Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Standard Classification of Porosity and Other Volume Deficits in Cast Parts
Uploaded by
BielXDOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard Classification of Porosity and Other Volume Deficits in Cast Parts
Uploaded by
BielXDCopyright:
Available Formats
Historic, replaced by DBL 4949 (2018-05)
Mercedes-Benz DBL 4949
Company Standard Edition: 2017-09
Transition period: 3 months
Total no. of pages (including Annex): 8
Person in charge: Jens Hüger
E-Mail: jens.hueger@daimler.com
Plant: 010; Dept.: PT/TWL
Date of translation: 2017-11 Phone: +49 (0) 711 17 31713
Standard classification of porosity and other volume
deficits in cast parts
Foreword
This supply specification describes casting-related volume deficits in cast parts exposed during
processing.
This edition supersedes the former edition of this standard.
Changes
In comparison with edition 2014-06, the following changes have been made:
• The alternative term for all volume deficits is now “defect” (instead of “pore”)
corresponding change to “defect class”
• Alteration of definition and treatment of defect nests (breakdown into three execution
types)
• Introduction of minimum specification of the measuring equipment as indirect detection
limit
Note: This translation is for information purpose only.
The German version shall prevail above all others.
Copyright Daimler AG
Historical document/uncontrolled copy when printed TP/ECE: Marco Belzner, 2018-12-03
Historic, replaced by DBL 4949 (2018-05)
DBL 4949:2017-09, page 2
Contents
1 Scope of application..........................................................................................................................2
2 References........................................................................................................................................2
3 Terms and definitions........................................................................................................................2
4 General requirements .......................................................................................................................3
5 Abbreviated material designation for documentation ........................................................................3
6 General instructions ..........................................................................................................................3
7 Application of defect classes.............................................................................................................3
7.1 Definitions and specifications............................................................................................................3
7.2 Method to verify the defect class ......................................................................................................5
8 Requirements for internal threads in aluminum components............................................................7
1 Scope of application
The DBL shall apply for all cast parts, the casting-related fault forms of which have to be characterized on
processed function surfaces. The objective is to ensure the density of contact surfaces and the local
strength requirements.
Accumulation of fault forms (defect nests) have to be assessed differently depending on the function of the
surface. In order to meet different requirements, the DBL is divided up into various execution types (see
Table 1 ).
Table 1 Execution versions, overview
Execution version Description
DBL 4949.10 Defect nests are approved
DBL 4949.20 Defect nests are not approved
DBL 4949.30 Defect nests as from a certain individual defect size are not approved
2 References
The following referenced documents are required for the application of this document. For dated
references, only the referenced edition applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the
referenced document (including any changes) applies.
DBL 8585 General Requirements – Environmental Protection, Hazardous Substances,
Dangerous Goods – Negative Substance List for the Selection of Materials
DIN EN ISO 14253 Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS) - Inspection by Measurement of
Workpieces and Measuring Equipment
MBN 32004 Threaded Connections - Lengths of Thread Engagement - Design Standard
3 Terms and definitions
a Defect-edge distance
ag Limit-edge distance for defect nests (execution version .30 only)
d Defect expansion (max. Feret)
ag Limit expansion for individual defects for defect nests (execution version .30 only)
dmin Smallest defect expansion to be processed
dmax Maximum permissible defect expansion
dk Maximum defect expansion (max. Feret) combined defects
DKi Defect classes
f Distance factor for edge distance conditions
Ferret diameter vertical distance of two parallels tangentially laid to a defect
G Limit deviation
RE Resolution
T Tolerance
Copyright Daimler AG
Historical document/uncontrolled copy when printed TP/ECE: Marco Belzner, 2018-12-03
Historic, replaced by DBL 4949 (2018-05)
DBL 4949:2017-09, page 3
4 General requirements
With regard to safety requirements and product quality as well as to fulfill certification requirements, all
relevant statutory regulations and laws shall be complied with. In addition, the relevant requirements of the
Daimler Group shall apply.
In terms of ingredients and recyclability, materials, procedure and process engineering, components and
systems shall comply with all applicable legal requirements.
DBL 8585 shall be observed.
5 Abbreviated material designation for documentation
Not applicable.
6 General instructions
Process-specific casting faults are present in every cast component depending on the component
geometry and the casting-related boundary conditions (casting technology, gate system, casting
parameter). The typical process-specific defects are micro and macro blowholes, gas porosity, hot cracks,
cold laps, cast-related caused chipping and flaking.
Hereinafter the term “defect” is used.
The defect classes indicate standardized defect sizes, defect distribution and defect loss surface for
component parts which are produced by casting. They are used for machined surfaces, but not as X-ray
standard for volumetric testing.
In general, cracks, cold laps as well as sink marks are impermissible fault forms which continue to be
visible after processing. Pore and blowhole nests and chains are taken into consideration by the pore
dimensions and distances, and depending on the execution version are permissible, not permissible or
partially permissible.
The depth of imperfections is not defined for this standard. The specifications are valid for 2D surfaces.
The application of this DBL is useful only for processed, function-relevant areas of a component part (if not
specified otherwise) and has to be indicated in the drawing along with a specified defect class. Such areas
are, for example, sealing surfaces, functional bores (camshaft bearings, crankshaft bearing boreholes,
etc.), threads, fastening boreholes and coating surfaces.
7 Application of defect classes
7.1 Definitions and specifications
Defect class DKi: Classification unit for defects when applying criteria of maximum defect
expansion and maximum loss surface relative to a specified measurement area.
The specification of a defect class in technical product documentation places
demands on a complete geometry element or on a marked scope of application
(reference surface). In order to meet the requirements of a defect class, the limit
values of all criteria have to be met.
The designations of the defect classes and the appertaining limit values are
shown inTable 2. Deviating definitions or specifications are mentioned in the
technical documentation.
Defect expansion d: The maximum Ferret diameter of the defect is determined (see Fig.1). This must
not exceed the permissible maximum value d max. of the respective defect class.
All defects recorded, the maximum Ferret diameter of which are below the limit
value d min. are not included in the analysis.
Defect edge distance a: Smallest possible edge distance to neighboring defects.
Copyright Daimler AG
Historical document/uncontrolled copy when printed TP/ECE: Marco Belzner, 2018-12-03
Historic, replaced by DBL 4949 (2018-05)
DBL 4949:2017-09, page 4
Defect nests: Amassing of individual defects. Depending on the execution version, defect
nests are defined by an edge distance condition. The edge distance condition
can be varied by means of the distance factor f. If the technical documentation
does not indicate a distance factor, then f = 1. If the distance factor is f = 0,
defect nests are permitted in general. An edge distance inspection is not
required in this case.
Execution version .10 and .20: If the defect edge distance a of neighboring
defects is smaller than the defect expansion d of the smaller defect multiplied
with distance factor f, the defects are considered and treated as a defect nest.
Execution version .10 only: Defect nests are combined to a large defect, and
correspondingly treated and analysed as single defect with a combined defect
expansion d k (max. Ferret diameter) for the test of the max. defect expansion d
max.
Edge distance condition: ai-j ≤ Min(di|dj) · f
Execution version .30: If the defect edge distance a of neighboring defects, of
which the defect expansion d is larger or equal the limit expansion d g, is smaller
or equal the limit distance a g, the edge distance condition is fulfilled, and these
defects are considered as a defect nest. Defects with defect expansions smaller
than the limit expansion are not included in the defect nest consideration, and
are only considered by the defect share.
Edge distance condition: ai-j ≤ ag · f (for defects with d ≥ dg)
Reference surface: Surface indicated in technical documentation, for which a defect class has been
defined.
Measurement area: The size (the content) of the measurement area depends on the defect class. It
has a quadratic shape. Divergent sizes and shapes, such as circles or squares
(with maximum aspect ratio 2 to 1), can be used as agreed. Within every
measurement area, the requirements for the specified defect class have to be
fulfilled.
Defect share: Surface share of all defects recorded relative to the measurement area. Every
defect class is assigned a maximal value which must not be exceeded.
Test system: An image-processing system has to be designed in such a way that the
tolerance T of the respective defect class can be checked. The specifications
relating to the maximum permissible limit deviation G and resolution RE (max. 5
% of tolerance T) of the measuring equipment have to be complied with (see
Table 2).
Copyright Daimler AG
Historical document/uncontrolled copy when printed TP/ECE: Marco Belzner, 2018-12-03
Historic, replaced by DBL 4949 (2018-05)
DBL 4949:2017-09, page 5
Fig.1: Determination of the defect expansion d as maximum Ferret diameter
Copyright Daimler AG
Historical document/uncontrolled copy when printed TP/ECE: Marco Belzner, 2018-12-03
Historic, replaced by DBL 4949 (2018-05)
DBL 4949:2017-09, page 6
Table 2: Definitions of the defect classes
Defect class DK0.4 DK0.6 DK0.8 DK1.0 DK1.2 DK1.5
Max. defect expansion dmax. [mm] 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.5
Min. defect expansion dmin. [mm] 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3
Limit expansion dg [mm] * 0.3* 0.3* 0.4* 0.5* 0.6* 0.8*
Limit-edge distance dg [mm] * 0.4* 0.6* 0.8* 1.0* 1.2* 1.5*
Max. defect share [%] 2.5 3.5 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0
Measurement area [sqmm] 21 26 43 64 88 143
Tolerance T [mm] 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
Limit deviation G [µm] ≤ 100 ≤ 100 ≤ 100 ≤ 100 ≤ 100 ≤ 100
Resolution RE [µm] ≤ 50 ≤ 50 ≤ 50 ≤ 50 ≤ 50 ≤ 50
Defect class DK2.0 DK2.5 DK3.0 DK4.0 DK5.0
Max. defect expansion dmax. [mm] 2.0 2.5 3.0 4.0 5.0
Min. defect expansion dmin. [mm] 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3
Limit expansion dg* [mm] 1.0* 1.3* 1.5* 2.0* 2.5*
Limit-edge distance dg* [mm] 2.0* 2.5* 3.0* 4.0* 5.0*
Max. defect share [%] 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0
Measurement area [sqmm] 254 398 573 1010 1580
Tolerance T [mm] 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
Limit deviation G [µm] ≤ 100 ≤ 100 ≤ 100 ≤ 100 ≤ 100
Resolution RE [µm] ≤ 50 ≤ 50 ≤ 50 ≤ 50 ≤ 50
* only for execution version .30
7.2 Method to verify the defect class
The reference surfaces specified in technical documentation is examined in detail with respect to the
associated defect class. In the process, a measurement area according to the defect class required is
placed around the focus of largest defects or defect nests, and the fulfillment of the defect class is
checked. If image-processing systems are used, each defect within the reference surface is looked at
individually, whereby the measurement area each is laid around the focus of the defect that is being
looked into.
If no reference surface has been defined in the technical documentation, the measurement areas are
placed in such a way that they cover the area of the largest share of defects.
In order to ensure recording of all relevant defects, it is necessary that the image-processing system used
fulfills the minimum requirements indicated in the section on test systems in chapter 7.1. Within the
measurement area all defects recorded in this way as from a minimum dimension d min according to the
specified defect class Dki are taken into consideration in the analysis (see Table 2).
All defects considered are checked for exceedance of the maximum permissible defect expansion d max
and for the maximum defect share of the respective defect class (see Table 2 ). An exceedance of the
maximum values is not permissible.
If the technical documentation indicates a distance factor of f = 0, defect nests are permissible
independent of their expansion, and the distance need not be analyzed. In this case, only maximum
individual defect sizes and defect share are checked.
Apart from that, the distances of defects to each other have to be analyzed, whereby the method depends
on the execution version.
