Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classes of Food Carbohydrate Protein Fat Vitamin Mineral Fibre Water
Uploaded by
Noor FadzleezaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classes of Food Carbohydrate Protein Fat Vitamin Mineral Fibre Water
Uploaded by
Noor FadzleezaCopyright:
Available Formats
BAB 3 : NUTRISI
CHAPTER 3 : NUTRITION
3.1 Kelas makanan (1 jam) (m/s 46 – 50)
3.1 Classes of food (1 hour) (pg 46 – 50)
1. Nyatakan 7 kelas makanan.
State 7 classes of food.
Kelas makanan
Classes of food
Karbohidrat Protein Lemak Vitamin Mineral Pelawas Air
Carbohydrate Protein Fat Vitamin Mineral Fibre Water
2. Apakah perbezaan antara karbohidrat, protein dan lemak?
What are the differences between carbohydrate, protein and fat?
Karbohidrat Protein Lemak
Carbohydrate Protein Fat
Apakah unsur kelas makanan ini? C, H, O C, H, O, N C, H, O
What are the elements of this food?
Fungsi Bekal tenaga Baiki tisu rosak Bekal tenaga lebih tinggi berbanding
Function Provide energy Repair damaged karbohidrat
tissue Provide energy higher than
carbohydrate
Contoh - Nasi / Rice - Ayam / Chicken - Mentega / Butter
Examples - Kentang / Potato - Kekacang / Nuts - Minyak kelapa / Coconut oil
3. Jenis-jenis vitamin.
Types of vitamins.
Vitamin
Larut air / Water soluble Larut lemak / Fat soluble
B, C A, D, E, K
4.
Vitamin
Mengekalkan kesihatan / Maintain health
Mineral
Pelawas / Fibre Mengelakkan sembelit / Prevents constipation
Air / Water Mengawal atur suhu badan / Regulates body temperature
5. Namakan 5 jenis mineral dan kesan kekurangan.
Name 5 types of minerals dan effects of deficiency.
Mineral Kesan kekurangan / Effects of deficiency
(a) Natrium / Sodium
Kekejangan otot / Muscle cramps
(b) Kalium / Potassium
(c) Fosforus / Phosphorus
Riket / Rickets
(d) Kalsium / Calsium
(e) Besi / Iron Anemia / Anaemia
Aktiviti 3.1 (1 jam 30 minit) (m/s 51-52)
Activity 3.1 (1 hour and 30 minutes) (pg 51-52)
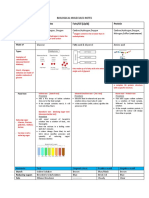
Ujian Uji Positif Negatif
Iodin Kanji Biru tua Warna perang
Iodine (Nasi, mi) Dark blue kekal
Starch Brown colour
(Rice, mee) remains
Benedict Glukosa Mendakan merah Biru tidak berubah
Benedict (Jus buah) Red precipitate No change
Glucose
4 ujian makanan (Fruit juice)
4 types of food Millon Protein Mendakan merah Tiada perubahan
tests Millon - ayam Red precipitate warna
- kacang tanah No change
Protein
- chicken
- ground nuts
Alkohol-emulsi Lemak Emulsi terhasil Tiada emulsi
Alcohol-emulsion - minyak sayur Emulsion appears lemak terhasil
Fat No emulsion
-vegetable oil
Soalan / Questions
1. Mengapakah pemanasan dalam ujian Benedict dan ujian Millon dijalankan di dalam kukus air?
Why is the heating in the Benedict’s test and Millon’s test carried out in a water bath?
Agar bahan dipanas seragam.
2. Anda diberi satu sampel makanan dalam bentuk serbuk. Bagaimanakah anda dapat menentukan kelas makanan
yang terdapat pada sampel makanan tersebut?
You are given a food sample in powder form. How do you determine the food class of the food sample?
Lakukan / carry out
Bancuh serbuk dengan air suling bahagi 4 ujian Iodin / Iodine’s test
ujian Millon / Millon’s test
ujian Benedict / Benedict’s test
alkohol-emulsi / Alcohol-emulsion test
3. Terangkan bagaimana ujian makanan dijalankan?
Explain how the food tests are carried out?
