Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Draft Assigment Bio 2
Uploaded by
puteri hanisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Draft Assigment Bio 2
Uploaded by
puteri hanisCopyright:
Available Formats
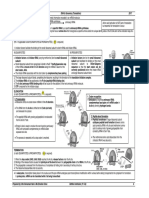
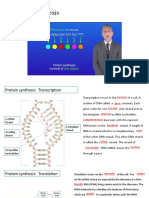
1) INITIATION Bozeman Science,2018
In the nucleus, RNA polymerase
binds at promoter on DNA. It
unwinds and unzips the the double
helix of DNA .
It moves along te direction of
transcription on DNA.
RNA polymerase breaks the
hydrogen bond between
complementary nitrogenous bases.
Both DNA strands separated into
single strand and one of the DNA
strand is used as a template.
2) ELONGATION
RNA polymerase add nucleotide in
the direction 0f 5’ to 3’ end and a free
ribonucleotide (complementary to
the base) on the template strand.
Uracil pair wih Adenine ( DNA ),
Cytosine pair with Guanine.
DNA-RNA hybrid is temporarily
Template strand formed.
Newly synthesized mRNA (upstream)
detaches from DNA template
3) TERMINATION
Elongation will continue until the RNA
polymerase encounters a stop
(termination) sequence in the gene.
When the RNA Polymerase reaches the
terminator it signals the RNA
Polymerase to stop and release from
the DNA.
Once separated the two DNA strands
Released
come back together and reform the
pre-mRNA
double helix
The newly formed pre-mRNA molecule
is then released
__ : location REFERENCE
__ : products Eric j. simon, jean l, dickey, Clemson university jane .b, reece, Berkeley. (2019).
__ : enzyme involved Campbell essential biology (7 edition). California. Pearson
__ : template https://courses.lumenlearning.com/bio1/chapter/reading-steps-of- genetic-
Transcription
__ : types of RNA involved
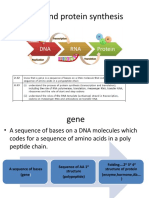
EXAMPLE OF PROTEIN
Protein: Insulin
3) TERMINATION Function: helps control blood glucose
Elongation continued until a stop codon (UAA, UAG,, levels
UGA) is reached the A site Level: quarternary structure
A stop codon in the mRNA is recognized by a protein
release factor. Classification: globular protein
A ribosomal enzyme then breaks the bond between Site of protein synthesized: only in Beta
the polypeptide and the tRNA in the P site, releasing cells in the pancreas
the polypeptide( protein)
Other ribosomal enzymes separate the ribosomal
subunits and free the intact strand of mRNA.
3
LadyofHats , 2008
Large
ribosomal
subunit
Small ribosomal
subunit
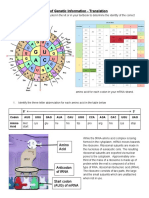
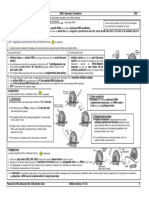
1) INITIATION 2) ELONGATION
In cytoplasm,small ribosomal subunit and the The aminoacyl-tRNA with specific amino acid binds to
initiator aminoacyl-tRNA binds to mRNA at start the codon in empty A site (aminoacyl site) of ribosome.
codon When a complementary tRNA binds to the A site,
sm(AUG) to form an initiation complex
This tRNA, carries the amino acid methionine ribosomal enzymes remove the amino acid from the
which is the first amino acid in a polypeptide. tRNA at the P site and attach it to the amino acid
Aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase attaches amino acid delivered to the A site by forming a peptide bond.
to tRNA. catalysed by peptidyl transferase.
Bozeman
The large Science.2018
ribosomal subunit joins the initiation The ribosome then moves one codon farther along the
complex, with tRNA now accupying the P site mRNA strand. The tRNA that was in the P site
(peptidyl site). (anticodon UAC) now enters the E site. It also exposes a
new codon in the A site. The released tRNA can now
Initiation factor (protein) are needed to assemble
bind another amino acid of the same type and repeat
the components together and the energy is
the cycle.
