Trigonometry Revision Exercise
Written by: CWW 1. On the diagram, AB = 8 cm, BC = 6 cm, and ABC = 90.
Calculate (i) AC (ii) sin ACB , expressing your answer in fraction. (iii) cos CAD , expressing your answer in fraction. 2. On the diagram below shows a right-angled triangle.
Given that cos ACD =
24 , calculate 25
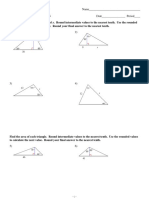
(i) AC (ii) AB (iii) sin BAC , expressing your answer in fraction. (units is in cm) 3. On each of the following diagrams, calculate the unknowns (units in cm). (a) (b)
(c)
(d)
4. On each of the following diagrams, calculate the unknown (units in cm).
�(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
5. For the following diagrams, calculate its area in cm. (a) (b)
(c)
(d)
6. A girl, G, sitting down and look at the bird, B, flying above point A. The distance between point A and the girl is 10 m and the angle of elevation of the bird from the girl is 38. Calculate the height between the bird and point A.
7. A boy sits on the edge of a cliff and look downwards to see a boat. The height of the cliff is 70 m and the distance between the foot of the cliff to the boat is 150 m. Calculate the angle of depression of the boat as seen from the boy. 8. A man, 1.7 m tall, is viewing the top of a tree, which is 12 m away from him. The angle of elevation of the top of the tree when viewed by the man is 30. Calculate the height of the tree. 9. A and B are two viewing points on the ground in front of a hill. The distance
�between the two points is 100 m. The angle of elevation of the top of the hill when viewed from point A and point B are 35 and 46 respectively. Calculate the height of the hill.
10. A, B and C are three points on the ground and lies on the same line. The distance between A and B is 150 m. There is a hot air balloon hovering directly above C. The angle of elevation of the hot air balloon when viewed from A and B are 30 and 45 respectively. Calculate the distance between the hot air balloon and point C. 11. In the diagram, a flag pole, BC, is standing at C, and there is a slope in front of it. It is given that the distance from A to D is 120 m, AD = 20 and AC = C B 22. Calculate the height of the flag pole, BC.
12. A, B and C are three points on the horizontal field. C is due east of A.
A (a)Given that AB = 76 m, BC = 81 m and BC = 110, calculate (i) AC (ii) AC B (iii) the bearing of B from A (iv) the bearing of A from B (v) the bearing of B from C. (b) A white dove D is flying directly above B at an altitude of 30 m. Calculate (i) the angle of elevation of the dove viewed from C; and (ii) the greatest angle of elevation of the dove viewed from AC.
�13. A, B and C are three different ports on the horizontal field. B is directly south of C.
A (a) Given that BC is 102, AB = 125 km and BC = 60 km, calculate (i) the bearing of A from B, (ii) AC (iii) AC B (iv) the bearing of C from A. (c) A cargo ship is travelling at a speed of 40 km/h from port A to port C through the route AC. Given that the cargo ship leave port A at 12 45, calculate (i) the time it reached C. (ii) the distance travelled by the cargo ship such that it is nearest to port B.
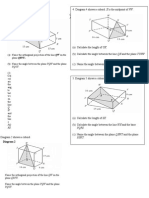
14. On the diagram shows a solid made up of a cuboid and a pyramid.
(a) Given that AB = 24 cm, BC = 18 cm, AE = 7 cm, calculate (i) AC (ii) CH (iii) BG (iv) GD B (b) Given that the midpoint of AC and BD is K, and the midpoint of EG and FH is J, calculate (i) BK A K (ii) J C (c) Given that KI = 11 cm, calculate (i) IJ G (ii) I F (d) Calculate the volume of the solid. 15. For each of the question, find x where 0 x 180 . (a) cos x = 0.731 (d sin x = 0.652 ) (b tan x = 1.48 (e) cos x = 0.719 )
�(c) sin x = 0.866
(f)
tan x = 0.918
ANSWER KEY
1 (i) (ii) (iii) 2 10 cm
4 5
4 5
(i) 25 cm (ii) 7 cm (iii) 24
25
36.9 15.9 cm 23.9 cm 21.5 cm 4 33.6 cm 31.3 cm 74.7 80.8 cm 28.4 x = 45.8 y = 53.8 5 (a) 695 cm (b) 112 cm (c) 4920 cm (d) 67.3 cm 6 7.81 m 7 25.0 8 8.63 m 9 216 m 10 205 m
(a) (b) (c) (d) (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f)
11 64.4 m 12 (a) (i) 129 m (ii) 36.3 (iii) 053.7 (iv) 233.7 (v) 303.7 (b) (i) 20.3 (ii) 33.7 13 (a) (i) 258 (ii) 149 km (iii) 23.1 (iv) 054.9 (b) (i) 16 29 (ii) 115 km 14 (a) (i) 30 cm (ii) 25 cm (iii) 19.3 cm (iv) 84.2 (b) (i) 51.3 (ii) 65.0 (c) (i) 4 cm (ii) 70.9 (d) 3600 cm 15 (a) 43.0 (b) 56.0 (c) 60.0, 120.0 (d) 40.7, 139.3 (e) 136.0 (f) 137.4