Ujian Iodin / Iodine Titis iodin positif – biru tua
test negatif – perang
Add iodine solution positive – dark blue
negative –brown
Ujian Benedict / Titik Benedict biru – kukus air positif – mendakan merah
Benedict’s test negatif – masih biru muda
Add Benedict solution - put in water bath positive - red precipitate
negative –blue colour remains
Ujian Millon / Titik Millon – kukus air positif – mendakan merah
Millon’s test negatif – tiada perubahan warna
Add Millon solution – put in water bath positive – red precipitate
negative – no change
Ujian alkohol-emulsi Titik minyak dalam etanol – goncang – masukkan air suling positif – emulsi terhasil
/ Alcohol-emulsion negatif – tiada emulsi
test terhasil
Add cooking oil into ethanol – shake – add distilled water positive – emulsion appear
negative – no emulsion
3.2 Kepentingan gizi seimbang (1 jam) (m/s 53-54)
3.2 Importance of balanced diet (1 hour) (pg 53-54)
1. Apakah itu gizi seimbang?
What is a balanced diet?
Mengandungi – semua kelas makanan – dalam kuantiti betul.
Contains – all classes of food – in correct quantity
2.
Umur / Age
a) kanak-kanak - masih membesar - perlu tenaga lebih banyak
children - still growing - need more energy
b) dewasa - aktif - perlu lebih banyak tenaga
- tidak aktif - tidak perlu tenaga lebih
adults - active - need more energy
- not active - did not need more energy
Pekerjaan / Work Jantina / Sex
Makan banyak atau a) lelaki - lebih berotot, melakukan
- kerja berat (cth: buruh binaan) - sedikit? Bergantung
perlu lebih banyak tenaga aktiviti lebih berat - perlu lebih banyak
kepada: tenaga
- do heavy work (eg : labourers) - (Faktor-faktor yang
need more energy men - more muscular, do more heavy
mempengaruhi activities - need more energy
keperluan kalori)
Factors that influence
calorific requirement
Keadaan kesihatan / State of health Iklim / Climate
a) diabetes - tidak boleh ambil - negara beriklim sejuk - perlu lebih banyak
karbohidrat & gula yang banyak tenaga - kerana lebih cepat kehilangan haba
diabetes - cannot take a lot of - cold climate countries - need more energy -
carbohydrates & sugar because lose heat quickly
3.3 Sistem pencernaan manusia (m/s 61-63)
3.3 Human digestive system (pg 61-63)
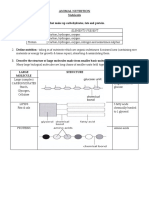
1. Nyatakan urutan aliran makanan.
State the flow of food particles.
Mulut Esofagus Perut Duodenum Usus kecil Usus besar Rektum Dubur
Mouth Oesophagus Stomach Duodenum Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus
2. Aliran makanan dalam salur pencernaan.
The flow of food in the digestive tract.
Mulut / Mouth
(a) Apa yang berlaku pada makanan di mulut?
What happen to the food in mouth?
Makanan dikunyah oleh gigi
Food is chewed by the teeth
(b) Enzim apa yang terdapat di dalam air liur?
What is the enzyme that can be found in saliva?
Enzim amilase / Amylase enzyme
(c) Apakah fungsi enzim amilase?
What is the function of amylase enzyme?
Menguraikan kanji kepada maltosa
Breaks down starch into maltose
Esofagus / Oesophagus
(a) Apa yang berlaku di esofagus?
What happen in oesophagus?
Proses peristalsis / Process of peristalsis
(b) Apa itu peristalsis?
What is peristalsis?
Proses pengecutan dan pengenduran otot esofagus
Constriction and relaxation of the muscles of the oesophagus
Perut / Stomach
(a) Apakah jus yang dirembes di dinding perut?
What is secreted at the walls of the stomach?
Jus gaster / Gastric juice
(b) Apakah yang terkandung dalam jus gaster?
What is contained in gastric juice?
i) Asid hidroklorik / Hydrochloric acid ii) Enzim protease / Protease enzyme
(c) Apakah fungsi asid hidroklorik?
