Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Steps For Decision-Making: Define The Problem
Uploaded by
R SOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Steps For Decision-Making: Define The Problem
Uploaded by
R SCopyright:
Available Formats
Business firms are a combination of manpower, financial, and physical resources
which help in making managerial decisions. Societies can be classified into two
main categories − production and consumption. Firms are the economic entities and
are on the production side, whereas consumers are on the consumption side.
The performances of firms get analyzed in the framework of an economic model.
The economic model of a firm is called the theory of the firm. Business decisions
include many vital decisions like whether a firm should undertake research and
development program, should a company launch a new product, etc.
Business decisions made by the managers are very important for the success and
failure of a firm. Complexity in the business world continuously grows making the
role of a manager or a decision maker of an organisation more challenging! The
impact of goods production, marketing, and technological changes highly contribute
to the complexity of the business environment.
Steps for Decision-Making
The steps for decision making like problem description, objective determination,
discovering alternatives, forecasting consequences are described below −
Define the Problem
What is the problem and how does it influence managerial objectives are the main
questions. Decisions are usually made in the firm’s planning process. Managerial
decisions are at times not very well defined and thus are sometimes source of a
problem.
Determine the Objective
The goal of an organization or decision maker is very important. In practice, there
may be many problems while setting the objectives of a firm related to profit
maximization and benefit cost analysis. Are the future benefits worth the present
capital? Should a firm make an investment for higher profits for over 8 to 10 years?
These are the questions asked before determining the objectives of a firm.
Discover the Alternatives
For a sound decision framework, there are many questions which are needed to be
answered such as − What are the alternatives? What factors are under the decision
maker’s control? What variables constrain the choice of options? The manager
needs to carefully formulate all such questions in order to weigh the attractive
alternatives.
Forecast the Consequences
Forecasting or predicting the consequences of each alternative should be
considered. Conditions could change by applying each alternative action so it is
crucial to decide which alternative action to use when outcomes are uncertain.
Make a Choice
Once all the analysis and scrutinizing is completed, the preferred course of action is
selected. This step of the process is said to occupy the lion’s share in analysis. In
this step, the objectives and outcomes are directly quantifiable. It all depends on
how the decision maker puts the problem, how he formalizes the objectives,
considers the appropriate alternatives, and finds out the most preferable course of
action.
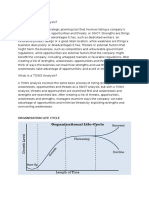
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis helps us in determining the strong features of the optimal choice
of action. It helps us to know how the optimal decision changes, if conditions related
to the solution are altered. Thus, it proves that the optimal solution chosen should
be based on the objective and well structured. Sensitivity analysis reflects how an
optimal solution is affected, if the important factors vary or are altered.
Managerial economics is competent enough for serving the purposes in decision
making. It focuses on the theory of the firm which considers profit maximization as
the main objective. The theory of the firm was developed in the nineteenth century
by French and English economists. Theory of the firm emphasizes on optimum
utilization of resources, cost control, and profits in a single time period. Theory of
the firm approach, with its focus on optimization, is relevant for small farms and
producers.
You might also like
- Unit 1 CC 4 PDFDocument21 pagesUnit 1 CC 4 PDFKamlesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and 2 Managerial EcoDocument85 pagesChapter 1 and 2 Managerial Ecodine62611No ratings yet
- Economics Seminar Reprot Sem 1Document4 pagesEconomics Seminar Reprot Sem 1Farukh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 (Nature of Managerial Economics) - 1 - 1127162208 PDFDocument10 pagesUnit 1 (Nature of Managerial Economics) - 1 - 1127162208 PDFdudanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 1 PDFKarrie SandersNo ratings yet
- Nature, Scope and Practice of Managerial Economics - Fb4b0cd5f16d2e5ad31128574223fDocument4 pagesNature, Scope and Practice of Managerial Economics - Fb4b0cd5f16d2e5ad31128574223fJet jet GonzalesNo ratings yet
