectric Discharge Test: Figure 1. Insulation Test Currents During Chargingpatelsuhas21No ratings yet
- Reference Material I 24-08-2021 Exp 3 Insulation ResistanceDocument10 pagesReference Material I 24-08-2021 Exp 3 Insulation Resistancerishika chhibberNo ratings yet
- Papcon 1997 595213Document3 pagesPapcon 1997 595213Tri WahdjoeNo ratings yet
- What Is Insulation TestingDocument5 pagesWhat Is Insulation Testingmohd_hasanudin4364No ratings yet
- Article Testing The State of High Voltage Insulation Hummel ENUDocument6 pagesArticle Testing The State of High Voltage Insulation Hummel ENUarnenylundNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance and Polarization Index Test of Generator & MotorDocument5 pagesInsulation Resistance and Polarization Index Test of Generator & MotorvenkatwsNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistances and Polarization Index Test of Electric MotorDocument19 pagesInsulation Resistances and Polarization Index Test of Electric MotorKrishna Jasha100% (1)
- Company 1Document16 pagesCompany 1Heera PrajapatNo ratings yet
- AgostoDocument4 pagesAgostoBoy TulaNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Insulation TestingDocument6 pagesThe Basics of Insulation TestingbhpNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Insulation TestingDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Insulation TestingAN.ADAMMSNo ratings yet
- Part Bhvunit8 170721153842 PDFDocument84 pagesPart Bhvunit8 170721153842 PDFFatima BuhlalNo ratings yet
- What Is Insulation TestingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Insulation Testingsender2000No ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance and Electrical Testing For HVAC - FlukeDocument4 pagesInsulation Resistance and Electrical Testing For HVAC - FlukeNoel Gregorio SantosNo ratings yet
- Imee 5Document8 pagesImee 5HirakNo ratings yet
- Comparative Tests On RTV Silicone Rubber Coated Porcelain Suspension Insulators in A Salt-Fog ChamberDocument7 pagesComparative Tests On RTV Silicone Rubber Coated Porcelain Suspension Insulators in A Salt-Fog ChamberDebojyoti MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 1guide To DC Testing of InsulationDocument10 pages1guide To DC Testing of InsulationNeeraj pathakNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Insulation Resistance Withstand of Cables: Experiment 6Document15 pagesMeasurement of Insulation Resistance Withstand of Cables: Experiment 6shalini nimsNo ratings yet
- A Review of Polarization Index and IEEE STDDocument4 pagesA Review of Polarization Index and IEEE STDted_mercedeNo ratings yet
- Introduction InsulatorsDocument14 pagesIntroduction InsulatorsEyad A. Feilat100% (1)
- Final Version - Impulse Testing and Insulation Deterioration in Electric MotorsDocument6 pagesFinal Version - Impulse Testing and Insulation Deterioration in Electric MotorsJoseph ChamiNo ratings yet
- Insulator 3 DDocument25 pagesInsulator 3 Dsachin HUNo ratings yet
- Effect of Arc Current On Properties of Composite Insulators For Overhead LinesDocument4 pagesEffect of Arc Current On Properties of Composite Insulators For Overhead LinesShafeek GhreebNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Transmission 4Document7 pagesElectrical Power Transmission 4FaisalSoNo ratings yet
- Section - Iii: Polymer Properties AND Single-Point TestingDocument26 pagesSection - Iii: Polymer Properties AND Single-Point TestingaymaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Insulation TestingDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Insulation TestingkarthikumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document3 pagesUnit 5Ahmed Essam Abd RabouNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 T&DDocument44 pagesUnit 3 T&DAish KrishNo ratings yet
- Davis Instruments Technical LibraryDocument12 pagesDavis Instruments Technical LibraryYutthapong TuppadungNo ratings yet
- Polarization Index TestDocument12 pagesPolarization Index Testamit41790% (1)
- Presentation On InsulationDocument23 pagesPresentation On InsulationMuhammad asifNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker TestingDocument4 pagesCircuit Breaker TestingAvishek SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Lightning ArresterDocument53 pagesLightning Arrestercik_sya870% (1)
- Sss Poland ArticleDocument5 pagesSss Poland Articlesaravanan jNo ratings yet
- School of Electrical Engineering Lab RecordDocument15 pagesSchool of Electrical Engineering Lab RecordSudesha BasuNo ratings yet
- Case Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesFrom EverandCase Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesNo ratings yet
- Insulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandInsulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Corrosion Testing for Metal Finishing: Institute of Metal FinishingFrom EverandCorrosion Testing for Metal Finishing: Institute of Metal FinishingNo ratings yet
