Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inverse PCR
Uploaded by
hasna muhadzib0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageOriginal Title
inverse PCR
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageInverse PCR
Uploaded by
hasna muhadzibCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
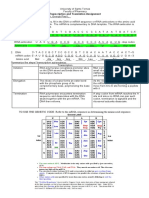
- inverse PCR uses for amplifying the DNA sequence that is still unknown
- RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism)
- polymorphism = many-shaped/differences among people in their DNA seq at sites recognized by
restriction enzymes
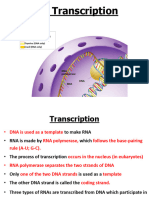
- RT-PCR (reverse transcriptase)
- more mRNA, more expression (e.g., if gene RED has less mRNA than gene BLUE and the inheritors will
become more blue, bcs blue gene carried by more proteins)
- cDNA is DNA that has RNA converted back into DNA copy
- mRNA : 5’-AUG GUC-3’
- cDNA : 3’-TAC CAG-5’ (complementary to mRNA)
- purpose of RT-PCR : to understand the mRNA, to make intron free DNA to manipulate
- in the electrophoresis, DNA is negative and should be run into positive (red wire) and opposite with the
positive (black wire)
- the more the RNA, the thicker the band it will be
- up regulated : more expression, down regulated : less expressed
- Differential Display PCR : combination of RAPD & RT-PCR
- oligo(dT) primers is used to amplified sequence
- the random primer, bcs of it is the mixture primer it will bind in somewhere in the mRNA
- compare the bands (e.g., smoker and non-smoker genes) and there will be some genes missing in the
non-smoker genes, which are appear in the smoker genes (bands). the genes for the smoker is up
regulating, so the bands could be cut-off and use the RT-PCR or qualitative PCR to know the sequence.
- RACE is used to rescue the lost ends of clone genes
- anchor sequence
- hybrid gene : bind overlap primers
- directed mutagenesis
- mismatch in the primer will make a bump
- bp = base pairs
- site directed mutations = mismatch in the primer
- AUC CGU GCU -> ile arg ala
- AUC ACG UGC U -> ile thr cys
- a one insertion could make the whole codons changed
You might also like
- PCR Based Molecualr, Genetic MarkersDocument59 pagesPCR Based Molecualr, Genetic MarkersRafay MirzaNo ratings yet
- PCR Amplification Lab ReportDocument5 pagesPCR Amplification Lab ReportWilson Chan100% (7)
- Dogma SentraDocument46 pagesDogma SentraindahonlyNo ratings yet
- Rna Isolation and PurificationDocument62 pagesRna Isolation and PurificationBio BookNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document67 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Derick SemNo ratings yet
- Expression ProfilingDocument8 pagesExpression ProfilingSreedurgalakshmi KNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument3 pagesPolymerase Chain ReactionShahriar ShamimNo ratings yet
- Ritobrata Goswami: Email: Tel: 03222-284570Document44 pagesRitobrata Goswami: Email: Tel: 03222-284570Ashmit RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.3 - Protein SynthesisDocument107 pagesChapter 6.3 - Protein Synthesisnie20060301No ratings yet
- Review: Quantitative RT-PCR: Pitfalls and PotentialDocument12 pagesReview: Quantitative RT-PCR: Pitfalls and PotentialGisele HolandaNo ratings yet
- Inverse Polymerase Chain Reaction (Inverse PCR) Is A Variant of TheDocument8 pagesInverse Polymerase Chain Reaction (Inverse PCR) Is A Variant of TheNiraj Agarwal100% (1)
- PCR, RT-PCR, Nested-Pcr, Multiplex PCR, Quantitative PCRDocument116 pagesPCR, RT-PCR, Nested-Pcr, Multiplex PCR, Quantitative PCRYunizardiNo ratings yet
- RNA Sequencing: An Introduction To Efficient Planning and Execution of RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) ExperimentsDocument6 pagesRNA Sequencing: An Introduction To Efficient Planning and Execution of RNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) ExperimentsnareshNo ratings yet
