Professional Documents
Culture Documents
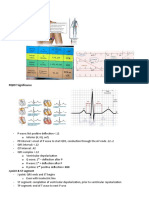
Normal R Wave - R Wave Height Gradually Increased Up To V4 and Then Decrease
Uploaded by
Nabighah Zukri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesOriginal Title
ecg notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesNormal R Wave - R Wave Height Gradually Increased Up To V4 and Then Decrease
Uploaded by
Nabighah ZukriCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
ECG NOTES
Normal R wave
-R wave height
gradually increased
up to V4 and then
decrease.
• Left ventricular • S in V1 + R in V5 or V6 > Causes of LVH :
hypertrophy 35mm
• R in aVL >11mm LV diastolic overload
-Mitral regurgitation
-Aortic regurgitation
-L-R shunt -VSD, PDA
LV systolic overload
-Systemic hypertension
-Aortic stenosis
-Coarctation of aorta
• Right ventricular Tall R in V1/V2 Differential diagnosis of tall R in
hypertrophy V1 :
-RBBB
-Dextrocardia
Normal cardiac axis
lies between -30 to
+90
• Left axis deviation • Lead I : R>S Causes of LAD :
(-30 to-90) • Lead III : S>R -LVH
-Left anterior hemiblock
-Inferior MI
• Right axis deviation • Lead I : S>R Causes of RAD :
(+90 to +180) • Lead III : R>S -RVH
-Pulmonary embolism
-Anterolateral MI
Normal P wave
-<0.12 sec in duration
-<2.5mm in height
• P mitrale of left atrial P wave become : Causes of P mitrale :
hypertrophy -M pattern -Mitral stenosis
-Biphasis -Mitral regurgitation
-Hypertension
• P pulmonale or right Tall and peaked P waves Causes of P pulmonale :
atrial hypertrophy -Pulmonary hypertension
-Cyanotic congenital heart
disease
• Atrial fibrillation Absent of P waves
• Complete heart block Dissociation between P waves
and QRS complex
PR interval
-0.12 to 0.5 sec in
duration
• 1st degree heart A prolonged PR interval
block implies delayed AV
conduction
• Wol-Parkinson-White • A short PR interval implies
syndrome fast AV conduction down an
accessory pathway
• Widened QRS complex
• Delta wave
QRS complex
-0.06 to 0.12 sec in
duration
• Pathological Q wave Q waves prolongation 0.04 s Causes of pathological Q wave :
and depression >25% R -transmural myocardial necrosis
• Pulmonary embolism • S in lead I
• Q wave in lead III
• T inversion in lead III
• Left bundle branch • M shaped QRS in lead V5/
block V6
• Wide QRS with loss of Q
wave resembling QS pattern
• Right bundle branch • M shaped QRS in lead V1/
block V2
• Wide S in lead I
ST segment
-isoelectric
• Ischemic changes • planar elevation >1mm OR
• planar depression > 0.5 mm
Hyperkalemia • Peaked T wave
• QRS widened
Hypokalemia • Flattened T wave
• U wave
Arrhythmia
• Supraventricular • Rate : 150-250 bpm
tachycadia • Rhythm : Regular
• P wave buried in preceding
T waves
• Normal QRS complex
• Atrial fibrillation Fibrillatory waves
• Atrial flutter Sawtooth pattern
• Ventricular • Wide QRS complex
tachycardia • Absent P wave
• Ventricular • Rate : 300-600 bpm
fibrillation • Rhythm : Extremely
irregular
• Absent P wave
Heart block
• First degree heart • One P wave per QRS
block complex
• Prolonged PR interval
• Second degree heart Progressive lengthening PR
block (Mobitz type interval
1)
• Second degree heart • Constant prolonged PR
block (Mobitz type 2) interval
• One P wave is not followed
by a QRS complex
• Second degree heart Two P waves per QRS
block (2:1 type) complex
• Complete heart block • P wave rate 90/min
• QRS complex rate 36/min
• No relationship between P
waves and QRS complexes.
