Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Radiography
Uploaded by
VIVEK TIWARIOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Radiography
Uploaded by
VIVEK TIWARICopyright:
Available Formats
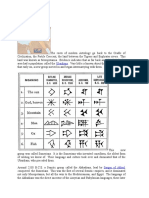
RADIOSCOPY eas or defects in a part show up as lighter
How x-ray inspection works Radioscopy (also called real-time radi-
ography) is a nondestructive test (NDT)
parts on the screen.
Radioscopy is a well-established method
method whereby an image is produced of NDT having applications in
electronically rather than on film so that ► automotive,
very little lag time occurs between the ► aviation and aerospace,
item being exposed to radiation and the ► nuclear power plants,
resulting image. In most cases, radio- ► electronics,
scopic images are produced by a screen ► length & spiral welded pipes,
coated with a material that illuminates ► food,
when exposed to x-rays. The more x- ► and shipyards and -builders
rays that reach a part of the screen, the among others.
brighter that part of the screen becomes.
The x-ray sensitive coating on the screen The use of radioscopy is increasing due
forms the x-ray image much as the grains to a reduction in the cost of the equip-
of silver form the image in film radiogra- ment and resolution of issues such as
phy. The image produced is the opposite the protection and storage of digital im-
of the negative image produced in film ages.
radiography. In other words, thinner ar-
RADIOSCOPY VERSUS RADIOGRA- ally positioned manually. Once the part
PHY SETUP is in place, the film or plate is exposed.
If film is used, it is developed, and can
The main difference between radiogra- be kept as hardcopy documentation or
phy and radioscopy is the intended out- scanned for digital storage. Reusable
put of the system. Radiography systems plates are scanned directly to digital for-
are designed to provide static, film or mat. Although it is possible to automate
plate based single images, while radios- radiographic inspection, it is usually not
copy systems provide dynamic, real-time cost effective. Radioscopic systems use
moving images. Because of the intended a single generator and unipolar tubes.
output, the setups of the two systems They also use real-time detectors, such
vary somewhat. In a radiographic setup, as image intensifiers, digital flat panel de-
there is an x-ray tube and detector, which tectors or linear diode arrays. Because
is film or reusable plate. There is also a they can see the parts in real time, the
generator, and sometimes two genera- parts are positioned using a robotic ma-
tors, if the tube is bipolar. There is also nipulator, allowing movement of the part
a cooling pump to cool the tube. In a during exposure. Exposure can be as long
radiographic system, the object is usu- or short as necessary to inspect the part.
Radioscopic setup
MAXItouch TM
controller MAXIsafety TM
safety package
RS-232C
Serial Port
Estop
Switches
- MAXItube TM MAXIcoolTM W
Door
Switches
MAXIvoltTM Unipolar Water Cooler
High Voltage
Generator (-) Monitor
160, 225kV Warning
Horn
Frame
Buffer
X-Ray On
Lights
MAXIvision TM
intensifier
image
Robot PC Image Acquisition,
Manipulator Noise Reduction and
Image Processing
Camera
Frame
CCD
Grabber
Robot Control
Jacobsen Real-Time
X-Ray Machinery Inc .
2 MAXIxray™
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The History of AstrologyDocument36 pagesThe History of AstrologyDharani Dharendra DasNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- What Is GohonzonDocument3 pagesWhat Is Gohonzonamol100% (1)
- Material Selection Chart Based On Operating TemperatureDocument1 pageMaterial Selection Chart Based On Operating TemperatureVIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Eatwell Guide BookletDocument12 pagesEatwell Guide BookletPaul des Perrieres100% (1)
- 2D Imaging en 0213 LowDocument25 pages2D Imaging en 0213 LowcreaelectronicaNo ratings yet
- 25 Drug Interactions QuestionsDocument7 pages25 Drug Interactions Questionssazaki22483% (6)
- Part1 WHOStandardAccupuncturePointLocationsDocument39 pagesPart1 WHOStandardAccupuncturePointLocationsJiman Ryu100% (1)
- Eil Steam Trap StanderedDocument56 pagesEil Steam Trap StanderedVIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- ME-GI Engine Fuelled by LNG - tcm144-473665Document25 pagesME-GI Engine Fuelled by LNG - tcm144-473665Muhammad Ikhwan KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Medical Device Risk Management - IsO 14971Document86 pagesMedical Device Risk Management - IsO 14971novdic71% (7)
- Close-Up B1+ Workbook Unit 7 PDFDocument6 pagesClose-Up B1+ Workbook Unit 7 PDFkyriaki tsigounakiNo ratings yet
