Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IDS Guide: Intrusion Detection Systems Explained
Uploaded by
Gopi Chand reddy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesAn intrusion detection system monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and issues alerts when such activity is detected. It scans for harmful activity or policy violations and reports malicious activity to an administrator. Intrusion detection systems need to be tuned when first installed to recognize normal network traffic patterns and differentiate them from malicious activity to avoid false alarms. Intrusion detection systems are classified into network-based, host-based, protocol-based, application-based, and hybrid systems depending on their detection method and location. They can use signature-based or anomaly-based detection methods. Intrusion detection systems complement firewalls by monitoring for attacks from inside the network and alerting after an intrusion occurs.
Original Description:
Original Title
Intrusion Detection System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn intrusion detection system monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and issues alerts when such activity is detected. It scans for harmful activity or policy violations and reports malicious activity to an administrator. Intrusion detection systems need to be tuned when first installed to recognize normal network traffic patterns and differentiate them from malicious activity to avoid false alarms. Intrusion detection systems are classified into network-based, host-based, protocol-based, application-based, and hybrid systems depending on their detection method and location. They can use signature-based or anomaly-based detection methods. Intrusion detection systems complement firewalls by monitoring for attacks from inside the network and alerting after an intrusion occurs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesIDS Guide: Intrusion Detection Systems Explained
Uploaded by
Gopi Chand reddyAn intrusion detection system monitors network traffic for suspicious activity and issues alerts when such activity is detected. It scans for harmful activity or policy violations and reports malicious activity to an administrator. Intrusion detection systems need to be tuned when first installed to recognize normal network traffic patterns and differentiate them from malicious activity to avoid false alarms. Intrusion detection systems are classified into network-based, host-based, protocol-based, application-based, and hybrid systems depending on their detection method and location. They can use signature-based or anomaly-based detection methods. Intrusion detection systems complement firewalls by monitoring for attacks from inside the network and alerting after an intrusion occurs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
An
Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a system that monitors network traffic for
suspicious activity and issues alerts when such activity is discovered. It is a software
application that scans a network or a system for the harmful activity or policy
breaching. Any malicious venture or violation is normally reported either to an
administrator or collected centrally using a security information and event
management (SIEM) system. A SIEM system integrates outputs from multiple sources
and uses alarm filtering techniques to differentiate malicious activity from false
alarms.
Although intrusion detection systems monitor networks for potentially malicious
activity, they are also disposed to false alarms. Hence, organizations need to fine-tune
their IDS products when they first install them. It means properly setting up the
intrusion detection systems to recognize what normal traffic on the network looks like
as compared to malicious activity.
Intrusion prevention systems also monitor network packets inbound the system to
check the malicious activities involved in it and at once send the warning
notifications.
Classification of Intrusion Detection System:
IDS are classified into 5 types:
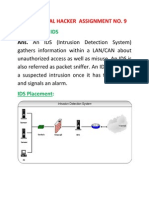
1. Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS):
Network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) are set up at a planned point within
the network to examine traffic from all devices on the network. It performs an
observation of passing traffic on the entire subnet and matches the traffic that is
passed on the subnets to the collection of known attacks. Once an attack is
identified or abnormal behavior is observed, the alert can be sent to the
administrator. An example of a NIDS is installing it on the subnet where firewalls
are located in order to see if someone is trying to crack the firewall.
2. Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS):
Host intrusion detection systems (HIDS) run on independent hosts or devices on
the network. A HIDS monitors the incoming and outgoing packets from the device
only and will alert the administrator if suspicious or malicious activity is detected.
It takes a snapshot of existing system files and compares it with the previous
snapshot. If the analytical system files were edited or deleted, an alert is sent to the
administrator to investigate. An example of HIDS usage can be seen on mission-
critical machines, which are not expected to change their layout.
3. Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (PIDS):
Protocol-based intrusion detection system (PIDS) comprises a system or agent that
would consistently resides at the front end of a server, controlling and interpreting
the protocol between a user/device and the server. It is trying to secure the web
server by regularly monitoring the HTTPS protocol stream and accept the related
HTTP protocol. As HTTPS is un-encrypted and before instantly entering its web
presentation layer then this system would need to reside in this interface, between
to use the HTTPS.
