Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WhatsApp Image 2021-12-16 at 7.19.47 PM
WhatsApp Image 2021-12-16 at 7.19.47 PM
Uploaded by
abhinav kota0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pagesw
Original Title
WhatsApp Image 2021-12-16 at 7.19.47 PM (1)-converted
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentw
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views5 pagesWhatsApp Image 2021-12-16 at 7.19.47 PM
WhatsApp Image 2021-12-16 at 7.19.47 PM
Uploaded by
abhinav kotaw
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
1. Complete each of the following sentences by
choosing the correct term from the word bank.
refraction, reflection, resonance, diffraction,
interference
(a) happens when a wave passes from one
medium to another at an angle.
(b) The bending of'a wave around a barrier is called
(©) occurs when a wave bounces back from
a barrier
qd) happens when two or more waves over-
lap.
() isa phenomenon that occurs when two
objects naturally vibrate at the same frequency
and the sound produced by one object causes the
other object to vibrate.
2. Complete each of the following sentences by
choosing the correct term from the word bank,
loudness, echoes, pitch, noise, solids, sound
quality, vibrations, wavelength, frequency, wave,
vacuum, amplitude, lesser, infrasonies, ultrasonics
(1) The
(2) Sound cannot travel through
(3) Vibrations of frequency less than 20 Hz are called
__ of a sound depends on its amplitude,
(4) Sound travels at speed than light,
(5) Reflected sound waves are called _
(6) The measure of how high or low a sound is called
@)
lar
unpleasant sound produced by irregu-
e patterns.
(8) Sound is produced by___.
(9) Oftthe three mediums, solids, liquids, and gases,
sound travels fastest in
(10) Two different instruments playing the same note
sound different because of
(11) When a body vibrates, the number of crests and
troughs made in a given time is called ___.
(12) The maximum displacement ofa wave on either
side of its mean position is called ___
(13) Sound waves having frequencies more than
20,000 Hz are called 2
(14) A is a disturbance that travels through
space or matter and transmits energy.
(15) The distance between any two successive crests
or compressions in a longitudinal wave is called
Cee eter eens)
3. What kinds of sounds are th
sou
lowing frequencies ? MS having
(a) 1SHz 0) 504 ty
(c) 600 Hz 4
@) 1500 4,
(e) 60000 Hz OH
4. With the help of the given clues
the letters to make a meaningfyy tty
5 c Word,
(a) BDECILE (unit of loudness Of sound)
(b) HCEO (A reflected sound wave) 7)
(c) NASRO (A device used in the
unseen underwater objects)
(4) CNSTURAIOL (Sound with fre
20 kHz).
(¢) ETHZR (unit of frequency of sound yay
() RAYXLN (produces sound in humans)
5. The picture shows a wave generated in a
tory. bon,
SHiP oy
‘ueney a,
om 4 2 3
(i) What is the wavelength of the wave
(a) 1.5em (b) 1.7 em
(©) 2.0 om (@) 2.7 om
i) Ifthe frequency of the wave shown were double,
what would be the wavelength of the wave ?
(@) 0.85 cm (b) 1.350
(c)3.4em (d) 54cm
(ii) What is the amplitude of the wave shown ?
(a) 0.85 cm (b) 1.7m
(©) 2.7 cm
(@) There is not enough information to deter
mine the answer.
6. Match correctly the items given in column A
and B in Q. 6 to 9.
Column A Column B
(a) Frequency (1) Amplitude
(b) Shrill sound (2) Low pitch sound
(c) Loudness ofsound (3) Hertz
(@ Time period (4) High pitch sound
(©) Bass (5) Time taken to complete
‘one vibration
124,
126,
127.
128,
130.
BI
133.
134,
PHYSICS
Work done is
(A) scalar quantity (B) vector quantity
(©) neither scalar nor vector (D) none of these
“Work done by a force depends on frame of reference”, choose the correct alternative
(A) true @B) false
(C) can or cannot depend on frame of reference (D) none of these
A constant force F~ 3i+2i+2k N acts on a particle displacing it from “| - i+]-2k mtoa
new position f; = 1-1 +3k m, the work done by force is given by
(A165 (B) 123 ()203 (D) 36
A body of mass ‘nr is being taken from the ground to a height *h’, what is the work done by
gravity?
(A) mgh (B) zero (C)-mgh (D) none of these
Work done by static friction on a body can be
(A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) all of these
Negative of work done by intemal conservative force on a body is__of the body.
(A) potential energy (B) kinetic energy (C) internal energy (DJ total mechanical energy
‘When a body is in a uniform circular motion
(A) its acceleration is always directed toward the centre.
(B) its motion is nox-uniform.
(C) its speed remains constant (D) allofthese
What should be the minimum velocity given to a bob of mass ‘m’ at the lowest point which is
connected to a rod so that it completes the vertical circular motion of radius ‘R”
(A) Year (B) \BaR (©) Jagr ©) oR
Why the roads on a sharp turns are banked?
(A) In order to speed up vehicle (B) In order to prevent skidding of vehicle.
(C) In order to slow down the vehicle. (D) none of these
A rotating disc of mass 250 g is rotated to an angular speed w = 20 rad/s is placed on the ground.
Which offers it an angular retardation of 2 raW/s*, how many revolution it will make before
coming to rest?
(a) 100 (B) 50/x (C) 100/x (D) none of these
The wave length of sound wave is %, then what is the distance between a compression and
immediate rarefaction is
(AyN3 (Bn (n2 O%
In longitudinal wave particles of medium vibrate to the direction of wave.
(A) perpendicular (B) parallel (©) alldirections —(D) none of these
Find the time period of the wave pulse frequency is 1500 Hz?
(A) 0.00263, (B) 0.00075 (C) 0.0005s (D) 0.001s
‘An echo is heard after 0.6 when a body fires a cracker, 99 m away from a tall building then the
speed of sound is
(A) 340 mis (B) 350 mvs (C) 330 mvs (D) 118.8 m/s
Colum,
couumn A nB
Or sonic sound (8) 20 Hz—~20,009 4,
i) eronee © humans (®) More than 20,000 yp
ee er medium (©) Faster trans
an sound not
.y unrasomie sound @ Less than 20 He
: edivm (©) slower :
Ba sean
. coma © cnt
* Sound produced by Ofna ae
) Sos of stetched
fq sundpeducedby (0) sting instumens
‘jbrations of stretched
membranes
3) Sound produced by
vibrations of one end
(©) Percussion
instruments
ofthe air column
(4) Violin, guitar, Veena
(6) Teumpet, Flute
6) Drom, Cymbals
9, How do we hear : Match the parts of a human
ear with their functions
cram Tsao
OK
the canal = produce electrical
pe
Column A Column B
(1) Pinna (a) magnify the vibrations
before passing them on to
the cochlea
(2) Ear drum (b) Inside it, the vibrating fluid
moves the tiny hair’s
which then produce
clectrical signals
(G) Bar bones (€) sends electrical signals to
the brain.
(4) Auditory nerve (4) collects sounds from the
air and directs them down
the ear canal to the ear
drum
Wave Motion and Sound Ch ®@
(©) picks up vibrations of air
in the canal
10. Interpreting graphies
Use the diagram of a wave below to answer the
{questions that follow.
ea0
(a) What kind of wave is this ?
(b) Label the compressions and rarefactions
(©) How do vibrations make these kind of w
11. Look at the waves shown below. Rank these waves
from highest energy to lowest energy and explain
your reasoning.
OY,
()
faves?
12. Inthe following graph, the displacements of a particle
of a progressive wave at different times are shown.
Refer to this graph and answer the questions given
below.
(@ Which one of the following is the amplitude of the
wave ?
(a) 1 metre (b) 10 metres
(©) 0.2 metre (©) 0.1 metre
(ii) The period of vibration of the particle is
(a) 0.1 sec (b) 1 see
(©) 2 seconds (@) 0.5 second
1a. expla with reas
wt
(2) Water in lakes and ponds
not freeze all at once |
3) Steam causes more severe bums than boiling |
Water at the same temperature
(A) Steam is used to run machines.
(8) lis colder after a hail storm than during a hail
storm,
Multiple Choice Questions : |
14, Two objects at different temperatures are in contact.
Which of the following happens to their thermal
(a) Their thermal energies remains the same
(b) Thermal cnengy passes tiom the cooler object 10
the warmer object
(©) Thermal energy passes from the warmer object
to the cooler abject.
(@) Thermal energy passes back and forth equally
between the two objects,
15, What determines a subs
es" state?
(a) the size of the particles
(b) the amount of the substance
(©) the speed of its particles and the attraction
between them,
(q) the chemical energy that the substance has.
16, The S.L unit of heat energy is
(b) Calorie
(d) none of these
@) Joule
(©) kilo calorie
1 Calorie equals
(a) 0425 () 425
(©) 4203 (@ 42001
18, 2000 J of energy is needed to heat | kg of paraffin
through 2°C, then its specific heat capacity is
(a) 4000 1kg°c (b) 10,000 J vkg°C
(©) 40,000 1ikg°c (@) 1000 / kg
19. Two blocks of metal, one twice as heavy as the other,
are both at 60°C. The ratio of the heat energy of the
heavier block to that ofthe lighter block is
(@) 05 1
©2 4
20. Ice does not melt rapidly because of
(a) high specific heat capacity
21. Water from the soil
(b) high latent of fusion
des not evaporate qui
to its i a =
(a) high specific heat capacity
(b) high latent heat of fasion
(©) high latent heat of vapourisation
(d) high evaporation constant
22, Two systems are in thermal equilibrium, The quan,
tity which is common for them is
(b) specific heat
(©) temperature (@) latent hes
23. A certain quantity of ice at 0°C is heated ttt ig
‘changes into steam at 100°C. Draw a time-tempera,
ture heating curve to represent it. Label the two
phase changes in your graph
24, Calculate the heat energy that wll be released when
5.0 kg of steam at 100°C condenses to form water
100°C. Express your answer in §.1. unit (specifi
heat of vapourisation of steam is 2268 kJ /kg)
25, Water falls from a height of 50 cm. Calculate the
rise in temperature of water when it strikes the bot.
