Professional Documents
Culture Documents
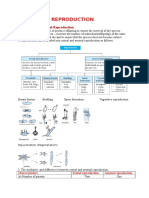
Human Reproduction
Uploaded by
samyukthaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Reproduction
Uploaded by
samyukthaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER -8
HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE?
Topic 2: SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS
1. Puberty -Time of growth when a person becomes sexually mature.
2. Secondary sexual characters-characters that help to distinguish between an adolescent boy and girl
Secondary sexual characters in boys Secondary sexual characters in girls
✓ Broadening of shoulder ✓ broadening of hips
✓ Widening of chest ✓ Widening of pelvic region
✓ Development of muscular body ✓ Development of breasts
✓ The testis starts to make sperms. ✓ Ovaries start to release eggs.
✓ voice deepens. ✓ Menstruation starts.
Hormone responsible for these changes-Testosterone Hormone responsible for these changes-Oestrogen
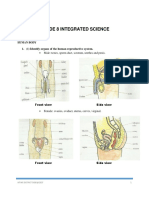
Male reproductive system
1. Parts -Pair of testis, scrotal sacs, sperm duct or Vas deferens, Urethra and Penis.
2. Each testis is located in a hollow bag like structure – scrotal sac which is outside the abdominal cavity
3. Scrotal sacs is located outside abdominal cavity to provide optimum temperature for formation of sperms.
4. Testes produces millions of sperms
5. Sperm has 3 parts- Head, middle piece and tail
6. From testis, Sperms move through tube like structures- sperm duct or Vas deferens
7. prostate glands and the seminal vesicles are two glands associated with Vas deferens. They secrete a fluid.
8. Function of the fluid: helps in easy movement of sperms and gives nourishment to sperms
8. Mixture of fluids and sperms is called semen.
9. Sperms travel down the urethra. It is common passage for sperms and urine.
10. From there sperms passes through penis
11. Penis transfers the sperms into the vagina.
Female reproductive system
1. Parts- Pair of ovaries, Oviducts or fallopian tubes, Uterus , Cervix –narrow part of uterus where it joins the vagina,
Vagina (birth canal)
2. every month one of the ovaries produces an egg. Release of egg by ovary is called OVULATION.
3. from the ovary the egg is carried to oviduct or fallopian tube.
4. The two oviducts unite to form an elastic bag-like structure known as the uterus.
5. The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix.
What happens to egg?
If fertilization takes place egg becomes zygote.
If fertilization does not take place egg waits for 1-2 days, then degenerates
What happens to uterus?
Every month inner lining of uterus (endometrium) becomes thick and spongy and is richly supplied with blood vessels in
anticipation of pregnancy
If fertilization takes place, inner lining of uterus nourishes the embryo
If fertilization does not take place inner lining of the uterus is removed in form of blood and mucus through vagina. This
is called Menstruation. It takes place every month for about 2-7 days.
DEVELOPMENT OF ZYGOTE
1. Zygote is a single cell. zygote divides to form a ball of cells called embryo
2. Embryo attaches to wall of uterus. It is called Implantation.
3. Placenta is a special tissue. It is disc shaped. It develops between embryo and uterine wall of the mother. It contains
villi on side of embryo and large blood spaces on mother’s side. It develops in the fourth week.It transfers oxygen and
glucose from mothers blood to embryo.It transfers wastes from embryo to mother’s blood. Placenta is connected to
the embryo by a string like structure called the UMBILICAL CORD.
4. The embryo develops body parts like head, legs, hands etc.The stage of the embryo where all body parts can be
identified is known as Foetus.
5. As the foetus grows the wall of uterus stretches to accommodate it.
6. When foetus is mature the muscles of the wall of uterus contracts and pushes the baby out. The process of delivery
of foetus is called PARTURITION.
7. The period for which baby develops inside the mother is called GESTATION period.
Reproductive health
Contraception: Prevention of pregnancy in women
CONTRACEPTIVE METHODS
1. BARRIER METHOD
2. ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
3. IMPLANTS or (IUCDs) -Intra Uterine Contraceptive Devices
4. Surgical methods
Principles involved in Contraceptive methods
1. Barrier method
a. Principle: does not allow sperm to reach the egg
b. Eg: condoms in males; cervical cap of diaphragm in females
c. Condoms are made of thin rubber. It used to cover the penis in males. Cervical cap is use to cover cervix. Diaphragm
fits inside vagina.
2. Oral contraceptives
principle: tablets are taken which prevents ovulation by changing hormonal balance.
Eg: oral pills
3. IMPLANTS or (IUCDs) -Intra Uterine Contraceptive Devices
a. Principle: prevents implantation
b. Eg: copper-T or loop are placed in the uterus. It does not allow zygote to implant to uterus
4. Surgical method
a. Principle: blocks are created
b. In males-vasectomy, the vas deferens is blocked. It does not allow sperm to enter into seminal fluid.
c. In females- tubectomy, the fallopian tubes are blocked .it does not allow fertilization.
Note:
1. Only contraceptive method which prevents STDs is use of Condoms as semen does not enter into female
reproductive tract.
2. Contraceptive method exclusively used by females: Oral contraceptives and Implants
3. Contraceptive methods used both by males and females are Barrier method and Surgical method
Reasons for adopting contraceptive methods/How does use of contraceptives have a direct effect on
the health and prosperity of a family?
1. It prevents frequent pregnancy which would otherwise affect health of female
2. It reduces the chances of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
3. It reduces poverty by controlling the number of children in a family.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
1. STDs are diseases which are spread by sexual contact with an infected person.
2. Gonorrhea and Syphilis are STDs caused by bacteria.
3. AIDS and Warts are STDs caused by virus.
AIDS is caused by HIV virus. (AIDS-Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome); HIV-Human Immuno Virus
REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
Reproductive Health means a total well-being in all aspects of reproductive, i.e., physical emotional, social and
behavioural.
FEMALE FOETICIDE
It refers to killing of the female foetus within the womb of the mother. Prenatal-sex determination has lead to
female foeticide.
Indicators of a Reproductively Healthy Society
1. balanced sex ratio
2. increased medical facilities for care if mother and child
3. Better detection and cure of Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
4. people are aware about use of contraceptive methods
You might also like
- MISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Document27 pagesMISOSA S51Quarter 2, Modules 1-3Di VianNo ratings yet
- Echidnas (/ɪ Kɪdnəz/), Sometimes Known As Spiny Anteaters. The FourDocument7 pagesEchidnas (/ɪ Kɪdnəz/), Sometimes Known As Spiny Anteaters. The FourHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationDocument13 pagesUnit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationAntonio PrietoNo ratings yet
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument44 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemLilona LilonaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Care of Mother, Child and ADOLESCENT (Well Clients)Document9 pagesBachelor of Science in Nursing: Care of Mother, Child and ADOLESCENT (Well Clients)Jerica Mae VenoyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReportDocument17 pagesAnatomy ReportMabeth PagatpatNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 8 & 9 FinalDocument54 pagesIntegrated Science 8 & 9 FinalKasman Kasonde MumbaNo ratings yet
- Ullang - NCM 107a Module1-2Document16 pagesUllang - NCM 107a Module1-2Rahima UllangNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 8 & 9 Final PDFDocument54 pagesIntegrated Science 8 & 9 Final PDFAnthony Mabaso SichaliNo ratings yet
- Reproduction 3Document4 pagesReproduction 3Benny JoseNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System HandoutDocument21 pagesReproductive System HandoutJei SanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSCIENCEjoannalyn gregorioNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans CLASS 10Document5 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans CLASS 10shallowNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument13 pagesReproductive SystemAlicia ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine and Reproductive SystemsDocument53 pagesEndocrine and Reproductive Systemsapi-287032631No ratings yet
- Normal PregnancyDocument65 pagesNormal PregnancyRhesie Joyce AguilarNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument66 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentBlessie NgitngitNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Document15 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Halizah RamthanNo ratings yet
- Caadlawon-Prenatal - Dev.and Infancy Nov.7Document36 pagesCaadlawon-Prenatal - Dev.and Infancy Nov.7Joan Rosanne CaadlawonNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemJoseph CristianNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Prenatal DevelopmentDocument11 pagesUnit 2: Prenatal DevelopmentAnanya GhoshNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Childhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Childhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions Manual PDFdoughnut.synocilj084s100% (9)
- Childhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChildhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions Manualaudiblycaribbeeuwiq100% (15)
- Unit 2 by SuryaDocument29 pagesUnit 2 by SuryayashiranjNo ratings yet
- CP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Document11 pagesCP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- 4 - Menstrual Disorders-104418Document42 pages4 - Menstrual Disorders-104418Izziddin YassineNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesExploring The Female Reproductive Systemlegall_650582301No ratings yet
- Adolescence: 1. Change in HeightDocument15 pagesAdolescence: 1. Change in HeightVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Chapter #17 Human ReproductionDocument18 pagesIGCSE Biology Chapter #17 Human ReproductionAazif JafriNo ratings yet
- MORANDocument3 pagesMORANCubillas P. DerNo ratings yet
- Childhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesChildhood and Adolescence Voyages in Development 6th Edition Rathus Solutions ManualJenniferAguilarrfiax100% (10)
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans NotesDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans NotesBongani MhlabaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and HeredityDocument10 pagesReproduction and HeredityMonkey LoverNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction FullDocument46 pagesSexual Reproduction FullSharara YMNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive System - Wikipedia PDFAubrey EuropeNo ratings yet
- Yr 8 WK 2 Bio NoteDocument3 pagesYr 8 WK 2 Bio Notesedrick ocheNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document14 pagesLec 2Tabark AliNo ratings yet
- The Process of ReproductionDocument4 pagesThe Process of ReproductionIvan BixenmanNo ratings yet
- Written by AHMED ATEF K-719610990 AHMED KHALIL K-719610923: Anatomy Assignment 2Document15 pagesWritten by AHMED ATEF K-719610990 AHMED KHALIL K-719610923: Anatomy Assignment 2Dr. Mohammad JamaliNo ratings yet
- Understading The Self NotesDocument15 pagesUnderstading The Self NotesdorothyzoeesbietoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 9 - Reproductive System - ORLINA, M.A.Document3 pagesQuiz 9 - Reproductive System - ORLINA, M.A.Mae Antonette OrlinaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Human Development Before BirthDocument3 pagesStages of Human Development Before BirthAaronotix GamingNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument5 pagesHuman ReproductionKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTION L2 (Prashant Kirad)Document32 pagesREPRODUCTION L2 (Prashant Kirad)superherosunny13No ratings yet
- Male & Female Reproductive SystemDocument211 pagesMale & Female Reproductive SystemDanica Marie SibayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiologyhey judeNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Document7 pagesHuman Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Zach ZaneNo ratings yet
- Second Term Science 5 Modules 1-4Document22 pagesSecond Term Science 5 Modules 1-4Kathleen FernandezNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Human.Document42 pagesSexual Reproduction in Human.wahab.7803No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology GCSDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology GCSSherry Ann FayeNo ratings yet