Copyright Daimler AG
Historical document/uncontrolled copy when printed TP/ECE: Marco Belzner, 2018-12-03
Historic, replaced by DBL 4949 (2018-05)
DBL 4949:2017-09, page 7
Execution version .10:
In case of neighboring defects, the respectively smallest defect expansion is used as distance criterion
(see chapter 7.1 Defect nests). Defects which fulfill the distance conditions have to be combined to a
larger defect, and shall be analyzed as such with the combined defect expansion d k (seeFig2 ). The
combined diameter expansions must not exceed the permissible maximum value d max. of the respective
defect class.
Execution version .20:
In case of neighboring defects, the respectively smallest defect expansion is used as distance criterion
(see chapter 7.1 Defect nests). Defects that fulfill the edge distance conditions are not permissible.
Execution version .30:
All defects with an expansion of larger or equal the limit expansion dg have to be subjected to a distance
analysis.
The limit-edge distance a g of the respective defect class is used as distance criterion (see chapter7.1
Defect nests). It is not permissible that the edge distance of neighboring defects is less than or equal to
the limit-edge distance.
The DBL shall be considered not fulfilled when one of the following scenarios occurs within the requested
execution version:
Execution version .10: Defect expansion di > dmax
Combined defect expansion dki > dmax (at f > 0)
Defect share > max. defect share
Execution version .20: Defect expansion di > dmax
Defect edge distance ai-j ≤ Min(di|dj) · f (at f > 0)
Defect share > max. defect share
Execution version .30: Defect expansion di > dmax
Defect edge distance ai-j ≤ ag · f (for defects with d ≥ dg; at f > 0)
Defect share > max. defect share
Copyright Daimler AG
Historical document/uncontrolled copy when printed TP/ECE: Marco Belzner, 2018-12-03
Historic, replaced by DBL 4949 (2018-05)
DBL 4949:2017-09, page 8
a1-2 < d1 → Combined defect D1 + D2 with dk1
a2-3 < d3 → Single defect D3
a4-5 > d4
→ Single defect D3
a5-6 > d6
a7-8 < d8
→ Combined defect D7 + D8 + D9 with dk2
a8-9 < d8
Fig2: Schematic diagram of defects and combined defects
(for execution version .10, f = 1)
8 Requirements for internal threads in aluminum components
This requirement shall only be applied if this point has been indicated on the technical product
specification (requirement on internal threads in conformity with DBL 4949).
The design specifications for internal-thread engagement length as per MBN 32004 shall form the
necessary basis of these requirements.
The specifications of DK0.6 shall apply for the first 4 threads.
Defects must not
o extend across more than 6 complete turns
o extend over an angle exceeding 90°
o damage more than 20 % of the supporting flanks
Defect nests are not permissible
The defect edge distance has to be larger than the maximum expansion of the largest
neighboring defect.
Any failed requirements shall require suitable qualification of the internal threads. In addition, it has to be
kept in mind that due to different manifestations of defects on internal threads a 100 % statistical certainty
is not possible.
