Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrochemical Cell Lab
Uploaded by
Hannah 晗❾Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrochemical Cell Lab
Uploaded by
Hannah 晗❾Copyright:
Available Formats
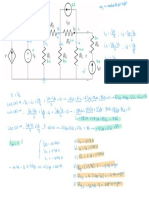
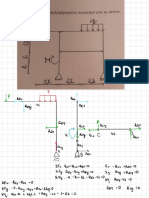
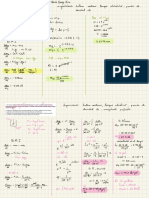
"
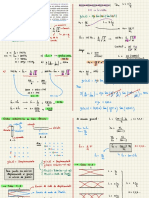
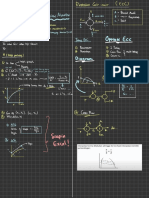
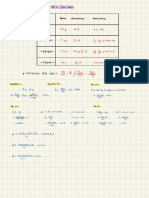
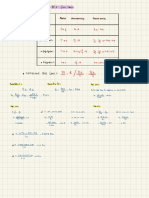
RED : Pb
Pb
"
☐ "
-12e- →
NO 5
Pb ( s) OX
① :
Fees )
No,
-
→
Fe
"
Fe 2++2e-
SOA 0A RA
⑤ + 2 e- Pbc RA
↓
→
0.13
f-
-
Increase
◦A "
Fe t 2 e- → -
o ¢4.
RA
OA
SRA
"
SRA =
Oxidation :
Fees ) →
Fe -12¢ Éo =
+0.44 V
"
SOA =
reduction :
Pb +2¢ → Pbls ) E- or
= -
0.13 V
✓
" "
Overall :
Fees, +
Pb →
Fe + Pb ( s ) E- cell =
0-31 V
Inquiry
:
a) If removed half cell
I salt
bridge is ,
polarization in each will stop the electrochemical cell
from
working .
"
b) Since oxidation occurs at anode by constantly losing e- positive charges ( Fe ) will build up
, , .
If there's no anion ( in this case NO 5) to keep the electrolyte neutral there will be an
increasing ,
"
between Fe The repulsion will be too and eventually discourages any oxidation
repulsion .
big
from Similarity the cathode side reduction leads build up
happening .
,
on .
happen which to
in
negative charge ( keep consuming Pb
"
) .
It makes cathode unable to
accept any more e- ,
which further discourages flow of e- .
If there's no more flow of electrons the .
battery stops working .
Application :
1 .
a) The reading would be 0 .
b) When the electrochemical cell reaches equilibrium it means oxidation and reduction happens at the
,
same rate . As a result , there will be no net flow of electrons No net flow of election means no electrical
.
potential difference ,
no voltage reading .
2 .
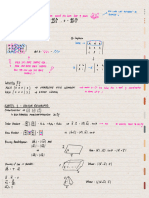
a) Pb } LPO 4) 2
"
b)
Voltage decreases If percipitate Pb } ( Poa), forms [Pb ] will decrease
.
,
.
According to Le Chatelier 's
principle the system will shift left where encourages production of Pb
"
, . This mean reduction in
cathode will happen less frequently . It reduces its capability to
accept e-
,
thus net e- flow decreases
and decreases
voltage .
0.298 V )
°
3 . OE =
0.327 V ( was
a) voltage increase .
"
b) Fe (s )
→
Fe t 2 e-
of Fe CNO })z
"
1- Fe I also decreases Le Chatelier 's
By decreasing the concentration ,
"
.
principle
suggest the
system will shift
right to counteract loss of Fe .
By shifting right ,
oxidation occurs
more frequently ,
more e- will be produced as well .
There will
any increase in electron flow in the
same time
period voltage ,
increases .
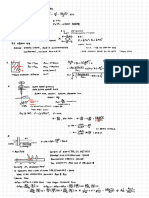
4A)
#gative charge
iron
Only
.
b) because cations will
migrate to cathode to balance build
up C due to loss of cation
"
at anode will
in reduction) . As a result
"
,
Fe
migrate to cathode through salt bridge .
It can
very unlikely to form percipitate with nitrate CNO 5) Nitrate with most
migrate because Fe is .
cations are soluble in water .
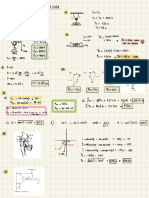
°
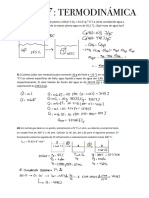
b- a) DE =
0 .
170 V
"
b) Anode :
OX : Fees, →
Fe + 2e- E 00 =
+ 0.44V
"
Cathode :
RED :
Wd + 2 e- →
Wd ( s) E°r =
?
"
Écei ,
"
Overall Feis ) + Wd →
Fe t wd es) =
0.17 V
EF
°
E Cell E
-
=
0
170 44
=
0 .
-
0 .
0.27 V
=
-
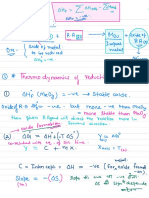
i. The standard reduction potential of who datium is -0.27 V.
"
6. Anode →
oxidation :
2h Is, → Zn -12¢ ÉO =
-10.76 ✓
> Fe "t2→ Fees, E°r = ? C- 0.44W )
" " ◦
1 :
2h ( s ) -1 Fe →
2h -1 Fees, E- cell
=
0.32 V
E- °r E. cell table of
strength of reducing reduction of
E°o According to and
oxidizing agent
= -
(+0.76 V7 iron standard reduction potential of 0.44 V.
=
0.32 -
has a
-
= -
0.44 V Thus iron LFE) is used as cathode .
You might also like
- Miniature Chlorate CellDocument36 pagesMiniature Chlorate Cell1hardwareguyNo ratings yet
- Health Benefits of Alkaline WaterDocument6 pagesHealth Benefits of Alkaline WaterNica C. AkoNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Ether Phenol PDFDocument16 pagesAlcohol Ether Phenol PDFHappy SinghNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument48 pagesElectrolysisGina100% (4)
- 2013 Chemistry (Stage 3) ExamDocument44 pages2013 Chemistry (Stage 3) ExamMichael BobNo ratings yet
- Cigre TB 625Document98 pagesCigre TB 625namsaigon316100% (3)
- Acids QuizDocument462 pagesAcids Quizwondimu0% (1)
- Chemistry Report On Rate of ReactionDocument6 pagesChemistry Report On Rate of ReactionMatthew Chu80% (5)
- German Problems 2013Document152 pagesGerman Problems 2013Stephen PramatyaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry 1 SyllabusDocument16 pagesAnalytical Chemistry 1 SyllabusReinette MelodiaNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument2 pagesNoteNhiên AnNo ratings yet
- S11 - Lab - 15 AbrilDocument5 pagesS11 - Lab - 15 AbrilJorge Bolívar MojicaNo ratings yet
- เคมีเพิ่มDocument5 pagesเคมีเพิ่มPavaridNo ratings yet
- Tarea+3 +Version+Preliminar+2-2023Document12 pagesTarea+3 +Version+Preliminar+2-2023sebastian.venegas.castroNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument4 pagesProblemssilverwing4220No ratings yet
- Ejemplo Formula General para pc4 DGE 2021Document1 pageEjemplo Formula General para pc4 DGE 2021EL PROFEگORTMNo ratings yet
- Reductioni - MN: StiffDocument4 pagesReductioni - MN: StiffAyushman JaiminiNo ratings yet
- Oxidation: ReductionDocument7 pagesOxidation: ReductionLeo SukhumvatNo ratings yet
- Untitled (Draft)Document3 pagesUntitled (Draft)aplhaing.infoNo ratings yet
- Ch8 SecondOrder (140362) PDFDocument19 pagesCh8 SecondOrder (140362) PDFNongPhatNo ratings yet
- E EaiDocument7 pagesE EaiAnonymous 9sYcK2k8No ratings yet
- Documento 2 GGDocument1 pageDocumento 2 GGpedroNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Ejercicios T7 Gulag FreeDocument4 pagesWuolah Free Ejercicios T7 Gulag FreeuserwuolahNo ratings yet
- Lac-Most (Ca/A (Yrha: Se+S Exrha-3'UbvDocument4 pagesLac-Most (Ca/A (Yrha: Se+S Exrha-3'UbvriicardlopezNo ratings yet
- Barrons AP Statistics 2Document10 pagesBarrons AP Statistics 2김지형No ratings yet
