Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abraham Maslow Popularized The Concept of Self
Uploaded by
Lamm ThongniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abraham Maslow Popularized The Concept of Self
Uploaded by
Lamm ThongniCopyright:
Available Formats
Abraham Maslow popularized the concept of self-actualization as a process that an individual
undergoes through life. He believed that most mentally healthy individuals follow a path called
growth motivation that allowed them to self-actualize and realize their true potential as they
grew older and matured. Maslow’s theory of self-actualization is synonymous with seminal
psychological, philosophical, and religious theories that support the noble human transition
from self-indulgence to selflessness and altruism.
The Significance of Maslow’s Concept of Self-actualization
Maslow (1943) proposed his hierarchy of needs theory which enlisted basic human needs in the
form of a hierarchy. The hierarchy of need theory is arguably the most prominent motivational
theory in the field of psychology. The five needs that were originally enlisted were physiological,
safety, love and belonging, esteem and self-actualization. Maslow further expanded self-
actualization into four needs, namely, cognitive, aesthetic, self-actualization and self-
transcendence. He called these latter needs “being needs” or B-needs and the former four
needs “deficient needs” or D-needs. He claimed that mentally healthy individuals follow a path
called growth motivation that allowed them to move up this hierarchy from D-needs to B-needs
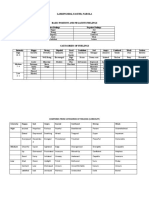
Need-based Activity Chart for Self-actualization
Since Maslow’s theory of self-actualization correlates strongly with prominent theories of
morality, spirituality and utilitarianism, a need-based activity chart has been developed to guide
individuals to self-actualize through the lifecycle. Table 1 shows a need-based activity chart
describing the amount of conscious time an individual might devote to different needs in order
to self-actualize as they move through the lifecycle. The activities involved could vary
significantly between individuals depending on their geographical locations, professions, and
circumstances. The chart is intended to be a guide to demonstrate how a normal self-actualizing
individual’s behavior and actions could gradually change throughout the lifecycle, with
decreasing focus on D- needs and increasing focus on B-needs as the individual grows and
matures
Characteristics of Self Actualizing People
Realistic
Realistically oriented, SA persons have a more efficient perception of reality, they have comfortable
relations with it. This is extended to all areas of life. SA persons are unthreatened, unfrightened by the
unknown. they have a superior ability to reason, to see the truth. They are logical and efficient.
Acceptance
Accept themselves, others and the natural world the way they are. Sees human nature as is, have a lack of
crippling guilt or shame, enjoy themselves without regret or apology, they have no unnecessary inhibitions.
Spontaneity, Simplicity, Naturalness
Spontaneous in their inner life, thoughts and impulses, they are unhampered by convention. Their ethics is
autonomous, they are individuals, and are motivated to continual growth.
Problem Centering
Focus on problems outside themselves, other centered. They have a mission in life requiring much energy,
their mission is their reason for existence. They are serene, characterized by a lack of worry, and are
devoted to duty.
EIGHT WAYS TO SELF ACTUALIZE
1. Experience things fully, vividly, selflessly. Throw yourself into the experiencing of something:
concentrate on it fully, let it totally absorb you.
2. Life is an ongoing process of choosing between safety (out of fear and need for defense) and risk
(for the sake of progress and growth): Make the growth choice a dozen times a day.
3. Let the self emerge. Try to shut out the external clues as to what you should think, feel, say, and so
on, and let your experience enable you to say what you truly feel.
4. When in doubt, be honest. If you look into yourself and are honest, you will also take
responsibility. Taking responsibility is self-actualizing.
5. Listen to your own tastes. Be prepared to be unpopular.
6. Use your intelligence, work to do well the things you want to do, no matter how insignificant they
seem to be.
7. Make peak experiencing more likely: get rid of illusions and false notions. Learn what you are
good at and what your potentialities are not.
8. Find out who you are, what you are, what you like and don't like, what is good and what is bad for
you, where you are going, what your mission is. Opening yourself up to yourself in this way
means identifying defenses--and then finding the courage to give them up.
elf-actualization is the final stage of development in Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
This stage occurs when a person is able to take full advantage of their talents while still
being mindful of their limitations.
The term is also used colloquially to refer to an enlightened maturity characterized by the
achievement of goals, acceptance of oneself, and an ability to self-assess in a realistic and
positive way. Self-actualization can be explored in therapy .
WHAT IS SELF-ACTUALIZATION?
The process of self-actualization is different for everyone, and not all individuals achieve all
levels of the hierarchy throughout their lives. While Maslow believed achieving self-
actualization is somewhat rare and posited that only about 1% of the adult population has
self-actualized, current research shows this number may be higher. Further, self-
actualization has not been found to correlate with age, gender, income level, or race.
Self-actualization is thought to be best conceptualized as the sum of its parts rather than as
traits viewed in isolation. For example, a person who has a creative spirit, which is one trait
of self-actualization, may still not be fully self-actualized. Some experts say the theory of
self-actualization is more about how open a person is to growth and health rather than about
achieving ideals such as perfection, success, or happiness.
In addition, those that do self-actualize will not necessarily remain in that state. People may
travel between several levels of the hierarchy over their lifespan, based on life
circumstances, individual choices, and mental health.
MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS
Although the concept of self-actualization was originally discussed by Gestalt psychologist
Kurt Goldstein, it is most often associated with humanistic psychology , particularly the
humanistic psychologist Maslow, who used self-actualization as the pinnacle of
his hierarchy of needs .
Maslow developed the concept of the hierarchy of needs to address both the basic and
esoteric needs of human existence. Its stages include physiological needs, safety needs,
the need for love and belonging, the need for esteem and, finally, self-actualization.
Once the most basic needs for an individual to remain alive have been met, desires that
concern safety and affection follow, then esteem needs. Once esteem needs such as self-
confidence and self-respect have been met, a person might begin to self-actualize. The
hierarchy also serves as a model of development in which babies start at the lowest level by
attempting to gain food, water, and shelter.
The needs associated with self-actualization include:
Acceptance of facts
Lack of prejudice
Ability to solve problems
Sense of morality
Creativity
Spontaneity
When these needs are met, a person may be more open to the process of self-actualization.
SELF-ACTUALIZATION CHARACTERISTICS AND TRAITS
For Maslow, self-actualization describes the desire that leads to the realization of one's full
potential: A self-actualizer is a person who has reached the apex of human existence. In
other words, that person has become everything they’re capable of becoming. This
realization of potential can occur in many ways but generally includes the achievement of
sound psychological health and a strong sense of fulfillment.
In general, self-actualized people:
Accept themselves and others
Have a well-developed sense of creativity, sometimes referred to as a “creative spirit”
Maintain deep and meaningful relationships
Can exist autonomously
Have a sense of humor, particularly an ability to find humor in their own mistakes
Accurately perceive reality, both as it pertains to the self and others
Have a sense of purpose and perform regular tasks geared toward that purpose
Experience frequent moments of profound happiness (what Maslow called “peak
experiences”)
Demonstrate empathy and compassion for others
Have an ongoing appreciation of the goodness of life. Some might refer to this trait
as childlike wonder.
Because self-actualization involves a strong sense of purpose and self-awareness as well
as the imperative that one's basic needs are met, it can be a challenging goal to reach.
However, people who do self-actualize at some point in life may be able to retain access to
this level because they have learned the necessary skills to achieve fulfillment.
Not all people seek self-actualization as a goal, and different people or cultures may have
differing opinions about what constitutes a self-actualized state of being.
EXAMPLES OF SELF-ACTUALIZATION
Self-actualization may manifest in many forms, and some of how a self-actualized person
may appear can depend on their age, culture, and other factors. A few examples of behavior
a self-actualized person might exhibit include:
Finding humor in a given situation
Getting enjoyment and satisfaction out of the present moment
Understanding what they need in order to gain a sense of fulfillment
Tendency to feel secure and unashamed in who they are
Becoming self-actualized is not always a straightforward process, and it can take years for
some people to reach self-actualization. To learn more about how therapy can help you
become more self-actualized, click here.
You might also like
- Humanism PDFDocument17 pagesHumanism PDFLEYENDSGHOST MOVIENo ratings yet
- Humanistic PsychologyDocument17 pagesHumanistic PsychologyHalimaNo ratings yet
- Psy Health, Insel & Roth, Core Concepts in Health 2008, Chap PDFDocument21 pagesPsy Health, Insel & Roth, Core Concepts in Health 2008, Chap PDFMarcelo Vial RoeheNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document6 pagesLesson 1Briones, Francine Claire, G.No ratings yet
- Nueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyDocument4 pagesNueva Ecija University of Science and TechnologyJefferson Fernando FernandezNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Week 3-4Document13 pagesPersonal Development Week 3-4Edilene Rosallosa CruzatNo ratings yet
- ExplainDocument4 pagesExplainJoshua CudalNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs & Humanistic PsychologyDocument12 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs & Humanistic PsychologyAkshita SinghNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument39 pagesUntitledCrizza Mae CuregNo ratings yet
- Self-Actualization-Guide-Scott-JeffreyDocument9 pagesSelf-Actualization-Guide-Scott-Jeffreyteateica94No ratings yet
- Humanistic Approach: Abraham MaslowDocument33 pagesHumanistic Approach: Abraham MaslowmarNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Theories and Big Five Trait TheoryDocument24 pagesHumanistic Theories and Big Five Trait TheoryArijit GuhaNo ratings yet
- Maslows HierarchyDocument4 pagesMaslows HierarchyLissie ArcherNo ratings yet
- OutlineDocument4 pagesOutlineJayson IsidroNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy of NeedsDocument54 pagesHierarchy of NeedsKevin Davidson AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Maslow and ROgerDocument30 pagesMaslow and ROgerMergelou LatayadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Self GrowthDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Self GrowthBhavana Lekshmidev Amrita Vishwa VidhyapeedamNo ratings yet
- Eudaimonic Well-Being Concept and ComponentsDocument3 pagesEudaimonic Well-Being Concept and ComponentsMatthew HealyNo ratings yet
- Self Actualization: Not Many People Reach Self-Actualization Stage. According To Maslow, Only Less Than 1% ofDocument1 pageSelf Actualization: Not Many People Reach Self-Actualization Stage. According To Maslow, Only Less Than 1% ofAleena AliNo ratings yet
- Week17 Psy100 LMDocument6 pagesWeek17 Psy100 LMNovelyn Degones DuyoganNo ratings yet
- Motivation 2Document30 pagesMotivation 2aysha farihaNo ratings yet
- Maslow: Holistic-Dynamic Theory Overview of Maslow's Holistic-Dynamic TheoryDocument43 pagesMaslow: Holistic-Dynamic Theory Overview of Maslow's Holistic-Dynamic TheoryMarianie AbarcarNo ratings yet
- Self-Awareness Key to Self-ActualizationDocument2 pagesSelf-Awareness Key to Self-ActualizationAnne Marielle AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Perdev.Document56 pagesChapter 1 Perdev.Marione MartinezNo ratings yet
- UTS Module SY 2020-2021Document91 pagesUTS Module SY 2020-2021Desiree Inoferio Adanza100% (1)
- Humanistic Approach and ST Thomas AquinasDocument90 pagesHumanistic Approach and ST Thomas Aquinasmaylene marquezNo ratings yet
- Need Hierchy Theory of MaslowDocument23 pagesNeed Hierchy Theory of MaslowmanuelNo ratings yet
- What Is Personal DevelopmentDocument6 pagesWhat Is Personal DevelopmentJoseph JboyNo ratings yet
- LESSON1 (Personal Development)Document42 pagesLESSON1 (Personal Development)Lu Cel100% (1)
- Theories of PersonalityDocument16 pagesTheories of PersonalityLeeYan SaliliNo ratings yet
- Abraham MaslowDocument42 pagesAbraham Maslowkavitha nagarjunakondaNo ratings yet
- W8a - Humanistic Learning TheoryDocument22 pagesW8a - Humanistic Learning TheoryTESL110621 Nur Zulaikha Binti ZahrollailNo ratings yet
- Abraham Maslow (Humanistic Theory & Heirarchy of Needs)Document25 pagesAbraham Maslow (Humanistic Theory & Heirarchy of Needs)Marissa Altarejos BrionesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 Abraham Maslow - Study of Self Actualizers 16112022 123331pmDocument19 pagesLecture 15 Abraham Maslow - Study of Self Actualizers 16112022 123331pmm.muneeb raufNo ratings yet
- All People - : MilestonesDocument19 pagesAll People - : MilestonesMarion TaylorNo ratings yet
- pER DEEVDocument36 pagespER DEEVEralith SENo ratings yet
- Personality: An Individual's Characteristic Pattern of Thinking, Feeling, and ActingDocument54 pagesPersonality: An Individual's Characteristic Pattern of Thinking, Feeling, and Actingprecious maningasNo ratings yet
- Self ConceptDocument9 pagesSelf ConcepthkhnNo ratings yet
- Abraham H. Maslow - Toward A Psychology of BeingDocument14 pagesAbraham H. Maslow - Toward A Psychology of BeingPradeep NagarajNo ratings yet
- Self Concept Self Esteem and Identity NotesDocument5 pagesSelf Concept Self Esteem and Identity NotesErnesto TorresNo ratings yet
- Humanistic or Phenomenological ApproachDocument21 pagesHumanistic or Phenomenological ApproachDidem KaraosmanoğluNo ratings yet
- Self ActualizationDocument14 pagesSelf Actualizationhina_afshinNo ratings yet
- Introduction: A New Hierarchy of NeedsDocument5 pagesIntroduction: A New Hierarchy of Needsgun2 block100% (1)
- Personal Development 2ND SemesterDocument101 pagesPersonal Development 2ND SemesterJoelyn Dela Vega De AsisNo ratings yet
- Cont of Chapter 1Document13 pagesCont of Chapter 1Reglos Sakura ShaineNo ratings yet
- Reading Assignment - Maslow's Theory (Theories of Personality)Document2 pagesReading Assignment - Maslow's Theory (Theories of Personality)Danielle Kate FontamillasNo ratings yet
- Amig Module 1Document12 pagesAmig Module 1ROSEMAY FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- Exercise 4: Toward Becoming An Ideal Filipino Citizen: PERFORMANCE TASK: July 7, 2021 (Pairwork)Document4 pagesExercise 4: Toward Becoming An Ideal Filipino Citizen: PERFORMANCE TASK: July 7, 2021 (Pairwork)Princess Therese Cañete0% (1)
- Overview of Holistic-Dynamic Theory: Personality, Needs Theory, and Self-Actualization TheoryDocument14 pagesOverview of Holistic-Dynamic Theory: Personality, Needs Theory, and Self-Actualization TheoryMark Jayson JuevesNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Module 2023Document23 pagesPersonal Development Module 2023SHAIRA MAE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Maslows Hierarchy of NeedsDocument7 pagesMaslows Hierarchy of Needsabdrae freqNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVESDocument6 pagesPSYCHOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVESChen FuchadchaNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory: A Concise OverviewDocument19 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory: A Concise OverviewErickson GarciaNo ratings yet
- Carl RogersDocument16 pagesCarl RogersMary Ivie ArlanNo ratings yet
- Self Concept: by Rabia Umer MS Clinical PsychologyDocument74 pagesSelf Concept: by Rabia Umer MS Clinical PsychologyRimshaNo ratings yet
- Abraham H. MaslowDocument4 pagesAbraham H. MaslownitinandsubahNo ratings yet
- Self ConceptDocument7 pagesSelf ConceptBarry Joel Desaine100% (3)
- National University of Modern LanguagesDocument24 pagesNational University of Modern LanguagesJawad AzizNo ratings yet
- Alfred Adler's Life and Individual Psychology TheoryDocument9 pagesAlfred Adler's Life and Individual Psychology TheoryLamm ThongniNo ratings yet
- How Family Support and Education Strengthen LeadershipDocument7 pagesHow Family Support and Education Strengthen LeadershipLamm ThongniNo ratings yet
- At Least Five ConceptsDocument3 pagesAt Least Five ConceptsLamm ThongniNo ratings yet
- Basic Positive and Negative Feeling1Document2 pagesBasic Positive and Negative Feeling1Lamm ThongniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document10 pagesAssignment 2Lamm ThongniNo ratings yet
- Critique On The Liberation Book of ExodusDocument11 pagesCritique On The Liberation Book of ExodusLamm ThongniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document5 pagesAssignment 2Lamm ThongniNo ratings yet
- The Promised LandDocument12 pagesThe Promised LandLamm ThongniNo ratings yet
