Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematics in The Modern World College 2
Uploaded by
Joycee Gutierrez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesThe document discusses sets, functions, relations, and binary operations in mathematics. It defines sets, subsets, infinite sets, empty sets, and provides examples. Properties of binary operations like addition and multiplication are covered, including closure, commutative, associative, identity, and distributive properties.
Original Description:
Mathematics
Original Title
MATHEMATICS-IN-THE-MODERN-WORLD-COLLEGE-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses sets, functions, relations, and binary operations in mathematics. It defines sets, subsets, infinite sets, empty sets, and provides examples. Properties of binary operations like addition and multiplication are covered, including closure, commutative, associative, identity, and distributive properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesMathematics in The Modern World College 2
Uploaded by
Joycee GutierrezThe document discusses sets, functions, relations, and binary operations in mathematics. It defines sets, subsets, infinite sets, empty sets, and provides examples. Properties of binary operations like addition and multiplication are covered, including closure, commutative, associative, identity, and distributive properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERN WORLD COLLEGE
Sets, Functions, Relations and Binary Operations
SET- A collection of any object. It is a mathematical expression in which a name is given to some
collection of objects. The set of integers is represented by the symbol Ζ.
Infinite Set- the numbers of elements in a set can be enumerated.
Empty set- a set that has no members which is denoted using {} or Ø.
List method is a way of describing the set in which the members are separated by commas and enclosed
in braces like set S={4,8,12}. The 3 elements which are 4,8 and 12.
Symbols used to represent the relationship of an element to a set:
Є read as “is in “/”is an element of”/”is a member of
Є read as “is not in”/”is not an element of”/”is not a member of” Example
of set:
S={1,2,3,4} the set {1},{2},{3},{4},{} they are called subsets. A subsets of a given set if any one of
the following three conditions holds: it is the given set, it is the empty set or each member of the set is
also an elements of the given set.
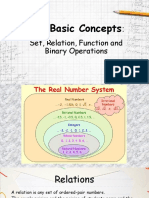
Functions and Relations
Relation- is a set of ordered pairs.
Function- is a relation in which each element of the first set (domain) corresponds to only one element
of the second set (range). A function may also be many to one correspondence.
Function= {(1,5),(2,4),(5,3)}
Binary Operations
A unary operation is a single number and assigns another number to it.
Addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication(x) and division (÷) are examples of
binary operations. The word “binary” means composition of two pieces. A binary
operations refers to joining two values to create a new one.
Properties of addition and multiplication as binary operations on the set of real number:
1. Closure property
Addition: the sum of any two real numbers is also a real number. Example: 12+34=46
Multiplication: the product of any two real numbers is also a real number. Example: 7x20=140
2. Commutative property
Addition: for any two real number x and y, x+y=y+x.
Example:1.5+7.8=7.8+1.5
9.3=9.3
Multiplication: the product of any two real numbers is also a real number.
Example: 8x5=5x8
40=40
3. Associative Property
Addition: for any two real numbers x,y and z, x+(y+z)=(x+y)+z.
Example: 3+(10+9)=(3+10)+9
3+19=13+9
22=22
Multiplication: for any two real numbers x, y and z, x·(y·z)=(x·y)·z.
Example: 3·(9·6)=3·9)·6
3·54=27·6
162=162
4. Identity Property
Addition: for any real number x, x+0=x. the number 0 is called the additive identity.
Example:78+0=78
Multiplication: for any real number x, x·1=x. the number 1 is called the multiplicative identity.
Example: 98·1=98
5. Distributive Property of Multiplication Over Addition: for any two real numbers x,y and
z,x(y+z)=xy+xz.
