Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Patient 2 Imst Ambo
Uploaded by
api-595102974Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Patient 2 Imst Ambo
Uploaded by
api-595102974Copyright:
Available Formats
IMST -
AMBO
Clinical handover is an integral part of the daily clinical
work that takes place between paramedics and Emergency
Department (ED) staff for every patient arriving at the hospital
by ambulance or helicopter.
An ineffective handover represents a breakdown in
communication of health information which in turn may
have deleterious effects on patient care and safety, including;
misdiagnosis or unnecessary delays in diagnosis; delays in
administration of treatment; administration of incorrect
treatment or medication errors; and omission of care.
The IMIST-AMBO tool guides the paramedic not only to
structure the communication but also to remember the
necessary data set that need to be conveyed during an urgent or
emergent clinical handover. When IMIST-AMBO is used, there
is a consistent ordering of the information, greater frequency
of the necessary data set being conveyed and a reduction in
information repetition.
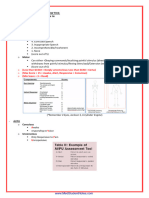
IMIST-AMBO
Clinical Handover Protocol
Approx Age: 80 years ☐ Adult ☐ Pediatic
I dentification:
Nationality
Greek
Gender:
☐ Male
☐ Female
Identify Age, Gender and
Time of Injury or Illness Time of injury/ illness onset: h or minutes ago
onset
M
Mechanism of injury/ Medical Complaint:
echanism/ medical The patient complains of severe chest pain, weakness and light-headedness.
complaint:
Describe the Mechanism
of Injury or the Medical
Complaint
I
Injuries or Illnesses
njuries/ information Had been heavily drinking the night prior.
relative to the complaint:
Patient assessment and
history relevant to
complaint
S
First set of Vital Signs:
igns: BP= 158/81 mm Hg HR = 83 bpm GCS: E=4 V=5 M=6 (15/15)
Vital signs and Glasgow SpO2= 100% RR=28 EtCO2=- ECG=-
Coma Scale (GCS) Symptoms: Severe chest pain, light-headedness and weakness.
Signs: Temperature 36.3 °C (Normal), elevated blood pressure 158/81 mm Hg,
sinus heart rate – 83 bpm.
T
Treatment and responses
reatments: -
Interventions and response
to treatment Medication and doses
The patient took Aspirin approximately 30 minutes ago.
llergies:
A
edications: M
B ackground:
ther:
O The patient’s dad had died of a heart attack – family history of
heart conditions.
Definitions
BP Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood
vessels.
HR Heart rate: The number of heartbeats per unit of time, (per minute).
Glasgow The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is used to objectively describe the extent of impaired
Coma Scale consciousness in all types of acute medical and trauma patients. The scale assesses
(GCS) patients according to three aspects of responsiveness: eye-opening (E), motor (M),
and verbal responses (V). Based on the responses a total is taken of each response
out of 15 for the GCS.
E Eye-opening (E), best score is 4:
1. No eye opening
2. Eye opening to pain
3. Eye opening to sound
4. Eyes open spontaneously
V Verbal responses (V), best score is 5:
1. No verbal response
2. Incomprehensible sounds
3. Inappropriate words
4. Confused
5. Orientated
M Motor (M) best score is 6:
1. No motor response.
2. Abnormal extension to pain
3. Abnormal flexion to pain
4. Withdrawal from pain
5. Localizing pain
6. Obeys commands
Sp02 SpO2, also known as oxygen saturation, is a measure of the amount of oxygen-
carrying hemoglobin in the blood relative to the amount of hemoglobin not carrying
oxygen.
RR Respiratory rate (RR), or the number of breaths per minute, is a clinical sign
that represents ventilation (the movement of air in and out of the lungs).
EtC02 End-tidal CO2 (EtCO2) monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the
partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) at the end of an
exhaled breath, which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg. The normal
values are 5% to 6% CO2, which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a medical test that detects cardiac (heart)
abnormalities by measuring the electrical activity generated by the heart as it
contracts.