- The IEE Wiring Regulations Explained and IllustratedFrom EverandThe IEE Wiring Regulations Explained and IllustratedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- The Science of Superhydrophobicity: Enhancing Outdoor Electrical InsulatorsFrom EverandThe Science of Superhydrophobicity: Enhancing Outdoor Electrical InsulatorsNo ratings yet
- Failure Trends of High-Voltage Porcelain Insulators Depending On The Constituents of The PorcelainDocument12 pagesFailure Trends of High-Voltage Porcelain Insulators Depending On The Constituents of The Porcelainموسي النحلهNo ratings yet
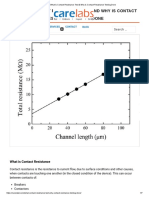
- What Is Contact Resistance Test & Why Is Contact Resistance Testing DoneDocument7 pagesWhat Is Contact Resistance Test & Why Is Contact Resistance Testing Doneموسي النحلهNo ratings yet
- CPC 100 User ManualDocument71 pagesCPC 100 User Manualموسي النحلهNo ratings yet
- Moe-13-Rusa-689 - Iom For 420KV GisDocument234 pagesMoe-13-Rusa-689 - Iom For 420KV Gisموسي النحلهNo ratings yet
- BW and CW GlandsDocument2 pagesBW and CW Glandsموسي النحلهNo ratings yet
- Earthing Transformer or Grounding TransformerDocument6 pagesEarthing Transformer or Grounding TransformerarunNo ratings yet
- Divergence Is An Operation On A Vector Yielding A Scalar, Just Like The Dot Product. We Define The Del Operator As A Vector OperatorDocument23 pagesDivergence Is An Operation On A Vector Yielding A Scalar, Just Like The Dot Product. We Define The Del Operator As A Vector OperatorKybs nyhuNo ratings yet
- BE184P Exercise 1.1a SpectrophotometryDocument9 pagesBE184P Exercise 1.1a SpectrophotometryDen CelestraNo ratings yet
- CPC 100 User Manual ENUDocument77 pagesCPC 100 User Manual ENUJose Ramirez TorresNo ratings yet
- Assigning R and SDocument12 pagesAssigning R and SApurba Sarker ApuNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Catalogo Tem3Document18 pages3.3 Catalogo Tem3Deison F. Arango A.No ratings yet
- B SC Sem 6 Laser PhysicsDocument40 pagesB SC Sem 6 Laser Physicssatyachaudhuri47No ratings yet
- ChoppiDocument12 pagesChoppiSarah Sanchez100% (1)
- Solutions - Maths Workbook - 2 - Complex NumbersDocument101 pagesSolutions - Maths Workbook - 2 - Complex NumbersravimcanitNo ratings yet
- CP1b Distance Time GraphsDocument22 pagesCP1b Distance Time GraphsMysticalNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 (Partial Differential Equations (PDE) For Engineers)Document3 pagesAssignment-1 (Partial Differential Equations (PDE) For Engineers)Shivam UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- MM All Units MCQDocument38 pagesMM All Units MCQkrishnabr100% (2)
- Low Vibration Track SystemDocument24 pagesLow Vibration Track Systemapa apaapaNo ratings yet
- Chen 801-T4Document22 pagesChen 801-T4hussainiNo ratings yet
- Proposed Two-Storey Building With Roof Deck (One Way Slab)Document49 pagesProposed Two-Storey Building With Roof Deck (One Way Slab)Papacarl NoromorNo ratings yet
- Investigation On Mechanical Properties of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (Waam) of 316L Stainless Steel Using Fem Simulation and ExperimentDocument10 pagesInvestigation On Mechanical Properties of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (Waam) of 316L Stainless Steel Using Fem Simulation and ExperimentMohd AymanNo ratings yet
- The Digital Oscilloscope and The Function Generator: Part I: Amplitude and Frequency MeasurementsDocument6 pagesThe Digital Oscilloscope and The Function Generator: Part I: Amplitude and Frequency MeasurementsNour ShamiNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: Harmonic Oscillation of A String PendulumDocument4 pagesMechanics: Harmonic Oscillation of A String Pendulumfatjonmusli2016100% (1)
- System1 Plots - Machinery-Diagnostic - Part1Document16 pagesSystem1 Plots - Machinery-Diagnostic - Part1Thyagaraju PalisettyNo ratings yet
- FCE 412 Geotechnical Engineering IIB: Lecture NotesDocument81 pagesFCE 412 Geotechnical Engineering IIB: Lecture NotesLovian MagandaNo ratings yet
- Fluid3a Trawneh PDFDocument39 pagesFluid3a Trawneh PDFWesam abo HalimehNo ratings yet
- LIT941 0618 Installation ManualDocument8 pagesLIT941 0618 Installation ManualBurhan SharafNo ratings yet
- 2009 Book PDFDocument256 pages2009 Book PDFfazli.samarNo ratings yet
- The Absolute BEST Dungeons, Dragons and SpaceShuttles Ti-Con MaterialsDocument42 pagesThe Absolute BEST Dungeons, Dragons and SpaceShuttles Ti-Con MaterialsCristiano LimaNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction WorksheetDocument2 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Worksheetdayanandan171% (7)
- Concepts of Oscillators: Phase-Locked LoopsDocument30 pagesConcepts of Oscillators: Phase-Locked LoopsManoj BoraNo ratings yet
- Modality and SyllabusDocument3 pagesModality and Syllabusuthso royNo ratings yet
- Dievar PropertiesDocument12 pagesDievar PropertiesSyed NawazNo ratings yet
- Class 2 Lever Effort Force CalculationDocument10 pagesClass 2 Lever Effort Force CalculationvenkateswaranNo ratings yet
- Conzerv Power Energy MetersDocument3 pagesConzerv Power Energy MetersAtchayavelNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevator Calculation Rev 1Document8 pagesBucket Elevator Calculation Rev 1Irfan AhmedNo ratings yet