0% found this document useful (0 votes)
191 views7 pagesPhysics Formulas for Students
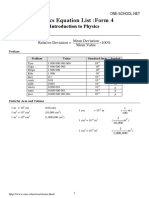
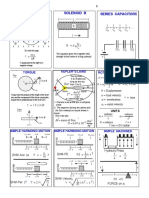
This document provides formulas and equations related to physics concepts including:
1. Newton's laws of motion, momentum, impulse, and equations of motion.
2. Pressure, work, power, potential and kinetic energy, and efficiency.
3. Hooke's law, gravitational force, Kepler's laws, and transformer and wave formulas.
4. Reflection and refraction at plane mirrors and lenses including magnification and focal length equations.
Uploaded by
Bhuvan RajivCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
191 views7 pagesPhysics Formulas for Students
This document provides formulas and equations related to physics concepts including:
1. Newton's laws of motion, momentum, impulse, and equations of motion.
2. Pressure, work, power, potential and kinetic energy, and efficiency.
3. Hooke's law, gravitational force, Kepler's laws, and transformer and wave formulas.
4. Reflection and refraction at plane mirrors and lenses including magnification and focal length equations.
Uploaded by
Bhuvan RajivCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd