Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mahendra Engineering College: Lecture Handouts
Uploaded by
hari vigneshOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mahendra Engineering College: Lecture Handouts
Uploaded by
hari vigneshCopyright:
Available Formats
L-01
MAHENDRA ENGINEERING COLLEGE
MAHENDHIRAPURI, MALLASAMUDRAM - 637503
Dept: ECE Semester/Year: IV/II
Lecture Handouts
Subject Name : ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION
Staff Name : M.Sweetline Sonia
Unit :I ANALOG COMMUNICATION
Topic of Lecture: Introduction to Communication System
Introduction :
Communication – Basic process of exchanging information from one location (source) to
destination (receiving end). The science of communication involving long distances is called
telecommunication. (Tele stands for long Distance)
Prerequisite knowledge for Complete learning of Topic:
Human communication model (Sender, Medium(Channel) and Receiver)
Signal parameter (Wavelength, Amplitude, Frequency & Phase Angle)
Functions of basic electronic system ( Transmitter, Channel and Receiver)
Detailed content of the Lecture:
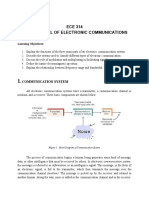
1.0 Introduction to Communication System:
Two of the main barriers in human communications are distances and languages
Fig. (1.1) Human Communication Model Fig. (1.2) Barriers of Human Communication
The distance problem is solved by means of Tele communication (Long distance
communication using Electronics systems)
The two basic types of communications systems are analog and digital.
Analog systems, both the information and the carrier are analog signals.
In digital, the digital pulses are transferred between two or more points in a
communication system.
1.1 General Communication System:
The basic communication components are
A transmitter,
A communication channel or medium. and
A receiver
Fig. (1.3) General Communication System
Fig. (1.4) General Electronic Wireless Communication System
Information Source:
The information signal can be analog or digital.
The original source information can be in analog form, such as the human voice, or
music, or in digital form, such as binary coded numbers of alphanumeric codes.
Transmitter:
A transmitter is a collection of electronic components and circuits designed to convert
the information into a signal suitable for transmission over c given communications
medium.
In addition to that it increases the power level of the signal. The power level should be
increased in order cover a wide range'
Communication Channel:
The communication channel is the medium by which the electrical signal is sent from
one place to another.
Depending on the type of communication channel, two types of communication systems
will exist.
Wire Communication or Line Communication:
The line communication systems use the communication medium like the simple wires
or cables or optical fibers. Here message transmission capability is also limited.
Wireless Communication or Radio Communication:
In wireless communication, the information signal is transmitted through free space by
electromagnetic waves called radio waves.
Radio waves are radiated from the transmitter in open space through a device called
antenna. Example radio or TV broadcasting, satellite communication
Wireless communication is mostly used for long distant communication as well as wide
coverage area.
Receiver:
The main functions of the receiver are,
(i) Receive the message signal from the channel and
(ii) Reproduce the message signal from the distorted signal which is received from channel.
Noise and Distortion:
Noise is random, undesirable electric energy that enters the communication system via
the communication medium and interferes with the transmitted message.
Distortion is the process of changing shape of the communicating signal that may
mislead message signal instead of reaching the destination.
Drawbacks of Base band Transmission (Without Modulation)
Excessively large antenna heights, Signals get mixed up, Short range of communication.
Multiplexing is not possible and poor quality of reception.
The above drawbacks can be overcome by means of modulation techniques.
1.2 Modulation:
Why Modulation?
In radio communication signals from various sources are transmitted through the free
space.
This causes interference among various signals, and useful message is received by the
receiver.
The problem of interference is solved by translating the message signals to different radio
frequency spectrum. This done by the transmitter by a process known as modulation.
Modulation
Modulation is a fundamental requisite for communication to achieve long distance
communication.
Modulation may be defined as the process by which some parameter of high frequency
signal termed as carrier, is varied in accordance with the information (modulating or
baseband) signal.
The carrier is supposed to carry the information from transmitter to receiver.
The term baseband designates the band of frequencies representing the signal supplied
by the source of information.
