Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ABG Notes
Uploaded by
Island Rae0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document discusses and compares the signs and causes of four types of acid-base imbalances: respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, and metabolic alkalosis. Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is CO2 retention in the lungs, and can be caused by hypoventilation. Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there is rapid loss of CO2 from the lungs, and can be caused by hyperventilation. Metabolic acidosis occurs when there is a decreased ability to excrete acid or conserve base, and can be caused by conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis. Metabolic alkalosis occurs when there is a decreased ability to excrete base or conserve acid, and can be caused by
Original Description:
Original Title
ABG notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses and compares the signs and causes of four types of acid-base imbalances: respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, and metabolic alkalosis. Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is CO2 retention in the lungs, and can be caused by hypoventilation. Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there is rapid loss of CO2 from the lungs, and can be caused by hyperventilation. Metabolic acidosis occurs when there is a decreased ability to excrete acid or conserve base, and can be caused by conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis. Metabolic alkalosis occurs when there is a decreased ability to excrete base or conserve acid, and can be caused by
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesABG Notes
Uploaded by
Island RaeThis document discusses and compares the signs and causes of four types of acid-base imbalances: respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, and metabolic alkalosis. Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is CO2 retention in the lungs, and can be caused by hypoventilation. Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there is rapid loss of CO2 from the lungs, and can be caused by hyperventilation. Metabolic acidosis occurs when there is a decreased ability to excrete acid or conserve base, and can be caused by conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis. Metabolic alkalosis occurs when there is a decreased ability to excrete base or conserve acid, and can be caused by
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
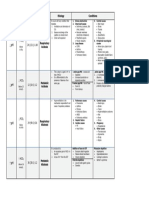
Respiratory Respiratory Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic
Acidosis Alkalosis Alkalosis
• Where there is CO2 • Where there is rapid • Where there is • Where there is a
retention in the lungs loss of CO2 from the decreased ability of the decreased ability of
lungs than is retained kidney to excrete acid the kidney to excrete
Or or conserve base base or conserve
acid
• Where the body
produces CO2 faster
than the lungs can
expel
• S/S: • S/S: • S/S: • S/S:
1. HYPOventilation 1. HYPERventilatio 1. Decreased BP 1. Compensatory
-> Hypoxia n (increased rate HYPOventilatio
and depth) • HYPERkalemia n
• Rapid, shallow
respirations • Tachycardia 3. Muscle twitching • Dysrhythmias
(tachycardia)
3. Low BP 3. Decreased or 4. Warm, flushed
normal BP skin (vasodilation) 3. Tremors,
4. Pale to cyanotic muscle cramps,
skin and/or 4. Numbness and 5. Changes in LOC tingling of
mucosa tingling of (confusion and fingers and toes
extremities increased
5. Headache drowsiness) 4. HYPOkalemia
5. Hyper-reflexes
6. Drowsiness, and muscle 6. Nausea, vomiting 5. Restlessness
dizziness and cramping and diarrhea followed by
disorientation lethargy
6. Increased 7. Kussmaul
7. Muscle anxiety respirations 6. Confusion,
weakness (compensatory decreased
hyperreflexia 7. Increased HYPERventilation LOC, dizzy and
irritability ) irritable
8. HYPERkalemia
8. HYPOkalemia
9. Dysrhythmias
(due to
increased
potassium
levels)
• Causes: • Causes: • Causes: • Causes:
1. Respiratory 1. HYPERventilatio 1. DKA 1. Severe
depression due n (due to anxiety, vomiting
to anesthesia, fear and • Severe diarrhea
drug overdose Pulmonary • Diuretics
(opioids, Edema) 3. Renal failure (you're losing a
benzodiazepines lot of
4. Shock potassium,
) and increased • Mechanical except for the
ICP ventilation 5. Lactic acidosis potassium-
sparing
• Airway medications)
obstruction
3. Excessive
3. Decreased NaHCO3
alveolar capillary (bicarbonate)
diffusion (in
pneumonia, 4. Excessive GI
COPD, ARDs, suctioning
PE)
5. Excess steroid/
antacid use
• Relationship between potassium and acid-base balance=> https://acutecaretesting.org/en/journal-
scans/on-the-relationship-between-potassium-and-acid-base-balance/
• Acid-base imbalances alter the potassium transport;
• Acidosis causes increased reabsorption of potassium in the collecting duct
• Alkalosis causes decreased reabsorption of potassium in the collecting duct
• In general acidemia (reduced blood pH) is associated with increased plasma
potassium concentration (hyperkalemia), whilst alkalemia (increased blood pH) is
associated with reduced plasma potassium concentration (hypokalemia).
