Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Information Security Assignment #4 FA19-BSE-401
Uploaded by
MOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesAn intrusion detection system (IDS) monitors network traffic and alerts administrators of potential malicious activity. There are several types of IDS: network IDS monitors traffic across an entire subnet; host IDS monitors individual devices; protocol-based IDS oversees communication protocols to servers; application protocol IDS focuses on application layers. A hybrid IDS combines approaches for comprehensive detection. Each type has distinct focus, scope, and methods making them suitable to different network security needs.
Original Description:
Original Title
information security Assignment #4 FA19-BSE-401
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn intrusion detection system (IDS) monitors network traffic and alerts administrators of potential malicious activity. There are several types of IDS: network IDS monitors traffic across an entire subnet; host IDS monitors individual devices; protocol-based IDS oversees communication protocols to servers; application protocol IDS focuses on application layers. A hybrid IDS combines approaches for comprehensive detection. Each type has distinct focus, scope, and methods making them suitable to different network security needs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views4 pagesInformation Security Assignment #4 FA19-BSE-401
Uploaded by
MOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFIAn intrusion detection system (IDS) monitors network traffic and alerts administrators of potential malicious activity. There are several types of IDS: network IDS monitors traffic across an entire subnet; host IDS monitors individual devices; protocol-based IDS oversees communication protocols to servers; application protocol IDS focuses on application layers. A hybrid IDS combines approaches for comprehensive detection. Each type has distinct focus, scope, and methods making them suitable to different network security needs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
information security
ASSIGNMENT # 4
DECEMBER 11, 2023
MOHAMMAD EMAL
FA19-BSE-401
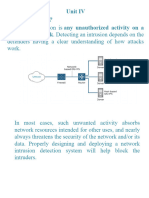
Intrusion Detection System:
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a security mechanism designed to observe network traffic
and promptly alert administrators to potential malicious activities. Functioning as software, an
IDS analyzes data traversing the network to detect abnormal patterns and behaviors. The system
employs predefined rules and patterns to compare network activities, aiming to identify any
signs of attacks or unauthorized intrusions. Upon detecting a match with these patterns, the IDS
issues an alert to the system administrator, who can then investigate and take appropriate
actions to mitigate potential damage or prevent further intrusion.
Type of intrusion Detection System
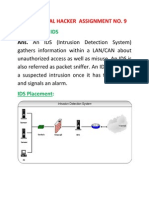
1. Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS):
NIDS is strategically placed within the network to monitor traffic from all connected devices.
It observes the entire subnet's passing traffic, comparing it to a database of known attacks.
When an attack or abnormal behavior is detected, an alert is sent to the administrator.
Example: Installation on the subnet where firewalls are located to detect attempts to
compromise the firewall.
2. Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS):
HIDS operates on individual hosts or devices within the network.
It monitors incoming and outgoing packets specific to the host, triggering an alert for suspicious
or malicious activity.
HIDS takes snapshots of system files and compares them, sending an alert if changes are
detected.
Example: Implementation on critical machines where the system layout is not expected to
change.
3. Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (PIDS):
PIDS resides at the front end of a server, overseeing and interpreting the protocol between a
user/device and the server.
It focuses on securing web servers by monitoring protocols like HTTPS and HTTP.
Example: Monitoring HTTPS traffic by residing between the user and the web server.
4. Application Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (APIDS):
APIDS typically resides within a group of servers, identifying intrusions by monitoring and
interpreting application-specific protocols.
It may, for instance, monitor the SQL protocol as transactions occur between middleware and
the database.
5. Hybrid Intrusion Detection System:
The Hybrid IDS combines two or more approaches to enhance overall intrusion detection
effectiveness.
It integrates host agent or system data with network information to provide a comprehensive
view of the network.
Example: Prelude serves as a Hybrid IDS, leveraging multiple detection methods for improved
security.
Differentiate among different types of intrusion detection systems.
1. Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS):
Focus: Monitors network traffic at a specific point within the network.
Scope: Examines traffic from all devices on the network.
Detection Method: Analyzes passing traffic on the entire subnet, comparing it to known attack
patterns.
Example Scenario: Installed on the subnet where firewalls are located to detect attempts to
breach the firewall.
2. Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS):
Focus: Monitors activities on individual hosts or devices.
Scope: Observes incoming and outgoing packets from the host it's installed on.
Detection Method: Compares snapshots of system files to identify changes indicating suspicious
or malicious activity.
Example Scenario: Used on mission-critical machines that are not expected to undergo
significant changes.
3. Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (PIDS):
Focus: Controls and interprets communication protocols between users/devices and servers.
