Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acid Base Comparison
Acid Base Comparison
Uploaded by
EmilyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid Base Comparison
Acid Base Comparison
Uploaded by
EmilyCopyright:
Available Formats
Acid Base Comparison
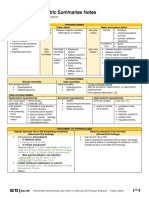
Metabolic Acidosis Respiratory Acidosis Metabolic Alkalosis Respiratory Alkalosis
• Accumulation of excess • A carbonic acid excess • Bicarbonate excess that • A carbonic acid deficit
metabolic acids OR resulting from any occurs from an increase in resulting from any
What it is
bicarbonate loss g not situation that i the rate of bicarb (orally or IV) OR situation that increases
respiratory or carbonic acid pulmonary ventilation or excess acid loss the pulmonary ventilation
related alveoli gas exchange or alveoli gas exchange
i pH and i HCO3 i pH and h CO2 h pH and h HCO3 h pH and i CO2
• Salicylate intoxication • Weakness of the resp. • Ingestion of large amounts • FAP:
(aspirin) muscles (shallow of bicarb or other antacids - Fever
• Hypoxiag shockg sepsisg breathing) (tums) - Anxiety
resulting in buildup of lactic • Severe resp. depression • Excess admin of bicarb - Pain
acid (brain injuries or sedation) • Loss of hydrochloric acid
Causes
• DKA • Obstruction to the resp. from stomachg vomiting
• Renal failure passage (COPD, asthma) or NGT suctioning
• Loss of bicarbonate via • Blocked alveoli gas • Diuretic therapy
stool exchange (COPD,
pulmonary edema)
• Call Her Daddy: • Visual disturbances *The signs and symptoms for metabolic and respiratory
- Confusion • Headaches alkalosis are the same*
- Hyperkalemia • Restlessness/agitation • Hypokalemia: all body systems i except UO and HR
- Dysrhythmias • Confusion, drowsiness, - Also have the 3 Ts: tingling, twitching, tetany
coma d/t vasodilation • Anxiety or irritability
S/S
• Hyperkalemia s/s: all body • Dizziness (hypotension)
system fxns h except for • Mental confusion
UO and HR • Paresthesia
• Seizures
• Treat the underlying cause • Positioning – elevate HOB • Stop the ingestion of • Treat the underlying cause
• Oxygen, fluids and • Oxygen bicarbonate to reduce CO2 loss
electrolyte monitoring • Meds – bronchodilators • Stop administration of • Fever – acetaminophen
• Dialysisg can regulate K+ • Incentive spirometer bicarbonate • Anxiety – antianxiety med,
and is used with renal • Mechanical ventilation • Give an antiemetic for brown paper bag
Interventions
patients • Ambulation vomiting • Pain – opioids, but be
• Antidiarrheal meds • PPI or H2 antagonist to careful not to throw them
(Imodium) stop the creation of acid in the other direction due
• Diureticsg loop or • Stop the loop or thiazide to sedation
thiazide, not a potassium diuretic
sparing one! Patient must • Fluid and electrolyte
be able to handle fluid loss replacement
(not for shock patients)
You might also like
- Rife Handbook 5th Ed SampleDocument150 pagesRife Handbook 5th Ed SampleBHAVANA VN86% (35)
- Tech Newsletter by SlidesgoDocument41 pagesTech Newsletter by SlidesgoAjla DžanoNo ratings yet
- Acid Base StudyGuide PDFDocument25 pagesAcid Base StudyGuide PDFMalik Ata Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Study ExamDocument54 pagesStudy ExamQadri HaitamNo ratings yet
- ABG NotesDocument2 pagesABG NotesIsland RaeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AcidosisDocument4 pagesRespiratory AcidosisMyca OcampoNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument57 pagesMedical Surgical NursingLowellyn Grezen VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Drug Intoxication and PoisoningDocument16 pagesDrug Intoxication and PoisoningErina NopiyantiNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base BalanceDocument67 pagesAcid-Base BalanceJocel Mae OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gases Mohammed Ibrahim Ali ObiedDocument25 pagesArterial Blood Gases Mohammed Ibrahim Ali ObiedmohammedrubyNo ratings yet
- Midterm Notes by F.L.F.Sanjuan, RMT, DtaDocument3 pagesMidterm Notes by F.L.F.Sanjuan, RMT, DtaIbtisam YusufNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 - Fluid & Electrolyte Balance2 - 21 Oct 2006Document28 pagesLecture 22 - Fluid & Electrolyte Balance2 - 21 Oct 2006api-3703352No ratings yet
- Hemolysis, Increase Serum K+: Ventricular Dysrrhytmias or Cardiac Arrest May OccurDocument2 pagesHemolysis, Increase Serum K+: Ventricular Dysrrhytmias or Cardiac Arrest May OccurArian BelogotNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Elctrolyte Balance.... Power PointDocument40 pagesFluid and Elctrolyte Balance.... Power PointMarwan M.100% (1)
