Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mind Maps MD: (© 2020 American Academy of Ophthalmology)
Uploaded by
Mido KimoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mind Maps MD: (© 2020 American Academy of Ophthalmology)
Uploaded by
Mido KimoCopyright:
Available Formats
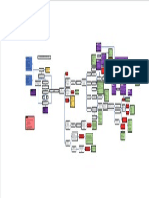
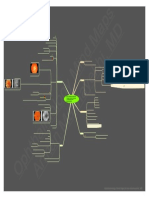
hyperpermeability of choroid (choriocapillaris) leakage at level of RPE
neurosensory RD
leakage into subretinal space
pathogenesis
impaired fluid removal from
subretinal space
healthy
35-55 years
demographics
M>F 3:1
no racial predilection
stress
thick choroid personality type
EDI-OCT tense driven personality (type A)
OCT
i, ps
(© 2020 American Academy of Ophthalmology)
endogenous hypercortisolism
(Cushing syndrome)
elevated levels of corticosteroids
corticosteroid administration systemic
etiology
systemic hypertension not intravitreal
sleep apnea
(© 2020 American Academy of Ophthalmology) psychopharmacologic
medications
posterior loculation of fluid in deep choroid
kh Ma
in areas where thickening is pregnancy
most prominent irregular wavy, shallow elevation of the RPE by a
D
CNV
layer of material with heterogeneous reflectivity +- bilateral aymmetric
blurred vision
dim vision
micropsia
symptoms suggen onset metamorphopsia
M
paracentral scotoma
white dots under retina are macrophages with accumulation of shed outer segments
fluorophores from phagocytized outer segments in subretinal space decreased color vision
prolonged afterimages
20/20-20/200 usually >20/30
visual acuity
ye d
improves with hyperopic
correction
(© 2020 American Academy of Ophthalmology) round or oval
serous detachment of sensory
retina localized often involves fovea
ha in
small whitish subretinal
precipitates
acute findings
under superior half of serous
fundus autofluorescence retinal detachment
other imaging modalities serous RPE detachment
without serous retinal
detachment
gray-white feather-edge subretinal material fibrin
as M
RPE defects focal hypoautofluorescence granular RPE pigmentation
widespread shallow detachment
photoreceptors atrophy
multiple small leaks on IVFA
chronic findings evidence of prior episodes
run-off/guttering
M gy
RPE atrophic areas thick choroid
clinical
pachychoroidal pigment
RPE alterations
(© 2020 American Academy of Ophthalmology) retinopathy
no serous retinal detachment
chronic CSC descending tracts
in ≤ 20% of patients >50 yr even without laser
lower levels of central macular
poorer vision
autofluorescence easy to detect with OCT angiography
CNV in 2% of eyes treated with
12.9.1. Central Serous photocoagulation
Chorioretinopathy (CSC)
o
in the immediate postoperative
choroidal vascular hyperpermeability BCSC 2020-2021
period in 2% of eyes after
photocoagulation
CNV
an ol
filling delays in choroidal arteries
& choriocapillaris
venous dilation
hyperpermeability of choroidal
vessels indocyanine green angiography
multifocal
m lm
choroidal vascular abnormalities
appear early
hyperfluorescent patches
slowly enlarge during angiogram
less prominent in late views
unchanged during clinically
washout pattern
inactive phases
occult CNV
helps to differentiate atypical
diffuse CSC in older patients
polypoidal choroidal
from
Ar ha
vasculopathy
detecting type 1 CNV OCT angiography
OCT demonstrates an irregular wavy, shallow elevation of the
RPE by a layer of material with heterogeneous reflectivity
type 1 CNV
differential diagnosis
FA findings overlap with CSC
(© 2020 American Academy of Ophthalmology)
polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV)
leakage from RPE appears early
chronic recurrent CSC
most common
good visual prognosis except
bullous CSC
+- multiple
t
80-90%
early phase of angiogram focal leak through RPE dot
dot form expansile dot
within 3-4 months
ph
pooling of dye in subretinal
visual recovery within 1 year space
late phase of angiogram
mild metamorphopsia 10-15 min
natural course
spontaneous resolution
faint scotomata tree-shaped
smokestack form
abnormal contrast sensitivity uncommon 10%
residual symptoms
mild color vision defictits
extensive gravity-dependent
serous retinal detachment
