Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map 3 1
Uploaded by
Kate CambelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map 3 1
Uploaded by
Kate CambelCopyright:
Available Formats
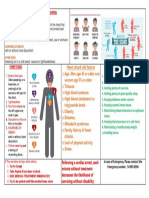
Signs & Symptoms
1. Unintentional weight loss
2. Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia) Signs & Symptoms
3. Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
4. Pounding of your heart (palpitations) 1. Fatigue
Thyroid Gland Disorders
5. Nervousness, anxiety and irritability 2. Increased sensitivity to cold
6. Tremor 3. Constipation
7. Sweating
4. Dry skin
8. Changes in menstrual patterns
9. Increased sensitivity to heat 5. Weight gain
10. Changes in bowel patterns, especially more frequent bowel 6. Puffy face
movements 7. Hoarseness
11. An enlarged thyroid gland (goiter), which may appear as a
By: Kate Cambel, Alessia Catequista, and Nicole Penit
8. Muscle weakness
swelling at the base of your neck 9. Elevated blood cholesterol level
12. Fatigue, muscle weakness
BSN 3
10. Muscle aches, tenderness and stiffness
13. Difficulty sleeping
11. Pain, stiffness or swelling in your joints
14. Skin thinning
15. Fine, brittle hair 12. Heavier than normal or irregular menstrual periods
Etiology 13.
14.
Thinning hair
Slowed heart rate
• 15. Depression
Etiology
Grave's Disease
Laboratory Results • Thyroiditis 16. Impaired memory
• Overreactive thyroid • Autoimmune disease.
17. Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
1. TSH nearly undetectable • Increased thyroid hormone medicine
2. Elevated FT4 or FT3
3. Mild leukopenia
4. N/N anemia
5.
6.
ESR elevated
↑LFT’s and alkphosph Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism Laboratory Results
7. Mild ↑ Ca++ 1. Elevated TSH
8. ↓Albumin a condition in which there a condition in which a 2. Low FT4
9. ↓Cholesterol 3. TPO Ab(+)
is an excessive amount person has too little thyroid 4. Macrocyticanemia due to VIT B12 deficiency
5. ↑CPK-MB
of thyroid hormones hormone or underproduction 6. ↑LDL,↑Chol (↓ lipid clearance)
Medical Management of thyroid hormones 7. Hyponatremia
1. Propylthiouracil (PTU)
Risk Factors Risk Factors
2. Sodium Iodide
Medical Management
3. Saturated solution of potassium iodide (SSKI)
4. Propanolol
5. Thyroidectomy ✓ Family History ✓ Female
1. Levothyroxine
✓ Female ✓ Are older than 60 2. Liothyronine
✓ A personal history of certain chronic ✓ Causaian or Asian
3. Dessicated Thyroid
Nursing Responsibilities illnesses
✓ Family history of Hashimoto’s thyoiditis
1. Provide adequate rest. ✓ History of Pregnancy
✓ Family history of thyroid disease
2. Obtain weight daily.
✓ Smoking
✓ Nursing Responsibilities
3. Provide a high-calorie diet. Have an autoimmune disease,
4. Administer antithyroid medications as prescribed. ✓ Taking iodine intake or an iodine-
✓ Have been treated with radioactive iodine
5. Administer iodine preparations that inhibit the release of containing medication 1. Promote rest.
thyroid hormone as prescribed. or anti-thyroid medications
6. Administer propranolol (Inderal) for tachycardia as ✓ Experiencing trauma to the thyroid gland
✓ Received radiation to your neck or upper
2.
3.
Protect against coldness.
Avoid external heat exposure.
prescribed.
7. Keep the patient comfortable: cool, quiet environment, calm ✓ Deficient in Vitamin D and selenium chest 4. Mind the temperature.
5. Increase fluid intake..
8.
(administer prescribed sedatives as needed)
Obtain daily weights (need to watch weigh due to weight
✓ Experiencing psychological stress ✓ Had thyroid surgery (partial thyroidectomy) 6. Provide foods high in fiber.
loss from the increased metabolic rate) ✓ History of Pregnancy
7.
8.
Manage respiratory symptoms..
Pulmonary exercises.