What is the function of hydrochloric acid?
i) Membunuh bakteria dalam makanan. ii) Menyediakan medium berasid untuk makanan.
i) Kills bacteria in the food. ii) Provide acidic medium for food.
(d) Apakah fungsi enzim protease?
What is the function of protease enzyme?
Mencerna protein kepada polipeptida
Breaks down protein into polypeptides
(e) Apa itu kim?
What is chyme?
Makanan separa cecair / Semi-liquid food
Duodenum
(a) Apakah jus yang diterima oleh duodenum?
What type of juice received by the duodenum?
i) Jus hempedu / Bile ii) Jus pankreas / Pancreatic juice
(b) Namakan organ yang menghasilkan jus hempedu dan jus pancreas.
Name the organs that produce bile and pancreatic juice.
i) Jus hempedu - hati. ii) Jus pancreas - pankreas
i) Bile - liver. ii) Pancreatic juice - pancreas
(c) Namakan organ yang menyimpan hempedu.
Name the organ that stores bile?
Pundi hempedu / Gall bladder
(d) Apakah fungsi jus hempedu?
What is the function of bile?
i) Mengemulsikan lemak menjadi titisan kecil. ii) Meneutralkan asid dalam kim.
i) Emulsifies fat into small droplets. ii) Neutralises the acid in the chyme.
(e) Apakah tujuan mengemulsikan lemak menjadi titisan kecil?
What is the purpose of emulsifying fat into small droplets?
Menambahkan luas permukaan makanan – untuk dicerna oleh enzim
Increase the surface area of food – to be digested by enzyme.
(f) Namakan enzim yang terdapat pada jus pankreas?
Name the enzymes that can be found in pancreatic juice?
PAL. P – Protease, A – Amylase, L – Lipase
(g) Tulis fungsi setiap enzim protease, amilase, lipase.
Write the function of protease, amilase, lipase enzyme.
i) Protease cerna polipeptida kepada dipeptida
Protease digests polipeptydes into dipeptides
ii) Amilase cerna kanji kepada maltosa
Amylase digests starch into maltose
i) Lipase cerna lemak kepada asid lemak dan gliserol
Lipase digests fat into fatty acids and glycerol
Usus kecil / Small intestine
(a) Apakah enzim yang dirembes oleh usus kecil?
What are the enzymes that secreted by the small intestine?
i) Protease ii) Maltase
(b) Apakah yang dicernakan oleh enzim maltase?
What is digested by the maltase enzyme?
Enzim maltase cerna maltosa kepada glukosa
Maltase enzyme digests maltose into glucose
(c) Apakah yang dicernakan oleh enzim protease?
What is digested by the protease enzyme?
Enzim protease cerna dipeptida kepada asid amino
Protease enzyme digests dipeptides into amino acids
Usus besar / Large intestine
(a) Makanan apakah yang masuk ke usus besar?
What food enters the large intestine?
Makanan tidak tercerna / Undigested food
(b) Apakah yang diserap semula oleh usus besar?
What is reabsorbed by the large intestine?
Air / Water
Rektum / Rectum
(a) Apakah nama lain bagi makanan tidak tercerna?
What is the other name of undigested food?
Tinja / faeces
(b) Di manakah tinja disimpan sebelum disingkirkan?
Where does the faeces are stored before excreted?
Rektum / Rectum
Dubur / Anus
(a) Apakah yang berlaku di dubur?
What happen at the anus?
