Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ESRT Workbook Set 2 Key Rocks
Uploaded by
Walter Orpilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
188 views9 pagesRock Cycle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRock Cycle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
188 views9 pagesESRT Workbook Set 2 Key Rocks
Uploaded by
Walter OrpillaRock Cycle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
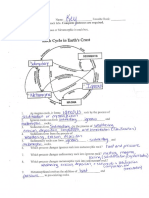
Set 2 — Rock Cycle in Earth’s Crust
8. The process of uplift is essential to 10. Which statement about an igneous rock
the rock eycle for is not supported by the rock cycle?
(1) increasing the weight necessary )\All igneous rocks eventually
for compaction, ‘become sedimentary rocks.
(2) forming ocean trenches where (2) An igneous rock may be remelted
erosion is dominant. and solidified into another type of
)sexposing rocks to the forces of igneous rock.
~ weathering and erosion (3) All igneous rocks must have
producing sediments. been a liquid at one time.
(4) increase the temperature needed (4) An igneous rock can undergo a
to produce magma, 8 metamorphism. 10 4
11. Uplift, weathering and erosion leads
9. The crystals of many metamorphic rocks to the formation of
are aligned in bands as a result of
(1) magma
(1) earthquake faulting @ sediments
(2) cooling and solidification G) cementation
(3) mechanical weathering (4) igneous rocks
@Bheat and pressure 9__ahe
Ten
12. State the rock family that
should be listed in the rectangle for: ecenloorret Seas
‘hanged tdopa
Sands reson
Weshng tn erent
Fook
wating
SA > Cenianks
——— Rock Cycle in Earth’s Crust Page 81
“opie Review Book Company
Set 2 — Relationship of Transported Particle Size to Water Velocity
9. Astream flowing at a velocity of 11. A stream with a velocity of
75 centimeters per second can transport 100 centimeters per second flows
into a lake. Which sediment-size
particles would the stream most likely
deposit first as it enters the lake?
(1) clay, only
(2) pebbles, only
)pedbles, sand, silt, and clay, only
(4) boulders, cobbles, pebbles, (I) boulders. Gpebbles ic
9 4 Jv nn
sand, silt, and clay (2)cobbles (4) sand
10. What is the minimum water velocity
necessary to maintain movement of 12. Which size particle will remain suspended
0. L-centimeter-diameter particles in a stream? longest as a river enters the ocean?
(1) 0.02 m/s (@) 5.0 cm/s (1) pebble (3) silt
(2)0.5em/s (4) 20.0cm/s_— 10. 3 fe (2) sand Ove 12 4
i
13. As water velocity ofa stream inereases from 62 to 206 centimeters per second, in which order
will particles of different sizes begin to move?
~ nk sand — pebbles — cobbles > boulders (3) cobbles — pebbles > sand — silt zZ
GBs" — sand ~ pebbles — cobbles (4) silt > pebbles + sand + cobbles. 13.
The accompanying profile shows the average diameter
of sediment that was sorted and deposited in specific
areas A, B, C, and D by a stream entering an ocean,
‘Suoam Osean
14, As compaction and cementation of these sediments i
eventually occur, which area will become siltstone? ‘i 1 Aiea op,
M4 @8 OY OD 44 ESE cmon
15. Which graph best shows the general relationship between stream velocity and the diameter
of particles transported by a stream?
g 8 g é|
3 8 a 3
3 ig assent
i i i f
é é é é|
ea aay Weed Veeely \
Q) @) (4) a ae
16, Identify vo factors that determine the rate of stream erosion. i"
i | Sl0PL 2 po Alicle 4 f 0 ota
‘Copmight@2017 Relationship of Transported Particle Page 77
eer Size to Water Velocity
13. The end product of the weathering of
gabbro or basalt rocks is a solution of
dissolved material that most likely
would contain high amounts of
@iiron and magnesium
(2) magnesium and potassium
(3) aluminum and iron
(4) aluminum and potassium
oH
14, The photograph below shows an igneous
rock.
‘What is the origin and rate of formation
of this rock?
(1) plutonic with slow cooling
(2) plutonic with rapid cooling
(3) voleanie with slow cooling
A
@voleanic with rapid cooking 14 & P
15. An igneous rock is aggrieeolored crystalline
| rock that formed when aflavatflow cooled and
solidified quickly on the surface of Earth. This
igneous rock is classified as an
(1) extrusive igneous rock with a coarse
texture and felsic composition
@ casasive igneous rock with a fine
texture and a maie.composition
(3) intrusive igneous rock with a coarse
texture and a felsic composition
(4) intrusive igneous rock with a fine
texture and a mafic composition 4
if
Set 2 — Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification
16. Which igneous rock has a vesicular
texture and contains the minerals
potassium feldspar and quartz?
(1) andesite @ypumiiee
(2) pegmatite (4) seoria
6S
17. Which diagram represents a landscape
where fine-grained igneous bedrock is
most likely to be found?
18, Which diagram best represents a sample
of an igneous rock?
19, The photograph below shows actual crystal
sizes in aglights@plored igneous rock that
contains several minerals, including
potassium feldspar, quartz, and biotite mica.