- Biophysical Aspects of PregnancyDocument34 pagesBiophysical Aspects of PregnancyRucrispi VirayoNo ratings yet
- 4 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pages4 Anatomy and PhysiologyRuel AdrianNo ratings yet
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument51 pagesFetal DevelopmentLhiet Aguilar Hipolito50% (2)
- 1st Periodical Test I Science ReviewerDocument7 pages1st Periodical Test I Science Reviewercatherine tamayoNo ratings yet
- Educ 101 ReviewerDocument27 pagesEduc 101 ReviewerRolando AmadNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction NotesDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction NotesZelNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document9 pagesModule 4Angelica MadronaNo ratings yet
- E Dies Astm d5963 CuttingdiesDocument1 pageE Dies Astm d5963 CuttingdiesNate MercerNo ratings yet
- Report Documentation Page: Major James R. VanceDocument26 pagesReport Documentation Page: Major James R. VanceQazma RarajNo ratings yet
- Manual Expert 7.1 - OXODocument1,324 pagesManual Expert 7.1 - OXOEduardo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Bicol State College of Applied Sciences and Technology: JANUARY 2021Document11 pagesBicol State College of Applied Sciences and Technology: JANUARY 2021Jay Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Networker MergedDocument261 pagesNetworker MergedShafee AhmadNo ratings yet
- Quantity Calculation FormatDocument8 pagesQuantity Calculation FormatNabraiz AnsariNo ratings yet
- Alxion: For Direct DriveDocument56 pagesAlxion: For Direct DriveAnselmo Aguado cortesNo ratings yet
- Aubrey Jaffer: Scheme Implementation Version 5f1Document149 pagesAubrey Jaffer: Scheme Implementation Version 5f1kevinmcguireNo ratings yet
- India: "Truth Alone Triumphs"Document103 pagesIndia: "Truth Alone Triumphs"Rajesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- Morning Report Case Presentation: APRIL 1, 2019Document14 pagesMorning Report Case Presentation: APRIL 1, 2019Emily EresumaNo ratings yet
- IVSS2.0: Intelligent Video Surveillance ServerDocument1 pageIVSS2.0: Intelligent Video Surveillance ServeralbertNo ratings yet
- How To ApplyDocument129 pagesHow To ApplySasa KasaNo ratings yet
- CC W3 AWS Basic InfraDocument57 pagesCC W3 AWS Basic InfraMuhammad Tehseen KhanNo ratings yet
- Misamis Oriental Vs Cagayan ElectricDocument7 pagesMisamis Oriental Vs Cagayan ElectricJovhilmar E. BrinquezNo ratings yet
- PolicySchedule PDFDocument1 pagePolicySchedule PDFSandeep Borse100% (1)
- W1 8GEC 2A Readings in The Philippine History IPED ModuleDocument74 pagesW1 8GEC 2A Readings in The Philippine History IPED ModuleMico S. IglesiaNo ratings yet
- Api-650 Storage Tank Design Calculations - DamasGate WikiDocument3 pagesApi-650 Storage Tank Design Calculations - DamasGate Wikipowder18No ratings yet
- Proposal 4psDocument6 pagesProposal 4psCaridad Avila67% (3)
- Project Report On Working-CapitalDocument74 pagesProject Report On Working-Capitalravikant2105100% (1)
- SDKFZ 251 Mittlere SchutzenpanzerwagenDocument108 pagesSDKFZ 251 Mittlere SchutzenpanzerwagenPeterD'Rock WithJason D'Argonaut83% (6)
- ECE Formula SheetDocument7 pagesECE Formula SheetMahendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- ٣. المنقذ (١٠٠ سؤال)Document44 pages٣. المنقذ (١٠٠ سؤال)ايمان عبد الشافىNo ratings yet
- Lovol - Fl936-Dhbo6g0131Document140 pagesLovol - Fl936-Dhbo6g0131LuzioNetoNo ratings yet
- The Igloo PartyDocument11 pagesThe Igloo PartyRaghav MalhotraNo ratings yet
- C.8 SOLUTIONS (Problems I - IX)Document9 pagesC.8 SOLUTIONS (Problems I - IX)Bianca AcoymoNo ratings yet
- 11th Bio Botany Important Questions For Volume 1 PDFDocument6 pages11th Bio Botany Important Questions For Volume 1 PDFNaren44% (9)
- Banking Financial InstitutionsDocument252 pagesBanking Financial Institutionspraise ferrerNo ratings yet
- Architectural Thesis PDFDocument7 pagesArchitectural Thesis PDFSuresh Balaji0% (1)
- Constructivism in Instrumental Music EducationDocument12 pagesConstructivism in Instrumental Music Educationapi-416613415No ratings yet
- Table of Specifications With Test in Science - Quarter 4 - (Week 3 and Week 4)Document4 pagesTable of Specifications With Test in Science - Quarter 4 - (Week 3 and Week 4)Sarah Jane Lagura Rele50% (2)