Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Controlling
Uploaded by
Nirmanyu Sood0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesControlling involves ensuring activities are performed according to plans by setting performance standards, measuring actual performance, comparing it to standards, analyzing deviations, and taking corrective action if needed. It is an ongoing process at all management levels aimed at efficiently achieving goals. Planning and controlling are interrelated, as controlling ensures plans are carried out properly and planning sets the standards controlling measures against. Some key steps in controlling are setting quantitative and qualitative standards, objectively measuring performance, determining acceptable performance ranges, and correcting deviations outside those ranges by modifying factors like materials, equipment, or processes used.
Original Description:
Controlling Chapter class 12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentControlling involves ensuring activities are performed according to plans by setting performance standards, measuring actual performance, comparing it to standards, analyzing deviations, and taking corrective action if needed. It is an ongoing process at all management levels aimed at efficiently achieving goals. Planning and controlling are interrelated, as controlling ensures plans are carried out properly and planning sets the standards controlling measures against. Some key steps in controlling are setting quantitative and qualitative standards, objectively measuring performance, determining acceptable performance ranges, and correcting deviations outside those ranges by modifying factors like materials, equipment, or processes used.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesControlling
Uploaded by
Nirmanyu SoodControlling involves ensuring activities are performed according to plans by setting performance standards, measuring actual performance, comparing it to standards, analyzing deviations, and taking corrective action if needed. It is an ongoing process at all management levels aimed at efficiently achieving goals. Planning and controlling are interrelated, as controlling ensures plans are carried out properly and planning sets the standards controlling measures against. Some key steps in controlling are setting quantitative and qualitative standards, objectively measuring performance, determining acceptable performance ranges, and correcting deviations outside those ranges by modifying factors like materials, equipment, or processes used.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Controlling
Controlling means ensuring that activities in an organization are performed as
per the plans.
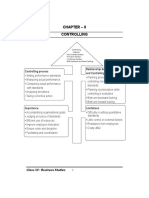
Nature/features of controlling PG LC
1. Controlling is a pervasive function
1.1.As it is required in all types of organizations and at all levels of
management – top, middle and lower.
2. Controlling is a goal-oriented function –
2.1.As it ensures that an organization’s resources are being used effectively
and efficiently for the achievement of pre-determined goals.
3. Controlling is both looking back and forward looking.
4. Controlling is a continuous function –
4.1.As it involves a constant review of actual performance to ensure that
activities in an organization are performed as per the plans.
Importance of controlling MSC ROG
1. Improves employee motivation
1.1.Employees know well in advance what they are expected to do and the
standards of performance on the basis of which they will be appraised.
1.2.This motivates them and helps them to give better performance.
2. Judging accuracy of standards
2.1.A good control system keeps a careful check on the changes taking
place in the organization and the environment and helps to review and
revise the standards in the light of such changes.
3. Facilitates coordination in action
3.1.Each department and employee are governed by pre-determined
standards which facilitates coordination in action.
4. Making efficient use of resources
4.1.Controlling seeks to reduce wastage and spoilage of resources as each
activity is performed in accordance with pre-determined standards and
norms.
5. Ensuring order and discipline
5.1.Controlling helps to minimize dishonest behavior on the part of the
employees by keeping a close check on their activities.
6. Accomplishing organizational goals
6.1.Controlling function measures the progress towards the organizational
goals by bringing to light, deviations if any and indicating corrective
action.
Relationship between planning and controlling
1. Controlling is blind without planning
1.1.Controlling takes place on the basis of standards developed by planning
because if the standards are not set in advance managers have nothing
to control. Thus, controlling is blind without planning
2. Planning without controlling is meaningless
2.1.Planning without controlling is meaningless because once a plan
becomes operational, controlling ensures that events conform to the
plans.
3. Planning is prescriptive whereas controlling is evaluative.
3.1.This is so, because, planning prescribes an appropriate course of action
for achieving objectives while controlling evaluates whether decisions
have been translated into desired actions.
4. Planning and controlling both are forward looking
4.1.because plans are prepared for the future and controlling seeks to
improve the future performance on the basis of past experience.
5. Planning and controlling are both looking back
5.1.Because planning is guided by past experience and controlling compares
the actual performance with the standards set in the pasts.
