100% found this document useful (2 votes)
498 views2 pagesRust Programming Quick Guide
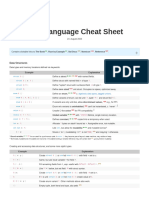
Rust is a programming language focusing on speed, concurrency, and safety. It uses cargo.toml to list library dependencies and dependencies are listed in code using use. Functions are declared with fn and return types designated with ->. Main is the default function and loops include while, loop, and for to iterate. Variables are immutable by default and declared with let, while mutable variables use mut.
Uploaded by
mutecamelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
498 views2 pagesRust Programming Quick Guide
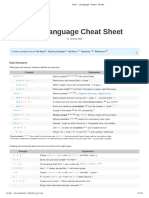
Rust is a programming language focusing on speed, concurrency, and safety. It uses cargo.toml to list library dependencies and dependencies are listed in code using use. Functions are declared with fn and return types designated with ->. Main is the default function and loops include while, loop, and for to iterate. Variables are immutable by default and declared with let, while mutable variables use mut.
Uploaded by
mutecamelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
![Rust Programming Cheat Sheet
Rust is a programming language focusing on speed, concurrency, and safety.
Includes
[package]
n](https://screenshots.scribd.com/Scribd/252_100_85/326/567948864/1.jpeg)