permanent diminished visual
acuity diffuse
extensive RPE changes
O
40-50% recurrence
without obvious leakage point
more rapid resorption of
5 weeks vs 23 weeks
subretinal fluid
fluorescein angiography
no improvement in final visual patterns
acuity
laser photocoagulation
no decrease in recurrence rate
no effect on choroidal thickness
sub-threshold laser photocoagulation
reduces or eliminates subretinal fluid
treatment
4% atrophy few complications
recurrence after successful PDT is rare photodynamic therapy with
verteporfin
decreases choroidal thickness and reduces
choroidal vascular hyperpermeability
standard (600 mW/cm2) to
reduced fluence (300 mW/cm2)
resolution of subretinal fluid in eplerenone
mineralocorticoid receptor
25% medical treatment
antagonists
spironolactone
(© 2020 American Academy of Ophthalmology)
Ophthalmology Mind Maps/Arman Mashayekhi, MD
You might also like
- Worksheet - Graphing Sine and CosineDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Graphing Sine and CosineRudi BerlianNo ratings yet
- Everything You Long For (New Jersey)Document9 pagesEverything You Long For (New Jersey)Katelyn HodgeNo ratings yet
- Stroke Scale NIHSS PDFDocument4 pagesStroke Scale NIHSS PDFFilipa Figueiredo100% (1)
- Rule Book 2nd Printing Part 1 PDFDocument25 pagesRule Book 2nd Printing Part 1 PDFRenato BorghiniNo ratings yet
- Master the Chamber: A Guide to Primary Care MedicineDocument28 pagesMaster the Chamber: A Guide to Primary Care MedicineMensa DigiWorldNo ratings yet
- February Monthly Collection, Grade 5From EverandFebruary Monthly Collection, Grade 5Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Myocardial Infarction: Definition, Pathophysiology, Types, Assessment, ManagementDocument8 pagesMyocardial Infarction: Definition, Pathophysiology, Types, Assessment, ManagementOdai AL KarkiiNo ratings yet
- Händel's "Eternal SourceDocument2 pagesHändel's "Eternal SourceColégio de Música de FiãesNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure During PregnancyDocument42 pagesChronic Renal Failure During PregnancyvincentsharonNo ratings yet
- Tus Ojos Bajo PDFDocument2 pagesTus Ojos Bajo PDFMackNo ratings yet
- Biliary Tract Surgery in Dogs and CatsDocument5 pagesBiliary Tract Surgery in Dogs and CatsEsther ArifinNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation: A Concise Guide to Kidney Function and Urine AnalysisDocument69 pagesUrine Formation: A Concise Guide to Kidney Function and Urine AnalysisAffan ElahiNo ratings yet
- Rule Book - 2P V9 PDFDocument52 pagesRule Book - 2P V9 PDFGergely NagyNo ratings yet
- (Zoology) FINAL EXAM (THEORY) BOT-705, Spring (Responses) - Form Responses 1Document1 page(Zoology) FINAL EXAM (THEORY) BOT-705, Spring (Responses) - Form Responses 1Nabeel TahirNo ratings yet
- DahoDocument29 pagesDahofodiy49587No ratings yet
- Oral Sur 3 FinalDocument20 pagesOral Sur 3 Finalnapat kidsanakaraketNo ratings yet
- Ca 7159 enDocument1 pageCa 7159 enmmarshalzNo ratings yet
- Haydn Aguns Dei Missa BrevisDocument6 pagesHaydn Aguns Dei Missa BrevisCoen SwinkelsNo ratings yet
- PSY354 Lecture 2 (Anatomy)Document24 pagesPSY354 Lecture 2 (Anatomy)kadiatou konateNo ratings yet
- Tracing the snaking etymology of windDocument1 pageTracing the snaking etymology of windTanya VillacisNo ratings yet
- Infinity Other Solar Systems: TrinityDocument1 pageInfinity Other Solar Systems: TrinityP Eng Suraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Por Unos Puertos Glosa TenorDocument1 pagePor Unos Puertos Glosa TenorFederico AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Morning Civ-Com CompleteDocument269 pagesDay 2 Morning Civ-Com CompletegbenjielizonNo ratings yet
- La Rosa y El Sauce - Carlos GuastavinoDocument4 pagesLa Rosa y El Sauce - Carlos GuastavinoMickaël COURDESSESNo ratings yet
- AspirationsDocument10 pagesAspirationsdr satnam kaurNo ratings yet
- 3d +2D eLEVATIONDocument1 page3d +2D eLEVATIONfaisal saifNo ratings yet
- Recalls Hamza SurgeryDocument2 pagesRecalls Hamza SurgeryNazem Abd RaboNo ratings yet
- Грабовський Concerto misteriosoDocument38 pagesГрабовський Concerto misteriosoElena LisovenkoNo ratings yet