• Why does Cushing syndrome cause metabolic alkalosis? Cushing syndrome is
when there is excessive cortisol produced. Under various chemical reactions, it is
due to the excessive cortisol that leads to hypokalemia, which in turn leads to
alkalosis
• Tips:
1. Acidosis leads to HYPERkalemia
2. Alkalosis leads to HYPOkalemia
• 6 components in an ABG:
1. pH: 7.35 - 7.45 (7.40 as the absolute normal)
2. PaO2: 75 to 100 mmHg
3. PaCO2: 35 - 45 mmHg (respiratory parameter)
4. HCO3: 22 - 26 mEq/L (metabolic parameter)
5. O2 sat.: 94 to 100%
6. Oxygen
You might also like
- MEDICAL - SURGICAL by John RicafortDocument9 pagesMEDICAL - SURGICAL by John RicafortTazneem Apostol Esmael100% (2)
- Acid Base StudyGuide PDFDocument25 pagesAcid Base StudyGuide PDFMalik Ata Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- SESSION 1 Difficulty in Performing Adaptive SkillsDocument84 pagesSESSION 1 Difficulty in Performing Adaptive SkillsJeferson Sardeng100% (1)
- Acid Base ComparisonDocument1 pageAcid Base ComparisonEmilyNo ratings yet
- 2 - Summary (A)Document3 pages2 - Summary (A)shougNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Session 6-7Document6 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Session 6-7AngieNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument4 pagesAcid Base BalanceHenric CasimiroNo ratings yet
- Oxygen, Nutri, ElimDocument74 pagesOxygen, Nutri, ElimNina Anne ParacadNo ratings yet
- Short NoteDocument2 pagesShort NoteMd Sherajul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cheat SheetDocument1 pageNursing Cheat Sheetnazbeen.ahmadiNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesFluid and Electrolytestantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes 5Document14 pagesFluids & Electrolytes 5Justin Angelo SildoraNo ratings yet
- Hemolysis, Increase Serum K+: Ventricular Dysrrhytmias or Cardiac Arrest May OccurDocument2 pagesHemolysis, Increase Serum K+: Ventricular Dysrrhytmias or Cardiac Arrest May OccurArian BelogotNo ratings yet
- Day 21 - Notes Lab ValuesDocument12 pagesDay 21 - Notes Lab ValuesMarilia FarensenaNo ratings yet
- NORCETDocument101 pagesNORCETDiksha DhillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Intoxication and PoisoningDocument16 pagesDrug Intoxication and PoisoningErina NopiyantiNo ratings yet
- Study ExamDocument54 pagesStudy ExamQadri HaitamNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument86 pagesShockmeadwaiet1999No ratings yet
- MS Respi (NLE)Document3 pagesMS Respi (NLE)Maginalyn CangasNo ratings yet
- Inhalation Injury and Systemic IntoxicationDocument7 pagesInhalation Injury and Systemic IntoxicationDaniel LesmanaNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Summary NotesDocument9 pagesElectrolyte Summary Notesnurhana faudziNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes BDocument4 pagesElectrolytes BJay AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesACERET, IVAN LAURENTINE G.No ratings yet
- จมน้ำdrowningถถDocument21 pagesจมน้ำdrowningถถRungtip RuangnaparatNo ratings yet
- Medsurg ElearningDocument46 pagesMedsurg ElearningNathaniel PulidoNo ratings yet
- Addison Dse & Cushing SyndromeDocument2 pagesAddison Dse & Cushing SyndromeLot RositNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument57 pagesMedical Surgical NursingLowellyn Grezen VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Drugs - ZarinaDocument25 pagesPsychiatric Drugs - Zarinaszarina_7No ratings yet
- Viii. Pathophysiology A. Overview of The Disease HypokalemiaDocument4 pagesViii. Pathophysiology A. Overview of The Disease HypokalemiaCleo Joyce C. CristalNo ratings yet
