Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Camel Analysis India Ranking
Uploaded by
Manita KunwarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Camel Analysis India Ranking
Uploaded by
Manita KunwarCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Management, IT & Engineering
Vol. 8 Issue 8, August 2018,
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119
Journal Homepage: http://www.ijmra.us, Email: editorijmie@gmail.com
Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal - Included in the International Serial
Directories Indexed & Listed at: Ulrich's Periodicals Directory ©, U.S.A., Open J-Gage as well as in Cabell’s
Directories of Publishing Opportunities, U.S.A
A CAMEL Model Analysis of Selected Public and Private Sector
Banks in India
Kajal Kiran1
Abstract
Banking is one of the fastest growing sectors in India. Banking sector helps in boosting capital formation,
innovation and monetization along with facilitation of monetary policy. Not only the depositors treat sound
financial health of a bank as the guarantee but it is equally significant for the shareholders, employees and whole
economy of a country as well. The present study measures the financial health of top public sector and private
sector banks operating in India using CAMEL Analysis. In the study, seven public sector bank namely State
Bank of India, Bank of Baroda, Bank of India, PNB Bank, Union Bank of India, Canara Bank and IDBI Bank
and four private sector Banks namely ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, AXIS Bank and Indusind Bank have been
selected as a sample. Data used for the study pertains from 2013-14 to 2016-17 and has been collected from the
annual reports of respective banks. To study every major variable use of various ratios have been made which
helps to analyze the variable in better way.
Keywords: Banks, CAMEL approach, Capital adequacy, Liquidity, asset quality, Management efficiency,
Earning Quality, Liquidity
1. Introduction
A strong, sustainable and viable banking system plays an important role in the overall development of an
economy. Banking sector has contributed in bringing a revolutionary change in reforming sector on the path of
economic growth. In fact, it is the backbone of the economy and one of the key indicators to assess the level of
development of any country. Performance of the banking sector is an effective measure and indicator to check
the performance of any economy to a large extent. The banking sector reforms were started in India as a follow
up measure of financial sector reforms and economic liberalization in the country. The banking sector being the
life line of the economy has been given due weightage in the financial sector reforms. More competitiveness,
productivity and efficiency and adherence to international accounting standards were the basic intentions behind
the initiation of reforms in Indian banking industry.
1
Assistant Professor in Commerce, JC DAV College, Dasuya, kajalkirankakkar@yahoo.in
257 International journal of Management, IT and Engineering
Email:
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Indian banking industry initiated in the early 1990s have been continued till now. As a result of these reforms, there have been
substantial changes in the bye laws, organization, scope and activity level of Indian Banking sector. Thus, Indian banking
industry has shown tremendous growth in the post liberalization era.
Banking performance is assessed by implementing a regulatory banking supervision framework. One of such measures of
supervisory regulation is the CAMEL rating system. In 1980s, US supervisory authorities introduced CAMEL rating system
as a system of rating the banks for on-site examinations of banking institutions. It proved to be a beneficial and efficient tool in
response to the financial crunch in 2008 by the U.S. government.
Camel approach is an effective tool to determine the relative financial strength of a bank and to suggest relevant measures to
improve shortcomings of a bank. In India, on the recommendations of Padmanabham Working Group (1995) committee, RBI
adopted this approach in 1996. At present, two Supervisory Rating Models CAMELS (capital adequacy, asset quality,
management quality, earnings, liquidity and sensitivity to market risk or systems & control) and CACS (capital, asset quality,
compliance and systems & control) are being used in India for rating of the Indian Commercial Banks and Foreign Banks
operating in India respectively.
2. Review of Literature
It has now been well recognized that that financial soundness of a bank depends on the different aspects and not only on the
profitability. A number of studies have been conducted to measure the operational and financial soundness of banks.
Misra and Aspal (2013) evaluate the performance and financial well being of State bank group encompassing State bank of
India, State bank of Hyderabad, State bank of Patiala, State bank of Mysore, State bank of Bikaner and Jaipur and State bank
of Travancore for a period of three years i.e. from 2009-2011.One way ANOVA is applied to determine whether significant
difference exists between the means of CAMEL ratio. They bring out that State bank of India needs to focus on Capital
adequacy and asset quality while State bank of Bikaner and Jaipur and state bank of Patiala have to work on improvement of
management efficiency and earning quality respectively. Gupta (2014) evaluates the performance of public sector banks in
India using CAMEL approach for a period of five years from 2009 to 2013 and brings out that Andhra Bank stood at first
position followed by Bank of Baroda and state bank of Hyderabad while United bank of India secured the least position. Singh
(2015) analyses the overall profitability of four private sector banks i.e. AXIS Bank, ICICI bank, Karur Vysya Bank and Yes
Bank. He measures the performance of the banks on the basis of profitability ratios like interest spread, return on long term
funds, net profit margin, adjusted cash margin, return on assets and return on net worth. ANOVA is also applied to find out the
significant relationship between interest spread, return on long term funds, net profit margin, adjusted cash margin, return on
assets and return on net worth among selected private sector banks. Garg and Kumari(2015) examine the different perspectives
of profitability of five major private banks for ten years from 2004 to 2014 using ratio analysis and ANOVA technique. They
conclude that HDFC Bank has been the excellent performer over the last decade. Meena (2016) assesses the performance of
different public sector and private sector banks by using CAMEL model. In his study, he also investigates the factors that
affect the financial performance of the selected public sector and private sector banks and finds that the management of NPAs
is the weakest area of private sector and public sector banks. Srinivasan and Saminathan (2016) apply CAMEL model to rank
the public sector, private sector and foreign banks on the basis of financial performance from 2012 to 2014.They also find out
that significant difference lies between the mean values of Camel ratios of public sector, private sector and foreign banks
during the period of study. Purohit and Bothra (2018) compare the performance of SBI and ICICI Bank using CAMEL
parameters. They conclude that ICICI bank needs to improve its position with regard to capital adequacy and asset quality
while SBI need to improve its position with regard to management efficiency, earning quality and liquidity.
3. Need of the study
The present study is undertaken to highlight the comparative analysis on financial performance of selected top public sector
and private sector banks in India through CAMEL Analysis Model. Through the study we would came to know the financial
position of the selected 11 top banks operating in India.
25 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
4. Objectives of the Study
The objectives of the study are:
To analyze the financial performance of selected Public sector and Private Sector banks in India on different
parameters of camel model.
To examine the overall relative financial position of selected Public sector and Private Sector banks in India .
To give recommendations for improvement in performance of public and private sector banks of India.
5. Research Methodology
5.1 Data Collection
The present study is based on Secondary data. The relevant data has been collected from the annual reports of selected banks.
In addition to the records of the bank, data were also collected from banking bulletin, websites, newspapers, magazines and
various journals.
5.2 Selected Banks for the study:
Seven public sector banks namely (State Bank of India, Bank of India, Bank of Baroda, Union Bank of India, PNB Bank,
IDBI Bank and Canara bank) and four Private sector banks (ICICI bank, HDFC Bank, AXIS Bank, Indusind Bank) have been
taken as sample
5.3 Time Period of the study:
The study covers a period of four financial years i.e. from 2013-14 to 2016-17.