- VTV-3281-LIT-9511-PP-DOC-030 Rev.2Document9 pagesVTV-3281-LIT-9511-PP-DOC-030 Rev.2VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-052 - Rev 0Document14 pagesVtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-052 - Rev 0VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-019 R6Document9 pagesVtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-019 R6VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-052 - Rev 1Document14 pagesVtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-052 - Rev 1VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- AEPCOM-QAP-3281-58548 Rev 1Document3 pagesAEPCOM-QAP-3281-58548 Rev 1VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Drg-026 R2Document4 pagesVtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Drg-026 R2VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-034 R3Document13 pagesVtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-034 R3VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Drg-027 R3Document11 pagesVtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Drg-027 R3VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Drg-029 R2Document12 pagesVtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Drg-029 R2VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-025 R3Document10 pagesVtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-025 R3VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-062 R2Document3 pagesVtv-3281-Lit-9511-Pp-Doc-062 R2VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Is 14164.2008-Insulation ApplicationDocument42 pagesIs 14164.2008-Insulation ApplicationVIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Vendor Itp - Ball Valve (Lot-2) : OwnerDocument3 pagesVendor Itp - Ball Valve (Lot-2) : OwnerVIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance Plan (Qap) For L.T.C.S. FittingsDocument2 pagesQuality Assurance Plan (Qap) For L.T.C.S. FittingsVIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- 10 Sec 1 PT PVG 168-171Document5 pages10 Sec 1 PT PVG 168-171VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Material Specifications1Document2 pagesMaterial Specifications1VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- 5 Sec 1 PT PWT 129-135Document7 pages5 Sec 1 PT PWT 129-135VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- 9 Sec 1 PT Peb 163-167Document5 pages9 Sec 1 PT Peb 163-167VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- 8 Sec 1 PT PMB 159-162Document4 pages8 Sec 1 PT PMB 159-162VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- API 6D Wafer Style Dual Plate Check Valves: Fig No: MV-1220Document15 pagesAPI 6D Wafer Style Dual Plate Check Valves: Fig No: MV-1220VIVEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- Piping Diagram SymbolsDocument1 pagePiping Diagram Symbolskumarrishabh7102002No ratings yet
- Araling Panlipunan ReportDocument4 pagesAraling Panlipunan ReporthaniNo ratings yet
- Introducing SigmaXL Version 5.3bDocument83 pagesIntroducing SigmaXL Version 5.3bYusranNo ratings yet
- Year 4 5 6 SimilesDocument5 pagesYear 4 5 6 SimilesRachel FaizatulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18Document30 pagesLecture 18Francisco Garcia de CortazarNo ratings yet
- Huggenberger EDU en 01Document1 pageHuggenberger EDU en 01filmulogNo ratings yet
- AcademyDocument172 pagesAcademykhoanNo ratings yet
- Catalogo ShantuiDocument8 pagesCatalogo Shantuicefuneslpez100% (3)
- Monuments of The Kathmandu Valley - John Sanday@Comics4nostalgiaDocument117 pagesMonuments of The Kathmandu Valley - John Sanday@Comics4nostalgiaBipin Bazracharya100% (1)
- Snacks For Children: Targeting A New Generation of Parents: April 2020Document38 pagesSnacks For Children: Targeting A New Generation of Parents: April 2020Nairit MondalNo ratings yet
- June 2007 Higher Paper 5Document24 pagesJune 2007 Higher Paper 5plop1234567890% (1)
- 2021 Summer Season Club Turban Thermal Fac Sheet - EngDocument12 pages2021 Summer Season Club Turban Thermal Fac Sheet - EngPENA LAURANo ratings yet
- Final Exam Psychology G11Document4 pagesFinal Exam Psychology G11Meetali ArchitNo ratings yet
- Bio FermentationDocument8 pagesBio FermentationCecil ClaveriaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Three Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage RotorDocument1 pageData Sheet: Three Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage Rotorasdsd dsdaNo ratings yet
- Public Spaces For Play Creating Natural Playspaces For Children 8-12 Years in Urban Landscapes That Support Free, Imaginativie and Creative PlayDocument7 pagesPublic Spaces For Play Creating Natural Playspaces For Children 8-12 Years in Urban Landscapes That Support Free, Imaginativie and Creative PlaySara ErnestNo ratings yet
- B.ed NotesDocument17 pagesB.ed Notesanees kakarNo ratings yet
- Stress Corrosion Cracking and Corrosion Fatigue of Steam-Turbine Rotor and Blade Materials'Document4 pagesStress Corrosion Cracking and Corrosion Fatigue of Steam-Turbine Rotor and Blade Materials'danikaoNo ratings yet
- INABELDocument10 pagesINABELAndrea YangNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Santiago OrtizNo ratings yet
- Land NavigationDocument7 pagesLand NavigationElijah Dave BuenaventuraNo ratings yet