- Tau Chempath - Acid Base Imbalance & Pahology of Resp FailureDocument31 pagesTau Chempath - Acid Base Imbalance & Pahology of Resp FailureChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Na/K/Cl Co-Transporter (NKCC2)Document3 pagesDiuretics: Na/K/Cl Co-Transporter (NKCC2)Safiya JamesNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Lesson2Document5 pagesNCM 112 Lesson2Trisha LopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HypovolemiaDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan HypovolemiaGusmila SariNo ratings yet
- Hypoxia: Lori HolmesDocument5 pagesHypoxia: Lori HolmesDanson Githinji ENo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document3 pagesQuiz 1Wiljohn de la CruzNo ratings yet
- FAK Pocket NotesDocument5 pagesFAK Pocket Noteskhairulazhan111No ratings yet
- DR Saroj PandaDocument45 pagesDR Saroj PandaPranshu Prajyot 67No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Drugsaliyahalexie6No ratings yet
- Organophosphate PoisoningDocument19 pagesOrganophosphate PoisoningapokawNo ratings yet
- Shock 22Document29 pagesShock 22Erina NopiyantiNo ratings yet
- Endo Session 3Document30 pagesEndo Session 3series recapNo ratings yet
- Indicator HCO:H CO Ratio Cause / Direction Etiology ConditionsDocument1 pageIndicator HCO:H CO Ratio Cause / Direction Etiology ConditionsSalve Rachelle BillenaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AcidosisDocument4 pagesRespiratory AcidosisMyca OcampoNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and AbgDocument32 pagesAcid Base and AbgSiti Nursuhada binti Mohd AminNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalances 103123Document14 pagesElectrolyte Imbalances 103123grazelantonette.calubNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion - JIDocument56 pagesPleural Effusion - JIpaulacabading.pcNo ratings yet
- Canonio t4 Calcium Magnesium Imbalances MedsurgDocument6 pagesCanonio t4 Calcium Magnesium Imbalances Medsurgchi kNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea N Resp FailureDocument63 pagesDyspnea N Resp FailurerujhanraqibiNo ratings yet
- High Altitude and Underwater PhysiologyDocument44 pagesHigh Altitude and Underwater PhysiologyKamyab SadeghzadehNo ratings yet
- Hypermagnesemia: Lim - Madalan - Madelo - MagalitDocument17 pagesHypermagnesemia: Lim - Madalan - Madelo - MagalitKyle De Sagun Oteda100% (1)
- History Taking in HematologyDocument1 pageHistory Taking in HematologyNarmin Abubaker AliNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument1 pageCirrhosis of LiverShaini ChristianNo ratings yet
- Continence Problem at HomeDocument71 pagesContinence Problem at HomeZayar HmunNo ratings yet
- Bio CH13 F4 Studywithadmin PDFDocument10 pagesBio CH13 F4 Studywithadmin PDFMUHAMMAD FAREEZ HAIKAL MOHD SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- Table 8-7 - The Eating Disorders and Subtypes From DSM-5Document1 pageTable 8-7 - The Eating Disorders and Subtypes From DSM-5Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance Chapter 19 StudentDocument5 pagesAcid Base Balance Chapter 19 StudentXiaoDuckyNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Bleeding: Late SignDocument12 pagesMinimizing Bleeding: Late SignMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- HyperkalemiaDocument2 pagesHyperkalemiaMaria KawilanNo ratings yet
- Overhydration and DehydrationDocument2 pagesOverhydration and DehydrationDr. NateqNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gases Mohammed Ibrahim Ali ObiedDocument25 pagesArterial Blood Gases Mohammed Ibrahim Ali ObiedmohammedrubyNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Anatomy CHP 13 NotesDocument5 pagesAnatomy CHP 13 NotesIsland RaeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy CHP 6 NotesDocument5 pagesAnatomy CHP 6 NotesIsland RaeNo ratings yet
- Pocketsized NandaDocument3 pagesPocketsized NandaIsland RaeNo ratings yet
- ECG QuizDocument6 pagesECG QuizIsland Rae100% (1)
- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy For Adults With ADHD21Document4 pagesCognitive Behavioural Therapy For Adults With ADHD21Michael HunterNo ratings yet
- Head Injuries ( Lesiones de Cabeza)Document5 pagesHead Injuries ( Lesiones de Cabeza)Camila BenitezNo ratings yet
- Aspects Cliniques Et Evolutifs Du Choc Septique en Reanimation Du Chu AndohatapenakaDocument8 pagesAspects Cliniques Et Evolutifs Du Choc Septique en Reanimation Du Chu AndohatapenakaIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax Part ADocument4 pagesPneumothorax Part ASoji0% (1)
- SchizophreniaDocument5 pagesSchizophreniamercyNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury Case Study FinalDocument46 pagesAcute Kidney Injury Case Study FinalSalwa KaramanNo ratings yet
- Seizure: Maria (Meritxell) OtoDocument4 pagesSeizure: Maria (Meritxell) OtoLuther ThengNo ratings yet
- DSM 5Document2 pagesDSM 5Alberto Preciado100% (1)
- SchizophreniaDocument31 pagesSchizophreniaSheena PasionNo ratings yet
- A Review of Bipolar Disorder Among Adults PDFDocument13 pagesA Review of Bipolar Disorder Among Adults PDFNadyaNo ratings yet
- Name: Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034Document2 pagesName: Delitya Islamy Putrie: F1021171027 Siti Eriyanti Mahpiyani: F1021171034Dyvatyha ThyaaNo ratings yet
- Soap NotesDocument6 pagesSoap NotesJust HelpingNo ratings yet
- Catatonia Revived. A Unique Syndrome UpdatedDocument10 pagesCatatonia Revived. A Unique Syndrome UpdatedElisa PavezNo ratings yet
- Soal Ujian EBM PraktekDocument6 pagesSoal Ujian EBM Praktekbobbyrianto2210No ratings yet
- Electric ShockDocument50 pagesElectric Shockfgghgkhk m m mNo ratings yet
- Identification Checklist For Children With Special Needs (CWSN)Document14 pagesIdentification Checklist For Children With Special Needs (CWSN)IE SSNo ratings yet
- Movement DisordersDocument127 pagesMovement DisordersDayanithi AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy IN Children: Presented by DR - Meera Pramil Department of KaumarabhrityaDocument60 pagesEpilepsy IN Children: Presented by DR - Meera Pramil Department of KaumarabhrityaAnil DasNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder: Bipolar I Disorder - Defined by Manic Episodes That Last at Least 7 Days, or by ManicDocument3 pagesBipolar Disorder: Bipolar I Disorder - Defined by Manic Episodes That Last at Least 7 Days, or by ManicVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Capstone Presentation Final With RefDocument15 pagesCapstone Presentation Final With Refapi-316250715No ratings yet
- Long QT SyndromeDocument15 pagesLong QT Syndromeprudhvi gallaNo ratings yet
- Kashi Naresh Government Post Graduate College Gyanpur, Bhadohi U.PDocument12 pagesKashi Naresh Government Post Graduate College Gyanpur, Bhadohi U.PAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument2 pagesDefinitionAlmustapha Babangida DanganiNo ratings yet
- Child Health NursingDocument5 pagesChild Health Nursingprincipalnursing rampurhat 2023No ratings yet
- Impared Physical Mobility Related To Hemiparesis As Evidenced by Right-Sided WeaknessDocument2 pagesImpared Physical Mobility Related To Hemiparesis As Evidenced by Right-Sided WeaknessMary Justine Nuyad-AfricaNo ratings yet
- Facts About Developmental DisabilitiesDocument5 pagesFacts About Developmental DisabilitiesrudylynNo ratings yet
- (Oxford American Psychiatry Library) Stephen Strakowski, Erik Nelson - Major Depressive Disorder-Oxford University Press (2015)Document113 pages(Oxford American Psychiatry Library) Stephen Strakowski, Erik Nelson - Major Depressive Disorder-Oxford University Press (2015)Angelica100% (3)
- Somatoform Disorders: NUR 444 FALL 2015Document37 pagesSomatoform Disorders: NUR 444 FALL 2015Amit TamboliNo ratings yet
- H&Y ScaleDocument17 pagesH&Y ScalezhansayaNo ratings yet