4. Application Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (APIDS):
Application Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (APIDS) is a system or
agent that generally resides within a group of servers. It identifies the intrusions
by monitoring and interpreting the communication on application-specific
protocols. For example, this would monitor the SQL protocol explicit to the
middleware as it transacts with the database in the web server.
5. Hybrid Intrusion Detection System :
Hybrid intrusion detection system is made by the combination of two or more
approaches of the intrusion detection system. In the hybrid intrusion detection
system, host agent or system data is combined with network information to
develop a complete view of the network system. Hybrid intrusion detection system
is more effective in comparison to the other intrusion detection system. Prelude is
an example of Hybrid IDS.
Detection Method of IDS:
1. Signature-based Method:
Signature-based IDS detects the attacks on the basis of the specific patterns such as
number of bytes or number of 1’s or number of 0’s in the network traffic. It also
detects on the basis of the already known malicious instruction sequence that is
used by the malware. The detected patterns in the IDS are known as signatures.
Signature-based IDS can easily detect the attacks whose pattern (signature) already
exists in system but it is quite difficult to detect the new malware attacks as their
pattern (signature) is not known.
2. Anomaly-based Method:
Anomaly-based IDS was introduced to detect unknown malware attacks as new
malware are developed rapidly. In anomaly-based IDS there is use of machine
learning to create a trustful activity model and anything coming is compared with
that model and it is declared suspicious if it is not found in model. Machine
learning-based method has a better-generalized property in comparison to
signature-based IDS as these models can be trained according to the applications
and hardware configurations.
Comparison of IDS with Firewalls:
IDS and firewall both are related to network security but an IDS differs from a firewall
as a firewall looks outwardly for intrusions in order to stop them from happening.
Firewalls restrict access between networks to prevent intrusion and if an attack is from
inside the network it doesn’t signal. An IDS describes a suspected intrusion once it has
happened and then signals an alarm.
You might also like
- CEH: Certified Ethical Hacker v11 : Exam Cram Notes - First Edition - 2021From EverandCEH: Certified Ethical Hacker v11 : Exam Cram Notes - First Edition - 2021No ratings yet
- Idms AdsoDocument156 pagesIdms Adsosambit_mech33% (3)
- Chapter 4 - Programming MethodologiesDocument5 pagesChapter 4 - Programming MethodologiesFreddy MutuaNo ratings yet
- Mock Test (Service Operation)Document4 pagesMock Test (Service Operation)Balaji Iyengar NarayananNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4TamannaNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument3 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemR. P. VermaNo ratings yet
- Section C Lecture 3Document16 pagesSection C Lecture 3Anushka NigamNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document19 pagesModule 5anandkumarshaw79923No ratings yet
- What are intrusion detection systemsDocument5 pagesWhat are intrusion detection systemsAbirami SekarNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument12 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemNew ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document20 pagesUnit 4Aniket Nsc0025No ratings yet
- Unit 5 IDSDocument11 pagesUnit 5 IDSYashNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System - WikipediaDocument15 pagesIntrusion Detection System - WikipediaHasnain Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Ids PDFDocument7 pagesIds PDFDASHRATH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument13 pagesIntrusion DetectionSharmila100% (1)
- Anomaly-Based IDS Methods ExplainedDocument14 pagesAnomaly-Based IDS Methods ExplainedhamidNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument13 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemMohamed Abdirahman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Intrustion Detection SystemDocument10 pagesIntrustion Detection SystemIsra CHNo ratings yet