(Shown to actual size)
‘The rock should be identified as
eranite
(2) gabbro
(3) basalt
(4) rhyolite
ae |
Page 88
Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification
Ccopyngnt © 2017
Tepel Revew Book Company
Base your answers to question 20 on the Rock Classification Flowchart. Letters 4, B, and C
represent specific rocks in this classification scheme.
Rock Classification Flowchart
Rocks
¥
‘Sedimentary Igneous: Metamorphic
7 | NN ' [
Glastic | [Grystatine | | Bioclastic Extrusive [ iri Foliated | Nontoliated [
|
20.) Rock B has aifine;yesicular texture and is composed mainly “J
of potassium feldspar and quartz. State the name of rock 8. WESCAC. © yok A
) Granite could be placed in the same position in the flowchart above as gabbro. Describe nvo
differences between granite and gabbro,
©) IfRock B is scoria, give two descriptions of itspropistigs.
Ne Siculan, glassy -E sesctore
21. Complete the table below, with descriptions of the observable characteristics used to identifibasat,
Characteristic of Basalt aos
Texture non esgic t
Color ee | : ; ~
Density Wigh.
22. Name a tanyesioulanrock made entirely ene that has a hardness |
of 6.5 and exhibits fracture (see page 207).
Tene / aliowe)
‘Soonenee 207 Scheme for Igneous Rock Identification Page 89
‘epic Review Bock Company
10. Which sedimentary rock may form as a
result of biologic processes?
(1) shale © fossil limestone
0S
(2) siltstone (4) breccia
11. Dolostone is classified as which type of rock?
(1) land-derived sedimentary rock
@Dehemically formed sedimentary rock
@G) nonfoliated metamorphic rock
(4) foliated metamorphic rock 1L_Z—
12. The block diagram below shows a portion
of the Earth’s crust. Letters 4, B, C, and D
indicate sedimentary layers.
metamorphisn|
Which processes produced rock layer B?
(1) subduction and melting
(2) uplift and solidification
(3) heat and pressure
@compaction and cementation 12_
crystals of mica, quartz, and feldspar,
Based on the composition and foliated
texture, this rock can best be identified as
(1) marble (3) slate
schist 4) anthracite coal ce
peoriate2017 Scheme for Metamorphic Rock Identification
[irs review Bk Consary
Page 103
18. Which sequence of change in rock type occurs as shale is subjected to increasing heat and pressure?
(1) shale —+ schist + phyllite + slate + gneiss
Qshale = slate — phyllite — schist — gneiss
(3) shale — gneiss > phyllite — slate + schist
(4) shale — gneiss — phyllite + schist > slate 1s_ GL
19. Which rock sample is most likely metamorphic rock?
gael
@ @)
Base your answers to question 20 on the diagram below which represent two magnified
views showing the arrangement of minerals before and after metamorphism of a rock.
20. a) State the name of Rock C.
ONDA
Mineral Arrangement
Before Metamerchism
5) Name two processes needed to cause the banding of minerals as shown in the second diagram.
(a). DYdrewne. palodsrt (2)
21, An igneous intrusion entered a layer of dolostone, The contact metamorphism of the dolostone would
produce what metamorphic rock? unrortte
tay
22, State the name of the rock, formed by Ebon
[E)ssendstene
E uneine Safer
Conglomerate
[>| contactmetamerphism
contact metamorphism;
at location A
at location 24u.ctaconclone at
23. When schist is exposed to greater heat and pressure during
‘metamorphism, it would change to what other metamorphic rock? —Gpiinde _
24, Identify one similarity and one difference between the metamorphic rocks slate and phyllite.
Similarity Ywurpngl a gunna Differen
Page 104 Scheme for Metamorphic Rock Identification ee
pc Reviow Book Company
cot rarou at
by
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCES - Google FormsDocument35 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SCIENCES - Google FormsWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- THIRD PERIODICAL EXAMINATION - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCES - Google FormsDocument32 pagesTHIRD PERIODICAL EXAMINATION - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCES - Google FormsWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Second Periodical Examination Science Grade 10Document6 pagesSecond Periodical Examination Science Grade 10Walter Orpilla100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- THIRD PERIODICAL TEST SCIENCE 7 - Google FormsDocument20 pagesTHIRD PERIODICAL TEST SCIENCE 7 - Google FormsWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Rocks Study Guide AnswersDocument4 pagesRocks Study Guide AnswersWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Third Periodical Test - DisasterDocument26 pagesThird Periodical Test - DisasterWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Philippine School in Greece: Fourth Periodical Examination Grade 12 - EntrepreneurshipDocument3 pagesPhilippine School in Greece: Fourth Periodical Examination Grade 12 - EntrepreneurshipWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Brief History and Nature of DanceDocument25 pagesBrief History and Nature of DanceWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Product Conceptualization and The Creative MindDocument1 pageProduct Conceptualization and The Creative MindWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Nuclear Physics: Basic Professional Training Course Module I Nuclear Physics and Reactor TheoryDocument50 pagesNuclear Physics: Basic Professional Training Course Module I Nuclear Physics and Reactor TheoryWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- PSG 2nd Mapeh Gr. 8 20Document5 pagesPSG 2nd Mapeh Gr. 8 20Walter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Festivals and Theatrical Forms of AsiaDocument14 pagesFestivals and Theatrical Forms of AsiaWalter OrpillaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)