Professional Documents
Culture Documents
E-Commerce Notes For BCA 6th Semester VBSPU PDF
Uploaded by
Jaspreet KaurOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
E-Commerce Notes For BCA 6th Semester VBSPU PDF
Uploaded by
Jaspreet KaurCopyright:
Available Formats
1
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Semester-6
BCA 602
E-Commerce
(According to Purvanchal University Syllabus)
“Full Line By Line Notes”
On June 26/08/2020
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
2
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Unit – 1
Introduction
Electronic Commerce-Technology & Prospect –
E-Commerce or Electronics Commerce is a methodology of modern business,
which addresses the requirements of business organizations. It can be broadly
defined as the process of buying or selling of goods or services using an
electronic medium such as the Internet.
Ecommerce refers to the paperless exchange of business information using
the following ways −
Electronic Data Exchange (EDI)
Electronic Mail (e-mail)
Electronic Bulletin Boards
Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT)
Other Network-based technologies
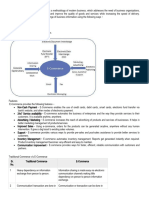
Features
E-Commerce provides the following features −
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
3
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Non-Cash Payment − E-Commerce enables the use of credit cards, debit
cards, smart cards, electronic fund transfer via bank's website, and
other modes of electronics payment.
24x7 Service availability − E-commerce automates the business of
enterprises and the way they provide services to their customers. It is
available anytime, anywhere.
Advertising / Marketing − E-commerce increases the reach of
advertising of products and services of businesses. It helps in better
marketing management of products/services.
Improved Sales − Using e-commerce, orders for the products can be
generated anytime, anywhere without any human intervention. It gives
a big boost to existing sales volumes.
Support − E-commerce provides various ways to provide pre-sales and
post-sales assistance to provide better services to customers.
Inventory Management − E-commerce automates inventory
management. Reports get generated instantly when required. Product
inventory management becomes very efficient and easy to maintain.
Communication improvement − E-commerce provides ways for faster,
efficient, reliable communication with customers and partners.
Traditional Commerce v/s E-Commerce
Sr. Traditional Commerce E-Commerce
No.
1 Heavy dependency on information Information sharing is made easy via
exchange from person to person. electronic communication channels
making little dependency on person to
person information exchange.
2 Communication/ transaction are Communication or transaction can be
done in synchronous way. Manual done in asynchronous way. Electronics
intervention is required for each system automatically handles when to
pass communication to required person
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
4
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
communication or transaction. or do the transactions.
3 It is difficult to establish and A uniform strategy can be easily
maintain standard practices in established and maintain in e-commerce.
traditional commerce.
4 Communications of business In e-Commerce or Electronic Market,
depends upon individual skills. there is no human intervention.
5 Unavailability of a uniform E-Commerce website provides user a
platform as traditional commerce platform where al l information is
depends heavily on personal available at one place.
communication.
6 No uniform platform for E-Commerce provides a universal
information sharing as it depends platform to support commercial /
heavily on personal business activities across the globe.
communication.
Electronic potential of E-commerce –
Electronic Commerce is a marriage between a rapidly evolving technical
environment and an increasingly pervasive set of ideas as to how
markets should function. However, markets involve complex interaction
between specific business/organizational factors, and general economic,
social and political factors.
The full economic potential of Electronic Commerce can only be
evaluated against a backdrop of rapid change on all of these fronts.
There are strong current indications that massive changes have already
begun to occur across the entire business spectrum.
Forces behind E-commerce –
The evolution and growth of e-commerce can be attributed to a combination
of technological, marketing and economic forces. Let us discuss some of the
driving forces of e-commerce.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
5
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Economic Forces:
1. E-commerce enables businesses to interact with suppliers, customers and
with players in the distribution channel at a lower cost.
2. The cost of installing and maintaining a website is much cheaper than
owning a physical store. This motivates the growth of e-commerce.
3. E-commerce generates greater profits due to less human intervention, lower
overhead cost, few clerical errors and more efficiency.
4. The cost of advertising is cheaper and provides access to global market at
low cost. This is something which encourages people engaged in business to
promote their business through electronic medium.
5. Reduction in communication cost and technological infrastructure expense
drive business towards e-business.
Technological Forces:
1. Technological advances have made business communication faster, easier,
economical and efficient. It has enabled the business to switch over from the
local market to the global market.
2. The growing popularity of cyber cafes has created a big role in attracting
internet population towards e-commerce.
3. Technological changes have given confidence to consumers to make
electronic payments in settlement of financial obligations.
Market Forces:
1. Business organizations are able to reach international markets by using
electronic medium for enhanced customer support and service.
2. E-commerce enables customers to make product comparison, place orders,
track orders and make payments at ease. Due to convenience, customers
prefer to purchase their desired goods or services over internet in the online
marketplace.
3. E-commerce also allows the customers to choose and order products
according to their personal and unique specifications. It paves way for mass
customization.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
6
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
4. The growing internet population stimulates business to switch over from an
additional business to e-business.
5. The great variety of commodities available online and reliable payment
methods are regarded as contributors to the increase of e-business.
Advantages & Disadvantages of E-Commerce –
E-Commerce advantages can be broadly classified in three major categories −
Advantages to Organizations
Advantages to Consumers
Advantages to Society
Advantages to Organizations
Using e-commerce, organizations can expand their market to national
and international markets with minimum capital investment. An
organization can easily locate more customers, best suppliers, and
suitable business partners across the globe.