Demodulation or Detection:
The process of extracting a modulating signal from the modulated signal is called
demodulation or detection
Need Of Modulation (Or) Advantages Of Modulation
The advantages of modulation are,
Easy of radiation, Adjustment of bandwidth, Reduction in height of antenna,
Avoids mixing of signals, Increases the range of communication, Multiplexing, and
Improves quality of reception
Video Content / Details of website for further learning :
1) https://youtu.be/TPm0XSPxld8
2) https://youtu.be/qy97FIbtwxU
Important Books/Journals for further learning including the page nos.:
1) Electronic and Communication Systems, Kennedy-Davis, Tata McGraw-Hill, Fourth Edition -
2008 (Page No: 1 To 5)
2) Communication Systems-I, J. S. Chitode, Technical Publication, Third Revised Edition – 2004
(Page No: 1 To 9)
Subject Teacher Verified by HOD
You might also like
- Eec 128Document23 pagesEec 128Adetayo Salawu67% (3)
- Chfiv9 Study Guide: Locard's Exchange Principle Takes Something Leaves SomethingDocument48 pagesChfiv9 Study Guide: Locard's Exchange Principle Takes Something Leaves SomethingSonu SharmaNo ratings yet
- EEC 128 TheoryDocument73 pagesEEC 128 TheoryHuu Uu100% (1)
- Telecom-Chapter OneDocument7 pagesTelecom-Chapter Onetsegab bekele100% (2)
- EEC 238 244 - Telecommunication Engineering II - For ND IIDocument62 pagesEEC 238 244 - Telecommunication Engineering II - For ND IIErnie EnokelaNo ratings yet
- 1st ChapterDocument15 pages1st ChapterMd Raton AliNo ratings yet
- EC8394 Analog and Digital Communication TechniquesDocument18 pagesEC8394 Analog and Digital Communication TechniquesEzhil Azhahi.AM Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- 0 - IntroductionDocument24 pages0 - IntroductionOmar AlzayatNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument51 pagesCommunication SystemsKinza MallickNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument123 pagesIntroduction To Communication SystemMichael Tesfaye100% (1)
- What-is-a-Communication-SystemDocument5 pagesWhat-is-a-Communication-Systemdanicadenisemalobo794No ratings yet
- Analog Communications-1Document20 pagesAnalog Communications-1v c sekhar gollaNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication (Ec-405) Unit-1Document57 pagesAnalog Communication (Ec-405) Unit-1Kritika SoniNo ratings yet
- Unit-I 17.07Document41 pagesUnit-I 17.07radhika.22210203No ratings yet
- SECA1303Document250 pagesSECA1303rqfkypprjtNo ratings yet
- A1!04!502E - Sto. Tomas, ShairaDocument4 pagesA1!04!502E - Sto. Tomas, ShairaSTO. TOMAS SHAIRA FRESCONo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communication SystemDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Communication Systemmohd_anip9774No ratings yet
- Communication Engineering Unit 1 Lecture 1Document22 pagesCommunication Engineering Unit 1 Lecture 1Deepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Basic Elements of Communication SystemDocument4 pagesBasic Elements of Communication SystemArunangshu PalNo ratings yet
- An electronic communications systemDocument22 pagesAn electronic communications systemZinan KakkodanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Basics of Communication SystemsDocument7 pagesLesson 1 - Basics of Communication SystemsLee Heng YewNo ratings yet
- Basics of Communication SystemsDocument14 pagesBasics of Communication Systemsmarxx100% (1)
- Block Diagram of Communication System With DetaileDocument5 pagesBlock Diagram of Communication System With Detaileravikumar rayalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 CommunicationsystemDocument33 pagesChapter5 CommunicationsystemRutvik BarbhaiNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 ITDocument154 pagesUnit-1 ITShashwat urmaliyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.0Document35 pagesChapter One 1.0Arazim Olorundare SheuNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationsDocument105 pagesAnalog CommunicationsSachin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1kedirNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument11 pagesCommunication Systems I: Department of Electrical EngineeringAyad A. ABDULKAFINo ratings yet