- Method and Result:: 2.1. Sg-RNA DesigningDocument9 pagesMethod and Result:: 2.1. Sg-RNA DesigningMasum Billah TuhinNo ratings yet
- Development of A Rapid and Inexpensive Method To Reveal Natural Antisense TranscriptsDocument8 pagesDevelopment of A Rapid and Inexpensive Method To Reveal Natural Antisense Transcriptschandran.vkrsdNo ratings yet
- Transcription: Department of Biochemistry Susan B. Caceres-Tengco, M.DDocument40 pagesTranscription: Department of Biochemistry Susan B. Caceres-Tengco, M.DLen ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Transcription: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemisty, Ph.D.Research ScholarDocument33 pagesTranscription: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemisty, Ph.D.Research ScholarDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Mol Breed - 2Document20 pagesMol Breed - 2Sukanta RoyNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Tole S.B. Asst. Prof. K.T.Patil College of Pharmacy, OsmanabadDocument22 pagesMrs. Tole S.B. Asst. Prof. K.T.Patil College of Pharmacy, OsmanabadShobha Tole100% (2)
- CLC Genetics Chapter 3Document51 pagesCLC Genetics Chapter 3Châu Anh TrầnNo ratings yet
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 SlidesDocument40 pages2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Slidesaidar.seralinNo ratings yet
- 2016-RNAseq-The Impact of Amplification On Diferential Expresion Analyses by RNA-seqDocument11 pages2016-RNAseq-The Impact of Amplification On Diferential Expresion Analyses by RNA-seqAntarToumaNo ratings yet
- Restriction Enzyme (Restriction Endonuclease)Document18 pagesRestriction Enzyme (Restriction Endonuclease)yusuf zihniNo ratings yet
- Contamination Proof-Reading: Mplification Ensitivity Pecificity Obustness Utomation Ell-Free Method Ase of Set-UpDocument4 pagesContamination Proof-Reading: Mplification Ensitivity Pecificity Obustness Utomation Ell-Free Method Ase of Set-UpSheila ChaiNo ratings yet
- GPB Notes part-IIDocument37 pagesGPB Notes part-IIChannabasavaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Biotechnology: Amplified Fragment Length PolymorphismDocument19 pagesAdvanced Biotechnology: Amplified Fragment Length PolymorphismTeflon SlimNo ratings yet
- T-ARMS PCR Genotyping of SNP rs445709131 Using Thermostable Strand Displacement PolymeraseDocument5 pagesT-ARMS PCR Genotyping of SNP rs445709131 Using Thermostable Strand Displacement PolymeraseAhmad SolihinNo ratings yet
- Transcription Notes Class 12Document9 pagesTranscription Notes Class 12Meeta BiswasNo ratings yet
- MB Chapter 5 TranscriptionDocument32 pagesMB Chapter 5 TranscriptionMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dna-Rna AamDocument25 pagesStruktur Dna-Rna AamMila DamayantiNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument31 pagesTranscriptionParth ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - Molecular MethodsDocument29 pagesChapter 13 - Molecular MethodsYoiceMartinaPawekaNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 5Document38 pages11 Chapter 5toobashafiNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression AssignmentDocument5 pagesGene Expression AssignmentLauren EatonNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation NarrativeDocument3 pagesTranscription and Translation NarrativeBridget Anne BenitezNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation AssignmentDocument2 pagesTranscription and Translation AssignmentPaul LucasNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: ADA School Biology DepartmentDocument27 pagesProtein Synthesis: ADA School Biology DepartmentAydan BadalliNo ratings yet
- CDU BIOINFORMATICS The Central DogmaDocument6 pagesCDU BIOINFORMATICS The Central DogmaKrisha Mae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: DNA Is The Genetic Material RNADocument49 pagesNucleic Acids: DNA Is The Genetic Material RNAAaron CzikNo ratings yet