Scope: Resides at the front end of a server, monitoring and interpreting protocols.
Detection Method: Regularly monitors specific protocols (e.g., HTTPS) to ensure the security of
the communication stream.
Example Scenario: Monitors the unencrypted HTTPS protocol stream before entering the web
presentation layer.
4. Application Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (APIDS):
Focus: Monitors and interprets communication on application-specific protocols.
Scope: Resides within a group of servers, identifying intrusions based on application-specific
protocols.
Detection Method: Monitors protocols such as SQL explicitly as they transact with databases in
the web server.
Example Scenario: Focuses on monitoring communication specific to the middleware and
database transactions.
5. Hybrid Intrusion Detection System:
Focus: Combines two or more approaches to intrusion detection.
Scope: Integrates both host-level and network-level information for a comprehensive view.
Detection Method: Utilizes a combination of host agent/system data and network information.
Example Scenario: Prelude is cited as an example, showcasing the effectiveness of combining
different intrusion detection approaches.
each type of IDS has its unique focus, scope, and detection methods, making them suitable for
different scenarios based on the specific security needs and network architecture of an
organization. Hybrid IDS, by combining multiple approaches, aims to provide a more robust and
comprehensive solution.
You might also like
- CISA Exam-Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)-Domain 5From EverandCISA Exam-Intrusion Detection System (IDS) & Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)-Domain 5No ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument2 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemGopi Chand reddyNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument3 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemR. P. VermaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4TamannaNo ratings yet
- Section C Lecture 3Document16 pagesSection C Lecture 3Anushka NigamNo ratings yet
- IntrudersDocument25 pagesIntruderskaushalnishant64No ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument48 pagesUnit IVYogita TiwariNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument23 pagesIntrusion Detection Systemabhijitkakati100% (1)
- What Are Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument5 pagesWhat Are Intrusion Detection SystemsAbirami SekarNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection System - WikipediaDocument15 pagesIntrusion Detection System - WikipediaHasnain Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document20 pagesUnit 4Aniket Nsc0025No ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument4 pagesIntrusion DetectionSolomon AkpanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 IDSDocument11 pagesUnit 5 IDSYashNo ratings yet
- Nama: Muhammad Bima Prasetyo NIM: 201250000354 Prodi: Information SystemDocument2 pagesNama: Muhammad Bima Prasetyo NIM: 201250000354 Prodi: Information SystemBima PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Case Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesCase Study Based On Intrusion Detection SystemAnonymous tIi0h0No ratings yet
- Terminology: TypesDocument4 pagesTerminology: TypesAbhiteja AbhiNo ratings yet
- IDPSDocument12 pagesIDPSمطيع برهومNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument12 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemNew ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document27 pagesUnit 519wj-1236 tejaswiNo ratings yet
- System For IntrusionDocument8 pagesSystem For IntrusionVictoria OdemakinNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection Tolerance Prevention System: TitleDocument6 pagesIntrusion Detection Tolerance Prevention System: Titleparul_purohitNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document19 pagesModule 5anandkumarshaw79923No ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Different IDS: Rajiv GuptaDocument9 pagesA Comparative Study of Different IDS: Rajiv GuptaRajiv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Surveillance"Document9 pagesNtroduction: Surveillance"aliov mezherNo ratings yet
- Seminar On IdsDocument17 pagesSeminar On IdsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- Risk Control StrategyDocument10 pagesRisk Control StrategyRubyNo ratings yet
- Volume 4 Issue 3 IJAIEM - Repaired - PDFDocument131 pagesVolume 4 Issue 3 IJAIEM - Repaired - PDFInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection and Prevention System: Varun GuptaVarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Network Security DesignDocument5 pagesNetwork Security DesignMahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Hamid F20rinft1m01089 (2M) Firewall, Ids, IpsDocument7 pagesMuhammad Hamid F20rinft1m01089 (2M) Firewall, Ids, IpshamidNo ratings yet
- Intrusion DetectionDocument13 pagesIntrusion DetectionSharmila100% (1)