Penyahtinjaan / Defecation
You might also like
- Testing For Biological MoleculesDocument7 pagesTesting For Biological MoleculesAqeelah IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument69 pagesForm 2 Chapter 3 NutritionNur Farhana Tahir80% (5)
- Test For Carbohydrates Activity 1Document2 pagesTest For Carbohydrates Activity 1HyvethJeshielleP.Bandoy60% (5)
- Food Tests - Required PracticalDocument13 pagesFood Tests - Required PracticalRay PeramathevanNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Biological Molecules Summary Sheets Model AnswersDocument2 pagesTopic 4 Biological Molecules Summary Sheets Model Answersmarcos.vaqueNo ratings yet
- Food Tests - Year 10Document17 pagesFood Tests - Year 10Alexandros Filippos LekkasNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition 1Document3 pagesAnimal Nutrition 1Azhan TariqNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Elements Present: 1. List The Chemical Elements That Make Up Carbohydrates, Fats and ProteinDocument3 pagesNutrient Elements Present: 1. List The Chemical Elements That Make Up Carbohydrates, Fats and ProteinozmanNo ratings yet
- Food Digestion To PrintDocument44 pagesFood Digestion To PrintMindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- 12G Lab3 GARCIADocument3 pages12G Lab3 GARCIARuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan BiomoleculesQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Two Types Of: Example of Chemoautotrophs: BacteriaDocument5 pagesNutrition Two Types Of: Example of Chemoautotrophs: BacteriaChessking Siew HeeNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Activity (Tayongtong)Document4 pagesBiomolecules Activity (Tayongtong)Jimskie TayongtongNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 5 Test For Fats and Proteins IDocument5 pagesExercise No. 5 Test For Fats and Proteins IMaureen VeraNo ratings yet
- B3 Biological Molecules Book Report - Duc MinhDocument7 pagesB3 Biological Molecules Book Report - Duc MinhMinh Hoàng ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules NotesDocument2 pagesBiological Molecules NotesJayasutha RamanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Notes Igcse Edexcel BiologyDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Notes Igcse Edexcel Biologyjhjsxwchk5No ratings yet
- Bab 6: Nutrisi: Nama: TingkatanDocument22 pagesBab 6: Nutrisi: Nama: Tingkatanaina azharNo ratings yet
- 8A NutrienDocument17 pages8A NutrienAron ProxyNo ratings yet
- Human NutritionDocument15 pagesHuman NutritionYoutubeChannel KNo ratings yet
- Identification of Biological Molecules in FoodDocument13 pagesIdentification of Biological Molecules in FoodNurul Ain AfiqahNo ratings yet
- CSEC Human and Social Biology Paper 2 2014Document3 pagesCSEC Human and Social Biology Paper 2 2014jules blancoNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument83 pagesForm 2 Chapter 3 Nutritionsiti latifahNo ratings yet
- L6 Chemical Tests For BiomoloculesDocument4 pagesL6 Chemical Tests For Biomoloculesaicelle272No ratings yet
- A Balanced Diet SchoologyDocument19 pagesA Balanced Diet Schoologydhia mehtaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-04-20 at 12.43.16Document56 pagesScreenshot 2021-04-20 at 12.43.16MichaelNo ratings yet
- General Biologi: SummeryDocument9 pagesGeneral Biologi: SummeryMamandaNo ratings yet
- Chemicals of Life: Bil - Ye R 10 - Tra 3Document7 pagesChemicals of Life: Bil - Ye R 10 - Tra 3mark smithNo ratings yet
- CH 1-DigestionDocument127 pagesCH 1-Digestionmajdkaraki9No ratings yet
- 03 Modul SC T2-Bab3 (Csy4p) PDFDocument22 pages03 Modul SC T2-Bab3 (Csy4p) PDFSitiRohaizaMatYusoffNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Macromolecules: Food Tests: Outu - Be/Slp8Dcnwnj GDocument4 pagesUnit 1: Macromolecules: Food Tests: Outu - Be/Slp8Dcnwnj GManan PatelNo ratings yet
- Biology Summary Test 1 - Biological MoleculesDocument19 pagesBiology Summary Test 1 - Biological MoleculesVALENTINA MÓNACONo ratings yet