Example: a(-x+y-z)=-ax+ay-az
6. Inverses of binary Operations
Addition: for any real number x,x+(-x)=0. Example:100+(-100)=0
Multiplication: for any real number x, x
Example: 98·
You might also like
- Chapter 2 - L1Document25 pagesChapter 2 - L1Anime OtakuNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Rieviewer - 1st - QuarterlyDocument11 pagesMath 7 Rieviewer - 1st - QuarterlyClarice PalattaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 in Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument5 pagesChapter 2 in Mathematics in The Modern WorldBalolot Ralph100% (1)
- Mathematical Language & SymbolsDocument20 pagesMathematical Language & SymbolsJAEZAR PHILIP GRAGASINNo ratings yet
- Vikassingh Tutorial 1Document4 pagesVikassingh Tutorial 1Vikas SinghNo ratings yet
- MATH Lecture 2Document21 pagesMATH Lecture 2Jefferson Ayubo BroncanoNo ratings yet
- PropertiesDocument5 pagesPropertiesDean Ariola-SanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 SetsDocument58 pagesUNIT 1 SetsKamal MittalNo ratings yet
- Module 3-5Document11 pagesModule 3-5Edrick G. EsparraguerraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics NewDocument27 pagesMathematics NewKumar SandeepNo ratings yet
- Class-Xi Set TheoryDocument2 pagesClass-Xi Set TheoryKamal Sharma100% (1)
- Wa0004.Document239 pagesWa0004.Abhishek meenaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Binary OperationDocument89 pagesTopic 4 - Binary OperationDomz SenseiNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math Module 3 Set NotationDocument20 pagesDiscrete Math Module 3 Set NotationJayNo ratings yet
- Maths. TaibaDocument11 pagesMaths. TaibaGânőőķ WäřņäNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math Module PrelimDocument10 pagesDiscrete Math Module PrelimFloyd LawtonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Midterm Math in Modern WorldDocument10 pagesReviewer Midterm Math in Modern WorldLuna ShiNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics Learning ModuleDocument22 pagesGeneral Mathematics Learning ModuleAbdul Majeed Dida-agunNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Relations & FunctionsDocument25 pagesWeek 3 Relations & Functionsdip8200No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Mathematical Language and Symbolshiro100% (1)
- Discrete MathematicsDocument75 pagesDiscrete MathematicsJean Rances Amparo RanidoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - The Four Basic Concepts of MathematicsDocument8 pagesLesson 2 - The Four Basic Concepts of MathematicsSTORM STARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 2 - Intro To FunctionsDocument32 pagesChapter 3 2 - Intro To Functionsapi-263209117No ratings yet
- Preparatory 11Document51 pagesPreparatory 11prasanthg_mba6239No ratings yet
- Polynomials Objectives:: element, is used. Thus, if a is an element of set A, we indicate this by writing "a ϵDocument11 pagesPolynomials Objectives:: element, is used. Thus, if a is an element of set A, we indicate this by writing "a ϵAlfredNo ratings yet
- Share GE 3 ReportingDocument13 pagesShare GE 3 ReportingApril CaldeoNo ratings yet
- Group Presentation: University of Education Faisalabad CampusDocument15 pagesGroup Presentation: University of Education Faisalabad CampusUrmika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Four Basic ConceptsDocument12 pagesFour Basic ConceptsMaria Trisha Ann Amparo71% (7)
- GE 04 Midterm Module 2.0Document14 pagesGE 04 Midterm Module 2.0Lorenzo B. FollosoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument120 pagesLesson 2 Mathematical Language and Symbolsrichelle nableNo ratings yet
- Real Number SystemDocument32 pagesReal Number SystemJoy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Inbound 5989627915125010531Document24 pagesInbound 5989627915125010531Casandra Erikka VelezNo ratings yet
- What Is A Function?: Input, Relationship, OutputDocument11 pagesWhat Is A Function?: Input, Relationship, OutputLuisa PereiraNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 5Document30 pagesModule 1 Lesson 5derp perdNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer MathDocument10 pagesLET Reviewer MathJohn Carlo Telan Panganiban80% (5)
- Algebra 2Document4 pagesAlgebra 2api-140032165No ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics: R. JohnsonbaughDocument70 pagesDiscrete Mathematics: R. JohnsonbaughRusdy SajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Python Litvin Chapter 12 Python Litvin Chapter 12 Python LitvinDocument18 pagesChapter 12 Python Litvin Chapter 12 Python Litvin Chapter 12 Python LitvinOmar AtreidesNo ratings yet
- Properties of IntegersDocument4 pagesProperties of IntegersjoshuaNo ratings yet
- Sets and Real NumbersDocument24 pagesSets and Real NumbersJerson BeloyNo ratings yet
- DiscreteDocument16 pagesDiscreteLoraineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part 1 - StudDocument31 pagesChapter 2 Part 1 - StudAshrafD.ZulkeflyNo ratings yet
- Module 5 in MathematicsDocument14 pagesModule 5 in Mathematicsmskhristine mNo ratings yet
- FunctionDocument107 pagesFunctionAh Naweed Najeeb SakhaNo ratings yet
- Ms-101-Introduction To SetsDocument36 pagesMs-101-Introduction To SetsRicHArdNo ratings yet
- Function AnalysisDocument202 pagesFunction AnalysisArun UmraoNo ratings yet
- DDCO Module 1Document25 pagesDDCO Module 1vijaylaxmi-cseNo ratings yet