E-commerce helps organizations to reduce the cost to create process,
distribute, retrieve and manage the paper based information by
digitizing the information.
E-commerce improves the brand image of the company.
E-commerce helps organization to provide better customer services.
E-commerce helps to simplify the business processes and makes them
faster and efficient.
E-commerce reduces the paper work.
E-commerce increases the productivity of organizations. It supports
"pull" type supply management. In "pull" type supply management, a
business process starts when a request comes from a customer and it
uses just-in-time manufacturing way.
Advantages to Customers
It provides 24x7 support. Customers can enquire about a product or
service and place orders anytime, anywhere from any location.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
7
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
E-commerce application provides users with more options and quicker
delivery of products.
E-commerce application provides users with more options to compare
and select the cheaper and better options.
A customer can put review comments about a product and can see what
others are buying, or see the review comments of other customers
before making a final purchase.
E-commerce provides options of virtual auctions.
It provides readily available information. A customer can see the
relevant detailed information within seconds, rather than waiting for
days or weeks.
E-Commerce increases the competition among organizations and as a
result, organizations provides substantial discounts to customers.
Advantages to Society
Customers need not travel to shop a product, thus less traffic on road
and low air pollution.
E-commerce helps in reducing the cost of products, so less affluent
people can also afford the products.
E-commerce has enabled rural areas to access services and products,
which are otherwise not available to them.
E-commerce helps the government to deliver public services such as
healthcare, education, social services at a reduced cost and in an
improved manner.
The disadvantages of e-commerce can be broadly classified into two major
categories −
Technical disadvantages
Non-Technical disadvantages
Technical Disadvantages
There can be lack of system security, reliability or standards owing to
poor implementation of e-commerce.
The software development industry is still evolving and keeps changing
rapidly.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
8
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
In many countries, network bandwidth might cause an issue.
Special types of web servers or other software might be required by the
vendor, setting the e-commerce environment apart from network
servers.
Sometimes, it becomes difficult to integrate an e-commerce software or
website with existing applications or databases.
There could be software/hardware compatibility issues, as some e-
commerce software may be incompatible with some operating system
or any other component.
Non-Technical Disadvantages
Initial cost − The cost of crea ng/building an e-commerce application
in-house may be very high. There could be delays in launching an e-
Commerce application due to mistakes, and lack of experience.
User resistance − Users may not trust the site being an unknown
faceless seller. Such mistrust makes it difficult to convince traditional
users to switch from physical stores to online/virtual stores.
Security/ Privacy − It is difficult to ensure the security or privacy on
online transactions.
Lack of touch or feel of products during online shopping is a drawback.
E-commerce applications are still evolving and changing rapidly.
Internet access is still not cheaper and is inconvenient to use for many
potential customers, for example, those living in remote villages.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
9
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Unit – 2
Mobile Commerce
Introduction –
Mobile commerce or simply M-Commerce means engaging users in a buy or
sell process via a mobile device. For instance, when someone buys an Android
app or an iPhone app, that person is engaged in m-commerce. There are a
number of content assets that can be bought and sold via a mobile device
such as games, applications, ringtones, subscriptions etc.
Wireless application protocol –
WAP stands for Wireless Application Protocol. The dictionary definition of
these terms are as follows −
Wireless − Lacking or not requiring a wire or wires pertaining to radio
transmission.
Application − A computer program or piece of computer so ware that
is designed to do a specific task.
Protocol − A set of technical rules about how informa on should be
transmitted and received using computers.
WAP is the set of rules governing the transmission and reception of data by
computer applications on or via wireless devices like mobile phones. WAP
allows wireless devices to view specifically designed pages from the Internet
using only plain text and very simple black-and-white pictures.
WAP is a standardized technology for cross-platform, distributed computing
very similar to the Internet's combination of Hypertext Markup Language
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
10
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
(HTML) and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), except that it is optimized
for:
low-display capability
low-memory
low-bandwidth devices, such as personal digital assistants (PDAs),
wireless phones, and pagers.
WAP is designed to scale across a broad range of wireless networks like GSM,
IS-95, IS-136, and PDC.
WAP Technology –
WAP stands for Wireless Application Protocol. The dictionary definition of
these terms are as follows −
Wireless − Lacking or not requiring a wire or wires pertaining to radio
transmission.
Application − A computer program or piece of computer software that
is designed to do a specific task.
Protocol − A set of technical rules about how informa on should be
transmitted and received using computers.
Mobile information device –
Over the years, mobile devices have become indispensable. There was a time
mobile devices were primarily used for making telephone calls. Nowadays,
mobile devices are ubiquitous and are used for a variety of purposes. From
finding transportation to doing taxes, mobile app solutions have been growing
at an exponential rate. One of the fastest growing mobile app verticals is
eCommerce.
Mobile computing application –
Wireless communication Mobile Computing and its applications that is generic
technology that refers to numerous devices that are supportable to access
transmitted data likes voice , video and text any time and any where over the
wireless network infrastructure and in which to include mobile communication,
mobile hardware, and mobile software and this react as human–computer
interaction. Cause of these has improved the quality of our lives.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
11
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Unit – 3
Web Security
Security is an essential part of any transaction that takes place over the
internet. Customers will lose his/her faith in e-business if its security is
compromised. Following are the essential requirements for safe e-
payments/transactions −
Confidentiality − Informa on should not be accessible to an
unauthorized person. It should not be intercepted during the
transmission.
Integrity − Informa on should not be altered during its transmission
over the network.