- Reminder B4Document7 pagesReminder B4Daniel thanh ducNo ratings yet
- Science ProjectDocument2 pagesScience ProjectNovi nataliaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules in My Food: Ka Hana Imi Na Auao - A Science Careers Curriculum Resource Go To: WWW - Cds.hawaii - Edu/kahanaDocument4 pagesBiomolecules in My Food: Ka Hana Imi Na Auao - A Science Careers Curriculum Resource Go To: WWW - Cds.hawaii - Edu/kahanaPM SemeraNo ratings yet
- CbSE 6th BookDocument10 pagesCbSE 6th BookLalita DhakeNo ratings yet
- Bio Ip 2Document4 pagesBio Ip 2Kayla WhiteNo ratings yet
- Food Test AssessmentDocument2 pagesFood Test AssessmentRaihaan BoodooNo ratings yet
- FT CD Fatty Acids Fatty AcidsDocument24 pagesFT CD Fatty Acids Fatty AcidsMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- Docu. Carbohydrates 1 2Document8 pagesDocu. Carbohydrates 1 2Merlyn Limbaga CastroverdeNo ratings yet
- Identification of Biochemicals in Pure Form and in Food SamplesDocument2 pagesIdentification of Biochemicals in Pure Form and in Food SamplesNick MillerNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 BiomoleculesDocument10 pagesNcert Solutions June6 For Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 BiomoleculesNilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13-Jul-2021Document22 pagesAdobe Scan 13-Jul-2021Poonam SinghNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN PRAKTIKUM BIOLOGIiiwaannDocument6 pagesLAPORAN PRAKTIKUM BIOLOGIiiwaannMohammad Ridwan HamdanyNo ratings yet
- Identifying Nutrients in FoodDocument4 pagesIdentifying Nutrients in Foodapi-263340585No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2anil.gelra5140No ratings yet
- Secondary Schools Book I. Then, Answer The Following Questions in Complete SentencesDocument8 pagesSecondary Schools Book I. Then, Answer The Following Questions in Complete SentencesedwinmasaiNo ratings yet
- 2 The Chemistry of FoodDocument13 pages2 The Chemistry of Foodgj2c74k59xNo ratings yet
- 08foodtests 111109062308 Phpapp01Document16 pages08foodtests 111109062308 Phpapp01Nirmala JosephineNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument7 pagesNutrition in AnimalsFX GeraldNo ratings yet
- Cecilia Guzman - IdentifyingNutrients Gizmo LabDocument4 pagesCecilia Guzman - IdentifyingNutrients Gizmo LabCecilia GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Ipod Lab 1819Document6 pagesIpod Lab 1819Alvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- MAC - Broiler Nutrition and Feed Management (De Heus)Document28 pagesMAC - Broiler Nutrition and Feed Management (De Heus)Agung NulhakimNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab Report (G2) PDFDocument10 pagesBio Lab Report (G2) PDFAina NabihaNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition-Part 1Document15 pagesHuman Nutrition-Part 1Kef7No ratings yet
- Metabolism Diet: Supreme Turbo Boost Your Metabolism To An Amazing Body: The Ultimate Metabolism Plan and Metabolic Typing Diet - Complete With Intermittent Fasting For Weight Loss & Fat LossFrom EverandMetabolism Diet: Supreme Turbo Boost Your Metabolism To An Amazing Body: The Ultimate Metabolism Plan and Metabolic Typing Diet - Complete With Intermittent Fasting For Weight Loss & Fat LossNo ratings yet
- Dukan Diet Decoded: A Simple Guide & Introduction to the Dukan Diet & Lifestyle: Diets Simplified, #3From EverandDukan Diet Decoded: A Simple Guide & Introduction to the Dukan Diet & Lifestyle: Diets Simplified, #3No ratings yet
- Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiencies: Food and Nutrition SeriesFrom EverandSigns of Vitamin B12 Deficiencies: Food and Nutrition SeriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Your Middle Years – Love Them. Live Them. Own Them.: A Book for the Menopause and BeyondFrom EverandYour Middle Years – Love Them. Live Them. Own Them.: A Book for the Menopause and BeyondNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1From EverandAQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chapter 1 Rational Numbers: MasteryDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Rational Numbers: MasteryijanishNo ratings yet
