0% found this document useful (0 votes)
212 views11 pagesA Ac B B: Formulae List
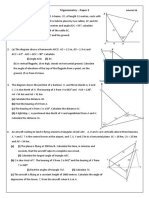
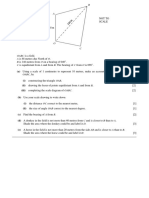
The document provides formulae for calculating:
- The roots of a quadratic equation
- Sine and cosine rules for triangles
- Area of a triangle
- Volumes of spheres, cones, pyramids
- Standard deviation
It also provides 29 practice questions involving using these formulae to calculate lengths, angles, areas and volumes in various geometric shapes and scenarios.
Uploaded by
Intania AyuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
212 views11 pagesA Ac B B: Formulae List
The document provides formulae for calculating:
- The roots of a quadratic equation
- Sine and cosine rules for triangles
- Area of a triangle
- Volumes of spheres, cones, pyramids
- Standard deviation
It also provides 29 practice questions involving using these formulae to calculate lengths, angles, areas and volumes in various geometric shapes and scenarios.
Uploaded by
Intania AyuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd