Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mumps: What Is Mumps and Who Can Get It?
Mumps: What Is Mumps and Who Can Get It?
Uploaded by
Sittinurul Fadhilah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageMumps is a contagious viral disease that causes swelling of the salivary glands and can affect anyone who has not had the disease or been vaccinated against it. Symptoms include puffy cheeks, pain when chewing, fever, headache, and tiredness. The MMR vaccine provides protection against mumps. To reduce spread, those infected should rest at home for five days and avoid sharing utensils or touching their face to prevent transmitting saliva to others or surfaces.
Original Description:
Original Title
Mumps 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMumps is a contagious viral disease that causes swelling of the salivary glands and can affect anyone who has not had the disease or been vaccinated against it. Symptoms include puffy cheeks, pain when chewing, fever, headache, and tiredness. The MMR vaccine provides protection against mumps. To reduce spread, those infected should rest at home for five days and avoid sharing utensils or touching their face to prevent transmitting saliva to others or surfaces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageMumps: What Is Mumps and Who Can Get It?
Mumps: What Is Mumps and Who Can Get It?
Uploaded by
Sittinurul FadhilahMumps is a contagious viral disease that causes swelling of the salivary glands and can affect anyone who has not had the disease or been vaccinated against it. Symptoms include puffy cheeks, pain when chewing, fever, headache, and tiredness. The MMR vaccine provides protection against mumps. To reduce spread, those infected should rest at home for five days and avoid sharing utensils or touching their face to prevent transmitting saliva to others or surfaces.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
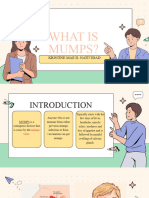
Mu m p s
What is Mumps and who can get it?
Mumps is a contagious viral disease that can cause swelling and soreness of the
salivary glands (cheek and jaw area), along with fever.
Mumps can affect any person at any age who has not had the disease or been
immunised against it. Most cases of Mumps now occur in young adults who have not
had two doses of the MMR (Measles, Mumps and Rubella) vaccine.
What are the How to reduce the
symptoms of Mumps? spread of Mumps:
• Puffy cheeks/swollen jaw Mumps is spread through direct contact with
• Pain in ear/jaw/chin, especially when saliva or mucus, so:
chewing • Don’t share drinks and eating utensils
• Fever • Cover coughs and sneezes
• Headache • Wash your hands regularly with soap and
• Loss of appetite Symptoms
water
• Muscle aches ca n last for
• Clean and disinfect surfaces
• Tiredness 7- 10 days
• Stay home while you feel unwell
What to do if you think you have Mumps:
There is no treatment for Mumps. The best course of action is:
• Bed rest. Stay at home for at least 5 days after the onset of symptoms to reduce spread.
• Drink plenty of fluid, especially if you find eating too painful.
• Use over-the-counter anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen to relieve pain and reduce
fever.
• Visit a doctor to confirm diagnosis.
• Notify studentlife@worc.ac.uk so that we can do
our part in trying to reduce the spread.
• Tell your PAT that you will not be attending
University for a few days.
Most people recover completely in a few weeks.
MMR vaccination is the best protection against Mumps – have you been vaccinated?
Talk to your GP if you are concerned you have not been vaccinated
You might also like
- The Ancient Solfeggio Frequencies and The Swine FluDocument131 pagesThe Ancient Solfeggio Frequencies and The Swine Fludavidpchristian100% (1)
- Leonard G Horowitz The Ancient Solfeggio Frequencies and The Swine Flu PDFDocument131 pagesLeonard G Horowitz The Ancient Solfeggio Frequencies and The Swine Flu PDFjsoto_4173810% (1)
- Memo PadDocument9 pagesMemo PadAndrea SandaloNo ratings yet
- Medical Bulletin - ChickenpoxDocument1 pageMedical Bulletin - ChickenpoxMonaliza MoralesNo ratings yet
- Skin DiseseasesDocument161 pagesSkin DiseseasesDanica Lacopia ZarsuelaNo ratings yet
- Influenza A Virus NotificationDocument1 pageInfluenza A Virus NotificationSyed Asim Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- HEALTH 8 (Communicable Disease)Document57 pagesHEALTH 8 (Communicable Disease)Lacasandile, Aira GanteNo ratings yet
- MumpsDocument1 pageMumpsshailesh284No ratings yet
- MUMPSDocument7 pagesMUMPSGlaiza BolanoNo ratings yet
- Pastel Cute Illustrative Business Report PresentationDocument18 pagesPastel Cute Illustrative Business Report PresentationdocgioreNo ratings yet
- Scabies-Tadulako Dec 2012Document40 pagesScabies-Tadulako Dec 2012Hasnapasuloi NanhaNo ratings yet
- Health MumpsDocument8 pagesHealth Mumpsapi-305343873No ratings yet