Availability − Informa on should be available wherever and whenever
required within a time limit specified.
Authenticity − There should be a mechanism to authen cate a user
before giving him/her an access to the required information.
Non-Repudiability − It is the protec on against the denial of order or
denial of payment. Once a sender sends a message, the sender should
not be able to deny sending the message. Similarly, the recipient of
message should not be able to deny the receipt.
Encryption − Information should be encrypted and decrypted only by an
authorized user.
Auditability − Data should be recorded in such a way that it can be
audited for integrity requirements.
Security issue on web –
Without proper security measures in place, these sites are at risk of losing
customers’ data and revenue. According to a study conducted on e-commerce
fraud, digital retail stores are more vulnerable to fraudulent transactions as
compared to physical retail stores.
Security risks associated with e-commerce can be as a result of human error,
an accident or unauthorized access to systems. Online retailers are most likely
to face credit card fraud or data errors. Their online stores are also likely to
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
12
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
face phishing attacks, distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks and man-in-
the-middle attacks as explained below.
Credit Card Fraud
Credit card fraud is the most common security threat that online retailers face.
It occurs when a hacker gains unauthorized access to customers’ personal and
payment information. To access this data, the hacker may penetrate the
database of an e-commerce site using malicious software programs. At times, a
hacker’s intention when stealing customers’ data is to sell it on black markets.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
This type of security threat aims at taking down an online retail store by
sending overwhelming requests to its servers. The attacks originate from
thousands of untraceable IP addresses. When this type of threat hits the
servers, they slow down or completely shut down. An e-commerce site can
also go offline temporarily when a DDoS attack affects its servers.
Man-in-the-middle Attacks
As hackers are becoming smarter with technology, they are devising ways of
listening to the communications made by users of an e-commerce website.
Through an approach known as a man-in-the-middle attack, these hackers
maliciously trick users into connecting to a public wireless network. They gain
access to people’s devices once they are on public wireless networks. Hackers
get to see a people’s browsing history, credit card numbers, passwords and
usernames if the websites they are visiting lack strong encryptions.
Bad Bots
Bots, either good or bad, are all over the worldwide web. Search engines such
as Bing and Google use good bots for indexing search results. On the other
hand, there are hackers that use malicious bots for gathering data such as
product data, inventories and pricing data. These bots are also capable of
accessing the database of an e-commerce site and listing the logins of user
accounts.
Malware
In information technology, malware simply refers to malicious software
programs. Attackers usually inject web pages or files with these malicious
programs to help them in gaining access to online retails stores. Through
means such as SQL injection, they can easily insert the malware into a
website’s database allowing it to compromise the data stored in the database.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
13
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Phishing Scams
E-commerce sites are also prone to phishing scams sent by known or unknown
people in form of emails. These scams focus on targeting important user data
like credit card numbers and login credentials. An attacker may use a scheme
known as social engineering to lure online shoppers to give out their personal
information. When sent in an email to an online shopper, a phishing scam may
contain a link to a malicious site that resembles an e-commerce site.
Firewall –
Firewall is a barrier between Local Area Network (LAN) and the Internet. It
allows keeping private resources confidential and minimizes the security risks.
It controls network traffic, in both directions.
The following diagram depicts a sample firewall between LAN and the
internet. The connection between the two is the point of vulnerability. Both
hardware and the software can be used at this point to filter network traffic.
Components of firewall –
Firewall is categorized into three basic types −
Packet filter (Stateless & Stateful)
Application-level gateway
Circuit-level gateway
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
14
E-Commerce
Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Stateless & Stateful Packet Filtering Firewall
In this type of firewall deployment, the internal network is connected to the
external network/Internet via a router firewall. The firewall inspects and
filters data packet-by-packet.
packet.
Packet-filtering
filtering firewalls allow or block
lock the packets mostly based on criteria
such as source and/or destination IP addresses, protocol, source and/or
destination port numbers, and various other parameters within the IP header.
Application Gateways
An application-level
level gateway acts as a rel
relay
ay node for the application-level
application
traffic. They intercept incoming and outgoing packets, run proxies that copy
and forward information across the gateway, and function as a proxy server,
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
15
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
preventing any direct connection between a trusted server or client and an
untrusted host.
The proxies are application specific. They can filter packets at the application
layer of the OSI model.
Circuit-Level Gateway
The circuit-level gateway is an intermediate solution between the packet filter
and the application gateway. It runs at the transport layer and hence can act
as proxy for any application.
Similar to an application gateway, the circuit-level gateway also does not
permit an end-to-end TCP connection across the gateway. It sets up two TCP
connections and relays the TCP segments from one network to the other. But,
it does not examine the application data like application gateway. Hence,
sometime it is called as ‘Pipe Proxy’.
Security threats –
E-commerce threat is occurring by using the internet for unfair means with the
intention of stealing, fraud and security breach. There are various types of e-
commerce threats. Some are accidental, some are purposeful, and some of
them are due to human error. The most common security threats are:
electronic payments system
e-cash
data misuse
credit/debit card frauds, etc.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
16
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Electronic Payment System-
With the rapid development of the computer, mobile, and network
technology, e-commerce has become a routine part of human life. In e-
commerce, the customer can order products at home and save time for doing
other things. There is no need of visiting a store or a shop. The customer can
select different stores on the Internet in a very short time and compare the
products with different characteristics such as price, colour, and quality.