You might also like
- Understanding Amp: (Amplified Musculoskeletal Pain Syndrome)From EverandUnderstanding Amp: (Amplified Musculoskeletal Pain Syndrome)No ratings yet
- Basic Personality InventoryDocument8 pagesBasic Personality InventoryElisa Mae Oranza Gura100% (1)
- Mnemonic SDocument42 pagesMnemonic SMcat Notension100% (1)
- Clin Cardiology CasesDocument34 pagesClin Cardiology CasesSunny Singh0% (1)
- SC WD 2 TechnologyHealthConcernsPaper Report 2Document5 pagesSC WD 2 TechnologyHealthConcernsPaper Report 2Joel Lindsay100% (1)
- Textbook of Operative Dentistry NISHA GARGDocument18 pagesTextbook of Operative Dentistry NISHA GARGSELLULARNo ratings yet
- ATLS Chapter Review Questions PDFDocument38 pagesATLS Chapter Review Questions PDFWaeel Hamouda0% (1)
- Emergency Room: Case Scenario (Group 1)Document40 pagesEmergency Room: Case Scenario (Group 1)Victoria Castillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- DC Systems & Battery Safety: Evolution Through Codes & Government RegulationsDocument51 pagesDC Systems & Battery Safety: Evolution Through Codes & Government RegulationsNelsonNo ratings yet
- AEMT - Trauma Exam PracticeDocument26 pagesAEMT - Trauma Exam PracticeEMS DirectorNo ratings yet
- Assessment & Reasoning Cardiac System: Suggested Cardiac Nursing Assessment Skills To Be DemonstratedDocument8 pagesAssessment & Reasoning Cardiac System: Suggested Cardiac Nursing Assessment Skills To Be DemonstratedSharon Tanveer100% (1)
- Baseline Vital Kefah 1ADocument38 pagesBaseline Vital Kefah 1AShahd Abu SnenehNo ratings yet
- Y3 OSCE PracticeDocument27 pagesY3 OSCE PracticenamwaNo ratings yet
- Chest Injury: College of Nursing Valenzuela Campus 120 Macarthur Highway, Marulas, Valenzuela CityDocument10 pagesChest Injury: College of Nursing Valenzuela Campus 120 Macarthur Highway, Marulas, Valenzuela CityDump Cherry33% (3)
- Anti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIIIFrom EverandAnti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIIINo ratings yet
- Nbme 5.1Document54 pagesNbme 5.1Hafsa SafdarNo ratings yet
- Obg Unit-1Document28 pagesObg Unit-1madhu.BNo ratings yet
- Cardiac EmergenciesDocument26 pagesCardiac Emergenciespreet kaurNo ratings yet
- Pentagon Review Royal PentagonDocument33 pagesPentagon Review Royal PentagonRichard Ines Valino99% (70)
- Patient 2Document4 pagesPatient 2api-595102974No ratings yet
- Patient 3 Imst AmboDocument4 pagesPatient 3 Imst Amboapi-595102974No ratings yet
- Patient 1 Imst AmboDocument4 pagesPatient 1 Imst Amboapi-595102974No ratings yet
- Patient 1Document4 pagesPatient 1api-595102974No ratings yet
- Patient 3Document4 pagesPatient 3api-595102974No ratings yet
- Nursing Case CadDocument26 pagesNursing Case CadShield DalenaNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument9 pagesChest PainIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Erm - All Files in OneDocument213 pagesErm - All Files in OneBryan GCNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument7 pagesCase ReportSela SumarniNo ratings yet
- Complex Regional Pain SyndromeDocument27 pagesComplex Regional Pain SyndromeKapil LakhwaraNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Assessment & Reasoning Cardiac SystemDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Assessment & Reasoning Cardiac SystemSharon TanveerNo ratings yet
