Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Legal Issues in Marketing: Personal Data
Legal Issues in Marketing: Personal Data
Uploaded by
Mare AndradeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Legal Issues in Marketing: Personal Data
Legal Issues in Marketing: Personal Data
Uploaded by
Mare AndradeCopyright:
Available Formats
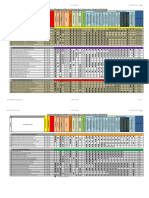
One piece of law, enforced regardless of the
The processing of PD is carried out by a controller or processor established within the EU
sector or business type
The offering of goods and services to
It applies if The processing of PD is carried out by a controller or data subjects living in the EU
processor established outside EU, but the processing
activities are related to: The monitoring of data subjects' behavior
taking place within the Union
PD that concerns the most intimate sphere of
Article 7 of EU Charter of Fundamental Rights Respect for privacy Individuals may be conditioned by these profiles individuals and requires special protection
Ability to collect, store and analyze a mass of personal data The profiles could be wrong Racial and ethnic origin, religious or political convictions or
opinions, adhesion to parties, health status, sexual life
The profiles may reveal some details that individuals prefer to hide
Sensitive data
Features, characteristics, habits, lifestyle, personal relationships, health, economic condition
Body which determines the purposes and
Controller
means of the processing of PD
Technical words
Body which processes PD on behalf of the controller
Actors
Processor
Identification data Names, surnames, personal images
Body in the Union who, designated by the controller or
Race and ethnic origin, religion, health, sexual life,
Traditionally Sensitive data Representative processor, represents them in regard to their
Legal Issues in Marketing Personal Data Data able to identify natural persons philosophical or political opinions, associations
respective obligations under the regulation
(data subjects)
Judicial data Judicial measures, defendant or suspect
Any operation or set of operations performed
Processing
Localization data Frequent places and travel on PD, whether automated or not
More recently Biometric data Fingerprints, topography of the hand, characteristic of handwritten signature Processed lawfully, fairly and in transparent manner
Online data IP or email address, cookies Collected for specified, explicit and legitimate
Omnibus approach (EU) purposes and not further processed
Developed in the late 1970s by the US Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
Adequate, relevant and limited
Fair Information Practice Principles In response to the growing use of automated data systems Data minimization and purpose of limitation
Personal data shall be to what is necessary
(FIPPs)
Substantive principles (purpose of limitation and data quality)
Kept in a form that permits identification for no longer than necessary
Mixture of
Served as foundation for self From Directive 95/46 to Regulation 2016/279 -> Mandatory, free, specific, informed
Procedural principles (consent and access) Accurate and up to date
regulation initiatives and laws General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) Consent is any freely given, specific, informed an Tacit or presumed consent is not
Born on the basis of FIPPs Processed in a manner that ensures security
unambiguous indication in which the DS agrees allowed (Ex: pre checked boxes)
of PD, integrity and confidentiality
OECD Privacy Guidelines of 1980 Recommended that OECD members consider these principles in internal legislation to the processing of PD (by statement or clear
Revocable, unequivocal (inaction is not
Article 8 of EU Charter of Fundamental Rights Protection of personal data The data subject has given affirmative action)
Do not have a binding nature, only provide a rough outline Either express consent or implied by a contract consent), explicit, demonstrable, valid from 16
consent for specific purposes
years onward (or parental consent)
Contract is sufficient when processing of PD is
Just for that purpose
linked to an activity essential for its fulfillment
The processing is lawful if
The performance of a contract
Main rules For compliance with a legal obligation the controller is subject
Protecting the vital interests of someone
Processing is necessary for
For the performance of a task carried out for public interest
EU gives a lot of importance to some FIPPs such as
The purpose of legitimate interests, except when they are
data minimization, collection limitation and
overridden by fundamental rights (specially of children)
individuals' right to notice, access and correct
Purpose of processing, categories of PD concerned, recipients,
Right of Access envisaged period, rectification or erasure, lodge a complaint, source,
existence of automatic decision making (profiling)
Modify, correct or update PD so it is truthful, not inaccurate
Right of rectification and erasure
and not suitable for altering personal identity
Cancellation of the PD when its not longer necessary or was processed
Some rights of the Data Subjects Right to be forgotten unlawfully, DS revokes consent or opposes the processing
Born as evolution of principle established by Google Spain
Allows DS to receive PD concerning him/her to transfer it to another data
Data portability
controller (if it doesn't affect the right of the original controller)
Rights about automated Decisions with legal effects or
DS can ask a review of the decision
decisions (profiling) significant consequences
No more basic compliance but more accountability of DC
-> be able to explain how PD is being protected
Both use international Accountability Every member has one, it can check complaints, forbid non compliant behaviors, promote
What about national laws?
principles but differently codes of conduct, carry out controls on the DPIA, enforce sanctions
Supervisory Authority that develops rules in data
Many and different rules for different
Sectoral approach (USA) processing and enforces compliance One stop shop principle and Lead Supervisory Authority
industrial and business sectors
GDPR novelties Supervisory Authorities now can apply sanctions and the fines
increased (up to 20 million euros, up to 4% of yearly sales)
You might also like
- Initial Brief On MeritsDocument69 pagesInitial Brief On MeritsAnonymous PbHV4H100% (2)
- Florida Vs Varsha Bevin - Case Number 20-TR-063015Document8 pagesFlorida Vs Varsha Bevin - Case Number 20-TR-06301520-TR-063015100% (3)
- Passage Planning Guide2011 PDFDocument1 pagePassage Planning Guide2011 PDFHuy Đình Vũ100% (1)
- Contract CheckListDocument2 pagesContract CheckListFatmah El WardagyNo ratings yet
- Shifts in The Low Touch Economy (2020-2023)Document1 pageShifts in The Low Touch Economy (2020-2023)Ali ElattarNo ratings yet
- 特殊 Goods PrincipleDocument1 page特殊 Goods Principle3213349886No ratings yet
- 6 Daily Performance Monitoring 101716Document2 pages6 Daily Performance Monitoring 101716Godfrey VelozNo ratings yet
- Hs Oa 21 00845-Context Colour Masterplan-878203Document1 pageHs Oa 21 00845-Context Colour Masterplan-878203api-193778159No ratings yet
- Ac 1664434154655Document8 pagesAc 1664434154655Alaa Abo ShamaaNo ratings yet
- Loading UnloadingDocument2 pagesLoading UnloadingArgaYurIstiawanNo ratings yet
- WA MelchiorriDocument70 pagesWA MelchiorriAbhishek DharNo ratings yet
- PTC Tempo - Academic ResearchDocument2 pagesPTC Tempo - Academic Researchakhil4006No ratings yet
- 9946Z - 0657-SP-SL-PL-C-G20-001 (P3) - Proposed Levels Plan (Sheet 1 of 2)Document1 page9946Z - 0657-SP-SL-PL-C-G20-001 (P3) - Proposed Levels Plan (Sheet 1 of 2)jmdavies.isNo ratings yet
- POWERDocument3 pagesPOWERanish.mohanNo ratings yet
- Smart Cameras As Embedded Systems-REPORTDocument17 pagesSmart Cameras As Embedded Systems-REPORTRajalaxmi Devagirkar Kangokar100% (1)
- DG NCD 400 0000 Ays DWG ST 300 0068430 - PDFDocument1 pageDG NCD 400 0000 Ays DWG ST 300 0068430 - PDFOsama KheadryNo ratings yet
- Radcom LTE Poster 2011Document1 pageRadcom LTE Poster 2011Sergiy RipskyyNo ratings yet
- VoipDocument1 pageVoipAdeel ShamsiNo ratings yet
- WWW - Tme.eu: Transfer Multisort ElektronikDocument3 pagesWWW - Tme.eu: Transfer Multisort Elektronikk.saikumarNo ratings yet
- 55-19007-DR-0013 C01 - Cross Sections - Sheet 1 of 2Document1 page55-19007-DR-0013 C01 - Cross Sections - Sheet 1 of 2Salam AlaikumNo ratings yet
- As Approved: GF - Fire Fighting Layout 1 01 - Fire Fighting Layout 2Document1 pageAs Approved: GF - Fire Fighting Layout 1 01 - Fire Fighting Layout 2Edgar Lenard GumapasNo ratings yet
- Laxcon Developments: Cardiff 029 2052 8140 London 0207 138 3560 Wrexham 01978 357 887 WWW - Lawray.co - UkDocument1 pageLaxcon Developments: Cardiff 029 2052 8140 London 0207 138 3560 Wrexham 01978 357 887 WWW - Lawray.co - Ukrajen raghwaniNo ratings yet
- Drwaing Full SetDocument18 pagesDrwaing Full Setserg234sok42No ratings yet
- Traffic Assignment Algorithm ComparisonDocument36 pagesTraffic Assignment Algorithm ComparisonSiervo Andrés Aguirre BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Modular MD: State-of-the-Art ICU Facilities For Rapid Medical ResponseDocument2 pagesModular MD: State-of-the-Art ICU Facilities For Rapid Medical ResponseakinravNo ratings yet
- Dubai HSE LAwDocument103 pagesDubai HSE LAwnoufalhse100% (2)
- S U R Fa C E Fa C I L I T I E S: Untergrundspeicher-Und Geotechnologie - Systeme GMBHDocument4 pagesS U R Fa C E Fa C I L I T I E S: Untergrundspeicher-Und Geotechnologie - Systeme GMBHPETITNo ratings yet
- Atr SPLL (Max) El DWG It l34 6045Document1 pageAtr SPLL (Max) El DWG It l34 6045Hirushan MenukaNo ratings yet
- Speaker and TV Connections/Conexiones Del Televisor y Los Altavoces BDV-E300Document1 pageSpeaker and TV Connections/Conexiones Del Televisor y Los Altavoces BDV-E300an nyNo ratings yet
- Differential Privacy of Hierarchical Census Data: An Optimization ApproachDocument17 pagesDifferential Privacy of Hierarchical Census Data: An Optimization ApproachJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- ASIC Implementation of Shared LUT Based Distributed Arithmetic in FIR FilterDocument4 pagesASIC Implementation of Shared LUT Based Distributed Arithmetic in FIR Filtermuneeb rahmanNo ratings yet
- Summary of International Accounting Standards PDFDocument6 pagesSummary of International Accounting Standards PDFSittie Norjanah MaunaNo ratings yet
- System Layout Twitter 27-11-18 PDFDocument3 pagesSystem Layout Twitter 27-11-18 PDFKevin ApostolNo ratings yet
- Reports-Sector Studies-Somaliland - Sector Functional Assessment - FINAL TECHNICAL MASTER - Geopolicity - April 19 2012 - Reduced SizeDocument189 pagesReports-Sector Studies-Somaliland - Sector Functional Assessment - FINAL TECHNICAL MASTER - Geopolicity - April 19 2012 - Reduced SizeMubarak Maal100% (1)
- AP20.CAP02.2.4 WS 4PL 100 101 Layout1Document1 pageAP20.CAP02.2.4 WS 4PL 100 101 Layout1m.elleithyNo ratings yet
- Computer Organisation and Architecture: David J. ScottDocument38 pagesComputer Organisation and Architecture: David J. ScottVO TRIEU ANHNo ratings yet
- Fibre As An Ecosystem ServiceDocument9 pagesFibre As An Ecosystem ServiceSimi ANo ratings yet
- Optical Proximity SensorsDocument3 pagesOptical Proximity SensorsEr. Piush JindalNo ratings yet
- Manual Handling and People Handling Policy 2018Document35 pagesManual Handling and People Handling Policy 2018QNo ratings yet
- Documentation PHENIX LIBERTY Anglais V05.00Document2 pagesDocumentation PHENIX LIBERTY Anglais V05.00Jose HernandezNo ratings yet
- Documentation PHENIX LIBERTY Anglais V05.00Document2 pagesDocumentation PHENIX LIBERTY Anglais V05.00klemionka2No ratings yet
- Tcbrochure enDocument4 pagesTcbrochure enyazedNo ratings yet
- 2021FPSO OffshoreDocument1 page2021FPSO OffshoreShafif SalehNo ratings yet
- Leaflet - HDFC Banking & Financial Services Fund (NFO)Document4 pagesLeaflet - HDFC Banking & Financial Services Fund (NFO)rakeshNo ratings yet
- 02 MODELO ProjectFinance GenericLetterOfIntent.V.1 01052019Document9 pages02 MODELO ProjectFinance GenericLetterOfIntent.V.1 01052019tucano8997jNo ratings yet
- Brochure Pcte FsiDocument5 pagesBrochure Pcte FsiDaniel FarcasNo ratings yet
- GRE - eec.D.99.CL.P.07576.12.014.01 Tracker Controller Cable ConnectionsDocument1 pageGRE - eec.D.99.CL.P.07576.12.014.01 Tracker Controller Cable ConnectionsJason DaNny FloResNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS: Property and Power. Mutual Gains and ConflictDocument8 pagesECONOMICS: Property and Power. Mutual Gains and ConflictmargaridaNo ratings yet
- Electro 323Document2 pagesElectro 323Pușcă MartinNo ratings yet
- رحال عبد القادر - ضوابط التصرفات الواردة على حرمة جسم الإنسان في الشريعة الإسلامية والتشريع الجزائري - التبرع بالأعضاء والأنسجة بين الأحياء والوصية بها أنموذجاDocument31 pagesرحال عبد القادر - ضوابط التصرفات الواردة على حرمة جسم الإنسان في الشريعة الإسلامية والتشريع الجزائري - التبرع بالأعضاء والأنسجة بين الأحياء والوصية بها أنموذجاAyouya AyaNo ratings yet
- User Manual-I9 PRO-MAX ANDROIDDocument2 pagesUser Manual-I9 PRO-MAX ANDROIDsnehithNo ratings yet
- 10026-DWG-S100000-AR-500001 (B) Superseded by No.10026-DWG-S100000-AR-600049 As Per HADL-RTRFI-000016Document1 page10026-DWG-S100000-AR-500001 (B) Superseded by No.10026-DWG-S100000-AR-600049 As Per HADL-RTRFI-000016Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Additional HC Weir ModelDocument1 pageAdditional HC Weir ModelsclbscplNo ratings yet
- Otn Fec Po Opt TM AeDocument1 pageOtn Fec Po Opt TM Aenobita3No ratings yet
- U03 - Reglementari Urbanistice - 2 PDFDocument1 pageU03 - Reglementari Urbanistice - 2 PDFBartha LaszloNo ratings yet
- Innovality Brochure Excellent-M Xb1046EDocument3 pagesInnovality Brochure Excellent-M Xb1046ERobert MontañezNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram: 7-1 Circuit DescriptionDocument8 pagesSchematic Diagram: 7-1 Circuit Descriptionoppa BaruNo ratings yet
- Express Card To Parallel & Serial Port Adapter, Windows 7 Installation GuideDocument13 pagesExpress Card To Parallel & Serial Port Adapter, Windows 7 Installation GuideMarco CatenaNo ratings yet
- Compiled CasesDocument32 pagesCompiled CasesAdriannaNo ratings yet
- Matthew David Kelly v. Clinton Sines, Et. Al.Document16 pagesMatthew David Kelly v. Clinton Sines, Et. Al.sandydocsNo ratings yet
- Bar Questions Answer - BLDDocument4 pagesBar Questions Answer - BLDErikha AranetaNo ratings yet
- Define Tort and Distinguish It From Crime and ContractDocument3 pagesDefine Tort and Distinguish It From Crime and ContractAnupama ANo ratings yet
- Income Tax AuthoritiesDocument12 pagesIncome Tax AuthoritiesSweety Roy100% (1)
- Jaime Araza vs. PP (G.R. No. 247429, September 08, 2020)Document4 pagesJaime Araza vs. PP (G.R. No. 247429, September 08, 2020)Tokie TokiNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. L-36409Document1 pageG.R. No. L-36409meerahNo ratings yet
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights Simplified VersionDocument7 pagesUniversal Declaration of Human Rights Simplified VersionMay Angelica TenezaNo ratings yet
- Moot Proposition LLB Sem V - 2021-2022Document46 pagesMoot Proposition LLB Sem V - 2021-2022Satish Gavate50% (4)
- Terms and ConditionsDocument8 pagesTerms and ConditionsValeriia SluchynskaNo ratings yet
- In The Name of God Most Gracious Most MercifulDocument124 pagesIn The Name of God Most Gracious Most MercifulSUPREME TRIBUNAL OF THE JURISNo ratings yet
- Special Proceedings Finals ReviewerDocument17 pagesSpecial Proceedings Finals ReviewerJapoy Regodon EsquilloNo ratings yet
- Marcos v. Heirs of NavarroDocument3 pagesMarcos v. Heirs of NavarroAARON JOHN VIRAYNo ratings yet
- Cagandahan and Silverio CaseDocument21 pagesCagandahan and Silverio Caseaceamulong0% (1)
- Tengco III v. People - 2023Document9 pagesTengco III v. People - 2023Eugene RoxasNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On CrimeDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Crimeaflsldrzy100% (1)
- Rocky Mountain Gun Owners, Et Al., v. Jared PolisDocument6 pagesRocky Mountain Gun Owners, Et Al., v. Jared PolisMichael_Roberts2019No ratings yet
- Module 2-Citizenship Training: Philippine ConstitutionDocument7 pagesModule 2-Citizenship Training: Philippine Constitutionprecious erica llanetaNo ratings yet
- Admin - Chapter 4 and 5 - Quasi-Legislative and Quasi-JudicialDocument76 pagesAdmin - Chapter 4 and 5 - Quasi-Legislative and Quasi-JudicialVinson Gabato100% (2)
- Sprinklr Kerala Mutual NDA Signed PDFDocument2 pagesSprinklr Kerala Mutual NDA Signed PDFvimaledrNo ratings yet
- T A N .5 P O:: Question 1: Five Accused Entered The House of The Victim Through The Roof After Dismantling ADocument8 pagesT A N .5 P O:: Question 1: Five Accused Entered The House of The Victim Through The Roof After Dismantling Anishi jainNo ratings yet
- 21.12.2022 Hon Minster of JusticeDocument3 pages21.12.2022 Hon Minster of JusticeISAAC MUSEKA LUPUPANo ratings yet
- CONFIDENTIALITY AND NON DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT AmendedDocument4 pagesCONFIDENTIALITY AND NON DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT Amendedvida.plobulacanNo ratings yet
- 2023 02 16 MSSC Sanction Against Judge Carlos MooreDocument20 pages2023 02 16 MSSC Sanction Against Judge Carlos Moorethe kingfishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Human DignityDocument69 pagesChapter 9 Human DignityShim-b TiuNo ratings yet
- BDU-JL Vol 6 No 1Document202 pagesBDU-JL Vol 6 No 1abebeadelp65No ratings yet
- ARTICLE 14. Aggravating Circumstances. - : Chapter Four Circumstances Which Aggravate Criminal LiabilityDocument1 pageARTICLE 14. Aggravating Circumstances. - : Chapter Four Circumstances Which Aggravate Criminal LiabilityJerry CaneNo ratings yet
- Eace Education LectureDocument46 pagesEace Education LectureMary ellen AltavanoNo ratings yet