provided by hydrolysis of GTP
You might also like
- Methods of DNA SequencingDocument50 pagesMethods of DNA SequencingDr.Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument58 pagesTranscription and Translationkevin_ramos007No ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis SummaryDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis SummaryTrinitee Wesner100% (1)
- Protein SynthesisDocument54 pagesProtein SynthesisYousef WardatNo ratings yet
- BIO-5dll 3rdDocument15 pagesBIO-5dll 3rdarlene dioknoNo ratings yet
- IB Past Paper Questions: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Acids (Incl DNA Replication)Document12 pagesIB Past Paper Questions: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Acids (Incl DNA Replication)John Osborne78% (9)
- Protein Synthesis (Gene Expression)Document63 pagesProtein Synthesis (Gene Expression)jaybeeclaireNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument35 pagesTranscription and TranslationMing mingNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaDocument29 pagesProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaHritik KumarNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 DNADocument19 pagesGrade 9 DNARitchwel FAJARDO100% (1)
- Compre MolbioDocument93 pagesCompre MolbioDeniebev'z OrillosNo ratings yet
- USMLE Flashcards: Biochemistry - Side by SideDocument137 pagesUSMLE Flashcards: Biochemistry - Side by SideMedSchoolStuffNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument9 pagesTranscription and TranslationlinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationDocument14 pagesChapter 17 - Transcription and TranslationAdonias NiyurukundoNo ratings yet
- Translation ProcessDocument1 pageTranslation ProcesscelineNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument44 pagesGene Expression20.020 Cahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument44 pagesGene ExpressionCahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Meridian Protein SynthesisDocument7 pagesMeridian Protein SynthesisjosewaltNo ratings yet
- Replication and Transciption of DnaDocument29 pagesReplication and Transciption of DnaTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument4 pagesProtein SynthesisAshwarya ChandNo ratings yet
- Biology Lesson 1.1Document16 pagesBiology Lesson 1.1Crystal Joy BondadNo ratings yet
- Key Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaDocument2 pagesKey Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaSeiza WinchesterNo ratings yet
- Genitics Asignment MD Asif Roll-088Document11 pagesGenitics Asignment MD Asif Roll-088Asif SheikhNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument9 pagesDna Replication and Protein Synthesisbravebrave2005No ratings yet
- 8d) Translation Summary - 9744 - 2017Document1 page8d) Translation Summary - 9744 - 2017saguNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceSneha HipparkarNo ratings yet
- 3D Molecular Translation Worksheetv21Document3 pages3D Molecular Translation Worksheetv21Jonas WelliverNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis With Video LinksDocument31 pagesProtein Synthesis With Video LinksSmilingNo ratings yet
- THE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutDocument6 pagesTHE CENTRAL DOGMA HandoutLeah AturoNo ratings yet
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyJoshuaMondejarNo ratings yet
- Learner's Activity Sheet: Science (Quarter III - Week 4)Document10 pagesLearner's Activity Sheet: Science (Quarter III - Week 4)MARITESS COLLADONo ratings yet
- RNA, DNA Transcription and RNA TranslationDocument5 pagesRNA, DNA Transcription and RNA TranslationHassan AljaberiNo ratings yet
- 05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechDocument26 pages05b. Part 2 of Nucleic Acids For BSRadTechBea Abigail BrocalNo ratings yet
- IB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticDocument37 pagesIB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticClàudia VicenteNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesProtein SynthesisDebbie NsefikNo ratings yet
- Agus Limanto Faculty of Medicine UkridaDocument26 pagesAgus Limanto Faculty of Medicine UkridaMrs GeekNo ratings yet
- Cell Disease LabDocument1 pageCell Disease Labapi-340815123No ratings yet
- Miniature Protein BIologyDocument83 pagesMiniature Protein BIologyPREET KANOOGANo ratings yet
- LECTURE 12 TranslationDocument17 pagesLECTURE 12 TranslationAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument58 pagesGene ExpressionJunirose PanesNo ratings yet
- Genetics 2Document52 pagesGenetics 2Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- 8c) Transcription Summary - 9744 - 2018Document1 page8c) Transcription Summary - 9744 - 20182022 EMMA WEN XUAN HANSONNo ratings yet
- Fenomena Biomedik Dari Transkripsi Gen Hingga MetabolismeDocument45 pagesFenomena Biomedik Dari Transkripsi Gen Hingga MetabolismeratuurizkyNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument25 pagesProtein Synthesisznayune82No ratings yet
- CO3 TranscriptionDocument8 pagesCO3 Transcriptionpriya27suranaNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation NarrativeDocument3 pagesTranscription and Translation NarrativeBridget Anne BenitezNo ratings yet
- 3.10 Protein-SynthesisDocument20 pages3.10 Protein-SynthesisPratika MNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Protein SynthesisMarc Laurence LadoresNo ratings yet