- ChangosDocument1 pageChangostenzo_xxNo ratings yet
- CBLN 19061017 0006Document1 pageCBLN 19061017 0006Aidel BelamideNo ratings yet
- Vestibulares PDFDocument8 pagesVestibulares PDFPedro Henrique BorgesNo ratings yet
- Actividades para Balance EnergíaDocument1 pageActividades para Balance EnergíaMaría José Lara RamosNo ratings yet
- 21900511 - 이성민 - Chapter 3 Reading SummaryDocument1 page21900511 - 이성민 - Chapter 3 Reading Summary이성민학부생No ratings yet
- Zé Passarinho Love StoryDocument2 pagesZé Passarinho Love StoryAlexandre GomesNo ratings yet
- Inyange Za Mariya CorrigéDocument1 pageInyange Za Mariya CorrigéFulgence Umuhoza CleverstarNo ratings yet
- Parenthood: General Dynamic Factors - Age - Gender - Ethnicity - Social Economic Status - Educational BackgroundDocument1 pageParenthood: General Dynamic Factors - Age - Gender - Ethnicity - Social Economic Status - Educational Backgroundjunebug3No ratings yet
- Sơ Đồ Không Gian Chữa Cháy Tự Động Xưởng Gmp Tầng 1 /Gmp Sprinkler System 3D Schematic Diagram 1st FLOORDocument1 pageSơ Đồ Không Gian Chữa Cháy Tự Động Xưởng Gmp Tầng 1 /Gmp Sprinkler System 3D Schematic Diagram 1st FLOORnhacotungNo ratings yet
- Stat Phys Exam Sample ProblemsDocument5 pagesStat Phys Exam Sample ProblemsReshamNo ratings yet
- Agile Product RoadmapDocument1 pageAgile Product RoadmapVitória SlompoNo ratings yet
- Digoxin effects on calcium movement and heart contractionDocument1 pageDigoxin effects on calcium movement and heart contractionAlyssa Mae RadamNo ratings yet
- La - Rosa - y - El - Sauce - Carlos - Guastavino. Do MineurDocument4 pagesLa - Rosa - y - El - Sauce - Carlos - Guastavino. Do MineurJon OlaberriaNo ratings yet
- P08 IBATINA AGUA PredioPozo SAT - v01Document1 pageP08 IBATINA AGUA PredioPozo SAT - v01Leonardo MiguezNo ratings yet
- 27 Bass EbDocument1 page27 Bass EbKlever GallegosNo ratings yet
- RoomsAreBoxes: Dealing with private and community living in minimalist spacesDocument1 pageRoomsAreBoxes: Dealing with private and community living in minimalist spacesMariana Rodríguez GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCheat Sheetlaurapersich2No ratings yet
- Tiger Moth Sheet 2 of 2: DihedralDocument1 pageTiger Moth Sheet 2 of 2: DihedralFarooq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Malancioiu Traulos 43876Document28 pagesGabriel Malancioiu Traulos 43876belgarath_89No ratings yet
- Individuation and Enlightenment: Luke OttevangerDocument2 pagesIndividuation and Enlightenment: Luke Ottevangerapi-3824232No ratings yet
- Ddo BrandDocument1 pageDdo BrandFatih GünerNo ratings yet
- Canvas Niji-Flowers-230928 0129Document1 pageCanvas Niji-Flowers-230928 0129solmirandamateoNo ratings yet
- LPUMC News & Views-March 2010Document6 pagesLPUMC News & Views-March 2010LafayetteParkUMCNo ratings yet
- Gatti Duettino - in - Mib - Magg.Document1 pageGatti Duettino - in - Mib - Magg.Alessandro FuocoNo ratings yet
- LPUMC News & Views-Jan-Dec 2010Document6 pagesLPUMC News & Views-Jan-Dec 2010LafayetteParkUMCNo ratings yet
- LPUMC News & Views-Dec 2009Document6 pagesLPUMC News & Views-Dec 2009LafayetteParkUMCNo ratings yet
- Dodington 2018 Companion Species WantedDocument3 pagesDodington 2018 Companion Species WantedAnna ConrickNo ratings yet
- BoojieposterDocument1 pageBoojieposterDeborah Elizabeth WhaleyNo ratings yet
- 考研 5500核心词汇全图Document1 page考研 5500核心词汇全图ugibb510No ratings yet
- Wooden Broomstick - BassonDocument2 pagesWooden Broomstick - BassonMathieu MoreaudNo ratings yet
- 75... GRECIA/susurro: Q 40 Jose Luis UrquietaDocument4 pages75... GRECIA/susurro: Q 40 Jose Luis UrquietaJose Luis UrquietaNo ratings yet
- CR (English (American) )Document15 pagesCR (English (American) )Dylan PlungNo ratings yet
- Nocturn en 2 Styles For PianoDocument23 pagesNocturn en 2 Styles For PianoNyanko NyankoNo ratings yet
- Adaptare de Amplasament Presupune Aducerea de Modificari Prezentului PlanDocument1 pageAdaptare de Amplasament Presupune Aducerea de Modificari Prezentului PlanOdi IvonaNo ratings yet
- Cha_Ca_Cha_del_TrenDocument23 pagesCha_Ca_Cha_del_TrenFermin Castillo NavarroNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our New Young Adult Minister!: Happenings at LpumcDocument6 pagesWelcome To Our New Young Adult Minister!: Happenings at LpumcLafayetteParkUMCNo ratings yet