- Sets, Functions, Relations, and Binary OperationsDocument10 pagesSets, Functions, Relations, and Binary OperationsDharen OlaNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionDocument12 pagesRelation and FunctionNikka Aubrey Tegui-inNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AlgebraDocument26 pagesFundamentals of AlgebraJustin Ace MallorcaNo ratings yet
- Acc 103 - Notes To ClassDocument7 pagesAcc 103 - Notes To Classlaredami64No ratings yet
- Discrete Math Module 1Document9 pagesDiscrete Math Module 1santillankathyrineNo ratings yet
- Notations and FormulasDocument8 pagesNotations and Formulasrin rosNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument4 pagesPolynomialsJoylene MirallesNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Vector Space : Introduction To VectorsDocument15 pages1.2 Vector Space : Introduction To VectorsVineetha LekkalaNo ratings yet
- What Is A FunctionDocument36 pagesWhat Is A Functionlakadia taylorNo ratings yet
- The Language of SetsDocument9 pagesThe Language of SetsMarc Loui RiveroNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Week 1Document7 pagesGen Math Week 1France Dave Mercado MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Math Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandMath Review: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vastra Grah .Pvt. LTD: In-House Manufacturing FacaltyDocument2 pagesVastra Grah .Pvt. LTD: In-House Manufacturing FacaltySaurabh JainNo ratings yet
- HLTARO001 HLTAROO05 Student Assessment Booklet 1 1Document68 pagesHLTARO001 HLTAROO05 Student Assessment Booklet 1 1Amber PreetNo ratings yet
- Functional Plant Manager 2. Geographical Vice PresidentDocument5 pagesFunctional Plant Manager 2. Geographical Vice PresidentVic FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Supplier Accreditation Application-V1 - RevisedDocument8 pagesSupplier Accreditation Application-V1 - RevisedCandiceCocuaco-ChanNo ratings yet
- Scania DC12 Operator's ManualDocument65 pagesScania DC12 Operator's ManualAlex Renne Chambi100% (3)
- Teacher Survey - Outdoor Classroom Feedback: Please Circle All That ApplyDocument3 pagesTeacher Survey - Outdoor Classroom Feedback: Please Circle All That ApplyBrooke Doran RoeNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Students Name Contact Number CAP 10TH: Ideal Institute of Pharamacy, Wada SESSION-2020-21Document12 pagesS.NO. Students Name Contact Number CAP 10TH: Ideal Institute of Pharamacy, Wada SESSION-2020-21DAMBALENo ratings yet
- Fire Master Mirine PlusDocument3 pagesFire Master Mirine PlusCarlos BarriosNo ratings yet
- Retail ImageDocument76 pagesRetail ImageayushiNo ratings yet
- Expt Lipid - Influence of Bile in The Action of LipaseDocument3 pagesExpt Lipid - Influence of Bile in The Action of LipaseAngela CaguitlaNo ratings yet
- 18TE72 - Wireless Communication Experiential Learning ReportDocument10 pages18TE72 - Wireless Communication Experiential Learning ReportRitika BakshiNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Key 2014Document15 pagesMachine Design Key 2014SouvikDasNo ratings yet
- TP PortalDocument25 pagesTP PortalSurendranNo ratings yet
- Resume Arun.A: Career ObjectiveDocument2 pagesResume Arun.A: Career ObjectiveajithkumarNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Research Work at Iit Indore: ProjectsDocument2 pagesProposal For Research Work at Iit Indore: ProjectsAman GargNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 12 - The Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesPertemuan Ke 12 - The Passive VoiceZarNo ratings yet
- The Challenge To Live According To The Gospel: 21 February 2021 1st Sunday of Lent Year BDocument4 pagesThe Challenge To Live According To The Gospel: 21 February 2021 1st Sunday of Lent Year BSam MaestroNo ratings yet
- 2946 1308 00 Leroy Somer LSA47.2 Installation & MaintenanceDocument20 pages2946 1308 00 Leroy Somer LSA47.2 Installation & MaintenanceJORGE ARMANDO CARRASCO TICLLENo ratings yet
- FreeBSD HandbookDocument26 pagesFreeBSD Handbookhembeck119No ratings yet
- I J E E: Nternational Ournal of Nergy and NvironmentDocument8 pagesI J E E: Nternational Ournal of Nergy and NvironmentsheilamegumiNo ratings yet
- Group 6G Revised Research Manuscript 1Document57 pagesGroup 6G Revised Research Manuscript 1Mc Rollyn VallespinNo ratings yet
- Walkie Talkie - 10 Codes - CommUSADocument1 pageWalkie Talkie - 10 Codes - CommUSASakthi VasuNo ratings yet
- 02 - Consumerism Then and NowDocument28 pages02 - Consumerism Then and NowGeorge TsangNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 5Document10 pagesAssignment No 5darshan KeskarNo ratings yet
- AQA Power and Conflict GCSE Revision Guide LADocument49 pagesAQA Power and Conflict GCSE Revision Guide LAderaw11557No ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Pre TestDocument7 pagesReading Comprehension Pre TestMimimiyuhNo ratings yet
- NS2-DVN-2540.Rev4 - Profomal Packing List BLR Piping Hanger Support Beam-Unit 2 - 20200710Document27 pagesNS2-DVN-2540.Rev4 - Profomal Packing List BLR Piping Hanger Support Beam-Unit 2 - 20200710PHAM PHI HUNGNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Benefits of Language LearningDocument11 pagesCognitive Benefits of Language LearningIlhamdi HafizNo ratings yet
- How To Draw The Platform Business Model Map-David RogersDocument5 pagesHow To Draw The Platform Business Model Map-David RogersworkneshNo ratings yet
- Portal 2 PresDocument15 pagesPortal 2 Presapi-666608332No ratings yet