Some of them are:
The Risk of Fraud
An electronic payment system has a huge risk of fraud. The computing devices
use an identity of the person for authorizing a payment such as passwords and
security questions. These authentications are not full proof in determining the
identity of a person. If the password and the answers to the security questions
are matched, the system doesn't care who is on the other side. If someone has
access to our password or the answers to our security question, he will gain
access to our money and can steal it from us.
The Risk of Tax Evasion
The Internal Revenue Service law requires that every business declare their
financial transactions and provide paper records so that tax compliance can be
verified. The problem with electronic systems is that they don't provide cleanly
into this paradigm. It makes the process of tax collection very frustrating for
the Internal Revenue Service. It is at the business's choice to disclose payments
received or made via electronic payment systems. The IRS has no way to know
that it is telling the truth or not that makes it easy to evade taxation.
The Risk of Payment Conflicts
In electronic payment systems, the payments are handled by an automated
electronic system, not by humans. The system is prone to errors when it
handles large amounts of payments on a frequent basis with more than one
recipients involved. It is essential to continually check our pay slip after every
pay period ends in order to ensure everything makes sense. If it is a failure to
do this, may result in conflicts of payment caused by technical glitches and
anomalies.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
17
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
e-cash-
E-cash is a paperless cash system which facilitates the transfer of funds
anonymously. E-cash is free to the user while the sellers have paid a fee for
this. The e-cash fund can be either stored on a card itself or in an account
which is associated with the card. The most common examples of e-cash
system are transit card, PayPal, GooglePay, Paytm, etc.
E-cash has four major components-
1. Issuers - They can be banks or a non-bank institution.
2. Customers - They are the users who spend the e-cash.
3. Merchants or Traders - They are the vendors who receive e-cash.
4. Regulators - They are related to authorities or state tax agencies.
In e-cash, we stored financial information on the computer, electronic device
or on the internet which is vulnerable to the hackers. Some of the major
threats related to e-cash system are-
Credit/Debit Card Frauds-
A credit card allows us to borrow money from a recipient bank to make
purchases. The issuer of the credit card has the condition that the cardholder
will pay back the borrowed money with an additional agreed-upon charge.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
18
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
A debit card is of a plastic card which issued by the financial organization to
account holder who has a savings deposit account that can be used instead of
cash to make purchases. The debit card can be used only when the fund is
available in the account.
Some of the important threats associated with the debit/credit card are-
ATM (Automated Teller Machine)-
It is the favourite place of the fraudster from there they can steal our card
details. Some of the important techniques which the criminals opt for getting
hold of our card information is:
Skimming-
It is the process of attaching a data-skimming device in the card reader of the
ATM. When the customer swipes their card in the ATM card reader, the
information is copied from the magnetic strip to the device. By doing this, the
criminals get to know the details of the Card number, name, CVV number,
expiry date of the card and other details.
Unwanted Presence-
It is a rule that not more than one user should use the ATM at a time. If we find
more than one people lurking around together, the intention behind this is to
overlook our card details while we were making our transaction.
Vishing/Phishing
Phishing is an activity in which an intruder obtained the sensitive information
of a user such as password, usernames, and credit card details, often for
malicious reasons, etc.
Network Security –
With the usage of Internet, a number of activities take place in your computer
which can be for good or bad and varies from identity thefts to people who
hack into computers and steal private passwords, documents and files. The
fact is that everything is online and opens us to these frauds and makes us
victims, unless you have taken the necessary steps to protect your computer.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
19
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
It is quite strange that till date, a lot of people don’t give much importance to
Internet Security. They think that their computers are invisible, but as soon as
they start using their computers for anything that involves logging onto the
Internet, they are an easy prey, even for a teenaged hacker.
Limitation of firewall –
firewalls do have the following limitations:
A firewall cannot prevent users or attackers with modems from dialing in
to or out of the internal network, thus bypassing the firewall and its
protection completely.
Firewalls cannot enforce your password policy or prevent misuse of
passwords. Your password policy is crucial in this area because it
outlines acceptable conduct and sets the ramifications of
noncompliance.
Firewalls are ineffective against nontechnical security risks such as social
engineering, as discussed in Chapter 1, “There Be Hackers Here.”
Firewalls cannot stop internal users from accessing websites with
malicious code, making user education critical.
Firewalls cannot protect you from poor decisions.
Firewalls cannot protect you when your security policy is too lax.
Unit – 4
Encryption
Encryption is a security method in which information is encoded in such a way
that only authorized user can read it. It uses encryption algorithm to generate
ciphertext that can only be read if decrypted.
Types of Encryption
There are two types of encryptions schemes as listed below:
Symmetric Key encryption
Public Key encryption
Symmetric Key encryption
Symmetric key encryption algorithm uses same cryptographic keys for both
encryption and decryption of cipher text.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
20
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Public Key encryption
Public key encryption algorithm uses pair of keys, one of which is a secret key
and one of which is public. These two keys are mathematically linked with
each other.
Symmetric encryption keys & data encryption
standard –
Symmetric encryption is a type of encryption where only one key (a
secret key) is used to both encrypt and decrypt electronic information.
The entities communicating via symmetric encryption must exchange
the key so that it can be used in the decryption process.
This encryption method differs from asymmetric encryption where a pair
of keys, one public and one private, is used to encrypt and decrypt
messages.
The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is an outdated symmetric-key
method of data encryption. DES works by using the same key
to encrypt and decrypt a message, so both the sender and the receiver
must know and use the same private key.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
21
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Triple encryption –
Triple Data Encryption or TDES is an ANSI sanctioned algorithm for encryption.