- Inside Ptmalloc2: Peng XuDocument27 pagesInside Ptmalloc2: Peng XuxkNo ratings yet
- It's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentFrom EverandIt's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Cornea-Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesCornea-Anatomy and PhysiologyMido KimoNo ratings yet
- Glucoma Cyclodiode LaserDocument2 pagesGlucoma Cyclodiode LaserMido KimoNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Mind Maps/Arman Mashayekhi, MDDocument1 pageOphthalmology Mind Maps/Arman Mashayekhi, MDMido KimoNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Mind Maps/Arman Mashayekhi, MDDocument1 pageOphthalmology Mind Maps/Arman Mashayekhi, MDMido KimoNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants Drug SnigDocument18 pagesAntidepressants Drug SnigSnigdha MishraNo ratings yet
- Ewen Vs National Hockey LeagueDocument80 pagesEwen Vs National Hockey LeagueAnonymous LRPtKqjQSyNo ratings yet
- Article 54th EASDAnnualMeetingOfTheEuroDocument620 pagesArticle 54th EASDAnnualMeetingOfTheEuroAwais ArshadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Lupus Affects The BodyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: How Lupus Affects The BodyJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Author: American College of Surgeons California Medical AssociationDocument13 pagesAuthor: American College of Surgeons California Medical AssociationhorenNo ratings yet
- Chast PainDocument4 pagesChast PainDesry UkatNo ratings yet
- Williams MLD 2010 PDFDocument9 pagesWilliams MLD 2010 PDFPreethi GopalanNo ratings yet
- Cognitive DisordersDocument105 pagesCognitive DisordersNicole Keesha MataNo ratings yet
- 1 - Perception and CoordinationDocument37 pages1 - Perception and CoordinationJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Acute Upper Gi Bleeding, Predict Need For Endoscopic TherapyDocument5 pagesAcute Upper Gi Bleeding, Predict Need For Endoscopic TherapyAsfiani PediatricianNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's BrochureDocument2 pagesAlzheimer's Brochurebluebeary22No ratings yet
- Diseases of Skeletal Muscle: Pathological Evaluation and Key FindingsDocument115 pagesDiseases of Skeletal Muscle: Pathological Evaluation and Key Findings이승재No ratings yet
- ENT HAQs 1st EDDocument34 pagesENT HAQs 1st EDranjanavnish142No ratings yet
- Neonatal Respiratory System Updates 2020Document824 pagesNeonatal Respiratory System Updates 2020link_wolfloboNo ratings yet
- Adenoma Velloso y ApendicitisDocument4 pagesAdenoma Velloso y ApendicitisLuis MenesesNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Chest PainDocument59 pagesAssessment of Chest PainMaria GarabajiuNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis: Oral Pathology 4 Stage DR - Hemn M.Sharif (B.D.S, MSC, O.Medicine) 2-4-2020Document18 pagesOsteomyelitis: Oral Pathology 4 Stage DR - Hemn M.Sharif (B.D.S, MSC, O.Medicine) 2-4-2020محمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian Drugs PDFDocument47 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugs PDFUmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics - Neonatal Jaundice PDFDocument2 pagesPediatrics - Neonatal Jaundice PDFJasmine KangNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesHuman Digestive SystemCrow LordNo ratings yet
- Mount Sinai Expert Guides Critical Care - (Part 3 Pulmonary Critical Care)Document13 pagesMount Sinai Expert Guides Critical Care - (Part 3 Pulmonary Critical Care)ShawnNo ratings yet
- Subcutaneous Emphysema PDFDocument5 pagesSubcutaneous Emphysema PDFMarcella SaputraNo ratings yet
- Silent But Deadly - How To Spot A Sarcoma: Craig Gerrand Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Freeman Hospital, NewcastleDocument31 pagesSilent But Deadly - How To Spot A Sarcoma: Craig Gerrand Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Freeman Hospital, NewcastleAfriade yolandaNo ratings yet
- Paget's Disease of BonesDocument40 pagesPaget's Disease of BonesOlga GoryachevaNo ratings yet