9. Monitor EKG, heart rate, blood pressure
9. Orient to present surroundings.
10. Educate about medications and treatment (radioactive
iodine therapy and thyroidectomy)
11. Monitor for Thyroid Storm: life-threatening that presents
with exaggerated signs/symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such
as fever, fast heart rate, HTN.
You might also like
- Table 8-7 - The Eating Disorders and Subtypes From DSM-5Document1 pageTable 8-7 - The Eating Disorders and Subtypes From DSM-5Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Health Check Up Form EmployeesDocument3 pagesHealth Check Up Form Employeessyed ishan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Nikka Scaffold 3 2Document6 pagesNikka Scaffold 3 2Bella PerezNo ratings yet
- Facial and Physical Signs of Tissue Salt DeficiencyDocument4 pagesFacial and Physical Signs of Tissue Salt DeficiencyFahad JavedNo ratings yet
- Review of SystemsDocument1 pageReview of Systemsmaverick dickyNo ratings yet
- Apa Itu Stroke ?: Bagaimana Anda Mengenali Stroke?Document3 pagesApa Itu Stroke ?: Bagaimana Anda Mengenali Stroke?riska widianingsihNo ratings yet
- NCM 114Document7 pagesNCM 114Anthony EmerencianaNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack-TawDocument1 pageHeart Attack-TawJOSE LUISNo ratings yet
- Chi Nei Tsangi 3 - Internal Organs Chi Massage PDFDocument59 pagesChi Nei Tsangi 3 - Internal Organs Chi Massage PDFAlexandra Ioana Niculescu100% (2)
- Herman Lesson Plan - Docx Rolyn VolleyballDocument7 pagesHerman Lesson Plan - Docx Rolyn VolleyballRolyn Drey Galleto HermanNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument10 pagesAnaphy ReviewerSamantha Joy VidalNo ratings yet
- 035 Heat StressDocument24 pages035 Heat StressSivaprasadNo ratings yet
- Advance Adult Care Nursing Case StudyDocument12 pagesAdvance Adult Care Nursing Case StudySima SaeedNo ratings yet
- Cara Mengatasi Stress Teknik RelaksasiDocument2 pagesCara Mengatasi Stress Teknik RelaksasiPuskesmas PetarukanNo ratings yet
- PNCDocument2 pagesPNClovelove DayoNo ratings yet
- Healthy Lifestyle: Dr. Gadistya Novitri ADocument36 pagesHealthy Lifestyle: Dr. Gadistya Novitri APrima Anggreini ArinNo ratings yet
- Tiredness: Dr. Mo SobhyDocument23 pagesTiredness: Dr. Mo SobhymuradkhanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledTzara Killian CarrawayNo ratings yet
- World English 2 - Workbook Unit 4Document7 pagesWorld English 2 - Workbook Unit 4carlos ariasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda TRIDOSH ChartDocument28 pagesAyurveda TRIDOSH ChartKalpesh JesalpuraNo ratings yet
- 03EnergyCodes - 19 Mod2 BESTReleaseDocument2 pages03EnergyCodes - 19 Mod2 BESTReleasezydeconycNo ratings yet
- Gora BL CorelDocument3 pagesGora BL CorelLinda AnandaNo ratings yet
- Heat Stress HSE PresentationDocument23 pagesHeat Stress HSE PresentationEtibar AliyevNo ratings yet
- One Point Acupressure Treatment - Acupressure Research, Training and Treatment Sansthan - AllahabadDocument91 pagesOne Point Acupressure Treatment - Acupressure Research, Training and Treatment Sansthan - AllahabadriyastempNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCj LowryNo ratings yet
- ONE POINT ACUPRESSURE TREATMENT - TCM Part 1 PDFDocument75 pagesONE POINT ACUPRESSURE TREATMENT - TCM Part 1 PDFshamim hijama83% (6)
- Benefits of BananaDocument1 pageBenefits of BananaManjula Jeewan KumaraNo ratings yet
- Leatflet Stroke IhatDocument1 pageLeatflet Stroke IhatSobihat RasyidNo ratings yet
- Care of The Older ClientDocument13 pagesCare of The Older Clientjemfortuna9No ratings yet