In TDES, block cipher algorithms are used and every data block gets the
application of the algorithms thrice. The size of the key is increased so that the
security can be improved and made better. There are 64 bits of data in every
block and the keys are three in number, called bundle keys. Every key has 56
bits, making TDES 168 bits.
Asymmetric encryption-Secret key encryption –
Asymmetric encryption uses computationally hard problems with a
secret(private), and shared (public) key. With asymmetric encryption,
a message encrypted with one’s public key can only be deciphered by
their private key and vice versa. Asymmetric encryption solves the
problem of having to share without secure communication by enabling
communicating parties to share their public keys and, using complex
math, encrypt data such that an eavesdropper cannot decipher the
message.
A secret key is the piece of information or parameter that is used
to encrypt and decrypt messages in a symmetric, or secret-
key, encryption. In assymetric encryption, two separate keys are used.
One is a public key and the other is a secret key. A secret key may also
be known as a private key.
Public & Private key encryption –
The public key is used to encrypt and a private key is used decrypt the
data. Private Key is used to both encrypt and decrypt the data and is shared
between the sender and receiver of encrypted data. ... The public key is only
used to encrypt data and to decrypt the data, the private key is used and is
shared.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
22
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Unit – 5
Electronic Payment
Overview –
E-commerce sites use electronic payment, where electronic payment refers to
paperless monetary transactions. Electronic payment has revolutionized the
business processing by reducing the paperwork, transaction costs, and labor
cost. Being user friendly and less time-consuming than manual processing, it
helps business organization to expand its market reach/expansion. Listed
below are some of the modes of electronic payments −
Credit Card
Debit Card
Smart Card
E-Money
Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT)
Payment gateway –
Payment Gateway is an online payment processing technology which helps
businesses to accept credit cards and electronic checks. In other words,
payment gateways are “Manin-the-middle” which are located between e-
commerce platforms and clients.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
23
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
A payment gateway allows you to −
Make and take payments quickly and easily.
Keep your customer's data (information) and money secure.
Gain trust of your customers, so they are willing to hand over their
money.
To choose the right payment gateway, you should follow the following
guidelines −
You should finalize that payment gateway which is supported in your
country, not all them operate globally.
You should check what payment gateways are supported better from
your ecommerce platform. For example, PayPal gateway is fully
supported by Magento because the same group have created them.
Payment gateway should be of 3.0 PCI data security standards.
Do you need payment gateway and merchant account or an all-in-one
payment service provider?
You must see the charges and fees that will be deducted per
transaction.
What payment method do they support? For example, VISA is a
payment method, Master Card is another.
Do they support your type of business? For example, some of them
don’t deal with businesses that sell adult materials, betting, gambling,
firearms selling, narcotics, etc.
Most Popular Payment Gateway Providers
Following is the list of the most widely used and popular payment getaway
providers along with a brief history about them.
PAYPAL − You can find all the terms and condi ons of their business
model on their URL – https://www.paypal.com/. PayPal is one of the
longest established and probably the best-known service for
transferring money online.
Amazon Payments − The URL of this immensely popular payment
getaway provider is – https://payments.amazon.com/. It was created in
2007, Amazon Payments provides your customers with the same
checkout experience they get on Amazon.com
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
24
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Stripe − The URL of this payment getaway is – https://stripe.com/. No
monthly fees, no extra charges for different cards and different
payment methods, also for different currencies. Stripe also offers a
great API (Application Program Interface) as well.
Authorize Net − The URL for this popular payment getaway provider
is https://www.authorize.net/. It is among the most powerful and well-
known payment gateways. It is well-supported by e-commerce
WordPress plugins.
2Checkout − The URL for this payment getaway provider is –
https://www.2checkout.com/. 2checkout is one of the most simple and
affordable credit card gateways.
Certificate –
Certification is a process through which we can first authenticate the customer
and merchant and any other parties that are involved in the payment, then
payment can be done. On the basis of these requirements, we proposed a
system which will provide the facility of providing the certificates to
authorities.
Digital tokens –
The digital token based payment system is a new form of electronic payment
system which is based on electronic tokens rather than e-cheque or e-cash.
The electronic tokens are generated by the bank or some financial institutions.
Hence we can say that the electronic tokens are equivalent to the cash which
are to be made by the bank.
Smart Card –
Smart card is again similar to a credit card or a debit card in appearance, but it
has a small microprocessor chip embedded in it. It has the capacity to store a
customer’s work-related and/or personal information. Smart cards are also
used to store money and the amount gets deducted after every transaction.
Smart cards can only be accessed using a PIN that every customer is assigned
with. Smart cards are secure, as they store information in encrypted format
and are less expensive/provides faster processing. Mondex and Visa Cash
cards are examples of smart cards.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
25
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
Credit Card –
Payment using credit card is one of most common mode of electronic
payment. Credit card is small plastic card with a unique number attached with
an account. It has also a magnetic strip embedded in it which is used to read
credit card via card readers. When a customer purchases a product via credit
card, credit card issuer bank pays on behalf of the customer and customer has
a certain time period after which he/she can pay the credit card bill. It is
usually credit card monthly payment cycle. Following are the actors in the
credit card system.
The card holder − Customer
The merchant − seller of product who can accept credit card payments.
The card issuer bank − card holder's bank
The acquirer bank − the merchant's bank
The card brand − for example , visa or Mastercard.