- Promoters and Plasmids PDFDocument4 pagesPromoters and Plasmids PDFAndika MardiantoNo ratings yet
- G (12) Ls Life Science 2020-2021 Revision Sheet: 3 Photosynthesis Part-2Document3 pagesG (12) Ls Life Science 2020-2021 Revision Sheet: 3 Photosynthesis Part-2Joelle AssafNo ratings yet
- Park Et Al. 2014Document8 pagesPark Et Al. 2014Benedikt EngelNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression 1Document28 pagesGene Expression 1ha88ial88No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of RT-QPCR - Thermo Fisher ScienDocument4 pagesBasic Principles of RT-QPCR - Thermo Fisher Scienعلي سرحان عليوي عليبNo ratings yet
- Corona VirusDocument6 pagesCorona VirusCourtny Lenz Maygay GapaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Retno Sutomo, PH.D, Sp.ADocument37 pagesDr. Retno Sutomo, PH.D, Sp.ADoni RevaiNo ratings yet
- GP Notes Unit 2&4Document1 pageGP Notes Unit 2&4Ponni ChandranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Nucleic Acid AmplificationDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Nucleic Acid AmplificationIsraa Al-AlemNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument34 pagesTranscriptiondrhydrogenNo ratings yet
- Transcription Is The First Step in Gene Expression. It InvolvesDocument8 pagesTranscription Is The First Step in Gene Expression. It InvolvesrendezvousfrNo ratings yet
- TranscriptionDocument13 pagesTranscriptionbiochemNo ratings yet
- Rapd - Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA: Remember! in Order For PCR To OccurDocument2 pagesRapd - Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA: Remember! in Order For PCR To OccurKimNo ratings yet
- Meredith Barb Homework-2 (25 Points) Due On Sept. 24 by 5:00pmDocument5 pagesMeredith Barb Homework-2 (25 Points) Due On Sept. 24 by 5:00pmMeredith BarbNo ratings yet
- The Polymerase Chain Reaction and Sequence-Tagged SitesDocument7 pagesThe Polymerase Chain Reaction and Sequence-Tagged SitesPisi MicaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Assessment: Concentration's Increment in Case of Insert and LigaseDocument8 pagesContinuous Assessment: Concentration's Increment in Case of Insert and LigaseDebapriya HazraNo ratings yet
- Correct BaseDocument2 pagesCorrect BaseRobotrixNo ratings yet
- Deep Cap Analysis Gene Expression (CAGE) : Genome-Wide Identification of Promoters, Quantifi-Cation of Their Expression, and Network InferenceDocument4 pagesDeep Cap Analysis Gene Expression (CAGE) : Genome-Wide Identification of Promoters, Quantifi-Cation of Their Expression, and Network InferenceAaNo ratings yet
- Full-Length cDNA Cloning and Determination of mRNA 5 and 3 Ends by Amplification of Adaptor-Ligated cDNADocument9 pagesFull-Length cDNA Cloning and Determination of mRNA 5 and 3 Ends by Amplification of Adaptor-Ligated cDNADiksha GahlotNo ratings yet
- DNA Methods in Food Safety: Molecular Typing of Foodborne and Waterborne Bacterial PathogensFrom EverandDNA Methods in Food Safety: Molecular Typing of Foodborne and Waterborne Bacterial PathogensNo ratings yet
- Dna AmplificationDocument1 pageDna Amplificationhasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- Neuro SystemDocument1 pageNeuro Systemhasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- ReovirusesDocument1 pageReoviruseshasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesMuscular Systemhasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- OncolyticDocument14 pagesOncolytichasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- Cancer JournalDocument14 pagesCancer Journalhasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- Cancer JournalDocument6 pagesCancer Journalhasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- Cancer JournalDocument13 pagesCancer Journalhasna muhadzibNo ratings yet
- Jcav 13 P 0051Document11 pagesJcav 13 P 0051hasna muhadzibNo ratings yet