Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LIPID - Duoc Lieu
Uploaded by
34Trần Thị Ái NhiD190 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
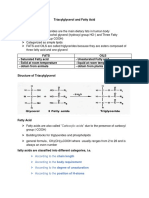
34 views6 pagesLipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that include fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols. They are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water, and soluble in organic solvents like hexane. Fatty acids are the main constituents of fats and oils and contain long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid group at one end. Triglycerides are the main form of lipid storage and are composed of three fatty acid chains linked to a glycerol molecule. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes and contain a phosphate-containing polar head and two fatty acid tails.
Original Description:
Original Title
LIPID- Duoc Lieu
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that include fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols. They are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water, and soluble in organic solvents like hexane. Fatty acids are the main constituents of fats and oils and contain long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid group at one end. Triglycerides are the main form of lipid storage and are composed of three fatty acid chains linked to a glycerol molecule. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes and contain a phosphate-containing polar head and two fatty acid tails.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views6 pagesLIPID - Duoc Lieu
Uploaded by
34Trần Thị Ái NhiD19Lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that include fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols. They are hydrophobic, or insoluble in water, and soluble in organic solvents like hexane. Fatty acids are the main constituents of fats and oils and contain long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid group at one end. Triglycerides are the main form of lipid storage and are composed of three fatty acid chains linked to a glycerol molecule. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes and contain a phosphate-containing polar head and two fatty acid tails.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
LIPID
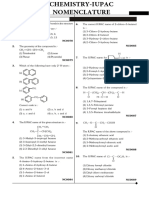
1. Biological fatty acids, are composed of
A. One or more carbon atoms with nitrogen atom in the ring
B. A hydrocarbon chain with one terminal carboxyl group
C. A carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atom, usually with a hydrogen-
oxygen atom ratio of 2:1
D. One or more sugars or a uronic acid with aglycon
2. Which is rancidity ( sự ôi thiu)
A. Condition produced by aerial oxidation of unsaturated fat,
marked by unpleasant odour or flavour
B. A macro biomolecule that is soluble in nonpolar solvents, such
as hydrocarbons, hexane, heptane..
C. The capacity to react with a strong base up to a given pH value,
determined by titration with NaOH up to the color change in
phenolphtalein ( pH 8-9)
D. The compounds easily evaporated at nomal temperatures and
aromatic odor
3. Fixed oil is soluble in
A. Dilute acid solution
B. Hexane
C. Hydro-alcoholic solution
D. Weak alkaline solution
4. Resins are soluble in
A. Organic solvents
B. Solvents with high polarity index
C. Mixture of water and chloroform
D. Solvens with highest dipole moment
5. Which chemical shifts ALWAYS present in 13C- NMR of fatty
acyls
A. 3-5 ppm
B. 74-76 ppm
C. 204-206 ppm
D. 173-174 ppm
6. Which is saturated fatty acid
A. Linoleic acid
B. Arachidonic acid
C. Palmitic acid
D. Oleic acid
7. Which is anteiso- fatty acyls
A. 11- Methyldodecanoic
B. 16- Methyheptadecanoic
C. 3- Methybutanoic
D. 8- Methyldecanoic
8. Octadecanoic acid is
A. Normal names
B. Trivial names
C. Numerical abbreviations
D. Systematic nomenclature (tên hệ thống)
9. Which are storage lipids
A. Glycerophospholipids
B. Saccharolipids
C. Triglycerols
D. Sphingolipids
10. Saturated fatty acids
A. Are linear chains of CH2 groups linked carbon- carbon single
bonds with one terminal carboxylic acid group
B. Are characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms
away from the terminal methyl group in their chemical structure
C. Are fatty acids in which at least one pair of double bonds is
separated by only one single bone
D. Have one or more carbon- carbon double bonds with two
terminal carboxylic acid groups
11. Which is definition of lipids for a long time
A. Crystals in three forms
B. Compounds from thioesters
C. Extracts in organic solvents
D. Substances isoprene- originated