- Information Security Assignment #4 FA19-BSE-401Document4 pagesInformation Security Assignment #4 FA19-BSE-401MOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFINo ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument4 pagesIntrusion DetectionSolomon AkpanNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Intrusion Detection System by TigerHATSDocument41 pagesAn Overview of Intrusion Detection System by TigerHATSTigerHATSNo ratings yet
- Seminar On IdsDocument17 pagesSeminar On IdsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- System For IntrusionDocument8 pagesSystem For IntrusionVictoria OdemakinNo ratings yet
- Case Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesCase Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemAnonymous tIi0h0No ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument29 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaVarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- CSC 411: IDS TypesDocument3 pagesCSC 411: IDS TypesCharles MasilaNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System: Submitted by Branch: Regn. No.Document16 pagesIntrusion Detection System: Submitted by Branch: Regn. No.preetam a rare dragonNo ratings yet
- Semi-Unsupervised Machine Learning IDSDocument2 pagesSemi-Unsupervised Machine Learning IDSBima PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Terminology: TypesDocument4 pagesTerminology: TypesAbhiteja AbhiNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument23 pagesIntrusion Detection Systemabhijitkakati100% (1)
- White Paper On Intrusion Detection and Intrusion PreventionDocument5 pagesWhite Paper On Intrusion Detection and Intrusion PreventiongynxNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document27 pagesUnit 519wj-1236 tejaswiNo ratings yet
- Your Network Is A Sitting Duck Without IDPDocument15 pagesYour Network Is A Sitting Duck Without IDPLucianBuzeaNo ratings yet
- Seminar IdsDocument19 pagesSeminar IdsudishaNo ratings yet
- Cse IdsDocument19 pagesCse IdsNarayan KunalNo ratings yet
- An Effective Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesAn Effective Intrusion Detection SystemmadhukedarNo ratings yet
- Host Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - Ver2Document23 pagesHost Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - Ver2Shaban MahekulaNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Different IDS: Rajiv GuptaDocument9 pagesA Comparative Study of Different IDS: Rajiv GuptaRajiv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Network Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Document4 pagesNetwork Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Âįmân ŚhêikhNo ratings yet
- IDS & FirewallsDocument10 pagesIDS & FirewallsPradyumna PadukoneNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III: Intrusion Detection System and Firewalls 1Document16 pagesUNIT-III: Intrusion Detection System and Firewalls 1VinayrajNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Technique (Idt) 4.1 Introduction To Intrusion Detection (ID)Document10 pagesIntrusion Detection Technique (Idt) 4.1 Introduction To Intrusion Detection (ID)Vaishali KodwalNo ratings yet
- NETWORK IDS DETECTS WEB APP ATTACKSDocument40 pagesNETWORK IDS DETECTS WEB APP ATTACKSPranjal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Surveillance"Document9 pagesNtroduction: Surveillance"aliov mezherNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053Document7 pagesAssignment-2 Introduction To Communication and Technology: (B-1) FA21-BCS-053KashifNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Hamid F20rinft1m01089 (2M) Firewall, Ids, IpsDocument7 pagesMuhammad Hamid F20rinft1m01089 (2M) Firewall, Ids, IpshamidNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)Document5 pagesDifference Between Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)afsfddasdNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument6 pagesNetworkingHD HDNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Unit 5Document12 pagesCyber Security Unit 5Amit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document15 pagesUnit 5Jil Poraskumar Bhatti -No ratings yet
- Distributed Host IDS Detects AttacksDocument6 pagesDistributed Host IDS Detects Attacksanand_gsoft3603No ratings yet
- IDS, Firewall & HoneypotDocument11 pagesIDS, Firewall & Honeypotanon_100036097100% (4)
- Introducing Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument14 pagesIntroducing Intrusion Detection SystemsTharun Reddy KuntollaNo ratings yet
- Network Intrusion Detection System Using Spark's Scalable Machine Learning LibraryDocument3 pagesNetwork Intrusion Detection System Using Spark's Scalable Machine Learning LibraryAnonymous lPvvgiQjRNo ratings yet