- Unit Vi - Communication Systems: Elements of Communication SystemDocument18 pagesUnit Vi - Communication Systems: Elements of Communication Systemsaras_indiaNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Dcs - Fall 2012 (M.SC)Document60 pagesLec 1 Dcs - Fall 2012 (M.SC)Basir UsmanNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument9 pagesCommunication Systemsmaria.rehmanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Electronic CommunicationDocument17 pagesFundamental of Electronic CommunicationLysa DeeNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Introd 2015Document19 pagesChap1 Introd 2015semakulaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Comms Sys Using SignalsDocument29 pagesElectronic Comms Sys Using SignalsZinan KakkodanNo ratings yet
- Ec8395 Ce Notes 1Document127 pagesEc8395 Ce Notes 1makNo ratings yet
- Data Comm and Comp Networking Lecture NoteDocument35 pagesData Comm and Comp Networking Lecture NoteMikiyas GetasewNo ratings yet
- DEE 072 Telecommunication Notes FinalDocument118 pagesDEE 072 Telecommunication Notes FinalFilbert Ombongi100% (1)
- LCP Lecture Note on Telecommunication EngineeringDocument49 pagesLCP Lecture Note on Telecommunication EngineeringOgidi FelixNo ratings yet
- Ec8395 Ce Notes 2Document127 pagesEc8395 Ce Notes 2makNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationsDocument117 pagesAnalog CommunicationsSusmitha SambaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Data Communication and Computer NetworkDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 5 Data Communication and Computer NetworkKinfe BeregaNo ratings yet
- Physics Communication System CoachingDocument9 pagesPhysics Communication System Coachingvishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- 1-2nd Year Electrical Comm.2023Document24 pages1-2nd Year Electrical Comm.2023MOSTAFA TEAIMANo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Unit2 VtuDocument76 pagesAnalog Communication Unit2 Vturaghudathesh100% (2)
- Elements of Optical Fibre Transmission LinksDocument7 pagesElements of Optical Fibre Transmission LinksSamir PaulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document16 pagesLecture 1marcelineparadzaiNo ratings yet
- CS6301 - Analog and Digital Communication (ADC) PDFDocument122 pagesCS6301 - Analog and Digital Communication (ADC) PDFparantnNo ratings yet
- ELXTE 312 Lesson 1 2021Document7 pagesELXTE 312 Lesson 1 2021Clea Marie Capacillo BatoonNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Notes Ch15 Communication SystemsDocument4 pages12 Physics Notes Ch15 Communication SystemsMayank Saini100% (1)
- Unit - I: Transmission of Signals in A Reliable and Efficient MatterDocument3 pagesUnit - I: Transmission of Signals in A Reliable and Efficient MatterPraveen SamadhiyaNo ratings yet
- Basic CommunicationDocument24 pagesBasic CommunicationSiam hasanNo ratings yet
- Effective CommunicationDocument2 pagesEffective CommunicationarmanNo ratings yet
- EC6501 - Digital Communications Lecture Notes Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument75 pagesEC6501 - Digital Communications Lecture Notes Chapter 1 IntroductionsangeetaNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Electronic CommunicationDocument56 pages1-Introduction To Electronic Communicationpraveen alwisNo ratings yet
- Analog Communications Dr Moh-1st TermDocument34 pagesAnalog Communications Dr Moh-1st Termalifadhil989898No ratings yet
- Intro To Communication SystemsDocument61 pagesIntro To Communication SystemsRemuel ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Communications SystemsDocument6 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Communications SystemsIdris Jeffrey MangueraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital Communications SystemsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Digital Communications SystemsYsrael M. TatlonghariNo ratings yet
- Information TechnologyDocument11 pagesInformation Technologysana taseerNo ratings yet