5.4 Analytical Tools:
To look at the financial soundness of the selected Public and Private sector banks in India, internationally accepted CAMEL
rating parameters have been applied. CAMEL is an acronym for five parameters (capital adequacy, assets quality,
management soundness, earnings and liquidity). CAMEL rating is a subjective model which assesses financial strength of a
bank, whereas CAMEL ranking indicates the banks comparative position with reference to other banks.
Ratios and averages have been used for analysis. Averages are calculated using MS-Excel.
6. Empirical Results and Discussion
6.1 Financial performance of Selected public and private sector banks in India on different
parameters of CAMEL model
(1) CAPITAL ADEQUACY
Capital Adequacy is a key indicator of financial well being of a bank. It describes whether the bank has adequate capital to
meet unexpected losses. It gives the indication of overall financial position of the banks and also the ability of the management
to meet the need for additional capital and also to maintain depositor’s confidence and preventing the bank from going
bankrupt. Capital adequacy of a bank can be measured by using following ratios:
25 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Capital adequacy ratio (Tier 1 Capital + Tier 2 Capital) a measure of the amount of a bank's core capital
Risk weighted Assets expressed as a percentage of its risk weighted Assets.
Higher the ratio better it is
Advance to assets ratio Total advances/ Total assets Aggressiveness of a bank in lending, thus resulting in
better profitability. Higher the ratio better it is
Debt equity ratio Outside liabilities /Net worth Higher ratio indicates less protection for the creditors
and depositors in the banking system.
Government securities to Govt.Securities/Total investment The higher the Government securities to investment
total investment ratio, the lower the risk involved in bank's investments.
A minimum Capital to risk-weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) prescribed by Reserve Bank of India for banks with regard to
credit risk, market risk and operational risk on an ongoing basis is 9 % as against Basel norms of 8 %. Ranking of the Banks
under study on the basis of CAR as per Table-1(annex.) indicates that ICICI bank ranks on the top position with highest CAR
of 17.19, followed by HDFC, AXIS, INDUSIND and SBI having CAR of 15.74, 15.35, 14.18 and 12.67. Advance to assets
ratio as per Table-2 (annex.) indicates that Union Bank of India bags the top position with highest advance to assets ratio of
0.65, followed by HDFC, INDUSIND, having values of 0.64, 0.63. ICICI bank secures the top position with respect to Debt
equity ratio with lowest Debt Equity ratio of 6.98, followed by INDUSIND, HDFC and AXIS having values of 8.12, 9.06 and
9.26 [Table 3 (annex.)]. Ranking of the Banks under study on the basis of Govt Securities to total investment [Table-
4(annex.)] indicates that BOI stands on the top position with highest Govt Securities to total investment value of 0.89,
followed by CANARA, BOB and PNB having values of 0.88, 0.85 and 0.80.
Result of the group averages of four ratios of capital adequacy is expressed in Table-5(annex.) which indicates that HDFC
bank and INDUSIND bank are jointly at Top in this category with group average of 3.50 followed by ICICI bank and AXIS
Bank with average of 4.0 and 4.75 due to better performance of these private sector banks in Debt Equity, Advances to Assets
ratio, and capital adequacy ratio.
(2) ASSET QUALITY
Asset quality assesses the soundness of financial institutions against loss of value in the assets .Asset impairment adversely
affects the solvency of the financial institutions. The level and severity of non-performing assets, adequacy of provisions,
distribution of assets etc impacts the asset quality. The ratios used to assess asset quality are:
Net NPAs to Net advances Lower ratio is a sign of credit efficiency of bank
Total Investment to total assets Higher ratio adversely affects the profitability of banks
Net NPAs to total assets Lower the ratio, better is the performance of bank
Ranking of the Banks under study on the basis of Net NPA to Net advances as per Table-6(annex.) demonstrates that HDFC
bank ranked on the top position with lowest Net NPA to Net Advances ratio of 0.28, followed by INDUSIND, AXIS and
ICICI having values of 0.35, 0.98 and 2.75. Total investment to total assets ratio [ Table-7(annex.)] indicates that BOB bank
is on the top position with lowest Total investment to total assets ratio of 0.18, followed by BOI, INDUSIND and UBI having
values of 0.20, 0.23 and 0.25. Net NPA to Total Assets as per Table-8(annex.) provides that HDFC bank and INDUSIND
Bank are jointly ranked on the top position with lowest Net NPA to Total assets ratio of 0.002, followed by AXIS, ICICI and
SBI having values of 0.006, 0.017 and 0.019.
Group averages of three ratios of Asset Quality [Table-9(annex.)] makes it clear that HDFC bank and INDUSIND bank are
jointly at Top in this category with group average of 2.0 followed by AXIS bank and BOB Bank with average of 3.33 and
3.67 due to better performance of these private sector banks in all three ratios of Asset Quality. Amongst Public sector banks
only Bank of Baroda has shown good asset quality management.
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
(3) MANAGEMENT EFFICIENCY
The management efficiency signifies the ability of banks top management to take right decisions. It enables the evaluation of
better management quality and discounting poorly managed ones and helps a bank to achieve sustainable growth. It sets vision
and goals for the business and checks out that it achieves them. The ratios in this element encompass subjective analysis to
determine the efficiency and effectiveness of management. The ratios used to evaluate management efficiency are:-
Total advances to total deposits Indicates the ability of the bank to convert deposits into high earning advances.
Higher ratio is better
Business per Employee Efficiency of the employees to generate business (total advances and total
deposits). The higher the ratio ,better it is.
Profit per Employee Efficiency of the employees to generate profit for the bank. Higher ratio is
better.
Return on Equity Profits available for shareholders. Higher ratio signifies efficiency of the bank.
Total Advances to Total Deposits ratio [Table-10(annex.)] indicates that ICICI bank is ranked on the top position with highest
Total Advances to Total Deposits ratio of 1.02, followed by INDUSIND, AXIS and HDFC having values of 0.92, 0.90 and
0.84. As per table11 (annex.) business per employee of IDBI bank is the maximum. Thus IDBI bags the top position with
highest Business per employee ratio of 248.73, followed by BOI, BOB and UBI having values of 194.20, 179.58 and
150.40.Profit per employee as shown in Table-12(annex.) brings out that AXIS bank secures the highest position with highest
Profit per employee ratio of 1.43, followed by ICICI, HDFC and INDUSIND having values of 1.40, 1.33 and 0.99. Table-
13(annex.) shows that HDFC bank gets the first rank with highest ROE ratio of 19.22, followed by INDUSIND , AXIS and
ICICI having values of 16.55, 14.69 and 12.58. The result of the group averages of four ratios of Management Efficiency is
expressed in Table-14(annex.), which indicates that AXIS bank is ranked at Top with group average of 3.25 followed by ICICI
Bank and HDFC Bank jointly second with average of 4.25 and INDUSIND Bank on third position with value 4.75 due to
better performance of these private sector banks in Total advances to total deposits, profit per employee and ROE. Public
sector banks have shown better performance only in Business per employee category under management efficiency
parameters.
(4) EARNING QUALITY
The sustainability in income and growth of future earnings indicates the quality of earnings. Interest rate policies and
sufficiency of provisioning help to evaluate the earnings and profitability. The ratios that are used to evaluate earning quality
are:-
Interest income to total income Represent the share of interest income in total income. Higher ratio is better
Operating profits to total assets Indicates operating income of the bank per rupee invested in total assets. Higher
ratio is better.