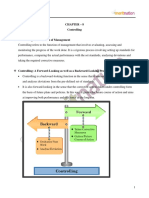
Steps in controlling process
1. Setting performance standards
1.1.Standards are the criterions against which actual performance would be
measured.
1.2.Standards can be set in both quantitative terms
1.2.1. Cost to be incurred
1.2.2. Revenue to be earned
1.2.3. Product units to be produced and sold
1.2.4. Time to be spent in performing a task.
1.3.As well as the qualitative terms
1.3.1. Improving goodwill
1.3.2. Motivation level of employees
1.4.Standards set should be flexible enough to be modified whenever
required.
2. Measurement of actual performance
2.1.Actual performance should be measured in an objective and reliable
manner.
2.2.Measurement is normally done after the task is completed but
wherever possible, it should be done during the performance.
2.3.There are several techniques for measurement of performance
2.3.1. Personal observation
2.3.2. Sample checking
2.3.3. Performance reports
2.4.As far as possible, performance should be measured in the same units in
which standards are set as this would make their comparison easier.
3. Comparing actual performance with standards
3.1.Actual performance is compared with standards to find out the
deviation between actual and desired result.
3.2.Comparison becomes easier when standards are set in quantitative
terms.
4. Analyzing deviations.
4.1.Some deviations in performance can be expected in all activities
4.2.It is therefore important to determine the acceptable range of
deviations.
4.3.Also, deviations in key areas of business need to be attended more
urgently as compared to deviations in certain insignificant areas.
5. Taking corrective action
5.1.Corrective action is taken if deviations go beyond the acceptable limits.
5.2.However, no corrective action is required when the deviation is within
the acceptable limits.
5.3.If the deviations cannot be corrected by managerial action, the
standards may have to be revised.
S no. Cause of deviation Corrective action to be taken
1. Defective material Change the quality specification for the
material used.
2. Defective machinery Repair the existing machine. Replace the
machinery if it cannot be repaired
3. Obsolete machinery Undertake technological upgradation of
machinery
4. Defective process Modify the existing process
5. Defective physical Improve the physical condition of work.
conditions of work
You might also like
- ISO 13053-2 2011 (E) PDF DocumentDocument56 pagesISO 13053-2 2011 (E) PDF DocumentmacprorababNo ratings yet
- Blitz Case Write-UpDocument2 pagesBlitz Case Write-Upvivek100% (2)
- Controlling Function Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument4 pagesControlling Function Advantages and DisadvantagesMhasibu Mhasibu100% (1)
- IR Pegasus 15-37Document8 pagesIR Pegasus 15-37Didi IswantoNo ratings yet
- Sample Electrical Safety Training ProgrammeDocument2 pagesSample Electrical Safety Training ProgrammePillai Sreejith100% (2)
- Controlling Class 12 Cbse NotesDocument24 pagesControlling Class 12 Cbse Notesviraj100% (1)
- Controlling NotesDocument3 pagesControlling Noteszahran0zannu01No ratings yet
- CONTROLLING2Document30 pagesCONTROLLING2Shantanu MohantyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Chapter 8. Controlling-1599071834870Document3 pagesChapter 8 Chapter 8. Controlling-1599071834870Harsh SahukarNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document9 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!yogesh kumarNo ratings yet
- BST - CHP 8Document3 pagesBST - CHP 8JOrdanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Controlling Notes PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 8 - Controlling Notes PDFabhishekNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 8 ControllingDocument6 pagesChapter - 8 ControllingyusraNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 ControllingDocument3 pagesChapter-8 ControllingPaavane ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 8 ControllingDocument4 pages8 Controllingadhishreesinghal24No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ControllingDocument9 pagesChapter 8 ControllingLatha VarugheseNo ratings yet