- Acid and Base ImbalanceDocument49 pagesAcid and Base ImbalanceHidayah JaffriNo ratings yet
- PEDIA2 2.01b Fluids Electrolytes Summary TablesDocument4 pagesPEDIA2 2.01b Fluids Electrolytes Summary TablesVon HippoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolytes Acid Base BalanceDocument18 pagesFluid Electrolytes Acid Base BalanceVin Lorenzo Campbell100% (1)
- Hepatic Encephalopathy and DkaDocument6 pagesHepatic Encephalopathy and Dkajames garciaNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesFluid and Electrolytestantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalance: NURS601: Fundamentals of Acute Nursing Practice DR Sara NapierDocument89 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Imbalance: NURS601: Fundamentals of Acute Nursing Practice DR Sara NapierFano AsiataNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes - HypokalamiaDocument21 pagesElectrolytes - HypokalamiamympomNo ratings yet
- Lab Day: Michele BrynelsenDocument30 pagesLab Day: Michele BrynelsenCrystal LynaeNo ratings yet
- Created By: Dr. ArdilesDocument12 pagesCreated By: Dr. ArdilesDilessandro PieroNo ratings yet
- (Part 3) Acid-Base Balance-1Document7 pages(Part 3) Acid-Base Balance-1lapyem thomasNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument95 pagesAcid BaseMiracle For NursesNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Fluid & ElectrolytesDocument80 pages2.2 Fluid & ElectrolytesAizza ZarateNo ratings yet
- Nurs 13 Lec AbgDocument3 pagesNurs 13 Lec Abgcheskalyka.asiloNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument74 pagesAcid BaseMiracle For NursesNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes Session 6-7Document6 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Session 6-7AngieNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Fluids and ElectrolitesDocument38 pagesTopic 4 Fluids and ElectrolitesAbang ZilNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcaemia and Hypercalciuria: JamieDocument11 pagesHypercalcaemia and Hypercalciuria: JamieAymen OmerNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Imbalance 2Document26 pagesAcid Base Imbalance 2Female calmNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument8 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesACERET, IVAN LAURENTINE G.No ratings yet
- A Patient of Poisoning in ICU (Ankit Jain)Document48 pagesA Patient of Poisoning in ICU (Ankit Jain)SharryNo ratings yet
- Hyperglycemic CrisisDocument25 pagesHyperglycemic CrisisVentya Edita Madelyn SimamoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Electrolytes and Blood GasesDocument35 pagesLecture 7 Electrolytes and Blood GasesDuduetsang MosalakataneNo ratings yet
- The Renal System: Kidney ProcessesDocument29 pagesThe Renal System: Kidney ProcessesJOHN PEARL FERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Biochem Blood BuffersDocument4 pagesBiochem Blood BuffersLouis TecsonNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base DisordersDocument35 pagesAcid-Base DisordersAnonymous eson90100% (2)
- Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Dynamics: Human Anatomy and Physiology II Oklahoma City Community CollegeDocument59 pagesFluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Dynamics: Human Anatomy and Physiology II Oklahoma City Community CollegeSuwahono, M.PdNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Basis of Acid Base BalanceDocument103 pagesBiochemical Basis of Acid Base BalanceSidraRanaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Disturbances: Hypo Hyper Deficit ExcessDocument24 pagesFluid Volume Disturbances: Hypo Hyper Deficit ExcessMichael Baylon DueñasNo ratings yet
- 7 Acidbase-ImbalanceDocument5 pages7 Acidbase-ImbalanceMarie Louise Nicole TuvillaNo ratings yet
- 0 - Management of Life-Threatening Electrolyte and Metabolic Disturbances 3Document32 pages0 - Management of Life-Threatening Electrolyte and Metabolic Disturbances 3Roqoyyah MursyidNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDocument83 pagesFluid and Electrolyte BalanceRubinaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Electrolyte BalanceDocument59 pagesFluid Electrolyte BalanceLuqman RamzanNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Derrangements: by Christopher MazisDocument7 pagesElectrolyte Derrangements: by Christopher MazisChris MazisNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument41 pagesElectrolyte ImbalancesReignallienn Inocencio MartinNo ratings yet
- Fluid, Electrolytes, Acid Base BalanceDocument18 pagesFluid, Electrolytes, Acid Base Balanceashdmb217100% (5)
- ABG Interpretation and Acid-Base Emergency PDFDocument31 pagesABG Interpretation and Acid-Base Emergency PDFafhamazmanNo ratings yet