Net interest margin to total assets Excess of interest earned over interest expended relative to total assets
Return on assets Efficiency with which bank uses its assets to generate net income.
Interest income to total income shown in Table 15 (annex.) indicates that UBI and BOI are jointly on the top position with
highest interest income to total income ratio of 0.90, followed by CANARA , BOB and IDBI (jointly second) and PNB having
values of 0.89 and 0.88 respectively. Operating profit to total assets as per Table-16(annex.) brings out that ICICI Bank
secures the top position with highest operating profit to total asset ratio of 3.29, followed by INDUSIND, HDFC and AXIS
having values of 3.25, 3.22 and 3.16 respectively. Table 17 (annex.) provides that Net interest margin to total assets ratio of
HDFC Bank is the highest i.e. 4.14 followed by INDUSIND, AXIS and ICICI having values of 3.59, 3.30 and 3.00
respectively. Ranking of the Banks under study on the basis of ROA shown in Table-18(annex.) indicates that HDFC bank is
ranked on the top position with highest ROA ratio of 1.95, followed by INDUSIND , ICICI and AXIS having values of 1.87,
1.62 and 1.50 respectively. Results of the group averages of three ratios of Earning Quality is expressed in Table-19(annex.),
which indicates that HDFC bank is ranked at Top in this category with group average of 2.25 followed by INDUSIND bank
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
and ICICI bank with average of 3.00 and 3.75 due to better performance of these private sector banks in Operating profit to
total assets and NIM to Total Assets and ROA. Public sector banks have shown better performance only in Interest income to
total income category under earning quality parameters.
(5) LIQUIDITY:
Liquidity is the capability of banks to meet its financial obligations. Too low liquidity hampers the capacity of banks to meet
its current financial liabilities. On other hand, too high liquidity indicates that banks are not making the proper use of their
cash and hence blocking the way of profitability. Thus a proper equilibrium is necessary in liquidity to balance high profit as
well as liquidity. The ratios suggested to measure liquidity under CAMEL Model are:-
Liquid assets to total assets Higher ratio is better .
Liquid assets to demand deposits Higher ratio is better
Liquid assets to total deposits Higher ratio is better
Approved securities to total assets Higher ratio is better
Ranking of the Banks under study on the basis of Liquid assets to total assets is shown in Table-20, which indicates that BOB
Bank is ranked on the top position with highest Liquid Assets to total asset ratio of 0.21, followed by BOI, PNB and
CANARA(Jointly third) having values of 0.14 and0.10 (both PNB and CANARA). Ranking of the Banks under study on the
basis of Liquid Assets to Demand Deposits is shown in Table-21, which indicates that BOI Bank is ranked on the top position
with highest Liquid Assets to Demand Deposit ratio of 3.50, followed by BOB, CANARA and PNB having values of 3.21,
2.61 and 1.77. Ranking of the Banks under study on the basis of Liquid Assets to Total Deposits is shown in Table-22, which
indicates that BOB Bank is ranked on the top position with highest Liquid Assets to Total Deposit ratio of 0.24, followed by
BOI, ICICI and INDUSIND (jointly third) having values of 0.16 and 0.13 (both ICICI and INDUSIND). Ranking of the
Banks under study on the basis of Approved Securities to Total Assets is shown in Table-23, which indicates that IDBI Bank
and CANARA Bank are jointly ranked on the top position with highest Approved Securities to Total Assets ratio of 0.23,
followed by PNB and SBI(Jointly second) and HDFC and UBI (jointly third) having values of 0.20 (both PNB and SBI) and
0.19 (both HDFC and UBI).
Result of the group averages of four ratios of Liquidity is expressed in Table-24, which indicates that BOI bank is ranked at
Top in this category with group average of 2.25 followed by BOB bank, CANARA bank and PNB with average of 2.75, 3.00
and 3.25 due to better performance of these public sector banks in all the four parameters of Liquidity. Private sector banks
have to make more efforts in terms of Liquidity parameter to get better results in future.
6.2 Composite Ranking (Overall Performance) of Selected Public and Private sector Banks
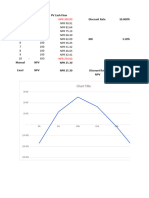
Composite Ranking of the all the 11 Banks under study on the basis of CAMEL Analysis is shown in Table-25(annex.) on the
basis of performance in last four Financial years 2014-2017, the Table depicts that on the basis of this analysis INDUSIND
Bank is at First Position followed by HDFC Bank , ICICI Bank and AXIS Bank. SBI is at fifth position and top among the
public sector banks.
6.3 Findings and Suggestions
The paper brings out that Indusind bank, HDFC bank, ICICI bank, AXIS bank and SBI bank are occupying the top five
positions while BOB, BOI, PNB, UBI , Canara bank and IDBI are on bottom six positions. In top five positions, only one
public sector bank i.e. SBI has managed to secure the position and the other four are all selected private sector banks. All the
bottom six banks are public sector banks. The minute analysis of the present study puts the light on the fact that all private
sector banks have shown sound performance on capital adequacy, asset quality, management efficiency and earning quality
parameter. However, on the basis of liquidity, public sector banks have shown better performance as compared to private
sector banks. Amongst public sector banks, only SBI has shown consistent performance on all the parameters and has fitted
itself among top five banks on the yardstick of CAMEL model. All the other public sector banks have to work to improve
capital adequacy, asset quality, management efficiency and earning quality.
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
7. Conclusion
Banking system of a country influences its economy significantly. Reserve bank of India adopted CAMEL rating system in
1996 along with other existing techniques and procedures in order to evaluate the performance of the banks. The present study
analyses the performance of eleven banks (4 private sector and 7 public sector ) on the basis of CAMEL model. The results
show that private sector banks outperform public sector banks and first four ranks go to the credit of all the selected private
sector banks. The private sector banks have to improve performance on liquidity aspect and public sector banks have to focus
on capital adequacy, asset quality, management efficiency and earning quality.
References
Articles
a) A Purohit, P. B. (2018). A Camel model analysis of selected public and private sector banks in India. ASAR International
Conference.
b) Garg, K. (2015). An empirical analysis of profitability position of selected private sector banks in India. Journal of Management
Sciences and Technology , 2 (3), 22-28.
c) Meena. (2016). Financial Analysis of Select Banks using Camel approach a study with reference to Indian Banking
Industry. International Journal of reseach and scientific innovation , 3 (10), 30-35.
d) Misra, A. (2013). A Camel Model analysis of State Bank Group. World Journal of Social Sciences , 3 (4), 36-55.
e) R, G. (2014). An analysis of Indian Public sector Banks using Camel approach. IOSR Journal of Business and
Management , 16 (1), 94-102.
f) Singh, A. K. (2015). An analysis of profitability position of private banks in India. International Journal of Scientific
and Research Publications , 5 (5), 1-11.
g) Srinivasan, S. (2016). A Camel model analysis of Public,Private and Foreign Sector Banks in India. Pacific Business
Review International , 8 (9), 45-57.