- Response 13 EPC 2Document4 pagesResponse 13 EPC 2Steven HimawanNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio Hiperestatico EnrejadoDocument2 pagesEjercicio Hiperestatico EnrejadoScarlett ParedesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 2Document14 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2Tiên PhạmNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 CIVE207 W24Document10 pagesAssignment2 CIVE207 W24Andrew WatsonNo ratings yet
- Response 9 ECC 2Document4 pagesResponse 9 ECC 2Steven HimawanNo ratings yet
- Mathemat I KDocument1 pageMathemat I KkerosietmNo ratings yet
- Rayocs: DiscussedDocument4 pagesRayocs: DiscussedMatthew ListroNo ratings yet
- Test Física T5Document5 pagesTest Física T5Julia AcevedoNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document2 pagesHW 5qgbpt58cyjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document1 pageChapter 6Shaurya JainNo ratings yet
- Teoría de Control I Ejem 1 JorgeD12Document1 pageTeoría de Control I Ejem 1 JorgeD12jorgeNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction Short Notes - Learning Tales 2Document3 pagesRedox Reaction Short Notes - Learning Tales 2Preet KaurNo ratings yet
- FTP - NR# - : EconomyDocument2 pagesFTP - NR# - : EconomyKentud SapiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Saah SirDocument119 pagesBiochemistry Saah SirMrHoneyBunnyNo ratings yet
- MatekDocument1 pageMatekGyevnar GergoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Family Mind MapDocument1 pageCarbon Family Mind Maparyangavli19No ratings yet
- Hidráulica I 3Document1 pageHidráulica I 3Emily MartinezNo ratings yet
- PCS - Moving Q - MagnetismDocument2 pagesPCS - Moving Q - MagnetismAkanshaNo ratings yet
- Letzte KlausurDocument3 pagesLetzte Klausur48hzg6b8jpNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument1 pageCHEMISTRYAYA SABAH FAREEDNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument1 pageCHEMISTRYAYA SABAH FAREEDNo ratings yet
- MWM 3 PDFDocument3 pagesMWM 3 PDFAnastasia DostankoNo ratings yet
- Ya.i-N-Tyzntctznc-Ya2tn - To/-2nc-4acn - C-Y: EllipseDocument8 pagesYa.i-N-Tyzntctznc-Ya2tn - To/-2nc-4acn - C-Y: EllipseSoham KejriwalNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry NotesDocument1 pageTrigonometry NotesRainbow100% (1)
- Newtons Laws Part 2Document9 pagesNewtons Laws Part 2Robel ManaloNo ratings yet
- Untitled (Draft)Document2 pagesUntitled (Draft)tanannudt.srNo ratings yet
- Review CHEM 2Document1 pageReview CHEM 2Michelle SortoNo ratings yet
- Bloc de Notas Sin TítuloDocument1 pageBloc de Notas Sin Títulomaria paula uribe coyNo ratings yet
- Redox Reaction Short Notes - Nitesh DevnaniDocument3 pagesRedox Reaction Short Notes - Nitesh DevnaniVansh DeshwalNo ratings yet
- Capacitor PDFDocument3 pagesCapacitor PDFshashikantNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument24 pagesUntitledJosieNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document7 pagesModule 3bobby brownNo ratings yet
- Ingeniería de ProcesosDocument2 pagesIngeniería de ProcesosValeria PunzoNo ratings yet
- Bevlangsreng BRP: LajurxDocument3 pagesBevlangsreng BRP: Lajurxbella graciaNo ratings yet
- Summary MathematicsDocument6 pagesSummary Mathematicst9mhcq77p5No ratings yet