- Acidosis and Alkalosis SlidesDocument8 pagesAcidosis and Alkalosis SlidesNikhatNo ratings yet
- Fluid & Electrolyte, Acid-Base Imbalance (MS REPORT)Document41 pagesFluid & Electrolyte, Acid-Base Imbalance (MS REPORT)Jane BelvisNo ratings yet
- Toxocology: Abdullah Alolayan, R4Document6 pagesToxocology: Abdullah Alolayan, R4soulstakersNo ratings yet
- Acidosis, Alkalosis, Compensation. DR NaimDocument77 pagesAcidosis, Alkalosis, Compensation. DR NaimEren YNo ratings yet
- DR Saroj PandaDocument45 pagesDR Saroj PandaPranshu Prajyot 67No ratings yet
- Drug-Study 2Document3 pagesDrug-Study 2Macy MarquezNo ratings yet
- ABG (Arterial Blood Gas) : DR Sudhir Kumar SinghDocument30 pagesABG (Arterial Blood Gas) : DR Sudhir Kumar SinghVaso BalakhashviliNo ratings yet
- จมน้ำdrowningถถDocument21 pagesจมน้ำdrowningถถRungtip RuangnaparatNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycaemic Hyperosmolar StateDocument4 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycaemic Hyperosmolar StatemuhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in AcidDocument11 pagesDisturbances in AcidShannen Alija M. LaoNo ratings yet
- Theory 10 - Lipid Profile - Electrolytes Part 2Document71 pagesTheory 10 - Lipid Profile - Electrolytes Part 2Navoda ThathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Booklet On DAD Guest House - Transit Facilities PDFDocument35 pagesBooklet On DAD Guest House - Transit Facilities PDFSURAJ PRASADNo ratings yet
- Orange ConfitDocument4 pagesOrange ConfitAnishNo ratings yet
- Architects Certificate 3Document3 pagesArchitects Certificate 3Sethia DarshanNo ratings yet
- (SUMMARY) OB Chapter 11Document4 pages(SUMMARY) OB Chapter 11Keane Indira NariswariNo ratings yet
- SABIC Flat ProductDocument15 pagesSABIC Flat ProductAiman AliNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument14 pagesMaths ProjectY.Sreshta ReddyNo ratings yet
- Formosa Air Permit 19168Document195 pagesFormosa Air Permit 19168Victoria AdvocateNo ratings yet
- Poseidon Edition - Compressor N2Document32 pagesPoseidon Edition - Compressor N2arieprachman100% (1)
- JVC XV Fa90 ManualDocument88 pagesJVC XV Fa90 ManualFernandoNo ratings yet
- MGT610 - Final Term Notes 1-Pages-1Document110 pagesMGT610 - Final Term Notes 1-Pages-1Muniba Ch100% (2)
- Manual SharpDocument156 pagesManual SharpIon VasilescuNo ratings yet
- A Project ON New Product Development: Submitted by Col Manish ManchandaDocument23 pagesA Project ON New Product Development: Submitted by Col Manish ManchandaJahanvi ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Operation On Low-Sulphur Fuels: MAN B&W Two-Stroke EnginesDocument24 pagesOperation On Low-Sulphur Fuels: MAN B&W Two-Stroke EnginesRinaldi SiahaanNo ratings yet
- GAOHOU PH 0-14 Value Detect Sensor Module + Electrode Probe BNCDocument10 pagesGAOHOU PH 0-14 Value Detect Sensor Module + Electrode Probe BNCSapry EL GammalNo ratings yet
- Simatic HMI Option+Document121 pagesSimatic HMI Option+hdswt_mNo ratings yet
- Material Handling Procedure of CWC Pipes (Ver.3) : Project, 407700 - Baltic ConnectorDocument14 pagesMaterial Handling Procedure of CWC Pipes (Ver.3) : Project, 407700 - Baltic Connectorsteve aNo ratings yet
- 6 Categories of Information SystemDocument10 pages6 Categories of Information SystemCharmaine MagtangobNo ratings yet
- MM 5th National Moot Court Competition 2022 UpdatedDocument15 pagesMM 5th National Moot Court Competition 2022 UpdatedsssNo ratings yet
- Antifibrinolytic Therapy and Perioperative ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesAntifibrinolytic Therapy and Perioperative Considerationsandrey wahyudiNo ratings yet
- World Top 10 Inteligence Agencies - WWW - Theworldtoptens - ComDocument43 pagesWorld Top 10 Inteligence Agencies - WWW - Theworldtoptens - Commahbobullah rahmaniNo ratings yet
- Microteaching Lesson CoreDocument4 pagesMicroteaching Lesson Coreapi-316731131No ratings yet
- Bower Boiler SteelsDocument3 pagesBower Boiler Steelsraut_1234100% (1)
- Clarkston Lights Christmas Tree: Ex-Gpc President Wants Job BackDocument24 pagesClarkston Lights Christmas Tree: Ex-Gpc President Wants Job BackDonna S. SeayNo ratings yet
- Tech Trends ReportDocument248 pagesTech Trends ReportDevadasRajaramNo ratings yet
- Poem Rubric 12TH GRADEDocument1 pagePoem Rubric 12TH GRADEyulitza burgosNo ratings yet
- Primary Leaving Certificate PDFDocument3 pagesPrimary Leaving Certificate PDFDennis MwangiNo ratings yet
- Gluten-Casein Peptides TestDocument2 pagesGluten-Casein Peptides TestjmkcbeNo ratings yet
- Re-Thinking Sustainable DeveloDocument27 pagesRe-Thinking Sustainable DeveloFarhan AlvianaNo ratings yet