- Mastery Q 1.4Document2 pagesMastery Q 1.4Noor FadzleezaNo ratings yet
- Lembaran Modul Math T1 (Bab1.2)Document5 pagesLembaran Modul Math T1 (Bab1.2)Noor FadzleezaNo ratings yet
- Kata Kata HikmahDocument21 pagesKata Kata HikmahNoor FadzleezaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Matematik T1 Pentaksiran Matematik SMDocument6 pagesSoalan Matematik T1 Pentaksiran Matematik SMNoor FadzleezaNo ratings yet
- ScheduleDocument1 pageScheduleparag7676No ratings yet
- ELC609F12 Lec0 IntroductionDocument16 pagesELC609F12 Lec0 IntroductionMohammed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Business Model Navigator Whitepaper - 2019Document9 pagesBusiness Model Navigator Whitepaper - 2019Zaw Ye HtikeNo ratings yet
- Vibrations - NptelDocument3 pagesVibrations - NptelMSK65No ratings yet
- Chemistry Mid Term Exam 2014Document8 pagesChemistry Mid Term Exam 2014Adham TamerNo ratings yet
- 2606 PDFDocument6 pages2606 PDFzainab jehangirNo ratings yet
- Nano ScienceDocument2 pagesNano ScienceNipun SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Tech Manual 1396 Rev. B: 3.06/4.06" 15,000 Psi ES BOPDocument39 pagesTech Manual 1396 Rev. B: 3.06/4.06" 15,000 Psi ES BOPEl Mundo De Yosed100% (1)
- Lec 8-10Document5 pagesLec 8-10osamamahmood333No ratings yet
- Paper 2 With Solution MathematicsDocument17 pagesPaper 2 With Solution MathematicsFaiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Art1 2Document24 pagesArt1 2Peter Paul Rebucan PerudaNo ratings yet
- Resource Access ControlDocument19 pagesResource Access Controlusamadar707No ratings yet
- Chuyên Đề ConjunctionDocument5 pagesChuyên Đề ConjunctionKhánh Linh TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Digital Trail Camera: Instruction ManualDocument20 pagesDigital Trail Camera: Instruction Manualdavid churaNo ratings yet
- Earth Bonding LeadsDocument2 pagesEarth Bonding LeadsrocketvtNo ratings yet
- High Performance Dialysis GuideDocument28 pagesHigh Performance Dialysis GuideRoxana ElenaNo ratings yet
- Monk - Way of The Elements RevisedDocument3 pagesMonk - Way of The Elements Revisedluigipokeboy0% (1)
- An Experimental Investigation On Abrasive Jet Machining by Erosion Abrasive GrainDocument3 pagesAn Experimental Investigation On Abrasive Jet Machining by Erosion Abrasive GrainPkNo ratings yet
- Diels-Alder Reaction: MechanismDocument5 pagesDiels-Alder Reaction: MechanismJavier RamirezNo ratings yet
- IMS Institute BelgradeDocument10 pagesIMS Institute BelgradeBoško JanjuševićNo ratings yet
- ManufactureDocument2 pagesManufactureRahima Akter RakhiNo ratings yet
- Modern Views Catalogue/Sotheby's BenefitDocument36 pagesModern Views Catalogue/Sotheby's BenefitStudio AdjayeNo ratings yet
- Phonetics ReportDocument53 pagesPhonetics ReportR-jhay Mepusa AceNo ratings yet
- Deld12070 CC18 GT 371 C CDocument1 pageDeld12070 CC18 GT 371 C CDEBASIS BARMANNo ratings yet
- Eoi QAMDocument6 pagesEoi QAMPeeyush SachanNo ratings yet
- The Explanation of The Fundamentals of Islamic BeliefDocument95 pagesThe Explanation of The Fundamentals of Islamic BeliefbooksofthesalafNo ratings yet
- Mwangi, Thyne, Rao - 2013 - Extensive Experimental Wettability Study in Sandstone and Carbonate-Oil-Brine Systems Part 1 - Screening ToDocument7 pagesMwangi, Thyne, Rao - 2013 - Extensive Experimental Wettability Study in Sandstone and Carbonate-Oil-Brine Systems Part 1 - Screening ToMateo AponteNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Definition:: Economic Infrastructure Includes BroadlyDocument3 pagesInfrastructure Definition:: Economic Infrastructure Includes Broadlyabraha gebruNo ratings yet
- Ultimate GuideDocument33 pagesUltimate GuidemrosamusicNo ratings yet
- The World S Finest Ideas in Cooling!: A Division ofDocument4 pagesThe World S Finest Ideas in Cooling!: A Division ofChiragNo ratings yet