Websites
1) www.moneycontrol.com/financials/
2) https://www.sbi.co.in/
3) https://www.pnbindia.in/
4) www.bankofbaroda.co.in/
5) www.hdfcbank.com/
6) www.icicibank.com/
7) www.axisbank.com/
8) https://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/AnnualReportMainDisplay.aspx
9) www.canarabank.in
10) www.unionbankofindia.co.in
11) www.bankofindia.co.in
12) www.idbi.com
13) www.indusind.com
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Annexure
Table 1: Capital Adequacy Ratio Table 2: Advance To Assets Ratio
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
SBI 12.44 12 13.12 13.11 12.67 5 SBI 0.66 0.63 0.63 0.55 0.62 4
HDFC 16.07 16.79 15.53 14.55 15.74 2 HDFC 0.62 0.62 0.66 0.64 0.64 2
ICICI Table
17.7 3: Debt16.64
17.02 Equity17.39
Ratio 17.19 1 ICICI Table0.6
4:Govt.
0.6 Sec.0.6To Total
0.6 Investment
0.60 5
PNB 11.52 12.21 11.28 11.66 11.67 7 PNB 0.64 0.64 0.63 0.58 0.62 4
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
AXIS 16.07 15.09 15.29 14.95 15.35 3 AXIS 0.6 0.61 0.64 0.62 0.62 4
SBI 14.73 15.18 14.9 14.4 14.80 6 SBI 0.76 0.76 0.77 0.77 0.77 6
Canara 10.63 10.56 11.08 12.86 11.28 9 Canara 0.61 0.6 0.59 0.59 0.60 5
HDFC 10.31 8.52 8.75 8.66 9.06 3 HDFC 0.78 0.72 0.77 0.76 0.76 7
BOB 12.28 12.61 13.18 12.24 12.58 6 BOB 0.6 0.6 0.57 0.55 0.58 6
ICICI 7.12 7.03 7.03 6.72 6.98 1 ICICI 0.54 0.58 0.7 0.7 0.63 9
UBI 10.8 10.22 10.08 11.79 10.72 11 UBI 0.65 0.67 0.66 0.63 0.65 1
PNB 13.92 13.93 15.76 15.69 14.83 7 PNB 0.78 0.82 0.8 0.79 0.80 4
IDBI 11.68 11.76 11.67 10.7 11.45 8 IDBI 0.6 0.59 0.58 0.53 0.58 6
AXIS 9.03 9.34 8.88 9.79 9.26 4 AXIS 0.61 0.62 0.71 0.72 0.67 8
BOI 9.97 10.73 12.01 12.14 11.21 10 BOI 0.65 0.65 0.59 0.59 0.62 4
Canara 15.61 16.2 16.5 16.32 16.16 8 Canara 0.85 0.86 0.89 0.9 0.88 2
Indusind 13.83 12.09 15.5 15.31 14.18 4 Indusind 0.63 0.63 0.63 0.63 0.63 3
BOB 17.33 16.95 15.7 16.24 16.56 9 BOB 0.83 0.81 0.86 0.88 0.85 3
UBI 18.15 18.27 16.67 17.88 17.74 10 UBI 0.74 0.78 0.8 0.79 0.78 5
IDBI 12.92 13.6 12.34 14.58 13.36 5 IDBI 0.65 0.69 0.88 0.9 0.78 5
BOI 18.16 18.67 18.66 19.36 19.71 11 BOI 0.88 0.88 0.9 0.89 0.89 1
Indusind 8.64 9.26 6.92 7.66 8.12 2 Indusind 0.71 0.72 0.81 0.86 0.78 5
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Table 5: Composite Capital Adequacy
Capital Adequacy Advance to Total Govt Securities to Total
BANK Debt Equity Group Rank
Ratio Assets Investment
Ratio Rank Ratio Rank Ratio Rank Ratio Rank AVG Rank
SBI 12.67 5 0.62 4 14.80 6 0.77 6 5.25 4
HDFC 15.74 2 0.64 2 9.06 3 0.76 7 3.50 1
ICICI 17.19 1 0.60 5 6.98 1 0.63 9 4.00 2
PNB 11.67 7 0.62 4 14.83 7 0.80 4 5.50 5
AXIS 15.35 3 0.62 4 9.26 4 0.67 8 4.75 3
Canara 11.28 9 0.60 5 16.16 8 0.88 2 6.00 6
BOB 12.58 6 0.58 6 16.56 9 0.85 3 6.00 6
UBI 10.72 11 0.65 1 17.74 10 0.78 5 6.75 8
IDBI 11.45 8 0.58 6 13.36 5 0.78 5 6.00 6
BOI 11.21 10 0.62 4 19.71 11 0.89 1 6.50 7
Indusind 14.18 4 0.63 3 8.12 2 0.78 5 3.50 1
Table 6: Net NPAs to net advances Table 7: Total investment to total assets
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
SBI 2.57 2.12 3.81 3.71 3.05 5 SBI 0.24 0.26 0.24 0.3 0.26 5
HDFC 0.27 0.25 0.28 0.33 0.28 1 HDFC 0.25 0.28 0.23 0.25 0.25 4
ICICI 0.97 1.61 2.98 5.43 2.75 4 ICICI 0.3 0.29 0.22 0.21 0.26 5
PNB 2.85 4.06 8.61 7.81 5.83 10 PNB 0.26 0.25 0.24 0.26 0.25 4
AXIS 0.44 0.46 0.74 2.27 0.98 3 AXIS 0.3 0.29 0.23 0.21 0.26 5
Canara 1.98 2.65 6.42 6.33 4.35 8 Canara 0.26 0.27 0.26 0.26 0.26 5
BOB 1.52 1.89 5.06 4.72 3.30 6 BOB 0.18 0.17 0.18 0.19 0.18 1
UBI 2.33 2.71 5.25 6.57 4.22 7 UBI 0.26 0.25 0.22 0.25 0.25 4
IDBI 2.48 2.88 6.78 13.21 6.34 11 IDBI 0.31 0.34 0.26 0.26 0.29 6
BOI 2 3.36 7.79 6.9 5.01 9 BOI 0.2 0.19 0.19 0.2 0.20 2
Indusind 0.33 0.31 0.36 0.39 0.35 2 Indusind 0.25 0.23 0.22 0.21 0.23 3
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Table 8 : Net NPAs To Total Assets
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
SBI 0.013 0.01 0.023 0.028 0.019 4
HDFC 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 1
ICICI 0.006 0.01 0.018 0.033 0.017 3
PNB 0.018 0.024 0.053 0.045 0.035 8
AXIS 0.003 0.003 0.005 0.014 0.006 2
Canara 0.012 0.016 0.038 0.037 0.026 5
BOB 0.009 0.011 0.028 0.026 0.019 4
UBI 0.015 0.018 0.035 0.042 0.028 6
IDBI 0.015 0.017 0.039 0.069 0.035 8
BOI 0.013 0.022 0.046 0.04 0.030 7
Indusind 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 1
Table 9 : Composite Asset Quality
BANK Net NPA to Net Advances Total Investment to Total Assets Net NPA to Total Assets Group Rank
Ratio Rank Ratio Rank Ratio Rank AVG Rank
SBI 3.05 5 0.26 5 0.019 5 4.67 5
HDFC 0.28 1 0.25 4 0.002 1 2.00 1
ICICI 2.75 4 0.26 5 0.017 4 4.00 4
PNB 5.83 10 0.25 4 0.035 9 7.33 8
AXIS 0.98 3 0.26 5 0.006 3 3.33 2
Canara 4.35 8 0.26 5 0.026 6 6.00 7
BOB 3.30 6 0.18 1 0.019 5 3.67 3
UBI 4.22 7 0.25 4 0.028 7 5.67 6
IDBI 6.34 11 0.29 6 0.035 9 8.33 9
BOI 5.01 9 0.20 2 0.030 8 6.00 7
Indusind 0.35 2 0.23 3 0.002 1 2.00 1
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Table 10: Total Advances to Total Deposits Table 11: Business Per Employee
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
SBI 0.86 0.82 0.85 0.77 0.83 5 SBI 106.38 123.4 141.1 162.4 133.32 8
HDFC 0.82 0.81 0.85 0.86 0.84 4 HDFC 89 101 113.9 123.6 106.88 9
Table 12:Profit Per Employee Table 13: Return on Equity
ICICI 1.02 1.07 1.03 0.95 1.02 1 ICICI 74.7 83.2 94.3 98.9 87.78 10
PNB 0.77 0.76 0.78 0.67 0.75 8 PNB 128.3 131.9 135.9 141.7 134.45 7