- White Paper On Intrusion Detection and Intrusion PreventionDocument5 pagesWhite Paper On Intrusion Detection and Intrusion PreventiongynxNo ratings yet
- Cse IdsDocument19 pagesCse IdsNarayan KunalNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument13 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemMohamed Abdirahman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Network Behavior-Analysis Systems With The Use of Learning Set and Decision Rules Based On DistanceDocument12 pagesNetwork Behavior-Analysis Systems With The Use of Learning Set and Decision Rules Based On DistanceThanh Mon100% (1)
- Intrusion Detection: CS 432 - Computer and Network Security Sabancı UniversityDocument30 pagesIntrusion Detection: CS 432 - Computer and Network Security Sabancı UniversityKillerbeeNo ratings yet
- Ids/IpsDocument7 pagesIds/Ipszaiby41No ratings yet
- CSC 411: Computer Network Security: Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument3 pagesCSC 411: Computer Network Security: Intrusion Detection SystemsCharles MasilaNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2023-24 BCSE353E ETH VL2023240100850 2023-06-03 Reference-Material-IDocument27 pagesFALLSEM2023-24 BCSE353E ETH VL2023240100850 2023-06-03 Reference-Material-Idsa dsaNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Web-SecurityDocument21 pagesUnit-5 Web-SecurityJay ZalaNo ratings yet
- IDS, Firewall & HoneypotDocument11 pagesIDS, Firewall & Honeypotanon_100036097100% (4)
- 01-2020 DL CNNDocument17 pages01-2020 DL CNNSayeed HabeebNo ratings yet
- Host Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - Ver2Document23 pagesHost Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) - Ver2Shaban MahekulaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Current Computing Research Aimed at Improving Online Security: Intrusion Detection SystemDocument11 pagesEvaluation of Current Computing Research Aimed at Improving Online Security: Intrusion Detection SystemLame SegokgoNo ratings yet
- Network Defense 14gDocument36 pagesNetwork Defense 14gBolaji WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Ids PDFDocument7 pagesIds PDFDASHRATH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Weaknesses, Vulnerabilities and Elusion Strategies Against Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument11 pagesWeaknesses, Vulnerabilities and Elusion Strategies Against Intrusion Detection SystemsijcsesNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Review On Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument4 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Intrusion Detection SystemsSreenath MuraliNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument29 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemsDrushti DesaiNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection SystemDocument5 pagesIntrusion Detection SystemArchana AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Network Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Document4 pagesNetwork Security Assignment: Submitted To: Ma'am Komal Name: Aiman Rizwan Roll No: Info-Tech 16010 BS-IT (8)Âįmân ŚhêikhNo ratings yet
- Ids and IpsecDocument14 pagesIds and IpsecMahesh ThosarNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III: Intrusion Detection System and Firewalls 1Document16 pagesUNIT-III: Intrusion Detection System and Firewalls 1VinayrajNo ratings yet
- Cis300 Assignment1 09 Ajay Balami C30105210041Document9 pagesCis300 Assignment1 09 Ajay Balami C30105210041Sulav BalamiNo ratings yet
- Optimized Intrusion Detection System Using Deep Learning AlgorithmDocument8 pagesOptimized Intrusion Detection System Using Deep Learning AlgorithmPremavathiDamodharan100% (1)
- Intruders and Viruses-Definitive Guide PDFDocument37 pagesIntruders and Viruses-Definitive Guide PDFGhanshyam ShahNo ratings yet
- An Agent-Based Intrusion Detection SystemDocument6 pagesAn Agent-Based Intrusion Detection Systemanand_gsoft3603No ratings yet
- Ids PrimerDocument5 pagesIds PrimermathurashwaniNo ratings yet
- Is Unit5Document43 pagesIs Unit5Sudharsan BalaNo ratings yet
- Cypress Testing ToolDocument15 pagesCypress Testing ToolMOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFINo ratings yet
- SPM Lab Assignment # 3Document8 pagesSPM Lab Assignment # 3MOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFINo ratings yet
- Introduction To SociologyDocument19 pagesIntroduction To SociologyMOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Socialogy FA19-BSE-401Document4 pagesIntroduction To Socialogy FA19-BSE-401MOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFINo ratings yet
- COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Sessional I Examination - Semester Spring 2021Document2 pagesCOMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Sessional I Examination - Semester Spring 2021MOHAMMAD EMAL ZARIFINo ratings yet
- Philips 90rc328 90rc348 90rc388 SMDocument53 pagesPhilips 90rc328 90rc348 90rc388 SMZé Pontes DetCordNo ratings yet
- 10 Best Computer Networking Books For Beginners & ExpertsDocument16 pages10 Best Computer Networking Books For Beginners & ExpertsShanta WalkerNo ratings yet