- A Biblical Geology of BlessingDocument12 pagesA Biblical Geology of BlessingLamm ThongniNo ratings yet
- Ufo DictionaryDocument106 pagesUfo Dictionarysohelalam100% (1)
- Afterlife of Billy Fingers ExcerptDocument12 pagesAfterlife of Billy Fingers ExcerptYady Rosario100% (3)
- Psychology Encyclopedia of Infant and Early Childhood Development Volume 3 2008 PDFDocument419 pagesPsychology Encyclopedia of Infant and Early Childhood Development Volume 3 2008 PDFraduNo ratings yet
- Mythology & Rites of The British DruidsDocument662 pagesMythology & Rites of The British DruidsJeremy Watkins50% (2)
- Law of Explosive GrowthDocument2 pagesLaw of Explosive GrowthEmm GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- Englisg 10Document4 pagesEnglisg 10Djoana Rose Hiponia JunsayNo ratings yet
- Internet Encyclopedia of PhilosophyDocument19 pagesInternet Encyclopedia of PhilosophyStefie Laimeheriwa KybernNo ratings yet
- Yaksha PrasnamDocument9 pagesYaksha PrasnamYSRNo ratings yet
- (Bernard Stiegler) Technics and Time, 1 The FaultDocument313 pages(Bernard Stiegler) Technics and Time, 1 The FaultFedi GloNo ratings yet
- Identify Clauses and Construct Complex SentencesDocument5 pagesIdentify Clauses and Construct Complex SentencesJelo AnievasNo ratings yet
- Argumentative-Essay CounterargumentDocument2 pagesArgumentative-Essay CounterargumentVũ ĐỗNo ratings yet
- The Amazing Quotes of Lao TzuDocument23 pagesThe Amazing Quotes of Lao TzuElwilson PascualNo ratings yet
- Seen Presents - Alcohol Trends ReportDocument25 pagesSeen Presents - Alcohol Trends ReportAnonymous rjJZ8sSijNo ratings yet
- National Fine Arts Collection of The National MuseDocument8 pagesNational Fine Arts Collection of The National MuseJanna OrojoCafeNo ratings yet
- Franz Kogelmann Some Aspects of the Development of the Islamic Pious Endowments in Morocco, Algeria and Egypt in the 20th Century, in: Les fondations pieuses (waqf) en Méditerranée enjeux de société, enjeux de pouvoir. Edited by Randi Deguilhem and Abdelhamid HeniaDocument29 pagesFranz Kogelmann Some Aspects of the Development of the Islamic Pious Endowments in Morocco, Algeria and Egypt in the 20th Century, in: Les fondations pieuses (waqf) en Méditerranée enjeux de société, enjeux de pouvoir. Edited by Randi Deguilhem and Abdelhamid HeniaFranz KogelmannNo ratings yet
- GST 113 Revised NotesDocument15 pagesGST 113 Revised NotesAmi NatNo ratings yet
- Hon. Mayor Silvestre T. Lumarda of Inopacan, Leyte, PhilippinesDocument18 pagesHon. Mayor Silvestre T. Lumarda of Inopacan, Leyte, PhilippinesPerla Pelicano Corpez100% (1)
- Organisational Justice Climate, Social Capital and Firm PerformanceDocument16 pagesOrganisational Justice Climate, Social Capital and Firm PerformanceAnonymous YSA8CZ0Tz5No ratings yet
- Research Report On: "Perception of People Towards Water Purifier - A Study of Katni City"Document44 pagesResearch Report On: "Perception of People Towards Water Purifier - A Study of Katni City"Rendezvous Das100% (1)
- Protagoras WithinDocument278 pagesProtagoras WithinSerenaSanchez100% (3)
- Sight & BlindnessDocument7 pagesSight & BlindnessMd Mujib UllahNo ratings yet
- Taste For Truth - A 30 Day Weight Loss Bible Study PDFDocument128 pagesTaste For Truth - A 30 Day Weight Loss Bible Study PDFEdgar Entrambasaguas100% (7)
- 1.engineers Responsibility For Safety and RiskDocument17 pages1.engineers Responsibility For Safety and RiskPritam MedokNo ratings yet
- RamaswamyDocument94 pagesRamaswamyk.kalaiarasi6387No ratings yet
- The Tyger by William BlakeDocument1 pageThe Tyger by William BlakeKrystal Miller100% (1)
- Halal Diakui JAKIMDocument28 pagesHalal Diakui JAKIMwangnadaNo ratings yet
- Alfredo Espin1Document10 pagesAlfredo Espin1Ciber Genesis Rosario de MoraNo ratings yet
- PGD 102Document8 pagesPGD 102Nkosana NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Self Management Strategies of Patients On Long Term DialysisDocument57 pagesSelf Management Strategies of Patients On Long Term DialysisHarby Ongbay Abellanosa100% (1)
- Text Mining Applications and TheoryDocument223 pagesText Mining Applications and TheoryXiangcao Liu100% (4)