Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Makeup Spring 2012 - One Page
Uploaded by
Hazem MohamedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Makeup Spring 2012 - One Page
Uploaded by
Hazem MohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
Cairo University Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
Faculty of Engineering CHEM603 - Spring 2010
Chemical Engineering Department Makeup - Time: 1.5 hour
Open Book
If required data are missing, use data from the textbook. Maximum grade is 30.
Section I. True or False (6 marks)
101. The compressibility factor is the ratio between the volume of a system and its volume if it was ideal gas.
102. The Carnahan-Starling equation of state does not contain an attractive term.
103. When the electrostatic work is important in a process, the difference in the electric field causes the transfer of
charge across the system boundary.
104. PVT relations relate the behavior of pressure, volume and temperature for a fluid and cannot be used to calculate
energetic properties such as the heat of vaporization.
105. The curve the marks the incipient of mechanical instability for a fluid mixture must pass through the mixture’s
critical point.
106. In a metastable state, all intensive macroscopic properties, including temperature, have stationary values, yet
kinetic energies of bond vibration and rotation remain much higher than the translational kinetic energy.
Section II (24 marks)
201. At 30 C, binary liquid mixtures of methanol and heptane roughly obey Porter’s equation. The infinite dilution
chemical potential of methanol in heptane is 11. Determine whether, at 30 C, these mixtures exhibit liquid-liquid
phase splits over some range of compositions. If they do, what are the compositions of the two phases at equilibrium.
(3 marks)
202. For pure substance 1, which appears in Figure 9.18, draw a semiquantitative plot of the molar Gibbs energy as a
function of temperature from 0 to 100 C. (3 marks)
203. Steam and methane can react to form hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. (a) Obtain the
stoichiometric coefficients and a set of independent reactions for this system. (b) If a reactor initially contains 4 moles
of steam and 2 moles of methane, find the composition of the mixture when 2 moles of steam and 0.1 mole of
methane remain. (8 marks)
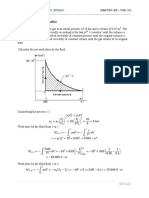
204. A vessel formed from rigid, thermally conducting walls is immersed in a heat bath at 25 C. The vessel has total
volume V and is divided into two compartments, and , by a rigid, movable, thermally conducting partition. The
partition can slide laterally with little friction; initially the partition is positioned so that one compartment has a
volume V=V/5. The partition is initially held in place by stops. Each compartment is loaded with ten moles of pure
nitrogen. A process is initiated by removing the stops, allowing the partition to irreversibly slide to a new equilibrium
position. Estimate the amount of entropy generated. (3 marks)
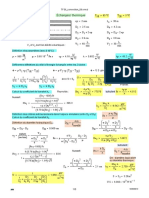
205. Tabitha the Untutored claims that a simple quadratic form such as
P RT A B v C v 2
should be sufficient to reproduce vapor-liquid equilibrium data for pure fluids. Here A, B, and C are empirical
parameters that depend only on temperature and can be positive or negative. Tabitha points out that at fixed P and
fixed T < Tc, such an equation could yield two roots for the volume: one could be that for saturated liquid, while the
other could be for saturated vapor. Do you agree with the claim that such a form is sufficient? Justify your position. (4
marks)
206. Sketch an isothermal-isobaric plot of the change of Gibbs energy on mixing gm vs. mole fraction x1 for a binary
mixture in three-phase vapor-liquid-liquid equilibrium. Include the tie lines on your plot and indicate the composition
of the three phases. (3 marks)
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Ahmed - Refay cc-2019Document7 pagesAhmed - Refay cc-2019Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Ahmed Ali 2020Document5 pagesAhmed Ali 2020Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Civil EngineerDocument2 pagesCivil EngineerHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- C.V MGDocument3 pagesC.V MGHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- AbdelRahman-Sabra-CV 2018Document2 pagesAbdelRahman-Sabra-CV 2018Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Muhamed Abd Elmohsen2018 SH 2011Document1 pageAhmed Muhamed Abd Elmohsen2018 SH 2011Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Eng Esslam AbdelhakimDocument2 pagesEng Esslam AbdelhakimHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Ahmed Mohammed EL Desouky 2007Document8 pagesAhmed Mohammed EL Desouky 2007Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Ahmed El Banna C.V EgyDocument4 pagesAhmed El Banna C.V EgyHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- CV Last Update 2020Document8 pagesCV Last Update 2020Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Civil Engineer (Site&technical Office)Document2 pagesCivil Engineer (Site&technical Office)Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument1 pageCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Mohamed Khiereldin Ali Elassily: Personal StatementDocument3 pagesMohamed Khiereldin Ali Elassily: Personal StatementHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Hazem Mohamed Abdallah CVDocument5 pagesHazem Mohamed Abdallah CVHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Adham 2 C.V 2016Document5 pagesAdham 2 C.V 2016Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Ahmed