- Case No. 2:: Chief ComplaintDocument10 pagesCase No. 2:: Chief ComplaintJayson TrajanoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care MCI CCU AssignmentDocument14 pagesCritical Care MCI CCU AssignmentTukiminNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument30 pagesChest PainLamya ZamanNo ratings yet
- Case Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNDocument5 pagesCase Study in Competency Appraisal II - ABC and EDNRogelio Saupan Jr100% (1)
- Case Study of Anterior Wall MI 48Document32 pagesCase Study of Anterior Wall MI 48سوما الشمريNo ratings yet
- A. A Sudden Change in How Brain Cells Send Electrical Signals To One AnotherDocument70 pagesA. A Sudden Change in How Brain Cells Send Electrical Signals To One AnotherMwansaay Twain HolyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Case Study Assignment 2023Document3 pagesNervous System Case Study Assignment 2023ariannaprice787No ratings yet
- Patient Diagnosed With Myocardial Infarct M006Document11 pagesPatient Diagnosed With Myocardial Infarct M006Kefix WritersHubNo ratings yet
- Unfolding Case Study-Hip FXDocument4 pagesUnfolding Case Study-Hip FXLiz GaskieNo ratings yet
- Group 13, Case 1 Neuro AssignmentDocument9 pagesGroup 13, Case 1 Neuro AssignmentRajat DeyNo ratings yet
- Dr. Farin's Grand Round Presentation 31.09.23Document75 pagesDr. Farin's Grand Round Presentation 31.09.23Anika TasnimNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Chest Pain in Primary Care Patients-AAFPDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Chest Pain in Primary Care Patients-AAFPnouval_iqbalNo ratings yet
- Case Study of BrucellaDocument20 pagesCase Study of BrucellaAseel ButmehNo ratings yet
- FPM FFPMRCA Example Questions 2016Document15 pagesFPM FFPMRCA Example Questions 2016hawraa tarhiniNo ratings yet
- Conference Paper: Rapid Physical Assessment of The Injured ChildDocument4 pagesConference Paper: Rapid Physical Assessment of The Injured ChildMaiush JbNo ratings yet
- CVS Physio Case Files p1Document4 pagesCVS Physio Case Files p1dawnparkNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medical Care For Trauma at The Pre-Hospital StageDocument125 pagesEmergency Medical Care For Trauma at The Pre-Hospital StageAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Emcase 04 Feb 2019 Dr. KometDocument56 pagesEmcase 04 Feb 2019 Dr. KometKomet Rama DaudNo ratings yet
- Medical English Presentation2Document17 pagesMedical English Presentation2N KNo ratings yet
- Single Ventricle MHI Belum SempurnaDocument30 pagesSingle Ventricle MHI Belum SempurnaMuhammad HidayatNo ratings yet
- T T A S: Hrombolytic Herapy in Cute TrokeDocument3 pagesT T A S: Hrombolytic Herapy in Cute TrokevivinNo ratings yet
- Ccu Case Study: Prepared By: AMEER JAMHOURDocument26 pagesCcu Case Study: Prepared By: AMEER JAMHOURYousef JafarNo ratings yet
- Making The Diagnosis of Cluster Headache: Vince Martin, MDDocument4 pagesMaking The Diagnosis of Cluster Headache: Vince Martin, MDAdinda NadiaNo ratings yet
- Im - RheumatologyDocument3 pagesIm - Rheumatologysnapb202No ratings yet
- Thomas 2021Document14 pagesThomas 2021Jonathan PanchiNo ratings yet
- MBChB4 5PastPapersDocument172 pagesMBChB4 5PastPapersHariharan NarendranNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz RegodosDocument4 pagesLong Quiz RegodosIan Cyrus RegodosNo ratings yet
- Hashim Major LogDocument26 pagesHashim Major LogHashim AlsammawiNo ratings yet
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Clinical GuideFrom EverandComplex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Clinical GuideErin F. LawsonNo ratings yet