tom. (g = 10 ms*, sp. heat capacity of water
= 4200 Jikg°C)
26. Apiece of ice of mass 40 g is dropped into 200 g of
water at 50°C. Calculate the final temperature of
‘ater afterall the ice has melted (sp. heat capacity
of water = 4200 J/kg°C, sp. latent heat of fusion of
ice = 336 * 10° Jig)
27. Athermos-flask of negligible heat capacity contains
100 g of ice and 30g of water. Calculate
(the mass of steam of 100°C needed to condense
in the flask so as to just melt the ice.
i) the amount of water in the flask after condensa-
tion. (Latent heat of ice = 336 Jg-'. Latent heat
of steam = 2260 Jg- sp. heat capacity of water
= 42527 °C!)
(Gli) Is itpossible to condense the water formed back
tice by adding ice at0°C. Explain giving asuit-
able reason to justify your answer.
28. A vessel of negligible heat capacity contains 40g of
ice at 0°C. 8g of steam at 100°C is passed into the
ice to melt it. Find the final temperature of mixture
(Latent heat of ice = 336 J g*, Latent heat of steam
= 2268 Je. Sp. heat capacity of water= 4.2 J g°C')
(a) heat
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Mole Concept BOUNCEBACKDocument154 pagesMole Concept BOUNCEBACKabhinav kota100% (2)
- Drip IrrigationDocument1 pageDrip Irrigationabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- 1Document10 pages1abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Disha Lakshya JEE Main 2021Document440 pagesDisha Lakshya JEE Main 2021abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02 Feb 2022Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 02 Feb 2022abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 15-Jan-2022Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 15-Jan-2022abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- 16july21 Physics TuitionDocument9 pages16july21 Physics Tuitionabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Mat GK Questions 11-09-21Document3 pagesMat GK Questions 11-09-21abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
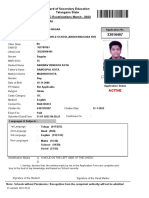
- Telangana State Board of Secondary Education SSC Examinations March - 2022Document1 pageTelangana State Board of Secondary Education SSC Examinations March - 2022abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- 3Document15 pages3abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- PET-2 JR 050722 RESULT - PostDocument1 pagePET-2 JR 050722 RESULT - Postabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.bio NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 5.bio Notesabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRY MergedDocument18 pagesTRIGONOMETRY Mergedabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Print Culture and The Modern World MCQDocument7 pagesPrint Culture and The Modern World MCQabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Note 12-Jul-2022Document12 pagesNote 12-Jul-2022abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- JEEM-2 Results 18-07-2022 - F24 Batches-MDP JuniorsDocument5 pagesJEEM-2 Results 18-07-2022 - F24 Batches-MDP Juniorsabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- JEEM-1 (MAIN-2020) RESULTS - 05-07-2022 (MDP Jrs-F24)Document4 pagesJEEM-1 (MAIN-2020) RESULTS - 05-07-2022 (MDP Jrs-F24)abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- JEEM-2 (JEE MAIN-2020) 18-07-2022 (F24 MDP-Juniors) - KEY (2sides)Document1 pageJEEM-2 (JEE MAIN-2020) 18-07-2022 (F24 MDP-Juniors) - KEY (2sides)abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- (JPP-1) - (JEE 3.0) - Vectors - 30th April.Document40 pages(JPP-1) - (JEE 3.0) - Vectors - 30th April.abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Biology Project 2-AlkaloidsDocument5 pagesBiology Project 2-Alkaloidsabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Project - Animals Which Communicate With Infrasonic SoundsDocument3 pagesProject - Animals Which Communicate With Infrasonic Soundsabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Image 2022-06-17 at 8.04.27 PMDocument6 pagesWhatsApp Image 2022-06-17 at 8.04.27 PMabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Syllabus 2022-23: ClassDocument2 pagesSample Paper Syllabus 2022-23: Classabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Ls 2 ECM NotesDocument5 pagesGrade 6 Ls 2 ECM Notesabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Deleted Academic Syllabus 1Document15 pagesClass 10th Deleted Academic Syllabus 1abhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- Recall - Explanation - : Learnin G Objectiv eDocument48 pagesRecall - Explanation - : Learnin G Objectiv eabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- UNIT TEST 3 (2021-2022) Revision Paper Subject: History and Civics Ls.5 The Vedic Period and Ls.6 Great PreachersDocument4 pagesUNIT TEST 3 (2021-2022) Revision Paper Subject: History and Civics Ls.5 The Vedic Period and Ls.6 Great Preachersabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- WhatsApp Image 2021-12-15 at 9.17.37 PMDocument8 pagesWhatsApp Image 2021-12-15 at 9.17.37 PMabhinav kotaNo ratings yet
- LS - NO 6 NOTES 2021 2022 Great PreachersDocument4 pagesLS - NO 6 NOTES 2021 2022 Great Preachersabhinav kotaNo ratings yet