Copyright Daimler AG
Historical document/uncontrolled copy when printed TP/ECE: Marco Belzner, 2018-12-03
You might also like
- Forensic BallisticDocument18 pagesForensic BallisticFranco Angelo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Worldwide Fastener Standard: WX 100 Finish Specification 1. ScopeDocument19 pagesWorldwide Fastener Standard: WX 100 Finish Specification 1. ScopeCarmen HernandezNo ratings yet
- IMT Technical Technical Specifications Specifications: Articulating Cranes Articulating CranesDocument2 pagesIMT Technical Technical Specifications Specifications: Articulating Cranes Articulating CranesMiguel Angel Vazquez ServinNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of Ship Platform ColissionDocument6 pagesRisk Assessment of Ship Platform Colission123habib123fikriNo ratings yet
- Operation ManualDocument42 pagesOperation ManualRadiología e Imagen para EstudiantesNo ratings yet
- AFS Pro 700 OM-engDocument218 pagesAFS Pro 700 OM-engVladNo ratings yet
- Drill Pipe Drill StringDocument11 pagesDrill Pipe Drill StringRodrigoBernardo50% (2)
- HeliCoil CatalogueDocument34 pagesHeliCoil Cataloguejarv7910No ratings yet
- Information sheet Standard fl ushing on MCR motors: Δp to shift the fl ushingDocument2 pagesInformation sheet Standard fl ushing on MCR motors: Δp to shift the fl ushingOrlando AriasNo ratings yet
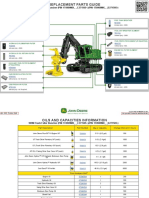
- 909M Tracked Feller Buncher PIN 1T0909MX C271505 PIN 1T0909MX D271505 Replacement Parts GuideDocument3 pages909M Tracked Feller Buncher PIN 1T0909MX C271505 PIN 1T0909MX D271505 Replacement Parts GuideNelson Andrade VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Iso 6489-3Document12 pagesIso 6489-3JonatasNo ratings yet
- PIV Exhaust Generic V11Document18 pagesPIV Exhaust Generic V11Alireza AameriNo ratings yet
- MQ SSL/TLS Channels Including V8 ChangesDocument23 pagesMQ SSL/TLS Channels Including V8 ChangesAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Diesel Engine: 1996 EPA and CARB Non-Road Emissions CertifiedDocument2 pagesIndustrial Diesel Engine: 1996 EPA and CARB Non-Road Emissions Certifiedporter1980No ratings yet
- Asme B5.8-2001 (2017)Document32 pagesAsme B5.8-2001 (2017)윤규섭No ratings yet
- Lenovo Xiaoxin Air-14iil 2020 - Flms0 La-J551p r02Document67 pagesLenovo Xiaoxin Air-14iil 2020 - Flms0 La-J551p r02TigerNo ratings yet
- STN - GMP Powertrain/Carbody Adaptation Interface Assembled Exhaust LineDocument42 pagesSTN - GMP Powertrain/Carbody Adaptation Interface Assembled Exhaust LineAlireza AameriNo ratings yet
- Zeta RevDocument46 pagesZeta Revsloba68100% (1)
- Conversao Racor Filtro Separador AguaDocument3 pagesConversao Racor Filtro Separador AguaRICHARD RONALD SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Orlander Text BookDocument783 pagesOrlander Text BookKai CaoNo ratings yet
- Gd825a-2 S/N 11001-UpDocument777 pagesGd825a-2 S/N 11001-UpMarcos Roberto Caresia da Cas100% (1)
- Man AcDocument32 pagesMan AcCharles Claudino SilvaNo ratings yet
- GL-T11R: Instruction ManualDocument8 pagesGL-T11R: Instruction ManualDayglis CostaNo ratings yet
- Manaul de Serviço cbr900 RR Fireblade (2000 2001) SistcombDocument62 pagesManaul de Serviço cbr900 RR Fireblade (2000 2001) SistcombCarlos LimaNo ratings yet
- Scom - CS74 76CS56 683 - Rehs4671 00Document52 pagesScom - CS74 76CS56 683 - Rehs4671 00Daniel PricopNo ratings yet
- Mando-Catalogue 2018Document259 pagesMando-Catalogue 2018Ericka BerreondoNo ratings yet
- CatalogoDocument574 pagesCatalogoCrisNo ratings yet