- Mahendra Engineering College: III SemesterDocument2 pagesMahendra Engineering College: III Semesterhari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Maximum Power Transfer Theorem ProblemsDocument3 pagesMaximum Power Transfer Theorem Problemshari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Lecture Handouts: Topic of Lecture: Norton Theorem ProblemsDocument5 pagesLecture Handouts: Topic of Lecture: Norton Theorem Problemshari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Lecture HandoutsDocument2 pagesLecture Handoutshari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Norton theorem circuit analysisDocument2 pagesNorton theorem circuit analysishari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Lecture HandoutsDocument2 pagesLecture Handoutshari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Lecture HandoutsDocument2 pagesLecture Handoutshari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Lecture HandoutsDocument4 pagesLecture Handoutshari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Lecture Handouts: Unit: I Lecture No.: 2 Date of LectureDocument2 pagesLecture Handouts: Unit: I Lecture No.: 2 Date of Lecturehari vigneshNo ratings yet
- Network Theorems Lecture HandoutDocument3 pagesNetwork Theorems Lecture Handouthari vigneshNo ratings yet
- New Examzoon Cisco-300-320 Dumps - Designing Cisco Network Service ArchitecturesDocument7 pagesNew Examzoon Cisco-300-320 Dumps - Designing Cisco Network Service ArchitecturesRyan V. NicholsonNo ratings yet
- Tempest AND Echelon: BY - Y.SruthiDocument19 pagesTempest AND Echelon: BY - Y.SruthiSruthi Yaram ReddyNo ratings yet
- How To Create Infographics in PowerPoint by HubSpotDocument10 pagesHow To Create Infographics in PowerPoint by HubSpotAkshay SetlurNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Systems Exam PaperDocument4 pagesMultimedia Systems Exam PaperwirdinaNo ratings yet
- ARS 3.1 Publication PDFDocument457 pagesARS 3.1 Publication PDFharry otterNo ratings yet
- Automation in Manufacturing: An IntroductionDocument3 pagesAutomation in Manufacturing: An Introductionhemal4379No ratings yet
- PIC Microcontroller Instruction SetDocument2 pagesPIC Microcontroller Instruction SetMuthamizh SelvanNo ratings yet
- Wake Up App Helps Tired CommutersDocument1 pageWake Up App Helps Tired CommutersZidan Gema RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structure by Ramamrutham PDFDocument1 pageDesign of Steel Structure by Ramamrutham PDFGhanshyam SahNo ratings yet
- Database Systems Concepts and Architecture: Dr. Yousry TahaDocument26 pagesDatabase Systems Concepts and Architecture: Dr. Yousry TahammcNo ratings yet
- Tech-Based Art QuarterlyDocument5 pagesTech-Based Art QuarterlyCaryl PenarubiaNo ratings yet
- PMP450x ReleaseNotes16.1.1.1Document35 pagesPMP450x ReleaseNotes16.1.1.1john villamilNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Purpose of This DocumentDocument6 pages1.1 Purpose of This DocumentBABU ANo ratings yet
- 1576101746Document1,450 pages1576101746Juju RaganNo ratings yet
- Custom PC - January 2017 PDFDocument116 pagesCustom PC - January 2017 PDFch miriNo ratings yet
- Load Runner Q&aDocument12 pagesLoad Runner Q&asumanyvNo ratings yet
- Final Exam CAAL 2020Document3 pagesFinal Exam CAAL 2020hassanNo ratings yet
- Customer Relationship ManagementDocument27 pagesCustomer Relationship Managementvidu12No ratings yet
- Opening and retrieving info for VMDK fileDocument2 pagesOpening and retrieving info for VMDK fileacunachaNo ratings yet
- Tech Note 112 - Rebuild Corrupt InTouch ApplicationDocument7 pagesTech Note 112 - Rebuild Corrupt InTouch Applicationcorreochafa9699No ratings yet
- AIDC Technologies Optimize Supply Chain OperationsDocument4 pagesAIDC Technologies Optimize Supply Chain OperationsShiba Narayan SahuNo ratings yet
- Byodletter 2019Document1 pageByodletter 2019api-466998220No ratings yet
- PMO - Create A PMO HandbookDocument12 pagesPMO - Create A PMO HandbookTariq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital TransformationDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Digital TransformationvrjgopiNo ratings yet
- We Ka ManualDocument327 pagesWe Ka Manualjavier_scribdNo ratings yet
- The Great AwkDocument3 pagesThe Great AwkharijiNo ratings yet
- Binary Cloning in Oracle 12cDocument3 pagesBinary Cloning in Oracle 12cLiloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Lists: 1.1 The List Data TypeDocument35 pagesChapter 1: Lists: 1.1 The List Data TypeAjay Patel K ANo ratings yet
- User Manual MgnregaDocument223 pagesUser Manual MgnregaJulfukar KhanNo ratings yet