You might also like
- MedicineDocument174 pagesMedicinewhoosh200895% (22)
- Electrocardiograms (Ecgs)Document86 pagesElectrocardiograms (Ecgs)nana wandhanaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiograms (Ecgs)Document80 pagesElectrocardiograms (Ecgs)heena solankiNo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument169 pagesElectrocardiogramjitendra magarNo ratings yet
- Technical AspectsDocument4 pagesTechnical AspectsNathan T. CheungNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG Interpretation GuideDocument61 pagesBasic ECG Interpretation GuideHayat Hamzah DawiNo ratings yet
- Dasar-Dasar Interpretasi EKGDocument61 pagesDasar-Dasar Interpretasi EKGFatmawati nersNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation DR - Rawan AlshreemDocument25 pagesECG Interpretation DR - Rawan AlshreemMarymii Al-sahlawiiNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument61 pagesBasic ECG InterpretationIndra ChristiantoNo ratings yet
- Read ECGDocument128 pagesRead ECGrehmatakuNo ratings yet
- Ecg Cheat Sheet 35Document2 pagesEcg Cheat Sheet 35jessjaylee80% (5)
- Topnotch ECG Interpretation For MoonlightersDocument25 pagesTopnotch ECG Interpretation For Moonlightersmefav7778520100% (1)
- ECG AbnormalDocument60 pagesECG Abnormalvidishmalaviya300No ratings yet
- Basic EKG 2: Dr. Wattana Wongtheptien M.D. Cardiologist Chiangrai Regional HospitalDocument79 pagesBasic EKG 2: Dr. Wattana Wongtheptien M.D. Cardiologist Chiangrai Regional HospitalVeerapong Vattanavanit0% (1)
- EKG Spot Diagnosis GuideDocument8 pagesEKG Spot Diagnosis GuideNote Sornkerd100% (1)
- EcgDocument6 pagesEcgMohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Abnormal ECG Findings ExplainedDocument26 pagesAbnormal ECG Findings ExplainedApriliani Nur Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Ws Ekg SakinahDocument40 pagesPresentasi Ws Ekg SakinahsiskaNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG Interpretation GuideDocument60 pagesBasic ECG Interpretation GuideLexadkNo ratings yet
- Cardiology/EKG Board Review: Michael J. Bradley D.O. DME/Program Director Family Medicine ResidencyDocument87 pagesCardiology/EKG Board Review: Michael J. Bradley D.O. DME/Program Director Family Medicine ResidencyummimalikihamidNo ratings yet
- Normal ECGDocument63 pagesNormal ECGMohd Johari Mohd ShafuwanNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument95 pagesECG InterpretationNur Rahmat Wibowo100% (9)
- Cardiocon ECG Workshop Basics of ECGDocument80 pagesCardiocon ECG Workshop Basics of ECGshazia kaziNo ratings yet
- ECG NotesDocument11 pagesECG NotesСео ЮнгааNo ratings yet
- 2019.02.04 - Dr. Alius - Basic ElectrocardiographyDocument104 pages2019.02.04 - Dr. Alius - Basic Electrocardiographyyohanes gabriel dwirianto w.aNo ratings yet
- ECG - Systematic-ApproachDocument12 pagesECG - Systematic-ApproachMicael MendesNo ratings yet
- Systematic Approach To ECGDocument12 pagesSystematic Approach To ECGAmr El TaherNo ratings yet
- ECG Study GuideDocument7 pagesECG Study GuideannaNo ratings yet
- ECG SummaryDocument57 pagesECG SummaryyenejeneparkNo ratings yet
- Common ECGsDocument40 pagesCommon ECGsTejwani MuskanNo ratings yet
- ECG Made Easy: A Guide to 12-Lead InterpretationDocument51 pagesECG Made Easy: A Guide to 12-Lead InterpretationElfha MonitaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal ECG 1Document26 pagesAbnormal ECG 1Apriliani Nur Puspita SariNo ratings yet
- Ekg Normal Dan Acs Sudin TimurDocument59 pagesEkg Normal Dan Acs Sudin TimurArum MaharaniNo ratings yet
- ECG and ArrythmiasDocument36 pagesECG and ArrythmiasMuhammad TajammalNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Guide: The 10 Key Steps for Reading EKGsDocument66 pagesEKG Interpretation Guide: The 10 Key Steps for Reading EKGsAltama L. SidartaNo ratings yet
- Basic EKG For DummiesDocument133 pagesBasic EKG For Dummieseduardocmoura86% (7)
- 15.2. ECG 2 (Chambers Enlargement)Document149 pages15.2. ECG 2 (Chambers Enlargement)mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument115 pagesECGBhakti WashilkarNo ratings yet
- Ecg Interpretation:: The BasicsDocument40 pagesEcg Interpretation:: The BasicsRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- THE NORMAL ELECTROCARDIOGRAM: DIAGNOSING MEDICAL PROBLEMS WITH AN ECGDocument63 pagesTHE NORMAL ELECTROCARDIOGRAM: DIAGNOSING MEDICAL PROBLEMS WITH AN ECGPuravin Crishan VeerasamyNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAMDocument63 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAMMbah GapinbissiNo ratings yet
- Approach To ECG PresentationDocument13 pagesApproach To ECG Presentationfck4wtgpckNo ratings yet
- Usage and Interpretation of 12-Lead ECGDocument49 pagesUsage and Interpretation of 12-Lead ECGEvelyne NatalieNo ratings yet
- Abnormal ECG Fadhly SharimanDocument55 pagesAbnormal ECG Fadhly SharimanFadhly SharimanNo ratings yet
- ECG Red BookDocument54 pagesECG Red BookHilbertHeungNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation of The Basics of EKGs From R Gentry Wilkerson. Uploaded 2015 PDFDocument102 pagesPowerpoint Presentation of The Basics of EKGs From R Gentry Wilkerson. Uploaded 2015 PDFVonAllenBatarioNo ratings yet
- Rudiments of ECGDocument101 pagesRudiments of ECGJacekNo ratings yet
- ECG Basics: An Overview of ElectrocardiographyDocument51 pagesECG Basics: An Overview of ElectrocardiographyJamuna PatelNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument40 pagesPDF DocumentsalikiqbalNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG Interpretation For CoassDocument61 pagesBasic ECG Interpretation For CoassSlamet Katib100% (1)
- Basics of Ecg: DR Shyama Assistant Professor General Medicine Aiims, PatnaDocument117 pagesBasics of Ecg: DR Shyama Assistant Professor General Medicine Aiims, PatnaSimran KothariNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesDocument58 pagesEKG Interpretation: UNC Emergency Medicine Medical Student Lecture SeriesrsadellaNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram: By:-Dr. Hina DangarDocument39 pagesElectrocardiogram: By:-Dr. Hina Dangarmahek lalaniNo ratings yet
- Bradi Si Tahi Cu Risc Vital FinalDocument67 pagesBradi Si Tahi Cu Risc Vital FinalAndreeaNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead ECG Intro To 12 Lead Ischemia Injury and Infarction 2022-2Document68 pages12 Lead ECG Intro To 12 Lead Ischemia Injury and Infarction 2022-2Ali GiriunasNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument198 pagesECGKatrina Maravilla100% (1)
- ECG - Doc 09Document11 pagesECG - Doc 09Rincy RajanNo ratings yet
- Ecg Abnormal 1-HpwDocument77 pagesEcg Abnormal 1-HpwAndre JuliantNo ratings yet
- Atrial and Ventricular EnlargementDocument47 pagesAtrial and Ventricular EnlargementNenyNo ratings yet
- PC AssessmentDocument6 pagesPC AssessmentNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Cerebral Palsy in ChildrenDocument5 pagesAssessing and Managing Cerebral Palsy in ChildrenNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Examination of HerniaDocument2 pagesExamination of HerniaNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- l8 Diabetes Melitus in PregnancyDocument23 pagesl8 Diabetes Melitus in PregnancyMohd Johari Mohd ShafuwanNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument9 pagesStrokeNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Management of Labor Pre Lecture QuesDocument1 pageManagement of Labor Pre Lecture QuesNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Mock Patient Record: Patient Management Record For Year 5 Clinical Posting Clerkship Patient ParticularsDocument9 pagesMock Patient Record: Patient Management Record For Year 5 Clinical Posting Clerkship Patient ParticularsNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Peripheral NerveDocument79 pagesPeripheral NerveNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Case Report 2Document7 pagesCase Report 2Nabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- End-Stage Renal Disease: by Jason KleinDocument11 pagesEnd-Stage Renal Disease: by Jason KleinNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation-Step by Step-Self AssessmentDocument2 pagesDefibrillation-Step by Step-Self AssessmentNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorders: BY: Pavithini Gopalan Priya Tharsini Shanaaz KhanDocument55 pagesEating Disorders: BY: Pavithini Gopalan Priya Tharsini Shanaaz KhanNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Disaster Surgery PlanningDocument50 pagesDisaster Surgery PlanningNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- BREAST CANCER MANAGEMENT GUIDEDocument50 pagesBREAST CANCER MANAGEMENT GUIDENabighah ZukriNo ratings yet
- Spine and Shoulder ExaminationDocument3 pagesSpine and Shoulder ExaminationNabighah ZukriNo ratings yet