- Nutrition Due To Lack of NutritionDocument1 pageNutrition Due To Lack of NutritionAprianto UntungNo ratings yet
- Health HandoutsDocument3 pagesHealth HandoutsIrene Alavanza SolayaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 FITNESS AWARENESS 1Document2 pagesLesson 2 FITNESS AWARENESS 1Liza Marie NeryNo ratings yet
- ABG NotesDocument2 pagesABG NotesIsland RaeNo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument3 pagesHealth AssessmentAndrea Jewel BaladjayNo ratings yet
- Bye, Psikosomatis!: Aisyah HelmadeviDocument16 pagesBye, Psikosomatis!: Aisyah HelmadeviTI BNo ratings yet
- One Point TreatmentDocument39 pagesOne Point TreatmentaummirraNo ratings yet
- (Rodriguez) Scenario 1Document3 pages(Rodriguez) Scenario 1Dinarkram Rabreca EculNo ratings yet
- RA NA S: Group 1 Wrist SplintingDocument15 pagesRA NA S: Group 1 Wrist SplintingRosh-eil AranasNo ratings yet
- Received Patient Robin Son, A 57 Years Old Male, Wearing Shades, Lethargic and Complaining of " Murag Gisipa Akong Ulo Sa Kasakit"Document3 pagesReceived Patient Robin Son, A 57 Years Old Male, Wearing Shades, Lethargic and Complaining of " Murag Gisipa Akong Ulo Sa Kasakit"Dinarkram Rabreca EculNo ratings yet
- Do You Symptoms?: 2 Jorge Basadre Grohmann National UniversityDocument4 pagesDo You Symptoms?: 2 Jorge Basadre Grohmann National UniversityDiana Vanessa Roque ChinoNo ratings yet
- Blue Green Photo Illustrated Golf Tournament Trifold BrochureDocument2 pagesBlue Green Photo Illustrated Golf Tournament Trifold BrochureCedrick CalalangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interview Guide To Collect Subjective Data From The Client Questions RationaleDocument19 pagesNursing Interview Guide To Collect Subjective Data From The Client Questions RationaleKent Rebong100% (1)
- 07 Aromatherapy Questionnaire PDFDocument1 page07 Aromatherapy Questionnaire PDFAgnesNo ratings yet
- CHF NewDocument7 pagesCHF NewJyoti SidhuNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanDocument3 pagesUrinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanRnspeakcomNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Care of Older People MidtermDocument5 pagesNCM 114 Care of Older People MidtermKM PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Taller Enfermedades GaboDocument6 pagesTaller Enfermedades GaboAndy RamirezNo ratings yet
- World English 2 - Workbook Unit 4Document6 pagesWorld English 2 - Workbook Unit 4Frank DiazNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Jeffrey FNo ratings yet
- One Point Acupressure Treatment AllDocument23 pagesOne Point Acupressure Treatment AllPraveen Kumar100% (1)
- Heart DiseaseDocument1 pageHeart DiseasePaulinaNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination in Animals - NotesDocument6 pagesControl and Coordination in Animals - NotesKarishmmNo ratings yet
- M3 DrugsDocument43 pagesM3 DrugsPaul ArubangNo ratings yet
- TCM Diagnosis Pattern ChartDocument16 pagesTCM Diagnosis Pattern Chartwhiteyasmin100% (1)
- Mombay 3a Neuman Ncm112 Module 2Document7 pagesMombay 3a Neuman Ncm112 Module 2Xena MombayNo ratings yet
- Week 8 - Assessing The Heart and Central Vessels ActivitiesDocument7 pagesWeek 8 - Assessing The Heart and Central Vessels ActivitiesJustine Martinez AmoresNo ratings yet
- ACCIDENTSDocument3 pagesACCIDENTSjohn_eisma_1No ratings yet
- Hosa Sleep Apnea 2021Document1 pageHosa Sleep Apnea 2021api-487231832No ratings yet
- Veterinary Parasitology Questionbank - 1Document5 pagesVeterinary Parasitology Questionbank - 1VIJAYNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI TIẾNG ANH 7 TEST 4Document4 pagesĐỀ THI TIẾNG ANH 7 TEST 4Rosa TangNo ratings yet