12. Cocos nucifera belongs to
A. Asteraceace
B. Arecaceae family
C. Sapindaceae
D. Guttiferae
13. Which is common configuration of double bonds in
unsaturated fatty acid
A. Syn
B. E
C. Trans
D. Cis
14. Which is the property of Castor oil ( thầu dầu)
A. High hydroxyl value
B. Volatile
C. Solid in room temperature
D. Yellow color
15. Which component is found in all sphingolipids
A. A negative charge
B. A carbohydrate
C. An amino alcohol
D. A phosphate group
16. Higher plants rarely have fatty acyls with:
A. No double bonds
B. Cis configuration
C. At least six double bonds
D. More than three double bonds
17. Which is produced from Arachis hypogaea
A. Essential oil ( tinh dầu)
B. Aroma oil (dầu thơm)
C. Peanut oil ( dầu lạc)
D. Castor oil (thàu dầu)
18. Margarine is ( bơ tv)
A. Trans fat produced synthetically by partial hydrohenation
B. Omega-6 fatty acid
C. Produced by microorganisms in the gut of ruminant animals
D. Polyunsaturated fatty acid
19. Which is correct
A. Sunflower oil is produced the folowers of Ricinus communis
B. A simple spectrophotometric method is used for determination
of lipids withoud derivatization
C. Lauric acid is highest amount in Coconut oil
D. Peanut oil is produced from Phaseolus vulgaris seeds
20. Carotenoids are
A. Phospholipids
B. Isoprenoid lipids
C. Triacylglycerol
D. Eicosanoids
21. Fixed oil can be extracted by
A. Press
B. Infusion
C. Distillation
D. Decoction
22. Which is NOT biological funtions of lipids
A. Transport of oligosaccharides across membranes
B. Protective agents against attacking by predators
C. Essential nutrients stored
D. Transport and metabolism of fatty acids in and out of
mitochondria
23. Which is monousaturated fatty acid
A. Palmitic acid
B. Linolenic acid
C. Oleic acid
D. Arachidonic acid
24. Which is the highest double bonds in molecular formula
A. EPA( timnodonic acid)
B. DHA (Cervonic acid)
C. AA ( Arachidonic acid)
D. ALA (alpha- Linolenic acid )
25. Which is correct
A. The degree of unsaturation of oils and fats
B. The content of ester linkages in oils and fats
C. Mineral impurities in oils and fats
D. The quantify the acidity of oils and fats
26. Which is correct
A. Omega-6 fatty acids contain six double bonds and three methyl
groups
B. An omega-3 fatty acid is a fatty acid with the first double bond
is between the third and fourth carbon atoms from the end of the
carbon atom chain
C. Omega-3-fats are healthy saturated fats. It is important that we
get them from the foods we eat. There are three types of omega-
3 fats: ALA (alpha linolenic acid)
D. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) contains carboxyl group, all trans-
double bonds. It is abundant in plant seeds
27. Iodine value can be used to measure
A. The degree of unsaturation of oils and fats
B. The quantify the acidity og oils and fats
C. The content of ester linkages in oils and fats
D. Mineral impurities in oils and fats
28. When fats oxidized, they become
A. Rancid
B. Crystalized
C. Volatile
D. Liquid
29. Which is functional group NOT found in fatty acids
A. Nitroso
B. Ether
C. Ester
D. Hydroxyl
30. Stearate is classified as
A. Sterol lipids
B. Fatty acyls
C. Sphingolipids
D. Glycerophospholipids
31. Lipid is soluble in
A. Nonpolar solvents
B. Dilute acid
C. Alkaline solution
D. Polar protic solvents
You might also like
- Nomenclature of Organic Compound (11th)Document16 pagesNomenclature of Organic Compound (11th)Raju Singh100% (1)
- LIPIDS BiochemistryDocument52 pagesLIPIDS BiochemistryMark BagamaspadNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument29 pagesLipidsdavid gomezNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument8 pagesMCQdrprambabu2011100% (6)
- BIOCHEM - LipidDocument323 pagesBIOCHEM - LipidPrincess Jeyan PagatpatanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Nutrition For Healthy Living 1st Edition 2011Document18 pagesTest Bank For Nutrition For Healthy Living 1st Edition 2011shanesmithbefqiyajrx100% (21)
- Functional Group Transformation NotebookDocument78 pagesFunctional Group Transformation NotebookchedhedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LipidsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To LipidsBharaniDeepan50% (2)
- Nutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSDocument62 pagesNutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSSalah AlsafiNo ratings yet
- Đáp Án Sach NMRDocument39 pagesĐáp Án Sach NMRThanh VyNo ratings yet