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
AXIS 0.83 0.88 0.96 0.92 0.90 3 AXIS 123 137.1 148.4 140 137.13 6
SBI 0.49 0.6 0.47 0.51 0.52 6 SBI 10.03 10.62 7.3 6.31 8.57 5
Canara 0.72 0.7 0.68 0.69 0.70 10 Canara 143.84 143.5 144.46 144.28 144.02 5
HDFC 1.2 1 1.5 1.6 1.33 3 HDFC 21.28 19.37 18.26 17.95 19.22 1
BOB 0.7 0.69 0.67 0.64 0.68 11 BOB 186.5 188.9 168 174.9 179.58 3
ICICI 1.4 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.4 2 ICICI 14.02 14.55 11.43 10.33 12.58 4
UBI 0.77 0.81 0.78 0.76 0.78 7 UBI 137.6 144.6 155.1 164.3 150.40 4
PNB 0.5 0.5 -0.6 0.2 0.15 9 PNB 9.75 8.17 5.81 3.31 6.76 7
IDBI 0.84 0.8 0.81 0.71 0.79 6 IDBI 246.53 262.1 251.8 234.5 248.73 1
AXIS 1.5 1.7 1.8 0.7 1.43 1 AXIS 17.43 17.75 16.81 6.76 14.69 3
BOI 0.78 0.76 0.7 0.68 0.73 9 BOI 196.3 206.9 179.6 194 194.20 2
Canara 0.5 0.5 -0.5 0.2 0.18 8 Canara 8.95 8.79 -8.86 3.44 3.08 8
Indusind 0.91 0.93 0.95 0.89 0.92 2 Indusind 71.71 71.92 76.46 91.63 77.93 11
BOB 1 0.7 -1 2.6 0.83 5 BOB 13.36 8.96 -13.48 3.44 3.07 9
UBI 0.5 0.5 0.4 0.2 0.4 7 UBI 9.48 9.32 6.34 2.37 6.88 6
IDBI 0.68 0.5 -2.1 -2.8 -0.93 11 IDBI 5.00 3.64 -14.08 -20.52 -6.49 11
BOI 0.63 0.37 -1.22 -0.32 -0.14 10 BOI 10.14 5.57 -19.5 -5.04 -2.21 10
Indusind 0.9 0.94 0.99 1.13 0.99 4 Indusind 16.89 18.22 16.14 14.96 16.55 2
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Table 14: Composite Management Efficiency
Total Advances to Total Business Per Profit Per Return on Equity
BANK Group Rank
Deposits Employee Employee Ratio
Ratio Rank Millions Rank Millions Rank Ratio Rank AVG Rank
SBI 0.83 5 133.32 8 0.52 6 8.57 5 6.00 4
HDFC 0.84 4 106.88 9 1.33 3 19.22 1 4.25 2
ICICI 1.02 1 87.78 10 1.4 2 12.58 4 4.25 2
PNB 0.75 8 134.45 7 0.15 9 6.76 7 7.75 7
AXIS 0.90 3 137.13 6 1.43 1 14.69 3 3.25 1
Canara 0.70 10 144.02 5 0.18 8 3.08 8 7.75 7
BOB 0.68 11 179.58 3 0.83 5 3.07 9 7.00 5
UBI 0.78 7 150.40 4 0.4 7 6.88 6 6.00 4
IDBI 0.79 6 248.73 1 -0.93 11 -6.49 11 7.25 6
BOI 0.73 9 194.20 2 -0.14 10 -2.21 10 7.75 7
Indusind 0.92 2 77.93 11 0.99 4 16.55 2 4.75 3
Table 15: Interest Income To Total Income Table 16: Operating Profit To Total Assets
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
SBI 0.83 0.81 0.81 0.77 0.81 5 SBI 1.91 2.1 1.96 2.01 2.00 6
HDFC 0.84 0.84 0.85 0.85 0.85 4 HDFC 3.22 3.22 3.21 3.21 3.22 3
ICICI 0.81 0.8 0.77 0.74 0.78 7 ICICI 2.93 3.18 3.49 3.55 3.29 1
PNB 0.9 0.89 0.88 0.84 0.88 3 PNB 2.21 2.07 1.78 2.1 2.04 5
AXIS 0.81 0.81 0.81 0.79 0.81 5 AXIS 3.17 3.17 3.22 3.08 3.16 4
Canara 0.91 0.91 0.9 0.85 0.89 2 Canara 1.5 1.34 1.3 1.57 1.43 10
BOB 0.9 0.91 0.9 0.86 0.89 2 BOB 1.54 1.44 1.27 1.61 1.47 9
UBI 0.91 0.9 0.9 0.87 0.90 1 UBI 1.57 1.58 1.44 1.73 1.58 7
IDBI 0.9 0.88 0.89 0.88 0.89 2 IDBI 1.74 1.67 1.47 1.24 1.53 8
BOI 0.9 0.91 0.92 0.85 0.90 1 BOI 1.64 1.26 0.98 1.57 1.36 11
Indusind 0.81 0.8 0.78 0.78 0.79 6 Indusind 3.24 3.12 3.25 3.39 3.25 2
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Table 17 :Net Interest Margin To Total Assets Table 18: Return on Assets
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
SBI 2.93 2.86 2.6 2.44 2.71 5 SBI 0.65 0.68 0.46 0.41 0.55 5
HDFC 4.14 4.14 4.15 4.13 4.14 1 HDFC 2 2.02 1.89 1.88 1.95 1
ICICI 2.91 3.07 3.11 2.91 3.00Table 419 :Composite
ICICI Earning
1.78 Quality
1.86 1.49 1.35 1.62 3
PNB 3.14 2.87 2.41 2.16 2.65 6 PNB 0.64 0.53 -0.61 0.19 0.19 7
AXIS 3.3 3.37Income
Interest 3.36to 3.17Operating
3.30 Profit
3 to AXIS
Net Interest1.78
Margin1.83 1.72 on0.65
Return Asset 1.5 4
BANK
Canara 1.98 Total
1.86Income
1.77 1.74 Total
1.84 Assets
10 to Total Assets
Canara 0.54 0.55 -0.52Ratio0.2 0.19 Group
7 Rank
BOB Ratio 1.92
1.98 Rank
1.84 Ratio 1.93
1.98 Rank
9 Ratio
BOB Rank 0.49 Ratio
0.75 -0.78 Rank 0.17AVG 8
0.2 Rank
SBIUBI 2.37 0.81
2.3 2.11 5 2.08 2.00
2.22 7 6 UBI2.71 0.52 5
0.49 0.55
0.35 0.13 50.37 5.25
6 5
HDFC
IDBI 1.85 0.85
1.68 1.66 4 1.56 3.22
1.69 11 3 IDBI4.14 0.41 1
0.29 1.95
-1.09 -1.37 1
-0.44 2.25
9 1
ICICI
BOI 2.11 0.78
1.91 1.91 7 1.91 3.29
1.96 8 1 BOI3.00 0.51 4
0.27 1.62
0.94 -0.24 30.37 3.75
6 3
PNB
Indusind 3.61 0.88
3.44 3.55 3 3.77 2.04
3.59 2 5 2.65
Indusind 1.81 61.9 0.19
1.91 1.86 71.87 5.25
2 5
AXIS 0.81 5 3.16 4 3.30 3 1.5 4 4.00 4
Canara 0.89 2 1.43 10 1.84 10 0.19 7 7.25 8
BOB 0.89 2 1.47 9 1.93 9 0.17 8 7.00 7
UBI 0.90 1 1.58 7 2.22 7 0.37 6 5.25 5
IDBI 0.89 2 1.53 8 1.69 11 -0.44 9 7.50 9
BOI 0.90 1 1.36 11 1.96 8 0.37 6 6.50 6
Indusind 0.79 6 3.25 2 3.59 2 1.87 2 3.00 2
26 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Table 20: Liquid Assets to Total Assets Table 21 :Liquid Assets to Demand Deposits
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
SBI 0.07 0.077 0.069 0.079 0.07 6 SBI 1.19 1.36 1.2 1.45 1.30 5
HDFC 0.64 0.49 0.44 0.42 0.50
HDFC
Table 0.081 0.062 0.055 0.057
22: Liquid 0.06
Assets to Total Deposits 7
Table 23 :Approved Securities to Total Assets11
ICICI 0.07 0.065 0.083 0.098 0.08 5 ICICI 0.96 0.85 1.02 1.01 0.96 7
PNB 0.082 0.092 0.108 0.123 0.10 3 PNB 1.44 1.69 2.03 1.93 1.77 4
BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK BANK 2014 2015 2016 2017 AVG RANK
AXIS 0.074 0.078 0.063 0.084 0.07 6 AXIS 0.58 0.64 0.52 0.58 0.58 10
SBI 0.091 0.102 0.091 0.105 0.10 6 SBI 0.186 0.196 0.185 0.231 0.20 2
Canara 0.091 0.089 0.103 0.101 0.10 3 Canara 2.53 2.45 2.86 2.61 2.61 3
HDFC 0.108 0.081 0.071 0.076 0.08 7 HDFC 0.193 0.204 0.177 0.188 0.19 3