- What Do You Think of This Page?Document26 pagesWhat Do You Think of This Page?gunjanjainghsNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics NotesDocument19 pagesManagerial Economics NotesPavithra GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Decision Modeling Notes2Document7 pagesDecision Modeling Notes2Priyanka kumariNo ratings yet
- Amare ManagerialDocument4 pagesAmare Managerialfentahunamanuel2No ratings yet
- Notes On Managerial EconomicsDocument28 pagesNotes On Managerial EconomicsShantilal HajeriNo ratings yet
- Eco 2Document4 pagesEco 2mehaik patwa , 20No ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument37 pagesChapter Onehamdi abdrhmanNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Report 34Document5 pagesStrategic Management Report 34Niño Morate CarletNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Financial StatementsDocument7 pagesLesson 6: Financial StatementsDorhea Kristha Guian SantosNo ratings yet
- Definition of Business PolicyDocument5 pagesDefinition of Business PolicyJessica LaguatanNo ratings yet
- Bba 1 Sem PPT EconomicDocument37 pagesBba 1 Sem PPT EconomicRishi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Corporate EvolutionDocument16 pagesStrategy and Corporate EvolutionSandeep Ghatuary100% (8)
- Module 1 MANA ECONDocument5 pagesModule 1 MANA ECONMeian De JesusNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Previous KnowledgeDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Previous KnowledgeshakeitoNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 CostDocument24 pagesCh-5 Costmubarek oumerNo ratings yet
- Game Theory: Managerial Decision ProcessDocument9 pagesGame Theory: Managerial Decision ProcessHimel NisarulNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument17 pagesManagerial EconomicsAnil NamosheNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument7 pagesStrategic ManagementsuryankpillaiNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Fundamentals of Economics, Management and Managerial EconomicsDocument10 pagesModule 1: Fundamentals of Economics, Management and Managerial EconomicsmichelleNo ratings yet
- Business DecisionsDocument4 pagesBusiness DecisionsПриветикNo ratings yet
- Econ Analysis Introduction 201516 1Document42 pagesEcon Analysis Introduction 201516 1Mohd Abidi NoranizahNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques For Decision-MakingDocument18 pagesQuantitative Techniques For Decision-MakingIlim Crystel Anne A.No ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument12 pagesManagerial EconomicsChinni DurgaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Managerial EconomicsPrayag rajNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument9 pagesModule 1 NotesCoreen ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Role of Managerial Economics in Decision MakingDocument2 pagesRole of Managerial Economics in Decision MakingFatimah TariqNo ratings yet
- Decision Making EnvironmentDocument8 pagesDecision Making EnvironmentJessie Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Economics Lecture NotesDocument40 pagesEconomics Lecture NotesYazNo ratings yet
- M EconomicsDocument30 pagesM Economicsbaikuntha pandeyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Nature and Scope of Managerial EconomicsDocument10 pagesUnit 1: The Nature and Scope of Managerial EconomicsBaharu AbebeNo ratings yet
- HSMC 301Document5 pagesHSMC 301this.is.goldensnowflakesNo ratings yet
- What Is A SWOT AnalysisDocument31 pagesWhat Is A SWOT AnalysisJagdish SainiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Managerial Economicsvasa praneethNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 (Chapter 5) PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 (Chapter 5) PDFHino NissanNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument13 pagesManagerial EconomicsaromoishaNo ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NotesDocument18 pagesMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS Notesmukulgarg47100% (11)
- Unit-II-Ethical Dilemmas and Ethical Decision MakingDocument6 pagesUnit-II-Ethical Dilemmas and Ethical Decision MakingGholam Syedain KhanNo ratings yet
- Assingment - Project ManagementDocument9 pagesAssingment - Project ManagementAlex T BinoyNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument7 pagesManagerial Economicsangel190693No ratings yet
- Business Economics EssayDocument7 pagesBusiness Economics EssayJain AkshatNo ratings yet
- CEE108 ThirdExamDocument3 pagesCEE108 ThirdExamrjoy07No ratings yet
- Notes of Managerial EconomicsDocument24 pagesNotes of Managerial EconomicsJaved HussainNo ratings yet
- Manegerial Economics: Nature of Managerial EconomicsDocument10 pagesManegerial Economics: Nature of Managerial Economicsaquarius_tarunNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Basics of Managerial Ecnomics LESSON 5-Tools and Technique of Decision MakingDocument5 pagesUnit - 1 Basics of Managerial Ecnomics LESSON 5-Tools and Technique of Decision Makingumeshk1No ratings yet
- I BDocument7 pagesI BMarimuthuNo ratings yet
- SMGT Notes On Some TopicsDocument30 pagesSMGT Notes On Some TopicsKritika Chauhan100% (1)