- Termodinamika 2Document1 pageTermodinamika 2mur tazaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Test 164 RevisedDocument29 pagesCircuit Test 164 Revisedsatang M.F.LNo ratings yet
- 01 31 2024Document12 pages01 31 2024John ConnorNo ratings yet
- Miscelánea de Dinamica - TrabajoDocument3 pagesMiscelánea de Dinamica - TrabajoSandra Quispe BeltránNo ratings yet
- Procesos IIDocument2 pagesProcesos IIMiranda Escamilla PerezNo ratings yet
- Mangan I ChromDocument1 pageMangan I Chromkarolina WaleńskaNo ratings yet
- Information Theory Lecture 7 Notes FullDocument5 pagesInformation Theory Lecture 7 Notes FullMUCKRAKERNo ratings yet
- Z80 - Esquema UALDocument1 pageZ80 - Esquema UALAlejandra CuadrosNo ratings yet
- 5.5 Balancing Redox Reactions OnlineDocument15 pages5.5 Balancing Redox Reactions OnlinealiNo ratings yet
- Antioxidants Science Technology and ApplicationsDocument61 pagesAntioxidants Science Technology and ApplicationsNguyễn Trung HiếuNo ratings yet
- Redox Chemistry of SoilsDocument7 pagesRedox Chemistry of SoilsAthena NocetoNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Book Back and Additional Questions With Answers EM 221181Document75 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Book Back and Additional Questions With Answers EM 22118111B CHARAN ANANDNo ratings yet
- Lipid Oxidation Measurement MethodDocument29 pagesLipid Oxidation Measurement MethodEric TestroetNo ratings yet
- PaperDocument18 pagesPaperrahul_camNo ratings yet
- Ozone Oxidation of Cyanide-Contaminated WastewaterDocument1 pageOzone Oxidation of Cyanide-Contaminated WastewaterAnonymous c6AG7aHrrTNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TutorialsDocument28 pagesChemistry TutorialsDomionNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Water - WikipediaDocument21 pagesElectrolysis of Water - WikipediaEusebia MaedzwaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non MetalsHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- 313 E Book2 PDFDocument453 pages313 E Book2 PDFdanhemNo ratings yet
- ORP Management in Wastewater As An Indicator of Process EfficiencyDocument2 pagesORP Management in Wastewater As An Indicator of Process EfficiencyJose IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetDocument5 pagesLab Report: Shahjalal University of Science & Technology, SylhetMd Afif AbrarNo ratings yet
- Methylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)Document18 pagesMethylene Blue Reduction Test (MBRT)SHAIKH100% (2)
- Chemistry Stage 3 Exam 2012Document40 pagesChemistry Stage 3 Exam 2012Naomi David NewNo ratings yet
- 3B Reactivity of Metals Edrolo Study NotesDocument25 pages3B Reactivity of Metals Edrolo Study NotesMr FiddleNo ratings yet
- Waelz Process ImprovementDocument7 pagesWaelz Process ImprovementCeyhun TatarNo ratings yet
- 271 276 PDFDocument6 pages271 276 PDFFunkozor ShiftNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 4Th Edition David Klein Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesOrganic Chemistry 4Th Edition David Klein Download PDF Chapterjoseph.hutton828100% (5)
- Aluminium + Iron (III) Oxide Iron + Aluminium OxideDocument5 pagesAluminium + Iron (III) Oxide Iron + Aluminium OxideTaha Abid AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Redox Titrations - Subjects 0Document79 pagesUnit 11 - Redox Titrations - Subjects 0Siti AmirahNo ratings yet