Credit Card Payment Proces
Step Description
Step 1 Bank issues and activates a credit card to the customer on his/her
request.
Step 2 The customer presents the credit card information to the merchant
site or to the merchant from whom he/she wants to purchase a
product/service.
Step 3 Merchant validates the customer's identity by asking for approval
from the card brand company.
Step 4 Card brand company authenticates the credit card and pays the
transaction by credit. Merchant keeps the sales slip.
Step 5 Merchant submits the sales slip to acquirer banks and gets the service
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
26
E-Commerce Notes For BCA VBSPU Created by DPMishra
charges paid to him/her.
Step 6 Acquirer bank requests the card brand company to clear the credit
amount and gets the payment.
Step 6 Now the card brand company asks to clear the amount from the
issuer bank and the amount gets transferred to the card brand
company.
Magnetic strip card –
A magnetic stripe card is a type of pass that permits the user to
complete electronic transactions or access a locked physical space. The
"stripe" contains embedded information that identifies its user.
E-checks –
The electronic cheques are modeled on paper checks, except that they are
initiated electronically. They use digital signatures for signing and endorsing
and require the use of digital certificates to authenticate the payer, the payer’s
bank and bank account. They are delivered either by direct transmission using
telephone lines or by public networks such as the Internet.
Online banking –
Internet banking, also known as online banking, e-banking or virtual banking,
is an electronic payment system that enables customers of a bank or other
financial institution to conduct a range of financial transactions through the
financial institution's website.
For More Info Visit: DPMISHRA.COM
You might also like
- Internet Its Applications PDFDocument71 pagesInternet Its Applications PDFDeepak Kumar100% (1)
- E Commerce Notes For Bca StudentsDocument87 pagesE Commerce Notes For Bca StudentsAshwani kumariNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics MCQ Question Bank 22318Document52 pagesComputer Graphics MCQ Question Bank 22318Rupali Sardar100% (3)
- Sna Bullet 8 McqsDocument12 pagesSna Bullet 8 McqsMursaleen UmerNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Questions BankDocument19 pagesE-Commerce Questions BankSambasiva Rao100% (1)
- Virtual Mouse Using Hand GesturesDocument12 pagesVirtual Mouse Using Hand Gesturessahil palNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Business Intelligence Applications: - Marketing Models - Logistic and Production Models - Case StudiesDocument39 pagesUnit Iv Business Intelligence Applications: - Marketing Models - Logistic and Production Models - Case StudiesGeorge FernandezNo ratings yet
- Tyit Iot Mcqs (E-Next - In)Document26 pagesTyit Iot Mcqs (E-Next - In)glen mnx100% (1)
- Abstract:: Introduction To Hotel Management System ProjectDocument2 pagesAbstract:: Introduction To Hotel Management System ProjectjeevikaNo ratings yet
- Index: 1.1 Key FeaturesDocument53 pagesIndex: 1.1 Key FeaturesPallavi PalluNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Mobile Application Development 18CSMP68Document47 pagesLaboratory Manual: Mobile Application Development 18CSMP68praveen psNo ratings yet
- Online Examination System Project ReportDocument125 pagesOnline Examination System Project Reportwale_ogunniran0% (2)
- Build PHP Chat App HTML CSS AJAXDocument8 pagesBuild PHP Chat App HTML CSS AJAXENGINEER HERENo ratings yet
- Hotel Management System Project ReportDocument10 pagesHotel Management System Project ReportbfhgrjkrjgiNo ratings yet
- Defect Tracking System AbstractDocument12 pagesDefect Tracking System AbstractTelika RamuNo ratings yet
- 607U2 - Cloud ComputingDocument22 pages607U2 - Cloud ComputingShubham Alavni100% (3)
- MCQ Mad MCQDocument31 pagesMCQ Mad MCQSaquibh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Knowledge ManagementDocument2 pagesMCQ On Knowledge ManagementPratik100% (1)
- Mini Project ReportDocument26 pagesMini Project ReportPooja0% (1)
- Online Doctor Synopsis534534Document35 pagesOnline Doctor Synopsis534534ArnabNo ratings yet
- Network Management Important and Super Important Questions-18CS742Document1 pageNetwork Management Important and Super Important Questions-18CS742nirmal jainNo ratings yet
- Stadium Ticket Booking SystemDocument1 pageStadium Ticket Booking SystemMaruthi TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Java Chat System (Synopsis)Document4 pagesJava Chat System (Synopsis)sanjaykumarguptaa100% (1)
- Cloud Computing Lab Manual 1Document25 pagesCloud Computing Lab Manual 1OMSAINATH MPONLINE100% (1)
- Mohit Garg - MIS (BCA VI Sem) - MODEL QUESTION PAPER - IIDocument11 pagesMohit Garg - MIS (BCA VI Sem) - MODEL QUESTION PAPER - IIMohit GargNo ratings yet
- LECTURE-1-SW LayeredDocument3 pagesLECTURE-1-SW Layereddivya0% (1)
- E-Bill Management System (Synopsis)Document7 pagesE-Bill Management System (Synopsis)Vinayak BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Combine 0 ETIDocument1,776 pagesCombine 0 ETIJimmy PathareNo ratings yet
- Staffing in Software ProjectsDocument26 pagesStaffing in Software Projectsabhishekgs100% (3)
- Unit 1Document13 pagesUnit 1ठाकुर अनमोल राजपूत100% (1)
- Android MCQDocument6 pagesAndroid MCQAli Saivi100% (2)
- Awp Unit-1 NotesDocument64 pagesAwp Unit-1 NotesFrancis Xavier0% (2)