- Young Star - One Pager - Version 1.4 - September 2021Document1 pageYoung Star - One Pager - Version 1.4 - September 2021ShihbNo ratings yet
- FAG Angular Ball BearingDocument43 pagesFAG Angular Ball BearingzeljkoanNo ratings yet
- Helicoil Aftermarket Products CatalogueDocument24 pagesHelicoil Aftermarket Products CatalogueGabriel StefanNo ratings yet
- Minimum Retirement Age of Workers Act - SinhalaDocument19 pagesMinimum Retirement Age of Workers Act - SinhalaDilan HasinthaNo ratings yet
- DTC Ecm 164.122Document31 pagesDTC Ecm 164.122Ionut BordieanuNo ratings yet
- Miltonroy Milroyal B ManualDocument32 pagesMiltonroy Milroyal B ManualjorgeNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual KTA Web PDFDocument64 pagesInstruction Manual KTA Web PDFSURFnskNo ratings yet
- Chat LogDocument2 pagesChat LogHI it's meNo ratings yet
- Programming For CNC LathesDocument106 pagesProgramming For CNC LathesGustavo Zamudio RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Consistently Consistent GreaseDocument4 pagesConsistently Consistent GreaseBrian Careel100% (1)
- Equivalencia GraxasDocument1 pageEquivalencia Graxasrobson robsonNo ratings yet
- DVI Prime ManualDocument71 pagesDVI Prime Manualvelvet0523No ratings yet
- Catalogo Rolamento ImaDocument90 pagesCatalogo Rolamento ImaJoao Victor FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Peças Trator 7225J Out 2014Document728 pagesCatalogo Peças Trator 7225J Out 2014Izael VieiraNo ratings yet
- Agma 920 A01 Materials For Plastic GearsDocument46 pagesAgma 920 A01 Materials For Plastic GearsNursena SEVİNÇNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Uncertainty - Concepts, Modelling and VerificationDocument67 pages1.2 Uncertainty - Concepts, Modelling and VerificationQuang Thang100% (1)
- 6.2 - Eixo TraseiroDocument92 pages6.2 - Eixo Traseirodavi henrique boazNo ratings yet
- Juno Net Con SP1 MNDocument5 pagesJuno Net Con SP1 MNCarlos Eberhard Diaz TorresNo ratings yet
- HL635ALDocument208 pagesHL635ALTelles Cristian Mendes PazNo ratings yet
- GearboxDocument20 pagesGearboxViknesh VikneshNo ratings yet
- Ixar Academy Cellphone Repair SyllabusPDFDocument3 pagesIxar Academy Cellphone Repair SyllabusPDFLawson SangoNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Bombas Centrifugas Grundfos CRDocument25 pagesCatalogo Bombas Centrifugas Grundfos CRhugo mendozaNo ratings yet
- Bosch EV6 3868 - 7626Document5 pagesBosch EV6 3868 - 7626hacvuaNo ratings yet
- 04 Convenient IvecoDocument30 pages04 Convenient Ivecomirel mNo ratings yet
- Ecs MCP61PM-GM Rev 2.4Document34 pagesEcs MCP61PM-GM Rev 2.4onimeno kuroi kenshiNo ratings yet
- Database NormalizationDocument7 pagesDatabase NormalizationmarcNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo de Variables de InstrumentacionDocument16 pagesEjemplo de Variables de InstrumentacionEduardo JiménezNo ratings yet
- Ncdex Lot SizeDocument6 pagesNcdex Lot Sizemahesaraswat100% (1)
- Dot Grwir-06103, Mar 2022Document23 pagesDot Grwir-06103, Mar 2022AbhijeetNo ratings yet
- PoE 25-100172-001Document2 pagesPoE 25-100172-001Jossemar Cristhian Bartolo OnayramNo ratings yet
- Code - (Modded) ALL CREW COLOURS (150+) Se7enSins Gaming CommunityDocument1 pageCode - (Modded) ALL CREW COLOURS (150+) Se7enSins Gaming CommunityEverhett HughesNo ratings yet