- LECT 6 - 10 LipidsDocument18 pagesLECT 6 - 10 LipidsRusho ArulrajNo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry 1B: Week 6 & Week 7 LipidsDocument37 pagesBiological Chemistry 1B: Week 6 & Week 7 Lipidsglenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1567258117004Document10 pagesOrca Share Media1567258117004Monique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Biochemistry Assignment On: LipidsDocument8 pagesSubject: Biochemistry Assignment On: LipidsMehran AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit II LipidsDocument2 pagesUnit II LipidsOVIYA M JNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Questions & AnswersDocument19 pagesBiochemistry: Questions & AnswersA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Lipids WS HWDocument5 pagesLipids WS HWTyh tytNo ratings yet
- Lê Mai Xuân Trúc - 1752578Document5 pagesLê Mai Xuân Trúc - 1752578Hoàng PhongNo ratings yet
- Biology ExamDocument1 pageBiology ExamZemetu Gimjaw AlemuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - LipidsDocument15 pagesLecture 4 - LipidsDoreenNo ratings yet
- Second Self-Assessment TestDocument2 pagesSecond Self-Assessment TestAbhay VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Nonpolar.: Dissolve in Non-Polar Solvents Such As Ether, Chloroform, and Acetone But Not Considerably in WaterDocument31 pagesNonpolar.: Dissolve in Non-Polar Solvents Such As Ether, Chloroform, and Acetone But Not Considerably in WaterNejib ReshadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument30 pagesChemistry of Lipidszahid mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Triacylglycerol and Fatty AcidDocument6 pagesTriacylglycerol and Fatty AcidGil Angelo VillaluzNo ratings yet
- Lipid UpdateDocument50 pagesLipid UpdateIlmi Dewi ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.1 - LipidsDocument35 pagesChapter 3.1 - LipidsDazell VarronNo ratings yet
- Pharm-D Biochemistry, LipidsDocument37 pagesPharm-D Biochemistry, LipidsShahid Ahmed100% (1)
- LipidsDocument22 pagesLipidsMary Grace CaasiNo ratings yet
- Lipids: A. Types B. Triacylglycerols C. Other ExamplesDocument26 pagesLipids: A. Types B. Triacylglycerols C. Other ExamplesAdrian Joshua BernagaNo ratings yet
- Cytology Lab DR Amal2018 SpringDocument4 pagesCytology Lab DR Amal2018 SpringAhmed Ali SofyNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument31 pagesLipidsMods PadernillaNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument80 pagesLipidMirza Salman BaigNo ratings yet
- Lipids ClassificationDocument7 pagesLipids ClassificationAdamFerdianNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Nursing 2022Document2 pagesQuestion Bank Nursing 2022Aya AimanNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Healthy Living 3Rd Edition Schiff Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument47 pagesNutrition For Healthy Living 3Rd Edition Schiff Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcomposeenwrap8gjoi100% (10)
- Classification of LipidsDocument3 pagesClassification of LipidsAhmad RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam HSN104 ANSWERSDocument13 pagesPractice Exam HSN104 ANSWERSRaha RajabigamasaeiNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids: Presentation Created by Mahpara Gondal Lecturer Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument29 pagesFatty Acids: Presentation Created by Mahpara Gondal Lecturer Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShahid AhmedNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Edible Oil From Groundnut by Using Solvents and EnzymesDocument11 pagesExtraction of Edible Oil From Groundnut by Using Solvents and EnzymesUgwu MmesomaNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Fats. Oils. EnergyDocument50 pagesLipids: Fats. Oils. EnergyRotsen B. VelascoNo ratings yet
- Lipid ChemistryDocument124 pagesLipid ChemistryRavisChNo ratings yet
- Ch.8 كيمياء Quiz and Test BankDocument13 pagesCh.8 كيمياء Quiz and Test BankD.3s YTNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Soal Latihan Karbohidrat Dan LipidDocument7 pagesJawaban Soal Latihan Karbohidrat Dan Lipidchildish_baned0% (1)
- Fats and Oils: Naemaa Mohamad Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARADocument65 pagesFats and Oils: Naemaa Mohamad Faculty of Applied Sciences Universiti Teknologi MARANaveenNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Healthy Living 3rd Edition Schiff Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesNutrition For Healthy Living 3rd Edition Schiff Solutions Manualnancyruizftycjqbnip100% (33)
- 1 04 LipidsDocument63 pages1 04 LipidsMonesa Christy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- CH. 3 Lipid ChemistryDocument51 pagesCH. 3 Lipid Chemistryanushkappatil20No ratings yet