- DNA Translation and Transcription PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Translation and Transcription PDFSim QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- 5 11transcription-2013Document30 pages5 11transcription-2013jernsssNo ratings yet
- 8d) Translation Summary - 9744 - 2018Document1 page8d) Translation Summary - 9744 - 20182022 EMMA WEN XUAN HANSONNo ratings yet
- CH 17 KEYDocument5 pagesCH 17 KEYJohnathan BeversNo ratings yet
- L7S12. Central Dogma and Genetic Engineering - FDocument35 pagesL7S12. Central Dogma and Genetic Engineering - FSichayra GamotiaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionDocument46 pages3rd Week (1) - TrancriptionyazicigaamzeNo ratings yet
- Transcription & TranslationDocument8 pagesTranscription & TranslationDr DapperNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Code and Transcription: Flow of Genetic InformationDocument10 pagesThe Genetic Code and Transcription: Flow of Genetic InformationRenz L. SalumbreNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 7. Molecular Basis of Heredity Gene Action Transcription and TranslationDocument5 pagesEXERCISE 7. Molecular Basis of Heredity Gene Action Transcription and TranslationMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument42 pagesTranslationDeeptanshu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument2 pagesDna Replication, Transcription and TranslationJenna PretalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - Genetics NotesDocument1 pageClass 12 - Genetics NotesDimas HernadyNo ratings yet
- CYTO DNA TranslationDocument4 pagesCYTO DNA TranslationTherese TimbalNo ratings yet
- DNA Kita Iiwan RNA CytoDocument3 pagesDNA Kita Iiwan RNA CytozairahNo ratings yet
- Poe Assignment GRP 12Document16 pagesPoe Assignment GRP 12puteri hanisNo ratings yet
- Project DataDocument192 pagesProject Dataputeri hanisNo ratings yet
- A211 Group Project 1 (Number Theory in Game Application)Document5 pagesA211 Group Project 1 (Number Theory in Game Application)puteri hanisNo ratings yet
- SQIT1013 Group Assignment 1Document12 pagesSQIT1013 Group Assignment 1puteri hanisNo ratings yet
- Sqit1013 Group 1 (Group Assignment 2)Document7 pagesSqit1013 Group 1 (Group Assignment 2)puteri hanisNo ratings yet
- NOTES SQQS1043 CHAPTER 5 - StudentDocument74 pagesNOTES SQQS1043 CHAPTER 5 - Studentputeri hanisNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 - FS Analysis (Lecture)Document60 pagesTopic 11 - FS Analysis (Lecture)puteri hanisNo ratings yet
- Cream and Brown Curvy Serif Typefaces Simple PresentationDocument25 pagesCream and Brown Curvy Serif Typefaces Simple Presentationputeri hanisNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma WebquestDocument4 pagesCentral Dogma Webquestapi-446838554No ratings yet
- Bioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Dna Structure and Replication (7.1)Document3 pagesBioknowledgy Quick Quiz On Dna Structure and Replication (7.1)priyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - DnaDocument23 pagesChapter 12 - Dnaapi-246719131No ratings yet
- G (12) Ls Life Science 2020-2021 Revision Sheet: 3 Photosynthesis Part-2Document3 pagesG (12) Ls Life Science 2020-2021 Revision Sheet: 3 Photosynthesis Part-2Joelle AssafNo ratings yet
- Els ReportDocument33 pagesEls ReportPrince Adrian P. PinesNo ratings yet
- From Gene To ProteinDocument42 pagesFrom Gene To ProteinNathan AdornadoNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document3 pagesLab 4Roben CasiongNo ratings yet
- Components of RNA and DNADocument26 pagesComponents of RNA and DNAKarla Javier PadinNo ratings yet
- GB 50119-2003-EnDocument40 pagesGB 50119-2003-En柳德米拉No ratings yet
- Amino Acid Biosynthesis and DegradationDocument11 pagesAmino Acid Biosynthesis and DegradationFarhana AktharNo ratings yet
- Module 6 RationaleDocument1 pageModule 6 RationaleG INo ratings yet
- EDT - Genetics - First Exam QuestionsDocument14 pagesEDT - Genetics - First Exam QuestionsRashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Dna Fill in The BlankDocument1 pageDna Fill in The Blankapi-338300948No ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidharshitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4A: DNA Replication & Protein SynthesisDocument34 pagesChapter 4A: DNA Replication & Protein SynthesisPikuNo ratings yet
- Mindmap DnaDocument7 pagesMindmap Dnafresh wooNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument23 pagesDna StructureAnonymous mHS76aNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidDocument2 pagesAmino AcidMervinlloyd Allawan BayhonNo ratings yet
- Ribosomes and Protein SynthesisDocument15 pagesRibosomes and Protein SynthesisRichard ShakespeareNo ratings yet
- DNA SamplexDocument6 pagesDNA SamplexNelica RotoniNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids QuestionsDocument5 pagesAmino Acids QuestionsKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 (Amino Acids) PDFDocument11 pagesSheet 1 (Amino Acids) PDFShailendra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- RNA Protein Synthesis Gizmo COMPLETEDDocument7 pagesRNA Protein Synthesis Gizmo COMPLETEDcokcreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 BiochipsDocument45 pagesLecture 1 Biochipskhalil alhatabNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument1 pagePROTEINSVaibhavMittalNo ratings yet
- 05 Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR Principle Steps ApplicationsDocument28 pages05 Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR Principle Steps ApplicationsBen AbellaNo ratings yet