- Lect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsDocument28 pagesLect 6 Security of Network, Systems, ApplicationsZak RyderNo ratings yet
- A Method of Tracing Intruders by Use of Mobile AgentsDocument7 pagesA Method of Tracing Intruders by Use of Mobile Agentsaditya_kumar_meNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Current Computing Research Aimed at Improving Online Security: Intrusion Detection SystemDocument11 pagesEvaluation of Current Computing Research Aimed at Improving Online Security: Intrusion Detection SystemLame SegokgoNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument9 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemKRRISH MAHESHWARINo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Intrusion Detection: Network BasedDocument9 pagesUnit 5 Intrusion Detection: Network BasednateshwarkNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection: CS 432 - Computer and Network Security Sabancı UniversityDocument30 pagesIntrusion Detection: CS 432 - Computer and Network Security Sabancı UniversityKillerbeeNo ratings yet
- Is Unit5Document43 pagesIs Unit5Sudharsan BalaNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)-Domain 5From EverandCISA Exam-Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)-Domain 5No ratings yet
- Stand-Alone Lab: Router Basics Part II: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesStand-Alone Lab: Router Basics Part II: ObjectiveSrinivas KumarNo ratings yet
- Fusion - Oracle Fusion ArchitectureDocument2 pagesFusion - Oracle Fusion Architecturearni tkdcsNo ratings yet
- HP Fortify SCA GuideDocument23 pagesHP Fortify SCA GuideJennifer HansenNo ratings yet
- Vmware Backup User GuideDocument770 pagesVmware Backup User GuideKevin YuNo ratings yet
- Azure Services Periodic Table v1 1Document1 pageAzure Services Periodic Table v1 1Jairo AguirreNo ratings yet
- Declare Array in Stored ProcedureDocument11 pagesDeclare Array in Stored ProcedureNiño Francisco AlamoNo ratings yet
- Context Diagram and Level 0 Diagram of a School Grading SystemDocument3 pagesContext Diagram and Level 0 Diagram of a School Grading SystemIzza WrapNo ratings yet
- Kubernetes Deployment of a MySQL DatabaseDocument8 pagesKubernetes Deployment of a MySQL Databaseenamul whabNo ratings yet
- SAD 04 Quiz 01 Object Oriented Concepts ANSWERSDocument2 pagesSAD 04 Quiz 01 Object Oriented Concepts ANSWERSSab Janjua RajputNo ratings yet
- Qa ProcessDocument4 pagesQa ProcessMandyNo ratings yet
- Software Zebris For Ceramill en R1.2Document78 pagesSoftware Zebris For Ceramill en R1.2Viorel IonNo ratings yet
- CSIS 110 - Chapter 4Document82 pagesCSIS 110 - Chapter 4khattarNo ratings yet
- Auto Service Request For Systems Security White Paper: Oracle, Inc. Date: May 2012Document9 pagesAuto Service Request For Systems Security White Paper: Oracle, Inc. Date: May 2012acchacalNo ratings yet
- I DocsDocument22 pagesI DocssirajsamadNo ratings yet
- Data Models & Relational Model CharacteristicsDocument56 pagesData Models & Relational Model CharacteristicsYuvaraj ElsusNo ratings yet
- DW Concepts ShivaDocument32 pagesDW Concepts ShivaJohn Perry ENo ratings yet
- SE Unit-3 Requirement Analysis (New)Document27 pagesSE Unit-3 Requirement Analysis (New)121 Kanani AjayNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Shop Management System (VSMSDocument5 pagesVegetable Shop Management System (VSMSJ MANJUSREENo ratings yet
- MQTT Library RevEDocument50 pagesMQTT Library RevEigNo ratings yet
- 10.6.11 Lab - Use Tera Term To Manage Router Configuration FilesDocument5 pages10.6.11 Lab - Use Tera Term To Manage Router Configuration FilesJoel DolotNo ratings yet
- Information Security & Risk ManagementDocument4 pagesInformation Security & Risk Managementarpan mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Org Chart Templates - HubSpotDocument8 pagesOrg Chart Templates - HubSpotVeanney CoNo ratings yet
- URS FI-AP-BT-16-01 Payment CreationDocument6 pagesURS FI-AP-BT-16-01 Payment CreationNisha MayurNo ratings yet
- Hacking Web SQL Injection PDFDocument3 pagesHacking Web SQL Injection PDFFernandoNo ratings yet
- Hibernate by Raghu SirDocument202 pagesHibernate by Raghu SirSaiKumar parate67% (3)
- SAP Practice Update May 2008Document8 pagesSAP Practice Update May 2008saichanduNo ratings yet
- Cherian Thomas Resume - IT Engineer Seeking New RoleDocument4 pagesCherian Thomas Resume - IT Engineer Seeking New RolenaveedahmedkwNo ratings yet