Hussin CV 2017Document1 pageAhmed Hussin CV 2017Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Abdelkader-Elgebaly-Resume 2018Document1 pageAbdelkader-Elgebaly-Resume 2018Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Ahmed Shamakh CV 11-1-2020 2018Document1 pageAhmed Shamakh CV 11-1-2020 2018Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Abdel Rahman Aly Abdel Rahman CV 2016Document2 pagesAbdel Rahman Aly Abdel Rahman CV 2016Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Hazem Mohamed AbdallahDocument3 pagesHazem Mohamed AbdallahHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Final Exam - January 2011Document2 pagesFinal Exam - January 2011Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Mohamed Hussein: Job SkillsDocument2 pagesMohamed Hussein: Job SkillsHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Azzam Mohamed Khalaf: Mail 01013961547Document2 pagesAhmed Azzam Mohamed Khalaf: Mail 01013961547Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineer: Work Experiences Personal SkillsDocument1 pageCivil Engineer: Work Experiences Personal SkillsHazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Mahmoud C.V 2012Document2 pagesAhmed Mahmoud C.V 2012Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- A7md Elbahnassy 2014Document1 pageA7md Elbahnassy 2014Hazem MohamedNo ratings yet
- Effect of Impurities On TheDocument6 pagesEffect of Impurities On TheBansal Shivansh100% (1)
- Gas Tables For Compressible Flow Calculations by S M Yahya - by LearnEngineering - inDocument159 pagesGas Tables For Compressible Flow Calculations by S M Yahya - by LearnEngineering - inAaron Eipe JohnNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1Document5 pagesThermodynamics 1ArgielJohn LlagasNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Chemistry 8: I. ObjectivesDocument13 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Chemistry 8: I. Objectivesgilmore ramoso100% (1)
- Kinematic ViscosityDocument10 pagesKinematic ViscosityMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Flow of FluidSDocument53 pagesFlow of FluidSAbas AcmadNo ratings yet
- ODO Measurement in Gas - Technical NoteDocument2 pagesODO Measurement in Gas - Technical Noteigize2No ratings yet
- Effect of Area Ratio On Flow Separation in Annular Diffuser PDFDocument9 pagesEffect of Area Ratio On Flow Separation in Annular Diffuser PDFArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 - Gas Laws and Ideal Gas EquationDocument1 pageWorksheet 4 - Gas Laws and Ideal Gas EquationannmarieNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document2 pagesTutorial 7Virendra SheoranNo ratings yet
- SGM2 - Study Guide For Module 2 PDFDocument32 pagesSGM2 - Study Guide For Module 2 PDFEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Manometer NotesDocument5 pagesManometer NotesRaju100% (1)
- Liquid Holdup Management by Predicting Steady Stat PDFDocument8 pagesLiquid Holdup Management by Predicting Steady Stat PDFIBIKUNLENo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Ideal Gas Processes AssessmentsDocument1 pageIdeal Gas Processes AssessmentsNigel Ceasar SilvaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0003491615003504 Main PDFDocument50 pages1 s2.0 S0003491615003504 Main PDFAishee ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- TF06 Convection 09Document3 pagesTF06 Convection 09thekrumpNo ratings yet
- Design Guide For Multi-Hole RO Plates With N 3 Holes: February 2016Document27 pagesDesign Guide For Multi-Hole RO Plates With N 3 Holes: February 2016Enrique RieraNo ratings yet
- Gaseous StateDocument70 pagesGaseous StatePoop MasterNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument38 pagesStates of MatterJack LupinoNo ratings yet
- Propiedades de RefrigerantesDocument70 pagesPropiedades de RefrigerantesBeatriz ReyesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties of R134a (1112-Tetrafluoroethane) PDFDocument11 pagesThermodynamic Properties of R134a (1112-Tetrafluoroethane) PDFJuan Daniel Perez LopezNo ratings yet
- Komparasi Inergen, FM-200, Dan Novec 1230Document4 pagesKomparasi Inergen, FM-200, Dan Novec 1230Bagus PrambudiNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsDocument9 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Exam 2018 Wirh SolutionsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Steam Nozzle Experiment (Power Planet Lab)Document21 pagesSteam Nozzle Experiment (Power Planet Lab)Ali Madrid0% (1)
- Generalization of Ideal Gas Behavior - 2Document27 pagesGeneralization of Ideal Gas Behavior - 2Husnil KhatimahNo ratings yet
- Properties of Dry GasesDocument27 pagesProperties of Dry GasesAlejandro PerezNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument50 pagesFluid MechanicsAnna Louise WyNo ratings yet
- 2021 August CH204-HDocument3 pages2021 August CH204-HMidhunNo ratings yet
- BScthesis On MDDocument46 pagesBScthesis On MDalka mehraNo ratings yet
- CH 03 - Pshychrometry - Oct 2020Document30 pagesCH 03 - Pshychrometry - Oct 2020Nur Atiqah NabilaNo ratings yet
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellFrom EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonFrom EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)
- Permaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreFrom EverandPermaculture for the Rest of Us: Abundant Living on Less than an AcreRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (33)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldFrom EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationFrom EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldFrom EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)