- Evolution of Computer Architecture from Generations 1-4Document2 pagesEvolution of Computer Architecture from Generations 1-4Dalton Mclean50% (2)
- UNIT I Unit V e Commerce 2 MarksDocument21 pagesUNIT I Unit V e Commerce 2 MarksPri YA Jayalakshmi75% (4)
- Mad 22617 McqsDocument19 pagesMad 22617 McqsSaurav MukeNo ratings yet
- Stock Management SynopsisDocument2 pagesStock Management SynopsisAnonymous m46I3FXO7575% (4)
- Understanding Computer ForensicsDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Computer ForensicsLakshmi Narayana ReddyNo ratings yet
- Intranet ChattingDocument37 pagesIntranet ChattingSubrat Patnaik67% (3)
- Tybsc It Internet of Things Sem VDocument43 pagesTybsc It Internet of Things Sem Vzyann da2No ratings yet
- Java Project ReportDocument77 pagesJava Project ReportSyaape0% (1)
- Laptop Price Prediction Using Machine Learning: International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile ComputingDocument5 pagesLaptop Price Prediction Using Machine Learning: International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile ComputingAaneill CrestNo ratings yet
- TYBBA (CA) Sem V Practical SlipsDocument30 pagesTYBBA (CA) Sem V Practical SlipsSurinder JaatNo ratings yet
- It6601 Mobile Computing 2 Marks With AnswersDocument24 pagesIt6601 Mobile Computing 2 Marks With AnswersPushpavalli Mohan100% (2)
- Online Notice Board: Project Report For Bachelor of Computer ApplicationDocument30 pagesOnline Notice Board: Project Report For Bachelor of Computer ApplicationAnUp KaSuLaNo ratings yet
- C One Mark QuestionsDocument17 pagesC One Mark QuestionsNithiya NithiNo ratings yet
- House Rental Website Project ReportDocument16 pagesHouse Rental Website Project ReportKevin Patel100% (1)
- Dbms Mini Project: Bhoomika Manjunath Vaidya 5 Sem Cse-A 1BG19CS022Document9 pagesDbms Mini Project: Bhoomika Manjunath Vaidya 5 Sem Cse-A 1BG19CS022Bhoomika VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Hotel Management System Project DocumentationDocument4 pagesHotel Management System Project Documentationdessie mulukn0% (1)
- PHP AssignmentDocument33 pagesPHP AssignmentAnand Gandhi100% (2)
- WT Assignment QuestionsDocument3 pagesWT Assignment QuestionsShruthin ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing BenefitsDocument7 pagesCloud Computing BenefitsNanga MadhuriNo ratings yet
- MCA (MANAGEMENT) 2020 PATTERN Sem2 AnswerDocument25 pagesMCA (MANAGEMENT) 2020 PATTERN Sem2 AnswerRohit0% (1)
- Database Management System Sample Question PaperDocument5 pagesDatabase Management System Sample Question Paperarvi.sardarNo ratings yet
- Toll Tax ManagementDocument53 pagesToll Tax ManagementpavithraNo ratings yet
- E Commerce (1)Document26 pagesE Commerce (1)rohitjangid587No ratings yet
- Merce Andhra University PDFDocument62 pagesMerce Andhra University PDFJayJairamNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Guide: Benefits, Payment Methods & MoreDocument18 pagesE-Commerce Guide: Benefits, Payment Methods & MoreIam developerNo ratings yet
- E Commerce Full NotesDocument63 pagesE Commerce Full NotesMickeal MunyakasaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EcommerceDocument3 pagesIntroduction To EcommerceDeepak HarbolaNo ratings yet
- E Commerce Full NotesDocument63 pagesE Commerce Full NotesBhaskaran Balamurali100% (1)
- 2checkout - SB - Payment Method Coverage - 2021Document26 pages2checkout - SB - Payment Method Coverage - 2021Ryan MichealNo ratings yet
- INVESTMENT AND COMPETITION LAW - Unit 2Document62 pagesINVESTMENT AND COMPETITION LAW - Unit 2saif aliNo ratings yet
- Your Bill For Mobile ServicesDocument10 pagesYour Bill For Mobile ServicesGabriel BrooksNo ratings yet
- HANA T-CODESDocument15 pagesHANA T-CODESCatapang Mona LizaNo ratings yet
- Council Tax 2023 - 2023-03-06 - 1Document2 pagesCouncil Tax 2023 - 2023-03-06 - 1tunlinoo.067433No ratings yet
- Kodak Motion Picture Products Price Catalog For The United StatesDocument42 pagesKodak Motion Picture Products Price Catalog For The United StatesloloNo ratings yet
- HDFC Bank We Understand Your WorldDocument5 pagesHDFC Bank We Understand Your Worldaaashu77No ratings yet
- Sales Judge Adviento BetterDocument27 pagesSales Judge Adviento BetterApple Ke-eNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsRheea de los SantosNo ratings yet
- Board Meeting FullDocument60 pagesBoard Meeting FullA Better Dumont (NJ, USA)No ratings yet
- Types of cheque crossingsDocument2 pagesTypes of cheque crossingsAnupamaNo ratings yet
- Employee Self Service - BSNL ERP User ManualDocument88 pagesEmployee Self Service - BSNL ERP User ManualsandyNo ratings yet
- PNB V National City Bank of New YorkDocument3 pagesPNB V National City Bank of New Yorkmma100% (1)
- Accounting Records Source DocumentsDocument3 pagesAccounting Records Source Documentsziad12321No ratings yet
- Sicat Financial Planning Consultant General Journal December, 2020Document3 pagesSicat Financial Planning Consultant General Journal December, 2020Madelyn SolesNo ratings yet
- Journalizing Sy 2019 2020Document1 pageJournalizing Sy 2019 2020Raissa MaeNo ratings yet
- IFTA® INTERNATIONAL STANDARD TERMS 2022 FinalDocument25 pagesIFTA® INTERNATIONAL STANDARD TERMS 2022 FinalBoosty PakNo ratings yet
- RCBC liable for damages due to failure to notify customer regarding unsigned checkDocument2 pagesRCBC liable for damages due to failure to notify customer regarding unsigned checkhmn_scribdNo ratings yet