- Declaracion de Conformidad (ES) - Recuperador de Calor Kosner KRC 5 ED BP-PH-SV 3650m3 - H Vertical Apto PDocument1 pageDeclaracion de Conformidad (ES) - Recuperador de Calor Kosner KRC 5 ED BP-PH-SV 3650m3 - H Vertical Apto PDani DGNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi 380Document8 pagesMitsubishi 380robertoNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument46 pagesManualelver galargaNo ratings yet
- Steer 2010Document8 pagesSteer 2010Lidia RaduNo ratings yet
- Drawing Standard: Drawing Sheet Sizes and FormatsDocument29 pagesDrawing Standard: Drawing Sheet Sizes and Formatssumit_saraf_5No ratings yet
- Catálogo Dexco 2020Document108 pagesCatálogo Dexco 2020Adalberto Santana JuniorNo ratings yet
- Daimler - MBN 36012 ENG - 03-09Document11 pagesDaimler - MBN 36012 ENG - 03-09ali haydarNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide VAMP 221-MCSet - V4Document16 pagesInstallation Guide VAMP 221-MCSet - V4cokicisneNo ratings yet
- Aqa Byb1 W QP Jun07Document12 pagesAqa Byb1 W QP Jun07李超然No ratings yet
- PugalenthiDocument7 pagesPugalenthiTHANI ORUVANNo ratings yet
- Inter Freq Handover Parameter Tuning: F2 Cell 2D/2F/2B Threshold OptimizationDocument19 pagesInter Freq Handover Parameter Tuning: F2 Cell 2D/2F/2B Threshold Optimizationedwin samaNo ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument71 pagesDigital Image ProcessingPratibha SharmaNo ratings yet
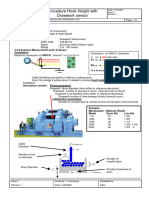
- Hook Height With Drawwork SensorDocument3 pagesHook Height With Drawwork SensorJose PalumboNo ratings yet
- Fund. Acerinox Horno ArcoDocument8 pagesFund. Acerinox Horno ArcoJavier Mauricio Neira CastrillonNo ratings yet
- Air Dan BiomolekulDocument61 pagesAir Dan BiomolekulgabbymonicaputriNo ratings yet
- Switching Theory and Logic DesignDocument89 pagesSwitching Theory and Logic DesignUppalaguptam Hari Satya PriyaNo ratings yet
- How To Implement A Distributed CommonJ Work Manager ESDocument20 pagesHow To Implement A Distributed CommonJ Work Manager ESAbmel Salim LopessierNo ratings yet
- DBMS Practice QueestionsDocument2 pagesDBMS Practice QueestionsAbhibhava Bhatt VIII [E] 4No ratings yet
- Supply Installation Commissioning of Worlld Largest MillDocument12 pagesSupply Installation Commissioning of Worlld Largest MillAbe ArdiNo ratings yet
- Hya3-6 M6 InsDocument3 pagesHya3-6 M6 InssuhuanajNo ratings yet
- Functions Equations Question BankDocument101 pagesFunctions Equations Question BankParth DesaiNo ratings yet
- Microwave Mini ProjectDocument21 pagesMicrowave Mini Projectfaizan4033No ratings yet
- Aviation Service ManualDocument28 pagesAviation Service ManualArmo MoralesNo ratings yet
- DA-100English ManualDocument10 pagesDA-100English ManualGiang TrườngNo ratings yet
- DDDD (Repaired)Document61 pagesDDDD (Repaired)Phung ba Quoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Anchor Lliberty Mpa ManDocument8 pagesAnchor Lliberty Mpa ManIgnacio Barriga NúñezNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 Nov 2004Document16 pagesPhysics Paper 2 Nov 2004tommyliuNo ratings yet
- Math Iv Chapter 3Document60 pagesMath Iv Chapter 3Benjamin AkingeneyeNo ratings yet
- File: OPL3.java Software Implementation of The Yamaha YMF262 Sound Generator. Version 1.0.6Document18 pagesFile: OPL3.java Software Implementation of The Yamaha YMF262 Sound Generator. Version 1.0.6mendofriulNo ratings yet
- LUXEN SERIES 5 182 144cells 530-550w MONOFACIALDocument2 pagesLUXEN SERIES 5 182 144cells 530-550w MONOFACIALOscar DuduNo ratings yet
- Beckman Coulter GenomeLab TroubleshootDocument56 pagesBeckman Coulter GenomeLab TroubleshootChrisNo ratings yet
- Solar and Lunar Eclipses1-1Document17 pagesSolar and Lunar Eclipses1-1THERESA JNo ratings yet