- Controlling NotesDocument7 pagesControlling NotesVrinda TayadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Controlling - 1.4Document66 pagesChapter 8 Controlling - 1.4Maria TitiNo ratings yet
- What Is Controlling?Document3 pagesWhat Is Controlling?Mary Judy GabisanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 (MGT Concepts and Practices)Document24 pagesChapter 7 (MGT Concepts and Practices)waleNo ratings yet
- Controlling ProcessDocument5 pagesControlling ProcessSuryansh NiranjanNo ratings yet
- Controlling Definition:: Types of ControlDocument8 pagesControlling Definition:: Types of ControlJhonny EnglishNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument31 pagesControllingJoana CabaneroNo ratings yet
- Nature and Process of ControllingDocument25 pagesNature and Process of ControllingCfa Deepti Bindal100% (1)
- Controlling Is One of The Important Functions of A ManagerDocument4 pagesControlling Is One of The Important Functions of A ManagerMelkamu DessalegnNo ratings yet
- CONTROLINGDocument12 pagesCONTROLINGAum GoelNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument3 pagesControllingJeremy PanerioNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument6 pagesControllingsuhaib shaikhNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument6 pagesControllingNitish GargNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument6 pagesControllingShaik SuhaibNo ratings yet
- Controlling and Steps in Control Process: - Apoorva Kumar - Vishisht Soni - Jai Garkel - Arpit TibrewalDocument16 pagesControlling and Steps in Control Process: - Apoorva Kumar - Vishisht Soni - Jai Garkel - Arpit TibrewalShivam AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Controlling as-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesControlling as-WPS OfficeAko Si ShunNo ratings yet
- oRGANicayion ManabgetmentDocument4 pagesoRGANicayion ManabgetmentIrish LudoviceNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument5 pagesControllingHimkar GuptaNo ratings yet
- LS 12 ControllingDocument24 pagesLS 12 ControllingAnish Sidharth ChekuriNo ratings yet
- Controlling PPT Team-3Document57 pagesControlling PPT Team-3Vikram Kulkarni100% (1)
- BST Art Integration ActivityDocument12 pagesBST Art Integration ActivityVansh MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Organization and Management Week 2 Definition of ControllingDocument5 pagesLesson Organization and Management Week 2 Definition of ControllingJosiel Alcarez MercaderoNo ratings yet
- CONTROLLINGDocument5 pagesCONTROLLINGLilac_o9No ratings yet
- CH 7Document6 pagesCH 7King HeniNo ratings yet
- Block 3 Managerial Processes - Ii: Staffing & DirectingDocument70 pagesBlock 3 Managerial Processes - Ii: Staffing & DirectingManan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- PIP Policy & Process - TemplateDocument4 pagesPIP Policy & Process - TemplateAmita Wahi100% (1)
- Org&Mngt 3rdqtr Wk3!23!24 ControlDocument34 pagesOrg&Mngt 3rdqtr Wk3!23!24 ControlChai Samonte TejadaNo ratings yet
- 5 ControlDocument40 pages5 ControlEunice TzpNo ratings yet
- HRMG Unit 5Document10 pagesHRMG Unit 5Hemanth ParakhNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document11 pagesUnit 7Kundan SinhaNo ratings yet
- Apply 5S ProcedureDocument14 pagesApply 5S Proceduremelkamu endale100% (3)
- Notes Chapter 8Document17 pagesNotes Chapter 8Aman Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Group I MwangangiDocument10 pagesGroup I Mwangangijoansada23No ratings yet
- Chapter - 8 Controlling: Class XII: Business Studies 1Document6 pagesChapter - 8 Controlling: Class XII: Business Studies 1Mahlet100% (1)
- Controlling: Presented byDocument12 pagesControlling: Presented bysalini sasiNo ratings yet
- OF BST CHAPTER 8 (Controlling)Document14 pagesOF BST CHAPTER 8 (Controlling)ANKITHA BARMANNo ratings yet
- CH - 8 ControllingDocument11 pagesCH - 8 ControllingianNo ratings yet
