Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Apert Syndrome: Report of A Rare Congenital Malformation
Uploaded by
christian roblesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Apert Syndrome: Report of A Rare Congenital Malformation
Uploaded by
christian roblesCopyright:
Available Formats
Open Access
Case Report
Apert Syndrome:
Report of a rare congenital malformation
Ehsan Rathore1, Altaf Hussain Rathore2
SUMMARY
A rare case of an adult male with malformation of the skull, face, hands and feet called acrocephalosyndactly
or Apert syndrome is presented. Its probable cause, features and treatment is discussed. It is a unique
case who survived upto the age of 32 years without any operative intervention and adjusted in the society
though he has all the stigmas of the above syndrome. We have concluded and made a point that in the
adult sufferer, facial deformity is not so important and urgent for the treatment than syndactyly, which
handicaps the sufferer in performing the daily routine work.
KEY WORD: Apert syndrome, Rare congenital anomaly.
doi: https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.333.12878
How to cite this:
Rathore E, Rathore AH. Apert Syndrome: Report of a rare congenital malformation. Pak J Med Sci. 2017;33(3):773-775.
doi: https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.333.12878
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0),
which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
INTRODUCTION It occur in 1 in 200,000 to 1 in 160,000 live births4,5
but its incidence is 1 in 65000.6 It is characterised by
Apert syndrome is a rare congenital disorder. This high prominent forehead flat back of occiput, flat
syndrome was first described by Eugene Apert or concave face due to premature union of coronal
in 1906. It is caused by a defect on the fibroblast suture and deficient growth of midfaical bones
growth factor receptor 2 gene on chromosome leading to mandibular prognathism. Patient has
10.1 It is an autosomal dominant disorder or more also shallow orbit causing some degree of proptosis
commonly due to mutation in the F.G.F.R 2 gene.2 and hypertelorism.3 They may be accompanied by
It is characterize by early union of the coronal fusion of cervical vertabra specialy C5-6 7 and other
suture giving typical skull and facial deformity and visceral, skeletal C.N.S anomalies.8
sydactaly of hands and feet.3 The main difference from Cruzon syndrome is
that it is accompanied by syndactyly of hands and
1. Dr. Ehsan Rathore, BDS, MCPS (MFS).
Senior Registrar, Maxillo Facial Surgery,
feet.9 Its proper treatment is operation within first
Faryal Dental College, year of Birth10 to stop early fusion of the coronal su-
Lahore, Pakistan. ture otherwise they get increased intracranial pres-
2. Prof. Dr. Altaf Hussain Rathore, MBBS, D.A (London) FRCS (Edin).
Chief of Surgery, Foundation Hospital Rajana,
sure. They have difficulty in breathing causing sleep
Distt: Toba Tek Singh, Apnea and mouth breathing.11 They have usually
Punjab, Pakistan. middle ear infection resulting into some degree of
Correspondence: deafness and can also have some degree of visual
Dr. Ehsan Rathore loss.8 They are somewhat mentally subnormal and
Dental Syndicate, Office Number FF-12, have dentition problems. Their height is shorter
AB Heights, New Airport Road, than general population due to short limbs but not
Lahore Cantonment,
Lahore - Pakistan. as short as achondroplasia.8 As stated earlier those
E-mail: surgrathore@gmail.com who survive with or without some sort of coronal
suture surgery need maxillaofacial surgeon for ad-
* Received for Publication: November 17, 2016
* Edited and Corrected: December 26, 2016
vancement of fronto facial and mid facial part of
* Revision Received: January 5, 2017 skull to correct the proptosis and for cosmetic rea-
* Final Revision Accepted: April 5, 2017 son. Syndactyly has to be operated in stages within
Pak J Med Sci 2017 Vol. 33 No. 3 www.pjms.com.pk 773
Ehsan Rathore et al.
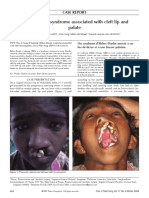
Fig2: 2A. Hoof shaped Hand.
2B: Syndactyly shape of a rose bud.
2C: Syndactyly of feet.
X-ray of skull (Fig.3A) was also typical of apert
Fig.1: 1A. Patient with Apert Syndrome.
1B. Face of the case.
syndrome and syndactyly of both hands was of
type III i.e fusion of all digits like a hoof or rosebud
1-2 years age10 by hand or plastic surgeon in type 3, (Fig.3B) by cartilage with one conjoined nail. Foot
4 for functioning of the hand specially thumb and syndactyly was of type IV.12
little finger Syndactyly of feet is usually left alone.
He was not bothered about his cosmetic
CASE REPORT appearance but was more concerned about hand,
so facial deformity was left for the first author (E.R)
A 32 year old short statured male (Fig.1) with
to be corrected later on.
low intelligence building and red eyes presented
Operation: After proper investigations he was
to us for syndactaly of both hand and syndactyly
operated under General Anesthesia. Tourniquate of
of feet. Fig.2-A,B,C. He had low intelligence and
could not tell about his pediatric and birth history arm was applied. As the blood supply of neighboring
as his parents died long ago. However no one else finger was complicated and construction of thumb
in the family had this defect. With this deformity of enough length with proper first web space
of hands, he could not do the daily routine work. was desired so we had to amputate the second
Therefore, he was more interested in operation digit. Right hand was operated in the first stage,
of the hands. His face, eyes, head and teeth were construction of the thumb and middle finger was
classical of craniosyntosis as describe earlier. done (Fig.3C) Separation of other fingers was left to
Fig.3: 3A: X-Ray Skull. 3B: X-Ray of the hand. 3C: Right hand after the operation.
774 Pak J Med Sci 2017 Vol. 33 No. 3 www.pjms.com.pk
Apert Syndrome
be managed later. Patient was discharged after 10 REFERENCES
days of the surgery. 1. Wilkie AO, Slaney SF, Oldridge M, Poole MD, Ashworth
GJ, Hockley AD, et al. Apert syndrome results from
DISCUSSION localized mutations of FGFR2 and is allelic with Crouzon
syndrome. Nature Genetics. 1995;9(2):165–172. doi: 10.1038/
We have reported a rare congenital malformation ng0295-165
Apert syndrome or achrocephalosyndactyly. Its 2. Goriely A, McVean GA, Röjmyr M, Ingemarsson B, Wilkie
incidence is 1:65000, so it is not so rare; Apert himself AO. Evidence for Selective Advantage of Pathogenic
reported 9 cases in 1906.6 They usually die in infancy FGFR2 Mutations in the Male Germ Line. Science.
2003;301(5633):643–646. doi: 10.1126/science.1085710
unless they are operated for coronal suture in early 3. Amar T, Krishna V, Sona K. Apert syndrome: A rare
infancy.13 Exact number of cases reported to date are presentation. J Indian Acad Clin Med. 2007;8:245–246.
not known. Our case is unusual that he survived upto 4. Phil Foreman. Education of Students with an Intellectual
the age of 35 years without any operation. He has Disability: Research and Practice (PB). IAP, 2009, p. 30.
5. Baker AB, Baker LH. Apert’s Syndrome. Clinical Neurology.
got all the minor stigmas of Apert Syndrome i.e low Medical Dept., Harper & Row, 1979;3:47.
intelligence, partial deafness, weak eye sight, short 6. Bhatia PV, Patel PS, Jani YV, Soni NC. Apert’s syndrome:
stature, facial deformity, bad dentition, mandibular Report of a rare case. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2013;17(2):294–
prognathism, fused digits of hands and feet . 297. doi: 10.4103/0973-029X.119782
7. Carinci F, Pezzetti F, Locci P, Becchetti E, Carls F,
At this age, he was least worried about his facial Avantaggiato A, et al. Apert and Crouzon syndromes:
features and adjustment in the society. His main Clinical findings, genes and extracellular matrix. J Craniofac
worry was about the syndactyly of his hands due to Surg. 2005;16:361-368.
his inability to perform the daily essential work like 8. Varoli FP, Santos KCP, Costa C, Oliveira JX. Apert
syndrome: clinical and radiographic features and case
washing, working, eating, writing etc. For adults report. Rev Odonto Cienc. 2011;26(1):96-99.
the surgeons should give preference to his hand 9. Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Chi AC. Oral and
surgery than facial deformity unless there are some Maxillofacial Pathology, 2016, Page 41.
serious respiratory problems. 10. Panchal J, Uttchin V. Management of craniosynostosis.
Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111:2032-2048. doi: 10.1097/01.
He had the most difficult syndactyly i.e. Type III PRS.0000056839.94034.47
so the patient was badly handicapped due to hoof 11. Doerga PN, Spruijt B, Mathijssen IM, Wolvius EB, Joosten KF,
shaped hands. In the first stage we constructed the van der Schroeff MP. Upper airway endoscopy to optimize
thumb and the first web space against the advice obstructive sleep apnea treatment in Apert and Crouzon
syndromes. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016;44(2):191-196.
of Zucker14 who recommended the release of first doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2015.11.004
and fourth web space in the first stage. In view of 12. Upton J. Apert Syndrome. Classification and
the severity of this deformity we amputated the pathologic anatomy of limb anomalies. Clin Plast Surg.
index finger to make a reasonable web space along 1991;18(2):321–355.
13. Ileri Z, Goyenc YR. Apert syndrome: A case report. Eur J
with construction of middle finger, which will take Dent. 2012;6(1):110–113.
the function of the index finger. Till the time of 14. Zucker RM. Syndactyly correction of the hand in Apert
reporting the patient is satisfied with his hand and syndrome. Clin Plast Surg. 1991;18(2):357–364.
he is washing, eating and writing himself by his
right hand. We are going to plan surgery of the left
hand and other fingers and facial deformity later on
when he will demand it.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We are grateful to Mr. Yasir Salim and Mr. Athar
Adrees of Foundation Hospital Rajana Distt. Toba
Tek Singh, Pakistan for their photographic and
secretarial help in preparing this manuscript.
Pak J Med Sci 2017 Vol. 33 No. 3 www.pjms.com.pk 775
You might also like
- Ijcpd 05 203Document5 pagesIjcpd 05 203yanyangNo ratings yet
- Article 1552613421 PDFDocument5 pagesArticle 1552613421 PDFLakshmi Sarvani ValluriNo ratings yet
- Apert Syndrome: A Case ReportDocument8 pagesApert Syndrome: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ehlers Danlos Syndrome Associated With Cleft Lip and PalateDocument3 pagesEhlers Danlos Syndrome Associated With Cleft Lip and PalateelmancuernoNo ratings yet
- JDattaMegheInstMedSciUniv144426-5775248 160232Document3 pagesJDattaMegheInstMedSciUniv144426-5775248 160232srigiri surathNo ratings yet
- 2016 SergioDocument10 pages2016 SergioazizhamoudNo ratings yet
- Treatment Timing and Multidisciplinary Approach in Apert SyndromeDocument6 pagesTreatment Timing and Multidisciplinary Approach in Apert SyndromeJulio AbarzuaNo ratings yet
- Ijcmr 3499Document4 pagesIjcmr 3499AlfirahmatikaNo ratings yet
- Thanatophoric Dysplasia: A Case Report: Uruj Jahan, Astha Sharma, Neena Gupta, Shruti Gupta, Fatima UsmaniDocument4 pagesThanatophoric Dysplasia: A Case Report: Uruj Jahan, Astha Sharma, Neena Gupta, Shruti Gupta, Fatima UsmaniPrima Hari PratamaNo ratings yet
- Microcephalic Osteodyplastic Primordial Dwarfism Type II, Case Report With Unique Oral Findingd and A New Mutation in The Pericentrin GeneDocument8 pagesMicrocephalic Osteodyplastic Primordial Dwarfism Type II, Case Report With Unique Oral Findingd and A New Mutation in The Pericentrin GeneFran GidiNo ratings yet
- Dentistry: Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesDentistry: Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia: A Case ReportkityamuwesiNo ratings yet
- The Apert and Crouzon Syndromes: General and Dental Aspects and Management in Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopaedics: A Review ArticleDocument10 pagesThe Apert and Crouzon Syndromes: General and Dental Aspects and Management in Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopaedics: A Review ArticleOral DentNo ratings yet
- Pearls July 2011Document2 pagesPearls July 2011Raja Fauzan FahleviNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0889540623002573 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0889540623002573 MainDANTE DELEGUERYNo ratings yet
- Manejo Dental ELADocument4 pagesManejo Dental ELAAline LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Apert Syndrome - Sultan BaroamaimDocument37 pagesApert Syndrome - Sultan BaroamaimsultanNo ratings yet
- 2020 Collet-Sicard Syndrome After Jefferson FractureDocument3 pages2020 Collet-Sicard Syndrome After Jefferson FractureJose ColinaNo ratings yet
- Parry-Romberg Syndrome: A Rare Case ReportDocument6 pagesParry-Romberg Syndrome: A Rare Case Reportafni manurungNo ratings yet
- Cabt 12 I 5 P 45Document6 pagesCabt 12 I 5 P 45abeer alrofaeyNo ratings yet
- 447Document3 pages447Faraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Management of Lefort Fractures: Vijay Ebenezer, R. Balakrishnan and Anatha PadmanabhanDocument4 pagesManagement of Lefort Fractures: Vijay Ebenezer, R. Balakrishnan and Anatha PadmanabhanSuci NourmalizaNo ratings yet
- Gorlin Syndrom SSDC.Document3 pagesGorlin Syndrom SSDC.HarjotBrarNo ratings yet
- Garré's Osteomyelitis of The JawDocument3 pagesGarré's Osteomyelitis of The JawLeDentiste Dental HealthNo ratings yet
- Cleidocranial DysostosisDocument4 pagesCleidocranial DysostosisAnonymous 9QxPDpNo ratings yet
- Surgical Correction of Bifid Nose Due To Tessier's No. 0 Cleft PDFDocument4 pagesSurgical Correction of Bifid Nose Due To Tessier's No. 0 Cleft PDFMichelle AthinaNo ratings yet
- Syndromes: ContentsDocument5 pagesSyndromes: ContentsRoshni SinghNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Features of Ollier 'S Disease - Two Case ReportsDocument5 pagesRadiographic Features of Ollier 'S Disease - Two Case ReportsAlfeus GradyNo ratings yet
- Sorge 1996Document4 pagesSorge 1996jahfdfgsdjad asdhsajhajdkNo ratings yet
- Otodental Syndrome, Oculo-Facio-Cardio-Dental (OFCD) Syndrome, and Lobodontia: Dental Disorders of Interest To The Pediatric RadiologistDocument3 pagesOtodental Syndrome, Oculo-Facio-Cardio-Dental (OFCD) Syndrome, and Lobodontia: Dental Disorders of Interest To The Pediatric Radiologistمحمد عبدالرحمنNo ratings yet
- A Case Report of Paget's Disease of Bone Involving Maxilla and Mandible: A Diagnostic DilemmaDocument8 pagesA Case Report of Paget's Disease of Bone Involving Maxilla and Mandible: A Diagnostic DilemmaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- EmbrioDocument3 pagesEmbrioAmmy ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Ocular and Adnexal Anomalies in Craniofacial MicrosomiaDocument8 pagesOcular and Adnexal Anomalies in Craniofacial MicrosomiaEerrmmaa Ssaarrell Rroommaann PpaarraaNo ratings yet
- Identifying A A RSK Og SyndromeDocument3 pagesIdentifying A A RSK Og SyndromeS. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Marfan Syndrome With Atypical PresentationDocument4 pagesMarfan Syndrome With Atypical PresentationaiNo ratings yet
- Final Case Report FinalDocument7 pagesFinal Case Report FinalPawan JarwalNo ratings yet
- Rowell SyndromeDocument3 pagesRowell SyndromeMostafaAhmedNo ratings yet
- 9d7f PDFDocument4 pages9d7f PDFMubarak HazaziNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of Ectodermal Dysplasia Case Using Unconventional Impression Techniques and Fabricating Hollow Denture A Case ReportDocument6 pagesProsthodontic Management of Ectodermal Dysplasia Case Using Unconventional Impression Techniques and Fabricating Hollow Denture A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Management of Le Fort II Fracture Accompanied With Blowout Fracture of Orbital Base (Case Report)Document4 pagesManagement of Le Fort II Fracture Accompanied With Blowout Fracture of Orbital Base (Case Report)Anonymous HyPucbHRNo ratings yet
- Periostitis Ossificans: Report of Two CasesDocument7 pagesPeriostitis Ossificans: Report of Two CasesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- (Polish Journal of Surgery) Rare Facial CleftsDocument6 pages(Polish Journal of Surgery) Rare Facial CleftspatrickpsilvaNo ratings yet
- mooneAMS 3 66Document6 pagesmooneAMS 3 66dikiprestya391No ratings yet
- Long-Term Follow-Up of A Patient With Achondroplasia Treated With An Orthodontic ApproachDocument11 pagesLong-Term Follow-Up of A Patient With Achondroplasia Treated With An Orthodontic ApproachThuyNo ratings yet
- v10 Literature Review Auricular Disorders Part 1 Physical and Thermal Change Related TraumasDocument6 pagesv10 Literature Review Auricular Disorders Part 1 Physical and Thermal Change Related TraumasAlisNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0889540613006197Document3 pagesPi Is 0889540613006197mutiaNo ratings yet
- Dent Update 2022 49 646-649Document4 pagesDent Update 2022 49 646-649Fatma HarmadaniNo ratings yet
- Congenital Isolated Aplasia of Lower Lateral Cartilage and Reconstruction Using Dorsal Hump MaterialDocument3 pagesCongenital Isolated Aplasia of Lower Lateral Cartilage and Reconstruction Using Dorsal Hump MaterialDiego A. Cuadros TorresNo ratings yet
- Entropion Correction in Dogs and Cats Using A Combination Hotz-Celsus and Lateral Eyelid Wedge Resection: Results in 311 EyesDocument6 pagesEntropion Correction in Dogs and Cats Using A Combination Hotz-Celsus and Lateral Eyelid Wedge Resection: Results in 311 EyesAndres Luna MendezNo ratings yet
- The Colobomaeye Syndrome - A Rare CasereportDocument11 pagesThe Colobomaeye Syndrome - A Rare CasereportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- FDSFCFDSFDocument10 pagesFDSFCFDSFBhumika ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Goldfarb 2008Document10 pagesGoldfarb 2008YesicaNo ratings yet
- Orhan 2012Document6 pagesOrhan 2012ShathaNo ratings yet
- Keratoconus in Cogan ReeseDocument3 pagesKeratoconus in Cogan ReeseDr. Abhishek OnkarNo ratings yet
- JIntOralHealth - OligodontiaDocument3 pagesJIntOralHealth - OligodontiaAnkita AroraNo ratings yet
- Oral Rehabilitation of A Child With Hypohidrotic Ectodermal DysplasiaDocument6 pagesOral Rehabilitation of A Child With Hypohidrotic Ectodermal DysplasiaTiara HapkaNo ratings yet
- Alveolar and Skeletal Dimensions AssociatedDocument10 pagesAlveolar and Skeletal Dimensions AssociatedSankhyaNo ratings yet
- Seow 20 03Document4 pagesSeow 20 03NizajaulNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Riga FedeDocument3 pagesJurnal Riga Fedegundul123No ratings yet
- Variants of Talon Cusp (Dens2017Document2 pagesVariants of Talon Cusp (Dens2017Hukjvccx JjyfdxxvbNo ratings yet
- Achondroplasia: Orocraniofacial Features and Orthodontic-Surgical Management Guidelines ProposalDocument6 pagesAchondroplasia: Orocraniofacial Features and Orthodontic-Surgical Management Guidelines Proposalchristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Quader 2018Document7 pagesQuader 2018christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Crucial and Overlapping Roles of Six1 and Six2 in Craniofacial DevelopmentDocument8 pagesCrucial and Overlapping Roles of Six1 and Six2 in Craniofacial Developmentchristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors Associated With Fetal Pleural Effusion in Prenatal Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study in A Single Institute in Southern ChinaDocument6 pagesRisk Factors Associated With Fetal Pleural Effusion in Prenatal Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study in A Single Institute in Southern Chinachristian roblesNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Achondroplasia: Development, Pathogenesis, and TherapyDocument36 pagesHHS Public Access: Achondroplasia: Development, Pathogenesis, and Therapychristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Maternal Aripiprazole Exposure Interacts With 7-Dehydrocholesterol Reductase Mutations and Alters Embryonic NeurodevelopmentDocument10 pagesMaternal Aripiprazole Exposure Interacts With 7-Dehydrocholesterol Reductase Mutations and Alters Embryonic Neurodevelopmentchristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Constriction Bands: Secondary Deformities and Their TreatmentsDocument6 pagesAmniotic Constriction Bands: Secondary Deformities and Their Treatmentschristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Gomez Ospina2016Document11 pagesGomez Ospina2016christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Dotters Katz2017Document15 pagesDotters Katz2017christian roblesNo ratings yet
- A Case of Acrocephalosyndactyly With Low Imperforate AnusDocument3 pagesA Case of Acrocephalosyndactyly With Low Imperforate Anuschristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Ijph 46 848Document4 pagesIjph 46 848christian roblesNo ratings yet
- A Tumor Profile in Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)Document9 pagesA Tumor Profile in Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Regression of Juvenile Idiopathic Scoliosis: William E. Stehbens and Rachel L. CooperDocument10 pagesRegression of Juvenile Idiopathic Scoliosis: William E. Stehbens and Rachel L. Cooperchristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice: The Spine From Birth To AdolescenceDocument6 pagesClinical Practice: The Spine From Birth To Adolescencechristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Evidence For The Oocyte Mosaicism Selection Model On The Origin of Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)Document7 pagesEvidence For The Oocyte Mosaicism Selection Model On The Origin of Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Drew 2016Document20 pagesDrew 2016christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Rapid Prenatal Aneuploidy Detection of Bacs-On-Beads Assay in 4961 Cases of Amniotic Fluid SamplesDocument8 pagesRapid Prenatal Aneuploidy Detection of Bacs-On-Beads Assay in 4961 Cases of Amniotic Fluid Sampleschristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Cavadino 2017Document6 pagesCavadino 2017christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Neuroradiological Findings of Trisomy 13 in A Rare Long-Term SurvivorDocument3 pagesNeuroradiological Findings of Trisomy 13 in A Rare Long-Term Survivorchristian roblesNo ratings yet
- 2018 Article 1600Document4 pages2018 Article 1600christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Syndromal Common Origin: Associations of of The Carotid ArteriesDocument10 pagesSyndromal Common Origin: Associations of of The Carotid Arterieschristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Sinus Pericranii in Achondroplasia: A Case Report and Review of The LiteratureDocument4 pagesSinus Pericranii in Achondroplasia: A Case Report and Review of The Literaturechristian roblesNo ratings yet
- D4Document6 pagesD4christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Book Stein 1987Document15 pagesBook Stein 1987christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Treacher Collins Syndrome: Clinical CharacteristicsDocument21 pagesTreacher Collins Syndrome: Clinical Characteristicschristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Review of The Genetic Basis of Jaw Malformations: Mairaj K. Ahmed Xiaoqian Ye Peter J. TaubDocument11 pagesReview of The Genetic Basis of Jaw Malformations: Mairaj K. Ahmed Xiaoqian Ye Peter J. Taubchristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Current Care and Investigational Therapies in AchondroplasiaDocument8 pagesCurrent Care and Investigational Therapies in Achondroplasiachristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations in Apert Syndrome: Case Presentation and A Brief Review of The LiteratureDocument4 pagesOral Manifestations in Apert Syndrome: Case Presentation and A Brief Review of The Literaturechristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Parameters and Cervical Root Resorption During Orthodontic Tooh Movement - Giannopoulou2008Document6 pagesPeriodontal Parameters and Cervical Root Resorption During Orthodontic Tooh Movement - Giannopoulou2008christian roblesNo ratings yet
- Dendritic Spines in Early Postnatal Fragile X Mice Are Insensitive To Novel Sensory ExperienceDocument8 pagesDendritic Spines in Early Postnatal Fragile X Mice Are Insensitive To Novel Sensory Experiencechristian roblesNo ratings yet
- Mind Diet TrialDocument10 pagesMind Diet TrialAhmed Imran KhanNo ratings yet