- Cfe SC 13 Germs and Diseases Powerpoint - Ver - 10Document12 pagesCfe SC 13 Germs and Diseases Powerpoint - Ver - 10verda khanNo ratings yet
- ConjunctivitisDocument26 pagesConjunctivitisNikki M. ArapolNo ratings yet
- Epidermolysis Bullosa: Dr. Prasant National Burns CentreDocument15 pagesEpidermolysis Bullosa: Dr. Prasant National Burns CentresandhyaNo ratings yet
- Mucositis Facts FilipinoDocument2 pagesMucositis Facts FilipinoPMV DeptNo ratings yet
- Santillan LeprosyDocument22 pagesSantillan Leprosylorella_abejuelaNo ratings yet
- Swine Flu InfoDocument22 pagesSwine Flu InfoyogasyrNo ratings yet
- HEALTH 8 (Communicable Disease) 2Document31 pagesHEALTH 8 (Communicable Disease) 2Lacasandile, Aira GanteNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Videos by DR RihamDocument31 pagesDermatology Videos by DR Rihamengr_shazzNo ratings yet
- Cold Sores Advanced DermatologyDocument1 pageCold Sores Advanced DermatologySarah KolarNo ratings yet
- ESC Brochure Canker Sores enDocument3 pagesESC Brochure Canker Sores eninhuyyNo ratings yet
- Herpes ZosterDocument1 pageHerpes ZosterIsmail Ali SyahbanaNo ratings yet
- 6435 SOAP NOTE Presentation Atopic DermatitisDocument21 pages6435 SOAP NOTE Presentation Atopic DermatitisMelinda Powell100% (2)
- TH THDocument4 pagesTH THdhen2_kyzluvdenNo ratings yet
- 4 Cold Sores and Mouth UlcersDocument41 pages4 Cold Sores and Mouth UlcersLQYNo ratings yet
- Mouth Ulcers Cold Sores PDFDocument15 pagesMouth Ulcers Cold Sores PDFaida aNo ratings yet
- Measles: Edward Joshua Gamiao Madria JRDocument23 pagesMeasles: Edward Joshua Gamiao Madria JRPaul JacksonNo ratings yet
- 16-Viral, Bacterial and Mycotic Infections of The MouthDocument24 pages16-Viral, Bacterial and Mycotic Infections of The Mouthحمزہ محبNo ratings yet
- Skin ConditionsDocument43 pagesSkin ConditionspdladvaNo ratings yet
- Swine Flu InfoDocument20 pagesSwine Flu InfoUdit SinghNo ratings yet
- Mpox VirusDocument5 pagesMpox Virusthunder beardedNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever: Special Care During Covid-19 PandemicDocument12 pagesDengue Fever: Special Care During Covid-19 PandemicSbNo ratings yet
- Home Health CareDocument222 pagesHome Health CareMylody Villaflor Magallon100% (1)
- Biology ProjectDocument10 pagesBiology ProjectananditaNo ratings yet
- Project: Feeling Good?: Por: Emmanuel Orozco Agudelo y Alejandro Bedoya BarcoDocument11 pagesProject: Feeling Good?: Por: Emmanuel Orozco Agudelo y Alejandro Bedoya BarcoAlejandro Bedoya BarcoNo ratings yet
- Disa Rashe PDFDocument2 pagesDisa Rashe PDFAlbanDedaNo ratings yet
- Review QuestionDocument11 pagesReview Questionaug.ntthNo ratings yet
- Boils TreatmentsDocument8 pagesBoils Treatmentsadampitt587No ratings yet
- Appearance Work of BreathingDocument6 pagesAppearance Work of BreathingRudi Saputra BskNo ratings yet
- MonkeypoxDocument5 pagesMonkeypoxrizaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Cervix and The VaginaDocument42 pagesDiseases of The Cervix and The VaginaBiancaGabatinoAbarcaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 The Common ColdDocument17 pagesLesson 4 The Common ColdAdan Xander MaralitNo ratings yet
- The Common Cold: Lesson 4 - HealthDocument17 pagesThe Common Cold: Lesson 4 - HealthAdan Xander MaralitNo ratings yet
- Mumps - Nguyen Thi Ngoc ThamDocument32 pagesMumps - Nguyen Thi Ngoc Thamnguyenthingoctham1208No ratings yet
- Gmail - Dengue AdvisoryDocument2 pagesGmail - Dengue AdvisoryPrashant JainNo ratings yet
- Colds, Flu and COVID-19Document4 pagesColds, Flu and COVID-19Khashayar MastooriNo ratings yet
- MumpsDocument14 pagesMumpsSarkhell ArazNo ratings yet
- Viral Disease To Work WithDocument155 pagesViral Disease To Work WitheveirenepassashNo ratings yet
- MOHAN Di. RAJU....... MOHAN Di. RAJU......Document32 pagesMOHAN Di. RAJU....... MOHAN Di. RAJU......Nagaraja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella - MeaslesDocument5 pagesMeasles, Mumps, Rubella - MeaslesRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Measles, Mumps, RubellaDocument5 pagesMeasles, Mumps, RubellaRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Measles BrochureDocument2 pagesMeasles Brochureapi-340763234No ratings yet
- Public Health: NSTP Ii Part 5Document21 pagesPublic Health: NSTP Ii Part 5Carl GilNo ratings yet
- Swine Flu InfoDocument20 pagesSwine Flu Infoik5610No ratings yet
- Dengue Fever: Heath and Pe1: 3rdblockDocument9 pagesDengue Fever: Heath and Pe1: 3rdblockcolioNo ratings yet
- MumpsDocument2 pagesMumpsArjunJainNo ratings yet
- 3.7 (Bio)Document15 pages3.7 (Bio)Sumaira AkramNo ratings yet
- Influenza (Flu) : Identification TreatmentDocument1 pageInfluenza (Flu) : Identification Treatmentapi-350983586No ratings yet
- The Best Home Remedy To Prevent Cold Sores (Lip Blisters) For LifeFrom EverandThe Best Home Remedy To Prevent Cold Sores (Lip Blisters) For LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (11)