- Sports Cardiology: Care of the Athletic Heart from the Clinic to the SidelinesFrom EverandSports Cardiology: Care of the Athletic Heart from the Clinic to the SidelinesDavid J. EngelNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Sports Recreational Satisfaction, and Involvement in Physical Activity Among Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM) StudentsDocument8 pagesThe Relationship Between Sports Recreational Satisfaction, and Involvement in Physical Activity Among Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM) StudentsIjahss JournalNo ratings yet
- Permit To Work DCPLDocument8 pagesPermit To Work DCPLRajat SonkarNo ratings yet
- TFN NotesDocument83 pagesTFN NotesBrianMarBeltranNo ratings yet
- Ed 508483Document187 pagesEd 508483awanaernestNo ratings yet
- Patient's Guide To TFCC InjuriesDocument10 pagesPatient's Guide To TFCC InjuriesLaineyNo ratings yet
- Penguard Primer: Technical DataDocument3 pagesPenguard Primer: Technical DataMohamed FarhanNo ratings yet
- Hart 1991Document6 pagesHart 1991Dana PascuNo ratings yet
- Burying The Dead The Philippines Silent Class WarDocument24 pagesBurying The Dead The Philippines Silent Class Warjulesniko23No ratings yet
- The STENTYS Self-Apposing® StentDocument3 pagesThe STENTYS Self-Apposing® StentRui FonteNo ratings yet
- Saving Lives and Saving MoneyDocument11 pagesSaving Lives and Saving MoneyDaniel MeloNo ratings yet
- A. Mabini ST., Malate 1004 Manila, Philippines - (632) 7087701 - WWW - Bsp.gov - PH - Bspmail@bsp - Gov.phDocument1 pageA. Mabini ST., Malate 1004 Manila, Philippines - (632) 7087701 - WWW - Bsp.gov - PH - Bspmail@bsp - Gov.phokto namikaNo ratings yet
- Ten CentersDocument4 pagesTen CentersJohn Christopher ReguindinNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Control of Intestinal SchistosomiasisDocument24 pagesEpidemiology and Control of Intestinal SchistosomiasisNafiu AliyuNo ratings yet
- Bmi Baseline Auto 2019-2020Document1 pageBmi Baseline Auto 2019-2020Angelo SinfuegoNo ratings yet
- Developing AN Entrepreneurial MindsetDocument12 pagesDeveloping AN Entrepreneurial MindsetMahnoor HameedNo ratings yet
- Res Ipsa Loquitor-Application in Medical Negligence: Journal of South India Medicolegal Association January 2014Document13 pagesRes Ipsa Loquitor-Application in Medical Negligence: Journal of South India Medicolegal Association January 2014Ian GreyNo ratings yet
- CA Oral CavityDocument53 pagesCA Oral Cavityaakash11No ratings yet
- 07 Crash Cart Medication - (App-Pha-007-V2)Document4 pages07 Crash Cart Medication - (App-Pha-007-V2)سلمىNo ratings yet
- 2nd SUMMATIVE 2019 in Science 3Document1 page2nd SUMMATIVE 2019 in Science 3Nash PerezNo ratings yet
- Rev B S10 AutosamplerDocument90 pagesRev B S10 AutosamplerevalenciaNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing in Dentistry!! A Dream or Reality??Document1 page3D Printing in Dentistry!! A Dream or Reality??aishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Why Use KYKO Personality TestDocument1 pageWhy Use KYKO Personality TestBernard Ah Thau TanNo ratings yet
- Kuang Yeu Medical Model FrontierDocument48 pagesKuang Yeu Medical Model FrontierSeyed Mohammad Hossein EmamiNo ratings yet
- PAGULAYAN, M - Week1ReflectionJournal109Document2 pagesPAGULAYAN, M - Week1ReflectionJournal109Marimiel PagulayanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Disease Anatomy and Phys Sheridan CollegeDocument7 pagesRespiratory Disease Anatomy and Phys Sheridan CollegeAudrey AndinoNo ratings yet