- Business Administration: SectionDocument27 pagesBusiness Administration: SectionAbdalrhman MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Monitor Implementation of Work Plan ActivitiesDocument27 pagesMonitor Implementation of Work Plan ActivitiesAmha SeyoumNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Revision NotesDocument6 pagesClass 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Revision NotesYash FattepuriaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Revision NotesDocument9 pagesClass 12 Business Studies Chapter 8 - Revision NotesSuchi SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 8 ControllingDocument3 pagesCH 8 Controllingshouryasethi98No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Controlling - 1.6Document3 pagesChapter 8 Controlling - 1.6Aishwarya MaradapuNo ratings yet
- Group 4 "Controlling": By:Yu, Moral, Manal, MendozaDocument11 pagesGroup 4 "Controlling": By:Yu, Moral, Manal, Mendozaangeles paranNo ratings yet
- Presentation 7 - ControllingDocument24 pagesPresentation 7 - Controllinggel.silvestre23No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 MPADocument17 pagesChapter 5 MPAAcharya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 5 Managerial ControlDocument54 pages5 Managerial ControlEunice TzpNo ratings yet
- Deep Sea Electronics PLC: Dse9000 Series Battery Charger Operator ManualDocument64 pagesDeep Sea Electronics PLC: Dse9000 Series Battery Charger Operator ManualJohn Mark LungubNo ratings yet
- SybaseDocument8 pagesSybaseapi-19965374No ratings yet
- Introduction of Airtel and JioDocument2 pagesIntroduction of Airtel and JioAbish ShekNo ratings yet
- LaticreteDocument44 pagesLaticreteHarsa VardhanNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: Magdalena Wrona, Davinson Pezo, Cristina NerinDocument7 pagesFood Chemistry: Magdalena Wrona, Davinson Pezo, Cristina NerinGema EscobedoNo ratings yet
- SmartX Controlle AS P Technical Leaflet 03 17031 06 en November 2015 PDFDocument6 pagesSmartX Controlle AS P Technical Leaflet 03 17031 06 en November 2015 PDFEdwin Zapata CardonaNo ratings yet
- Ashly Protea 4,24GDocument20 pagesAshly Protea 4,24GChristian DuboisNo ratings yet
- CNC Lathe Machine HistoryDocument2 pagesCNC Lathe Machine HistoryKesavan KesaNo ratings yet
- Wyse 7020 Thin Client DSDocument2 pagesWyse 7020 Thin Client DSJeffNo ratings yet
- Resistance Thermometer Measuring Transducer - MINI MCR-SL-PT100-UI - 2864435Document10 pagesResistance Thermometer Measuring Transducer - MINI MCR-SL-PT100-UI - 2864435nemoneoNo ratings yet
- Kz©Vewj I Abjvb B Av E'Bcî C Iy Kivi WbqgvewjDocument3 pagesKz©Vewj I Abjvb B Av E'Bcî C Iy Kivi WbqgvewjJames BondNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Tda 2616Document12 pagesData Sheet Tda 2616yaga0777No ratings yet
- DNP V3.00 Protocol Assignments: Electro Industries / GaugetechDocument159 pagesDNP V3.00 Protocol Assignments: Electro Industries / GaugetechiamxerxisNo ratings yet
- Binary XML Content Format Specification: Version 1.3, 25 July 2001Document30 pagesBinary XML Content Format Specification: Version 1.3, 25 July 2001Ilham BudionoNo ratings yet
- Ireless Ntuitive Robing Ystem: Wireless Intuitive Probing System W I P SDocument32 pagesIreless Ntuitive Robing Ystem: Wireless Intuitive Probing System W I P SGuillermo RamirezNo ratings yet
- As 4024.3301-2009 Safety of Machinery Robots For Industrial Environments - Safety RequirementsDocument7 pagesAs 4024.3301-2009 Safety of Machinery Robots For Industrial Environments - Safety RequirementsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Catalogo PC2000Document20 pagesCatalogo PC2000Fernando Contreras PanesNo ratings yet
- TTI Bundling ProcessDocument11 pagesTTI Bundling ProcessAbhay U. NagraleNo ratings yet
- Operator's Manual: TK 55666-1-OP (Rev. 2, 09/16)Document102 pagesOperator's Manual: TK 55666-1-OP (Rev. 2, 09/16)Vasti Diaz AguilarNo ratings yet
- Kito ER2 EnglishDocument40 pagesKito ER2 Englishkristina618No ratings yet
- La MinarDocument10 pagesLa MinarEntis Sustriya SindNo ratings yet
- Alchemy Training FirmDocument13 pagesAlchemy Training FirmRakhee Chatterjee0% (1)
- BSI - Machinery SafetyDocument56 pagesBSI - Machinery SafetybmjantoNo ratings yet
- INS-T-002, Tol. Shell Plt.Document3 pagesINS-T-002, Tol. Shell Plt.DeepakNo ratings yet
- Aircooler ManualDocument6 pagesAircooler ManualToby LimNo ratings yet
- ACS580 Replaces ACS550 Replacement GuideDocument24 pagesACS580 Replaces ACS550 Replacement GuideRudy A. TanNo ratings yet