- CN Assignment QuestionsDocument2 pagesCN Assignment Questions1js20ec036ksspoorthiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microstrip AntennasDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Microstrip AntennasSumeet SainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SociDocument39 pagesChapter 1 SociSonal Bandaware18No ratings yet
- Quickstart Guide of OpenVox GSM Gateway WGW1002G Connect With Asterisk ServerDocument4 pagesQuickstart Guide of OpenVox GSM Gateway WGW1002G Connect With Asterisk ServergermanNo ratings yet
- Bugcrowd Vulnerability Rating Taxonomy 1Document14 pagesBugcrowd Vulnerability Rating Taxonomy 1api-521939833No ratings yet
- Direct-Detection 25 GB/S Pon: Pros and Cons of Digital Signal Processing at The Transmitter SideDocument4 pagesDirect-Detection 25 GB/S Pon: Pros and Cons of Digital Signal Processing at The Transmitter SideElsaid SayedAhmedNo ratings yet
- History of Cable, Home Video, and The InternetDocument37 pagesHistory of Cable, Home Video, and The InternetAhmed BakirNo ratings yet
- B CSRGCP Chapter 00Document4 pagesB CSRGCP Chapter 00Juan RojasNo ratings yet
- Motorola IMS ApplicationsDocument8 pagesMotorola IMS ApplicationsJesus DominguezNo ratings yet
- Information Security Lab ManualDocument63 pagesInformation Security Lab ManualrishabhNo ratings yet
- Fortinet Product MatrixDocument4 pagesFortinet Product MatrixBayu AlamNo ratings yet
- CarbonCopyAgentHelp PDFDocument36 pagesCarbonCopyAgentHelp PDFgsocheNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document44 pagesUnit 2Kanimozhi Suguna SNo ratings yet
- Audio System For A Passenger Cabin of An AircraftDocument11 pagesAudio System For A Passenger Cabin of An Aircraftbo pengNo ratings yet
- 31.parametric Study of Vivaldi AntennaDocument4 pages31.parametric Study of Vivaldi AntennaAlteea MareNo ratings yet
- DASABCIPDocument234 pagesDASABCIPericNo ratings yet
- IA Series® Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)Document8 pagesIA Series® Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)Wisnu Hartono100% (1)
- Expt 8a-Study and Analysis of Hidden Terminal Problem in WLAN Using NetsimDocument5 pagesExpt 8a-Study and Analysis of Hidden Terminal Problem in WLAN Using NetsimKritika VermaNo ratings yet
- Audio SteganographyDocument17 pagesAudio SteganographyRashmitha ThallapelliNo ratings yet
- Open ROADM Network Model Whitepaper v1 1 PDFDocument45 pagesOpen ROADM Network Model Whitepaper v1 1 PDFAyman SeaudiNo ratings yet
- Export Call Report 20140919-235047Document982 pagesExport Call Report 20140919-235047Datta ForofficeNo ratings yet
- CS601 Assignment 1 SolutionDocument3 pagesCS601 Assignment 1 SolutionNo NameNo ratings yet
- CMTS1500 - ErrorCodes - v43Document126 pagesCMTS1500 - ErrorCodes - v43eb1200No ratings yet
- Ericsson rbs6000 Base Station BST Ericsson Rbs Telecom Equipment-97178383 PDFDocument3 pagesEricsson rbs6000 Base Station BST Ericsson Rbs Telecom Equipment-97178383 PDFHaKa100% (1)
- Configure Microphone and Setting Speaker Levels For Measurements in Dirac Live 2Document4 pagesConfigure Microphone and Setting Speaker Levels For Measurements in Dirac Live 2studskirbyNo ratings yet
- E85014-0003 - EST4 Remote AnnunciatorsDocument9 pagesE85014-0003 - EST4 Remote AnnunciatorsDhaval ChitaraNo ratings yet
- Mini-IoT 910T v1 2Document2 pagesMini-IoT 910T v1 2Anonymous zFkWvyTNo ratings yet
- Brother Internet Fax User GuideDocument67 pagesBrother Internet Fax User GuideJonathan BatesNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxFrom EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (67)
- Network+ Study Guide & Practice ExamsFrom EverandNetwork+ Study Guide & Practice ExamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- ITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideNo ratings yet
- CWNA Certified Wireless Network Administrator Study Guide: Exam CWNA-108From EverandCWNA Certified Wireless Network Administrator Study Guide: Exam CWNA-108No ratings yet
- Cybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityFrom EverandCybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNFrom EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Palo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsFrom EverandPalo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationFrom EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringFrom EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.From EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)From EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Networking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366From EverandNetworking Fundamentals: Develop the networking skills required to pass the Microsoft MTA Networking Fundamentals Exam 98-366No ratings yet
- Rick Gallahers MPLS Training Guide: Building Multi Protocol Label Switching NetworksFrom EverandRick Gallahers MPLS Training Guide: Building Multi Protocol Label Switching NetworksRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C01 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C01 ExamRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)