- Altretamine: Drug DosageDocument16 pagesAltretamine: Drug DosagePrincess CruzNo ratings yet
- Kidneys: Evaluating and Treating TheDocument42 pagesKidneys: Evaluating and Treating TheSebastián Hernández GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Lab Workup: Practical Nursing Mohawk College 2014Document2 pagesLab Workup: Practical Nursing Mohawk College 2014Pawel PietruszczakNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation of Influenza in Children 6.22Document7 pagesClinical Presentation of Influenza in Children 6.22akreditasi rsunhNo ratings yet
- Two Potentially Zoonotic Parasites Infecting Philippine Brown Deer (CervusDocument5 pagesTwo Potentially Zoonotic Parasites Infecting Philippine Brown Deer (CervusLemuel Lagasca Razalan IVNo ratings yet
- Shalya Case Sheet NEW-1Document7 pagesShalya Case Sheet NEW-1clazixiphoneNo ratings yet
- NOUNSDocument11 pagesNOUNSKAMALNo ratings yet
- Limci Gupta Valerie Thomas JaysoDocument285 pagesLimci Gupta Valerie Thomas JaysoNaima TariqNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Gravaboi Codes and NumbersDocument18 pagesDokumen - Tips - Gravaboi Codes and NumbersHaychiNo ratings yet
- Ebook Current Diagnosis Treatment in Rheumatology PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Current Diagnosis Treatment in Rheumatology PDF Full Chapter PDFbeth.hao417100% (27)
- 2 Laporan Rujukan RJ Dan RI PKM Sungai Sembilan Februari 2021Document21 pages2 Laporan Rujukan RJ Dan RI PKM Sungai Sembilan Februari 2021pusk.sei9No ratings yet
- Levels of PreventionDocument23 pagesLevels of Preventionkuruvagadda sagar100% (1)
- Mapeh Performance Task Preventing Communicable DiseaseDocument1 pageMapeh Performance Task Preventing Communicable Diseasenina pascualNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Exocrine PancreasDocument5 pagesPathology of The Exocrine PancreassatriayanuwardaniNo ratings yet
- Common Types of Learning DisabilitiesDocument4 pagesCommon Types of Learning DisabilitiesLuciaMacsimNo ratings yet
- Sas 1 60 Multiple Choice Converted CompressedDocument153 pagesSas 1 60 Multiple Choice Converted CompressedRoswell Almodiel EscaranNo ratings yet
- What If Ebook Top 10Document15 pagesWhat If Ebook Top 10Krishna TripathiNo ratings yet
- Macaraig Brillo Final Case Study HypertensionDocument67 pagesMacaraig Brillo Final Case Study HypertensionMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- NTCP MOP 5e FinalDocument192 pagesNTCP MOP 5e FinalcharmainegoNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument9 pagesAbdominal Aortic AneurysmIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Giardia & Giardiasis: (Intestinal Flagellate)Document22 pagesGiardia & Giardiasis: (Intestinal Flagellate)Naing Lin SoeNo ratings yet
- Health DeclarationDocument8 pagesHealth DeclarationmkwinijoanNo ratings yet
- 100 Item Comprehensive Exam II With Answers and RationaleDocument16 pages100 Item Comprehensive Exam II With Answers and RationaleVJ DeeNo ratings yet
- Clobeta GM Cream Induced: Adverse Drug Reaction ReportDocument21 pagesClobeta GM Cream Induced: Adverse Drug Reaction ReportAyushmanNo ratings yet
- P1337420319157 Inda Helma YunitaDocument2 pagesP1337420319157 Inda Helma YunitaInda HelmaNo ratings yet
- Laparaskopi PeritonitisDocument5 pagesLaparaskopi PeritonitisPutri RiszaNo ratings yet
- Predictive Homeopathy Course Review, Part I: Susanne Saltzman, MDDocument5 pagesPredictive Homeopathy Course Review, Part I: Susanne Saltzman, MDdr TotoNo ratings yet
- Asthma Patho CF UgDocument26 pagesAsthma Patho CF Ugtnandanwar91No ratings yet