- Introduction To Business EconomicsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Business Economicsalkajoshi123No ratings yet
- The Effect of Managerial Accounting For Quality Decision MakingDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Managerial Accounting For Quality Decision MakingAbul KhairNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Unit 1Document82 pagesManagerial Economics Unit 1Anand KumarNo ratings yet
- Business Finance FinalDocument5 pagesBusiness Finance FinalAnthony DeeNo ratings yet
- Course Material UGC ManagementDocument4 pagesCourse Material UGC ManagementpradeepsinghagNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Strategic ManagementDocument28 pagesBasic Concepts of Strategic ManagementMichaella EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On PD and LGD Estimation (EBA-GL-2017-16) - Chapters 1,2,3 (Only PD Estimation Part) PDFDocument200 pagesGuidelines On PD and LGD Estimation (EBA-GL-2017-16) - Chapters 1,2,3 (Only PD Estimation Part) PDFShankar RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Government Accounting QuizDocument2 pagesGovernment Accounting QuizKate Fernandez100% (2)
- Faq Transitional Issues Companies Act 2016 - Technical 2 2 2017 PDFDocument14 pagesFaq Transitional Issues Companies Act 2016 - Technical 2 2 2017 PDFazilaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies in ServicesDocument31 pagesMarketing Strategies in ServicesSakshi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Manufacturing Tutorial AnswersDocument12 pagesAdvanced Manufacturing Tutorial Answerswilfred chipanguraNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Human Resource Competency ModelDocument9 pagesA Critical Review of Human Resource Competency Modelpoomi KeaokaoNo ratings yet
- Summary Of: The Value of Saving A Life: Evidence From The Labor MarketDocument2 pagesSummary Of: The Value of Saving A Life: Evidence From The Labor MarketFreed DragsNo ratings yet
- Welfare ProvisionsDocument28 pagesWelfare ProvisionsMalik Khuram ShazadNo ratings yet
- JNE Hybrid - PACKING LIST BANG DEDE 13-OKTOBERDocument2 pagesJNE Hybrid - PACKING LIST BANG DEDE 13-OKTOBERFarhan SawieNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis AvonDocument4 pagesCase Analysis AvonRaj Paroha83% (6)
- Kshitij SrivastavaDocument47 pagesKshitij SrivastavaHarshit KashyapNo ratings yet
- Tax Due Diligence Checklist KurtzCPADocument5 pagesTax Due Diligence Checklist KurtzCPAarya1808100% (3)
- Vision: WWW - Visionias.inDocument19 pagesVision: WWW - Visionias.inDivyanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Thai Am RegulationDocument10 pagesThai Am Regulationdessi purnamasariNo ratings yet
- Accountancy (055) Set 67-5-1,2,3 Marking Scheme 2020Document89 pagesAccountancy (055) Set 67-5-1,2,3 Marking Scheme 2020Mrityunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- GSK E 3 2020 Case StudyDocument3 pagesGSK E 3 2020 Case StudynikhilNo ratings yet
- DMI Finance Private Limited (CIN No. U65929DL2008PTC182749) : Customercare@dmifinance - inDocument2 pagesDMI Finance Private Limited (CIN No. U65929DL2008PTC182749) : Customercare@dmifinance - insaberoam 666No ratings yet
- Teh Hsin BrochureDocument10 pagesTeh Hsin Brochurelitecounter1111No ratings yet
- DownloadDocument1 pageDownloadRasika JadhavNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property Law-REPORTING SCHEDULE: Reportin G Date Topic Case NO. Case Title Reporter RemarksDocument2 pagesIntellectual Property Law-REPORTING SCHEDULE: Reportin G Date Topic Case NO. Case Title Reporter RemarksArrianne ObiasNo ratings yet
- Module 3.2 - Preferential Taxation Keyworded Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesModule 3.2 - Preferential Taxation Keyworded Lecture NotesGabs SolivenNo ratings yet
- E00B5 Employee-Engagement - CognizaintDocument84 pagesE00B5 Employee-Engagement - CognizaintwebstdsnrNo ratings yet
- Imp Question Listing Inter Nov 23 ExamDocument3 pagesImp Question Listing Inter Nov 23 Examg6rb6nz0No ratings yet
- Dollar General: Group B6 Chiranjib Mukherjee Chitransh Chaudhary Ishika Gupta Naireeta de Sudeshna Halder Varshika DhariaDocument6 pagesDollar General: Group B6 Chiranjib Mukherjee Chitransh Chaudhary Ishika Gupta Naireeta de Sudeshna Halder Varshika DhariaNo nameNo ratings yet
- Mini Importation Business Masterclass - Make Money in Nigeria With Mini ImportationDocument26 pagesMini Importation Business Masterclass - Make Money in Nigeria With Mini ImportationAzubuike Henry OziomaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Analsyis For Fish Farming BusinessDocument12 pagesMarketing Analsyis For Fish Farming BusinessNabeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Anticipated Final AccountDocument1 pageAnticipated Final AccountJelson RumuarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - Standards On Auditing (SA 300 and 315)Document8 pagesLecture 16 - Standards On Auditing (SA 300 and 315)Aruna RajappaNo ratings yet
- DOC-20240502-WA0002. (1)Document4 pagesDOC-20240502-WA0002. (1)sirsamarvind866No ratings yet
- Rockwell Deep Freezer InvoiceDocument2 pagesRockwell Deep Freezer InvoiceKuldeep KushwahaNo ratings yet