BOB 0.198 0.207 0.199 0.217 0.21 1 BOB 2.61 2.81 3.87 3.54 3.21 2
ICICI 0.125 0.117 0.142 0.155 0.13 3 ICICI 0.161 0.166 0.157 0.146 0.16 6
UBI 0.065 0.059 0.072 0.073 0.07 6 UBI 1.02 1.06 0.98 1.25 1.08 6
PNB 0.1 0.113 0.135 0.142 0.12 4 PNB 0.204 0.202 0.185 0.205 0.20 2
IDBI 0.051 0.041 0.044 0.09 0.06 7 IDBI 0.68 0.48 0.57 0.96 0.67 9
AXIS 0.101 0.112 0.093 0.121 0.11 5 AXIS 0.182 0.178 0.166 0.155 0.17 5
BOI 0.107 0.123 0.163 0.153 0.14 2 BOI 2.84 3.56 4.22 3.38 3.50 1
Canara 0.107 0.103 0.118 0.119 0.11 5 Canara 0.219 0.229 0.23 0.233 0.23 1
Indusind 0.078 0.099 0.072 0.104 0.09 4 Indusind 0.69 0.87 0.65 0.95 0.79 8
BOB 0.23 0.24 0.233 0.25 0.24 1 BOB 0.147 0.138 0.154 0.164 0.15 7
UBI 0.078 0.071 0.085 0.087 0.08 7 UBI 0.197 0.193 0.179 0.197 0.19 3
IDBI 0.072 0.056 0.061 0.122 0.08 7 IDBI 0.204 0.235 0.233 0.232 0.23 1
BOI 0.129 0.144 0.193 0.178 0.16 2 BOI 0.175 0.17 0.176 0.181 0.18 4
Indusind 0.112 0.145 0.109 0.147 0.13 3 Indusind 0.177 0.164 0.18 0.176 0.17 5
27 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor:
Table 24 : Composite Liquidity
Liquid Assets to Liquid Assets to Liquid Assets to Approved Securities to
BANK Group Rank
Total Assets Demand Deposits Total Deposits Total Assets
Ratio Rank Ratio Rank Ratio Rank Ratio Rank AVG Rank
SBI 0.07 6 1.30 5 0.10 6 0.20 2 4.75 5
HDFC 0.06 7 0.50 11 0.08 7 0.19 3 7.00 11
ICICI 0.08 5 0.96 7 0.13 3 0.16 6 5.25 7
PNB 0.10 3 1.77 4 0.12 4 0.20 2 3.25 4
AXIS 0.07 6 0.58 10 0.11 5 0.17 5 6.50 10
Canara 0.10 3 2.61 3 0.11 5 0.23 1 3.00 3
BOB 0.21 1 3.21 2 0.24 1 0.15 7 2.75 2
UBI 0.07 6 1.08 6 0.08 7 0.19 3 5.50 8
IDBI 0.06 7 0.67 9 0.08 7 0.23 1 6.00 9
BOI 0.14 2 3.50 1 0.16 2 0.18 4 2.25 1
Indusind 0.09 4 0.79 8 0.13 3 0.17 5 5.00 6
Table 25: Composite Ranking (Overall Performance) of Selected Public and Selected Private Sector
Banks
BANK C A M E L Average Rank
SBI 5.25 4.67 6.00 5.25 4.75 5.18 5
HDFC 3.50 2.00 4.25 2.25 7.00 3.80 2
ICICI 4.00 4.00 4.25 3.75 5.25 4.25 3
PNB 5.50 7.33 7.75 5.25 3.25 5.82 8
AXIS 4.75 3.33 3.25 4.00 6.50 4.37 4
Canara 6.00 6.00 7.75 7.25 3.00 6.00 10
BOB 6.00 3.67 7.00 7.00 2.75 5.28 6
UBI 6.75 5.67 6.00 5.25 5.50 5.83 9
IDBI 6.00 8.33 7.25 7.50 6.00 7.02 11
BOI 6.50 6.00 7.75 6.50 2.25 5.80 7
Indusind 3.50 2.00 4.75 3.00 5.00 3.65 1
27 International journal of Management, IT and
Engineering
You might also like
- T R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)From EverandT R A N S F O R M A T I O N: THREE DECADES OF INDIA’S FINANCIAL AND BANKING SECTOR REFORMS (1991–2021)No ratings yet
- Camel Analysis India RankingDocument15 pagesCamel Analysis India RankingAmnaNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On Financial Performance of Public Sector Banks in India: An Analysis On Camel ModelDocument17 pagesA Comparative Study On Financial Performance of Public Sector Banks in India: An Analysis On Camel ModelkishoremeghaniNo ratings yet
- SYBBA Finance ProjectDocument10 pagesSYBBA Finance ProjectJanki PatilNo ratings yet
- CAMEL Model ReportDocument9 pagesCAMEL Model ReportAbdul Razzak100% (1)
- An Analysis of The Performance of Select Public Sector Banks Using Camel ApproachDocument17 pagesAn Analysis of The Performance of Select Public Sector Banks Using Camel Approachmithunraj packiyanathanNo ratings yet
- Measuring Efficiency in Indian Commercial Banks With DEA and Tobit RegressionDocument6 pagesMeasuring Efficiency in Indian Commercial Banks With DEA and Tobit RegressioncharanNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance of Axis Bank and Kotak Mahindra Bank in The Post Reform Era Analysis On CAMEL ModelDocument34 pagesFinancial Performance of Axis Bank and Kotak Mahindra Bank in The Post Reform Era Analysis On CAMEL ModelIjbemrJournalNo ratings yet
- A CAMEL MODEL ANALYSIS OF PUBLIC & PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS IN INDIACamels Rating PDFDocument23 pagesA CAMEL MODEL ANALYSIS OF PUBLIC & PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS IN INDIACamels Rating PDFsambhu_n100% (1)
- Camel Model in Banking Sector: Mathiraj - Sp@yahoo - Co.inDocument21 pagesCamel Model in Banking Sector: Mathiraj - Sp@yahoo - Co.inGokulapriyan ANo ratings yet
- Camel Model in Banking Sector: Mathiraj - Sp@yahoo - Co.inDocument21 pagesCamel Model in Banking Sector: Mathiraj - Sp@yahoo - Co.inRujuta KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis Using Camel Model-A Study of Select Private BanksDocument10 pagesPerformance Analysis Using Camel Model-A Study of Select Private BanksLIKHITHA RNo ratings yet
- 12 Chapter 2 - Review of LiteratureDocument49 pages12 Chapter 2 - Review of LiteratureSagar TiwariNo ratings yet
- A Study of Financial Performance Evaluation of Banks in IndiaDocument11 pagesA Study of Financial Performance Evaluation of Banks in IndiaRaghav AryaNo ratings yet
- Earning Quality of Scheduled Commercial Banks in India: Bank-Wise and Sector-Wise AnalysisDocument26 pagesEarning Quality of Scheduled Commercial Banks in India: Bank-Wise and Sector-Wise AnalysisPavithra GowthamNo ratings yet
- Performance of Sbi and Associate BanksDocument11 pagesPerformance of Sbi and Associate BanksAnjum Ansh KhanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Performance Evaluation of Private Sector Banks Pre Covid Crisis 1528 2635 25 5 761 PDFDocument11 pagesA Study On Performance Evaluation of Private Sector Banks Pre Covid Crisis 1528 2635 25 5 761 PDFAbirami ThevarNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance Analysis of PrivatDocument11 pagesFinancial Performance Analysis of Privatprteek kumarNo ratings yet