- Pharm ExamDocument25 pagesPharm ExamAbera LemmaNo ratings yet
- Lipid ChemistryDocument93 pagesLipid ChemistrySanreet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- 202004091956360737nalini Pandey LipidsDocument7 pages202004091956360737nalini Pandey Lipidsyigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- An Oil Is Any: 2 Exam Part I - MCQDocument5 pagesAn Oil Is Any: 2 Exam Part I - MCQQuenne Abonero BelocuraNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument39 pagesLIPIDSJustine Salvo EvaristoNo ratings yet
- Chebme2 Q1 031715Document6 pagesChebme2 Q1 031715MEOW41No ratings yet
- 4 LipidsDocument79 pages4 LipidsYashfa YasinNo ratings yet
- G10-Science 4TH Finals-TqDocument4 pagesG10-Science 4TH Finals-TqYvette Marie Yaneza NicolasNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Thi Minh Anh 1752075Document4 pagesNguyen Thi Minh Anh 1752075Hoàng PhongNo ratings yet
- Biochem Midterm Exam 2023 With AnswerDocument5 pagesBiochem Midterm Exam 2023 With AnswerJayson CambeNo ratings yet
- Fat Analysis: Dr. Arfaa Sajid Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry, UOLDocument22 pagesFat Analysis: Dr. Arfaa Sajid Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry, UOLzeeshan farooqNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Mcqs 2020Document3 pagesBiological Molecules Mcqs 2020PakistanWaqarMughalNo ratings yet
- C46 Lec6 LipidsDocument91 pagesC46 Lec6 LipidsMary Aniderf Cagape Maturan-GumanoyNo ratings yet
- Mcqs LipidsDocument27 pagesMcqs LipidsRohit BebartaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document65 pagesChapter 1maya adamNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportFrom EverandFast Facts: Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders: Understand, identify and supportNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds 1Document23 pagesCarbonyl Compounds 1Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Important Order and Facts of Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesImportant Order and Facts of Organic ChemistryDEEPAK KUMAR MALLICKNo ratings yet
- Ampi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THDocument1 pageAmpi+Salbactum Amo+ Clavulanate Piper+Tazobactam: ST ST ND ND ND ND TH ST ND TH TH TH RD RD RD TH THAnnieNo ratings yet
- Tanzania Product ListDocument1 pageTanzania Product ListMITON CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Setup Rak ObatDocument161 pagesSetup Rak Obatmuna barajaNo ratings yet
- MedicationsDocument2 pagesMedicationsHanna SeNo ratings yet
- Controlled Substances - Alphabetical OrderDocument14 pagesControlled Substances - Alphabetical Orderjacinc2No ratings yet
- Neet Lesson Plan - ChemDocument16 pagesNeet Lesson Plan - ChemVishwa NathNo ratings yet
- Product List AugustDocument76 pagesProduct List Augustahmedalwared66No ratings yet
- PKPADocument22 pagesPKPAYola SafitriNo ratings yet
- 2006-2010PesticideCatalog CHERSERVICEDocument146 pages2006-2010PesticideCatalog CHERSERVICEAlter R. ScudNo ratings yet
- DTL PendingDocument4 pagesDTL PendingAmir MughalNo ratings yet
- Iupac Ambad TestDocument4 pagesIupac Ambad Testmanish365No ratings yet
- Lista de Precios 2Document20 pagesLista de Precios 2David GuillenNo ratings yet
- US20020026015A1Document11 pagesUS20020026015A1Alexander Franco CastrillonNo ratings yet
- 3MS OrdersDocument8 pages3MS OrdersDiomar GulenNo ratings yet
- Part VIIIA January 2014Document92 pagesPart VIIIA January 2014jorsonNo ratings yet
- Lampiran Telahan StafDocument13 pagesLampiran Telahan StafIna Rama BahtiarNo ratings yet
- Fire DiamondDocument33 pagesFire DiamondArun HarpalaniNo ratings yet
- Tugas Komunikasi Informasi Dan Edukasi Farmasi "Contoh Obat"Document3 pagesTugas Komunikasi Informasi Dan Edukasi Farmasi "Contoh Obat"Tary MentaryNo ratings yet
- Capsaicin Synth - Vanillyl Acetamide Synth - A Capsaicin Derivative - Sciencemadness Discussion BoardDocument4 pagesCapsaicin Synth - Vanillyl Acetamide Synth - A Capsaicin Derivative - Sciencemadness Discussion BoardyunusNo ratings yet
- Goed MethodDocument6 pagesGoed MethodCarla Sánchez GallardoNo ratings yet
- VDG CamphorDocument40 pagesVDG CamphordrvijaygulkariNo ratings yet
- Narkotik PsikotropikDocument3 pagesNarkotik PsikotropikThesa HudanaNo ratings yet
- List of Hazardous Air Pollutants:: 75070 AcetaldehydeDocument5 pagesList of Hazardous Air Pollutants:: 75070 AcetaldehydeUmit SavasNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument78 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidSwapnil MandalNo ratings yet
- Au 31 Mei 2017Document124 pagesAu 31 Mei 2017Agnes CynthiaNo ratings yet