- Reliance Mutual Funds Compelete Application FormDocument10 pagesReliance Mutual Funds Compelete Application FormARVINDNo ratings yet
- Truth in Lending ActDocument30 pagesTruth in Lending ActjayrenielNo ratings yet
- Business Process Key Decisions Information Needs: Phoenix Appliance Center CoDocument11 pagesBusiness Process Key Decisions Information Needs: Phoenix Appliance Center CoAshlee DelunaNo ratings yet
- TD Statement Mar To AprrDocument4 pagesTD Statement Mar To Aprrslimple Smiles100% (2)
- Citibank'S Epay: Online Credit Card Payment. From Any BankDocument2 pagesCitibank'S Epay: Online Credit Card Payment. From Any BankHamsa KiranNo ratings yet
- Control Accounts Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesControl Accounts Practice Questionsmairaj0897% (36)
- Extinguishment of Obligation Final ExamDocument4 pagesExtinguishment of Obligation Final ExamGwyneth DalupingNo ratings yet
- FORM 16A CERTIFICATEDocument2 pagesFORM 16A CERTIFICATERashmi RanaNo ratings yet
- Power Cable Fault Location TrainingDocument4 pagesPower Cable Fault Location TrainingKrishan Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fall 2018 - COMI619 - 3 - MC170203120Document87 pagesFall 2018 - COMI619 - 3 - MC170203120AmirNo ratings yet
- PT. Said Saputra ManagementDocument3 pagesPT. Said Saputra ManagementSSM HoldingNo ratings yet
- Mar0525 PDFDocument24 pagesMar0525 PDFShubhamNo ratings yet
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityFrom EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellFrom EverandThe Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- The Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerFrom EverandThe Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (34)
- Python for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldFrom EverandPython for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldNo ratings yet
- So You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenFrom EverandSo You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (35)
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationFrom EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- How to Be Fine: What We Learned by Living by the Rules of 50 Self-Help BooksFrom EverandHow to Be Fine: What We Learned by Living by the Rules of 50 Self-Help BooksRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Ultimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business: Access more than 500 million people in 10 minutesFrom EverandUltimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business: Access more than 500 million people in 10 minutesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Content Rules: How to Create Killer Blogs, Podcasts, Videos, Ebooks, Webinars (and More) That Engage Customers and Ignite Your BusinessFrom EverandContent Rules: How to Create Killer Blogs, Podcasts, Videos, Ebooks, Webinars (and More) That Engage Customers and Ignite Your BusinessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- How to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyFrom EverandHow to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (421)
- Social Media Marketing 2024, 2025: Build Your Business, Skyrocket in Passive Income, Stop Working a 9-5 Lifestyle, True Online Working from HomeFrom EverandSocial Media Marketing 2024, 2025: Build Your Business, Skyrocket in Passive Income, Stop Working a 9-5 Lifestyle, True Online Working from HomeNo ratings yet
- Nine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersFrom EverandNine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- TikTok Algorithms 2024 $15,000/Month Guide To Escape Your Job And Build an Successful Social Media Marketing Business From Home Using Your Personal Account, Branding, SEO, InfluencerFrom EverandTikTok Algorithms 2024 $15,000/Month Guide To Escape Your Job And Build an Successful Social Media Marketing Business From Home Using Your Personal Account, Branding, SEO, InfluencerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Ultimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessFrom EverandUltimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- More Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingFrom EverandMore Porn - Faster!: 50 Tips & Tools for Faster and More Efficient Porn BrowsingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (23)
- HTML5 and CSS3 Masterclass: In-depth Web Design Training with Geolocation, the HTML5 Canvas, 2D and 3D CSS Transformations, Flexbox, CSS Grid, and More (English Edition)From EverandHTML5 and CSS3 Masterclass: In-depth Web Design Training with Geolocation, the HTML5 Canvas, 2D and 3D CSS Transformations, Flexbox, CSS Grid, and More (English Edition)No ratings yet
- SEO 2021: Learn search engine optimization with smart internet marketing strategiesFrom EverandSEO 2021: Learn search engine optimization with smart internet marketing strategiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- The $1,000,000 Web Designer Guide: A Practical Guide for Wealth and Freedom as an Online FreelancerFrom EverandThe $1,000,000 Web Designer Guide: A Practical Guide for Wealth and Freedom as an Online FreelancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (22)
- Monitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataFrom EverandMonitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Designer’s Guide to Figma: Master Prototyping, Collaboration, Handoff, and WorkflowFrom EverandThe Designer’s Guide to Figma: Master Prototyping, Collaboration, Handoff, and WorkflowNo ratings yet