- Cystein 3 PDFDocument6 pagesCystein 3 PDFNurul Kamilah SadliNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Lesson 1Document44 pagesThe Endocrine System Lesson 1Heaven Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Angiography: Presented By: Mulituba, Nairah DDocument9 pagesAngiography: Presented By: Mulituba, Nairah DAkazukin AineNo ratings yet
- Homoeopathic Intervention in PsoriasisDocument25 pagesHomoeopathic Intervention in PsoriasisAnil Subhash RathodNo ratings yet
- Soc Leg Case Digest 1Document8 pagesSoc Leg Case Digest 1AltheaNo ratings yet
- Surgery in Elderly 2Document41 pagesSurgery in Elderly 2Zeba NaveedNo ratings yet
- 262315968Document87 pages262315968Sunita RaniNo ratings yet
- CBLM Responding To EmergenciesDocument116 pagesCBLM Responding To EmergenciesAlice RaveloNo ratings yet
- The Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Blepharoptosis in Taiwanese PopulationDocument9 pagesThe Epidemiology and Clinical Features of Blepharoptosis in Taiwanese PopulationALYA MAULIDANo ratings yet
- Answers To Case 4: Folic Acid DeficiencyDocument2 pagesAnswers To Case 4: Folic Acid Deficiencyhttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- Pedia Nicu NotesDocument32 pagesPedia Nicu NotesChristian Noel Fernandez100% (2)
- Early Urine Output Predicts Graft Survival After KidneyDocument3 pagesEarly Urine Output Predicts Graft Survival After Kidneygiancarlor368No ratings yet
- Dialog Medic PacientDocument4 pagesDialog Medic PacientanaNo ratings yet
- SCUBA Diving and Asthma - Clinical Recommendations and SafetyDocument5 pagesSCUBA Diving and Asthma - Clinical Recommendations and SafetySara Leal100% (1)
- Virechana KarmaDocument28 pagesVirechana KarmaSurendra DavanagereNo ratings yet
- CHÍNH THỨC ĐỀ ĐỀ NGHỊ DUYÊN HẢIDocument20 pagesCHÍNH THỨC ĐỀ ĐỀ NGHỊ DUYÊN HẢIJennifer Watson0% (1)
- AJMC AJP1151 Obesity WebDocument56 pagesAJMC AJP1151 Obesity WebLoc Nguyen TanNo ratings yet
- DRRRTDocument10 pagesDRRRTanjilokapalliNo ratings yet
- Diffuse Toxic GoiterDocument64 pagesDiffuse Toxic GoiterMuftihat IsrarNo ratings yet
- Secondhand Smoke ConsumerDocument11 pagesSecondhand Smoke ConsumerДанила НеделкуNo ratings yet
- Hot Pack & Cold PackDocument10 pagesHot Pack & Cold Packm-7946796No ratings yet
- Mood, Anxiety and PersonalityDocument109 pagesMood, Anxiety and PersonalityRahul ShitoleNo ratings yet
- Principle of Fracture Management: Dr. Miawa RobertDocument63 pagesPrinciple of Fracture Management: Dr. Miawa Robertkajojo joyNo ratings yet
- Industrial Pollution by AnasDocument22 pagesIndustrial Pollution by AnasMuhubo MusseNo ratings yet
- Speech and Language GeneralDocument58 pagesSpeech and Language GeneralXlian Myzter YosaNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Pleura Dan Efusi Pleura: Wahyu SholekhuddinDocument25 pagesFisiologi Pleura Dan Efusi Pleura: Wahyu SholekhuddinWahyu SholekhuddinNo ratings yet
- Botany AssignmentDocument21 pagesBotany Assignmentabdul hadiNo ratings yet
- Medical Geography - Concepts, Techniques and Approaches: June 2020Document16 pagesMedical Geography - Concepts, Techniques and Approaches: June 2020Andrea RincónNo ratings yet
- Updateoncanineparvoviral Enteritis: Elisa M. MazzaferroDocument19 pagesUpdateoncanineparvoviral Enteritis: Elisa M. MazzaferroAlfian Yusak MuzakiNo ratings yet
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (84)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeFrom EverandThe Twentysomething Treatment: A Revolutionary Remedy for an Uncertain AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (40)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (267)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- I Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionFrom EverandI Shouldn't Feel This Way: Name What’s Hard, Tame Your Guilt, and Transform Self-Sabotage into Brave ActionNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)
- Self-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!From EverandSelf-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)