- Camel ModelDocument8 pagesCamel ModelRabinNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Financial Permormance of State Bank of India and ICICI BankDocument10 pagesA Comparative Study of Financial Permormance of State Bank of India and ICICI Bankprteek kumarNo ratings yet
- 07 Evaluating The Financial Soundness of Indian - Anita Makkar - FINC025Document15 pages07 Evaluating The Financial Soundness of Indian - Anita Makkar - FINC025shresth_801464No ratings yet
- Synopsys Report CAMEL-MODEL-ANALYSIS-OF-PUBLIC-PRIVATE-SECTOR-BANKS-IN-INDIACamels-rating PDFDocument23 pagesSynopsys Report CAMEL-MODEL-ANALYSIS-OF-PUBLIC-PRIVATE-SECTOR-BANKS-IN-INDIACamels-rating PDFsalmanNo ratings yet
- Vijay Hemant Sonaje and Dr. Shriram S. NerlekarDocument8 pagesVijay Hemant Sonaje and Dr. Shriram S. NerlekarsugeethaNo ratings yet
- Ijm 11 12 179Document11 pagesIjm 11 12 179Vinayak PadaveNo ratings yet
- SUSMITHADocument30 pagesSUSMITHAmithu mithuNo ratings yet
- 2dharmendra S Mistry - Pdfa Comparative Study of The Profitability Performance in TheDocument15 pages2dharmendra S Mistry - Pdfa Comparative Study of The Profitability Performance in ThePsubbu RajNo ratings yet
- Review of LiteratureDocument24 pagesReview of LiteratureShveta VatasNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Public Sector Banks PerfoDocument14 pagesAn Analysis of Public Sector Banks PerfoMurali Balaji M CNo ratings yet
- A Synopsis On PEoBDocument8 pagesA Synopsis On PEoBAsit kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Financial Performance of Canara Bank and Union Bank of India Dr. Veena K.P. Ms. Pragathi K.MDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study of Financial Performance of Canara Bank and Union Bank of India Dr. Veena K.P. Ms. Pragathi K.MMane DaralNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Financial Performance of Canara Bank and Union Bank of IndiaDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study of Financial Performance of Canara Bank and Union Bank of IndiaarcherselevatorsNo ratings yet
- Vol 1 Issue 1 Art 1Document17 pagesVol 1 Issue 1 Art 1Sabana AsmiNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Financial Performance of Canara Bank and Union Bank of India PDFDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study of Financial Performance of Canara Bank and Union Bank of India PDFPravin RnsNo ratings yet
- IJRAR19H1137Document10 pagesIJRAR19H1137Psubbu RajNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance of State Bank of India and Icici Bank - A Comparative StudyDocument9 pagesFinancial Performance of State Bank of India and Icici Bank - A Comparative StudyMrinali MahajanNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance Analysis of Syndicate Bank Using Camel ModelDocument11 pagesFinancial Performance Analysis of Syndicate Bank Using Camel ModelGokulapriyan ANo ratings yet
- Camel ModelDocument3 pagesCamel ModelGokulapriyan ANo ratings yet
- CAMELSFINALPAPERSAMAROH2018Document35 pagesCAMELSFINALPAPERSAMAROH2018VIGNESHSANNo ratings yet
- 1532 PDFDocument9 pages1532 PDFChandrashekhar GurnuleNo ratings yet
- India Paper CamelDocument16 pagesIndia Paper Camelmuhammad nawazNo ratings yet
- Bank Performance Analysis Through CAMEL ModelDocument3 pagesBank Performance Analysis Through CAMEL Modeldbkbk902No ratings yet
- November 2016 1478613409 68 PDFDocument4 pagesNovember 2016 1478613409 68 PDFBajrangNo ratings yet
- Ajrbf:: Performance Evaluation of Scheduled Commercial Banks in India-A Comparative StudyDocument21 pagesAjrbf:: Performance Evaluation of Scheduled Commercial Banks in India-A Comparative StudyManvi JainNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Performances of Select Nationalized Banks Using Camel ApproachDocument15 pagesEvaluating The Performances of Select Nationalized Banks Using Camel Approachharshita khadayteNo ratings yet
- Synopsys On Camel Model of Public & Private SectorDocument13 pagesSynopsys On Camel Model of Public & Private SectorsalmanNo ratings yet
- Title:-To Study The Financial Performance of HDFC Bank, Sbi Bank &Document5 pagesTitle:-To Study The Financial Performance of HDFC Bank, Sbi Bank &dhanesh bhandariNo ratings yet
- Title:-To Study The Financial Performance of HDFC Bank, Sbi Bank &Document5 pagesTitle:-To Study The Financial Performance of HDFC Bank, Sbi Bank &Divya BhandariNo ratings yet
- Bank 1 PDFDocument13 pagesBank 1 PDFallauddin nadafNo ratings yet
- Harish eDocument9 pagesHarish eTamil SelvamNo ratings yet
- Asian Journal of AccountingDocument24 pagesAsian Journal of AccountingDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- IJMSS2273Jan31 PDFDocument12 pagesIJMSS2273Jan31 PDFdsfgNo ratings yet
- A Study On Performance of Private Sector Banks in IndiaDocument13 pagesA Study On Performance of Private Sector Banks in IndiaPARAMASIVAN CHELLIAHNo ratings yet
- JETIR2302448Document7 pagesJETIR2302448Rupak RoyNo ratings yet
- CAMELS AnalysisDocument13 pagesCAMELS AnalysisChetan DedhiaNo ratings yet
- Camels Model AnalysisDocument11 pagesCamels Model AnalysisAlbert SmithNo ratings yet
- Synopsis GlobalisationDocument11 pagesSynopsis GlobalisationSumit Aggarwal100% (1)
- An Analysis of Indian Public Sector Banks Using Camel ApproachDocument9 pagesAn Analysis of Indian Public Sector Banks Using Camel ApproachAratiPatelNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study On Financial Performance of Public, Private and Foreign Banks in IndiaDocument21 pagesA Comparative Study On Financial Performance of Public, Private and Foreign Banks in IndiaMINESHNo ratings yet
- A Study On Performance of Private Sector Banks in IndiaDocument14 pagesA Study On Performance of Private Sector Banks in IndiaRekha ShawNo ratings yet
- Financial Risk Management (PROJECT)Document72 pagesFinancial Risk Management (PROJECT)Vinayak Halapeti100% (2)
- Nepsealpha Export Price OHL 2023-10-06 2023-10-26Document1 pageNepsealpha Export Price OHL 2023-10-06 2023-10-26Manita KunwarNo ratings yet
- Nepsealpha Export Price NABIL 2020-10-06 2023-10-26Document15 pagesNepsealpha Export Price NABIL 2020-10-06 2023-10-26Manita KunwarNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument8 pagesCapital BudgetingManita KunwarNo ratings yet
- Internationalization Project - Nepalese Sustainable Tea - Coffee in EuropeDocument2 pagesInternationalization Project - Nepalese Sustainable Tea - Coffee in EuropeManita KunwarNo ratings yet
- Business Development Strategy For Specialty CoffeeDocument11 pagesBusiness Development Strategy For Specialty CoffeeManita KunwarNo ratings yet
- Final Simulation HRDocument39 pagesFinal Simulation HRManita KunwarNo ratings yet
- Pricing Strategy For ItalyDocument5 pagesPricing Strategy For ItalyManita KunwarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Finance Corporation of IndiaDocument2 pagesIndustrial Finance Corporation of IndiaShruti Goyal100% (1)
- BRS Tax and InstDocument25 pagesBRS Tax and InstNivedhitha BalajiNo ratings yet
- Analisis Rasio Keuangan - PT Blue BirdDocument8 pagesAnalisis Rasio Keuangan - PT Blue BirdAzis HailyNo ratings yet
- Samplar Company Statement of Financial Position December 31, 2016 Assets Liabilities and EquityDocument6 pagesSamplar Company Statement of Financial Position December 31, 2016 Assets Liabilities and EquityStar RamirezNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips Problems and SolutionsDocument14 pagesSilo - Tips Problems and SolutionsSasi chNo ratings yet
- Networth Certificate: Sl. No. Source of Funds Indian Currency (INR) Foreign Currency (CAD) ReferenceDocument3 pagesNetworth Certificate: Sl. No. Source of Funds Indian Currency (INR) Foreign Currency (CAD) Referencesamraju1No ratings yet
- ACCT 5103 OL Sample Final ExamDocument7 pagesACCT 5103 OL Sample Final ExamEsther MpyisiNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document4 pagesCH 01Rabie Haroun50% (2)
- Cibil - Report (P - SANJEEV KAMAL - 12 - 05 - 2023 14 - 49 - 45)Document7 pagesCibil - Report (P - SANJEEV KAMAL - 12 - 05 - 2023 14 - 49 - 45)Miss PallaviNo ratings yet
- Accounting Equation ExercisesDocument2 pagesAccounting Equation ExercisesBert Rainier OpimoNo ratings yet
- DMGT512 Financial Institutions and ServicesDocument264 pagesDMGT512 Financial Institutions and Serviceskrisari9No ratings yet
- Uwa SopDocument1 pageUwa SopMonjurul HassanNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 2 - Financial Statements & Illustrative ProblemDocument6 pagesLecture No. 2 - Financial Statements & Illustrative ProblemJA LAYUG100% (1)
- School of Business & Management: Course Outline & Accompanying Teaching & Learning PlanDocument6 pagesSchool of Business & Management: Course Outline & Accompanying Teaching & Learning PlanGurmanjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Date Topics Activities or TasksDocument22 pagesLesson 1: Date Topics Activities or TasksKeeshia Mae Nashra ApilitNo ratings yet
- Kuawaiti CMA GlossaryDocument52 pagesKuawaiti CMA Glossaryammokhtar100No ratings yet
- Vikas CVDocument2 pagesVikas CVlegalitis.inNo ratings yet
- Laporan Keuangan Muhammad RiskiDocument10 pagesLaporan Keuangan Muhammad RiskiRizkyNo ratings yet
- Chapters Index Page No1111-1Document58 pagesChapters Index Page No1111-1Sangeeta S SoppimathNo ratings yet
- Crisl Rating Prime Bank LTD 2 PDFDocument1 pageCrisl Rating Prime Bank LTD 2 PDFgastro8606342No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Mechanics of Futures MarketsDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 2 Mechanics of Futures MarketsAishwarya RajeshNo ratings yet
- OSX FinancialAccounting ISM Ch12Document40 pagesOSX FinancialAccounting ISM Ch12eynullabeyliseymurNo ratings yet
- NF Company IncorporationDocument29 pagesNF Company Incorporationpirater.ak.47No ratings yet
- Value Added Subscription PlansDocument1 pageValue Added Subscription PlansChetna SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 09Document17 pagesCH 09AA BB MMNo ratings yet
- Indiana Loan Broker AgreementDocument2 pagesIndiana Loan Broker AgreementalokprasadNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Top of FormDocument96 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Top of Formchanfa3851No ratings yet
- Cost Accounting System: TopicDocument2 pagesCost Accounting System: Topicsamartha umbareNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2022 2023 258 264 1 2Document2 pagesAnnual Report 2022 2023 258 264 1 2jagu6143No ratings yet
- Cash Management:: Revenue DepositsDocument26 pagesCash Management:: Revenue DepositsMomel FatimaNo ratings yet